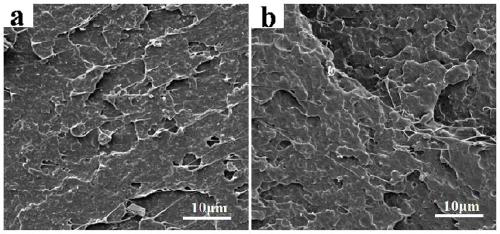
Preparation method of a biodegradable super-tough flame-retardant polylactic acid-based composite material
A composite material, polylactic acid technology, applied in the field of preparation of super-tough flame-retardant polylactic acid-based composite materials, can solve the problems of affecting the toughening effect, difficult to popularize and use, and phase separation of products, so as to improve impact strength and increase compatibility properties, improving toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
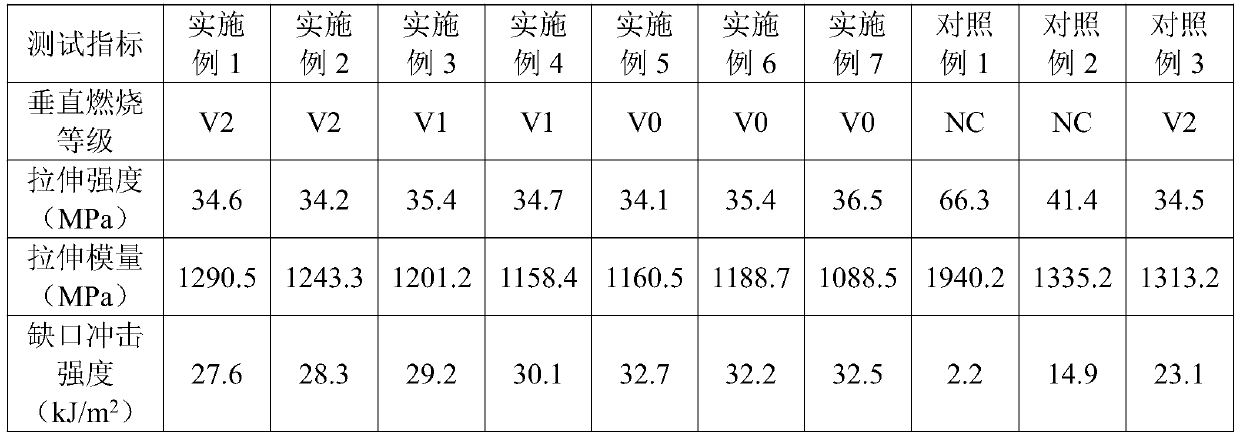
Embodiment 1
[0024] The polylactic acid and polybutylene succinate were dried at 80°C for 12h.
[0025] 80 parts of PLLA and 20 parts of PBS were added to the mixer, pre-blended at 60 rpm for 5 minutes at a temperature of 185 °C, 1.0 parts of TPP and 9.0 parts of TBT were added, and melt blending was continued for 15 minutes at 185 °C. , The super tough flame-retardant polylactic acid-based composite material was prepared by molding under the pressure of 6MPa for 10min.
Embodiment 2
[0027] The polylactic acid and polybutylene succinate were dried at 80°C for 12h.
[0028] 80 parts of PLLA and 20 parts of PBS were added to the mixer, pre-blended at 60 rpm for 5 minutes at a temperature of 185°C, 2.0 parts of TPP and 8.0 parts of TBT were added, and melt blending was continued for 15 minutes at 185°C. , The super tough flame-retardant polylactic acid-based composite material was prepared by molding under the pressure of 6MPa for 10min.
Embodiment 3
[0030] The polylactic acid and polybutylene succinate were dried at 80°C for 12h.
[0031] 80 parts of PLLA and 20 parts of PBS were added to the mixer, and after pre-blending at 60 rpm for 5 minutes at a temperature of 185°C, 3.0 parts of TPP and 7.0 parts of TBT were added, and melt blending was continued for 15 minutes at 185°C. , The super tough flame-retardant polylactic acid-based composite material was prepared by molding under the pressure of 6MPa for 10min.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com