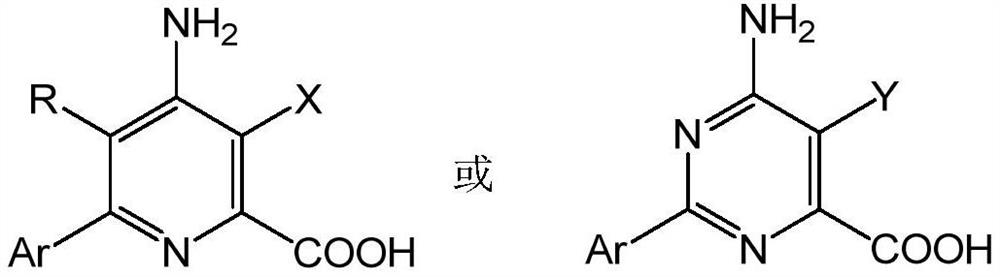
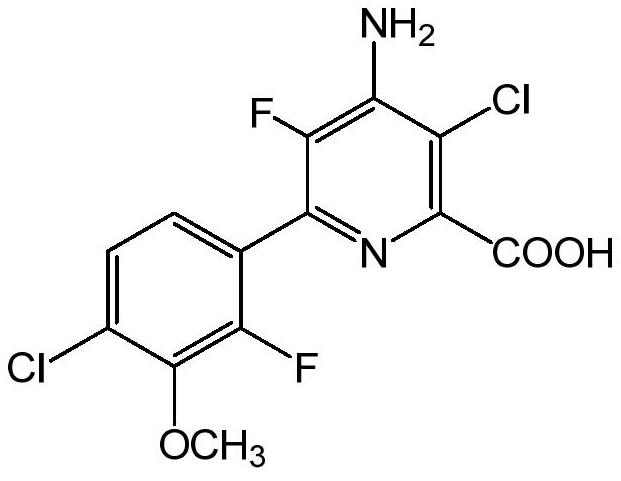
Solid herbicide composition containing fluorine to chlorine ratio
A fluorine-to-chlorine ratio, herbicide technology, applied in biocides, animal repellents, plant growth regulators, etc., can solve the problems of incompetent biological efficacy, inability to fully disperse solid preparations, and physical instability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
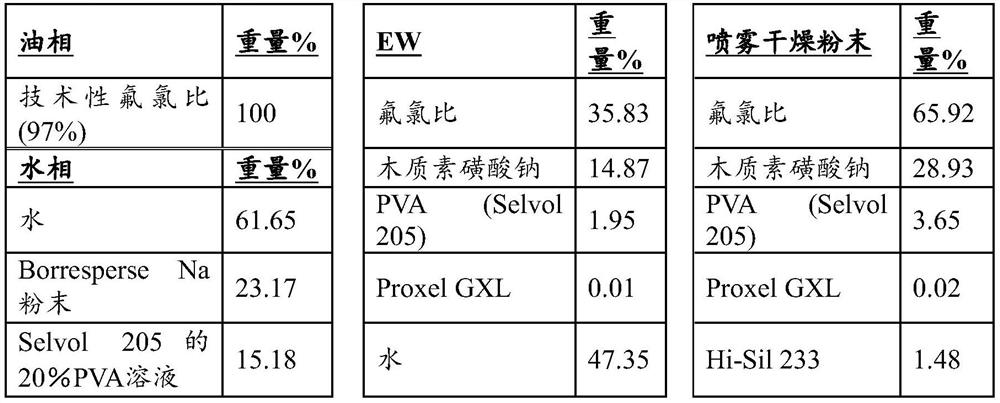
[0116] Example 1 . Preparation of said composition
[0117] sample 1 .Preparation of highly loaded herbicide granule compositions from spray-dried powders
[0118] The oil phase composition of the molten technical fluorine-to-chlorine ratio is heated between 70°C-80°C and a three-stage (coarse, medium and fine) type rotor-stator on-line homogenizer (IKA Magic LAB), with 1.79 water phase / oil phase flow ratio and the water phase (Table 1) also maintained between 70°C-80°C for on-line (in-line ) to form an oil-in-water emulsion having the following particle size distribution: d50 of about 3 micrometers (μm) and d90 of about 7 μm. A particle size distribution with a d50 of less than 2 μm is obtained when the tip speed is increased to about 25 m / s. Alternatively, an oil-in-water emulsion is prepared in batch mode by adding the heated oil phase to the heated water phase in a vessel with agitation and then recirculating it by passing it discretely through an in-line homogenizer ...
Embodiment 2
[0129] Example 2 .Storage Stability of Highly Loaded Herbicide Granular Compositions
[0130] Particle Size, Wet Sieving and Dispersion Time Test Methods
[0131] Particle size analysis : After dispersing a small sample of the extruded particles in 342 ppm hard water at room temperature, the particle size distribution of the resulting particle dispersion was determined using a Mastersizer 2000 laser diffraction particle size analyzer and reported as d in microns (μm) 50 / d 90 value.
[0132] wet sieve test : After dispersing a weighed sample of extruded particles in 342 ppm hard water at room temperature, the resulting particle dispersion and several water rinses were passed through a 200 mesh screen. The material remaining on the screen was dried, weighed and reported as weight % of the original test sample of extruded granules.
[0133] Dispersion time measurement
[0134] a) Weigh 0.1g of the particle sample into a 25mL beaker;
[0135] b) Add 100 mL of 342 ppm...
Embodiment 3
[0144] Example 3 . Differential Scanning Calorimetry Analysis of Spray Dried Powder (Sample 1)
[0145] Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) indicated that the fluorine to chlorine ratio contained in the spray-dried powder (Table 3) reached almost complete crystallinity within about 48 hours after spray-drying.
[0146] DSC thermal data heat flow (absorption)
[0147] 100% crystalline fluorine to chlorine ratio sample 70.01J / g
[0148] Spray-dried powder (65.92% fluorine to chlorine ratio) 43.28J / g
[0149] (Fluorine to Chlorine Ratio in Spray Dried Powder) Calculation of crystallinity
[0150] Heat flow into spray dried powder (if 100% crystallized) = (70.01J / g) x 65.92% = 46.15J / g
[0151] Crystallinity of spray-dried powder = [(43.28J / g) / (46.15J / g)] x 100 = 93.8%
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com