Method for predicting deformation of additive manufacturing part
A technology for additive manufacturing and parts, applied in the field of predicting the deformation of additive manufacturing parts, it can solve the problems of large-scale calculation and low efficiency of large and medium-sized parts in additive manufacturing, which can reduce the calculation time, simplify the calculation process, and improve the The effect of efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0026] The method for predicting deformation of additively manufactured parts according to the present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings.
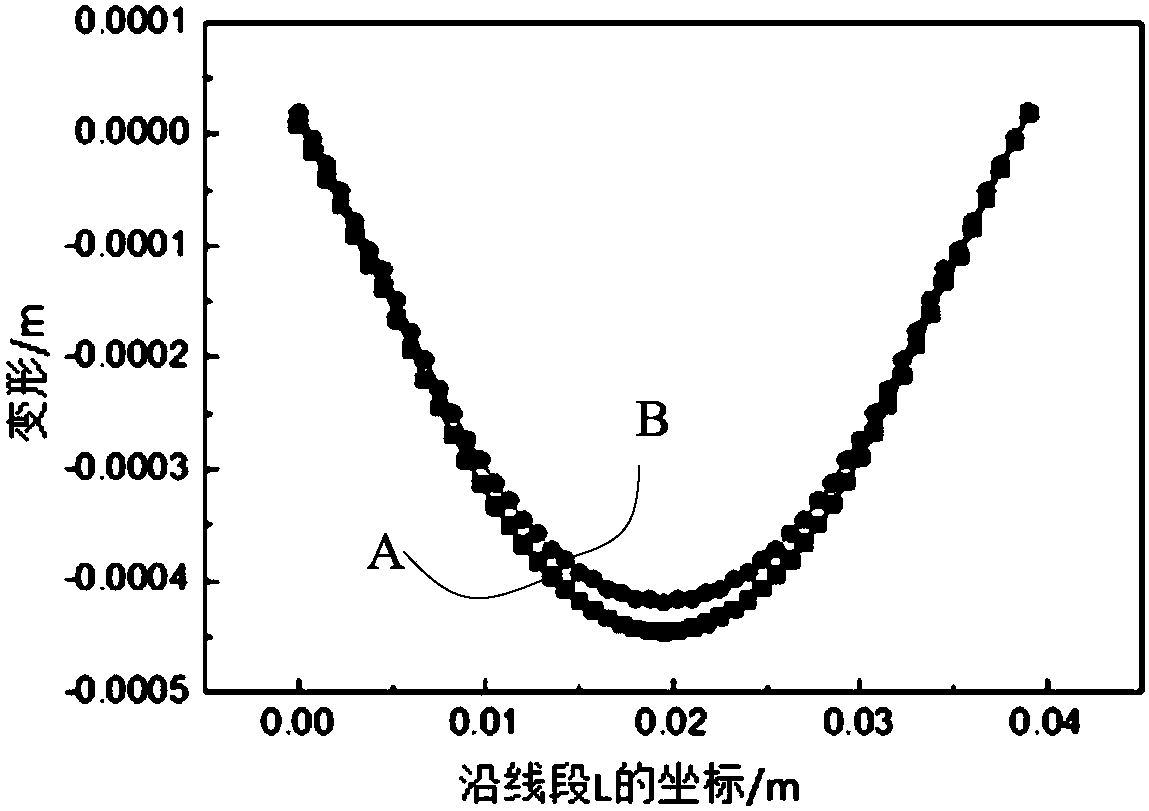
[0027] refer to Figure 1 to Figure 3 , the method for predicting the deformation of additively manufactured parts according to the present invention includes steps: S1, S2, S3 and S4.
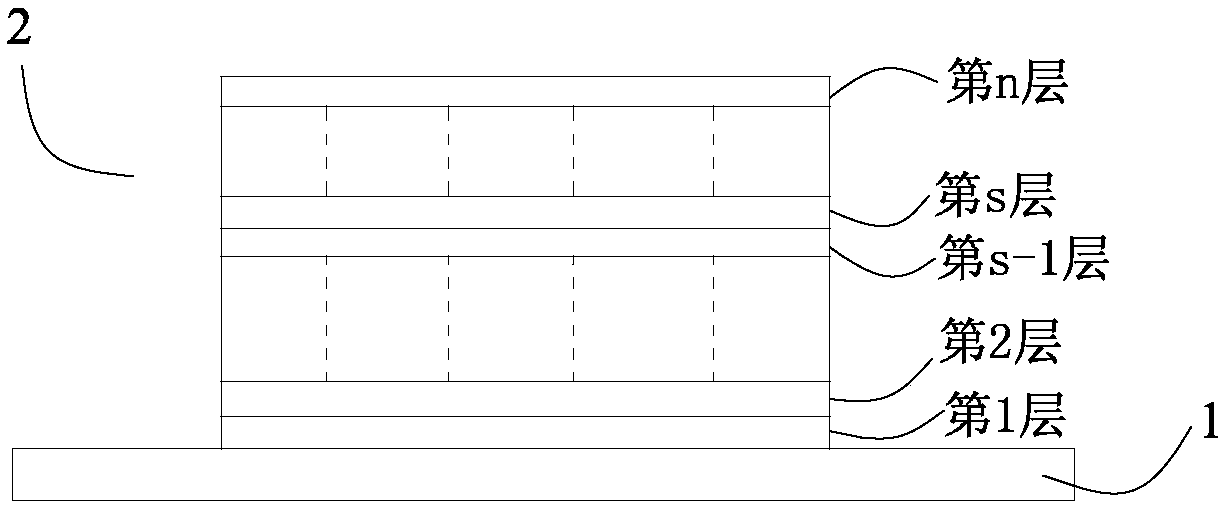
[0028] S1, establish a three-dimensional solid model 1 of a pre-printed part formed by stacking n-layer metal units on the substrate 2 (such as figure 1 shown), wherein the first layer metal unit is the lowermost metal unit of the three-dimensional solid model 1 of the pre-printed part, the n-th layer metal unit is the uppermost metal unit of the three-dimensional solid model 1 of the pre-printed part, and the pre-printed The length direction of the three-dimensional solid model 1 of the part is the x direction, the width direction is the y direction, the height direction is the z direction, and the ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com