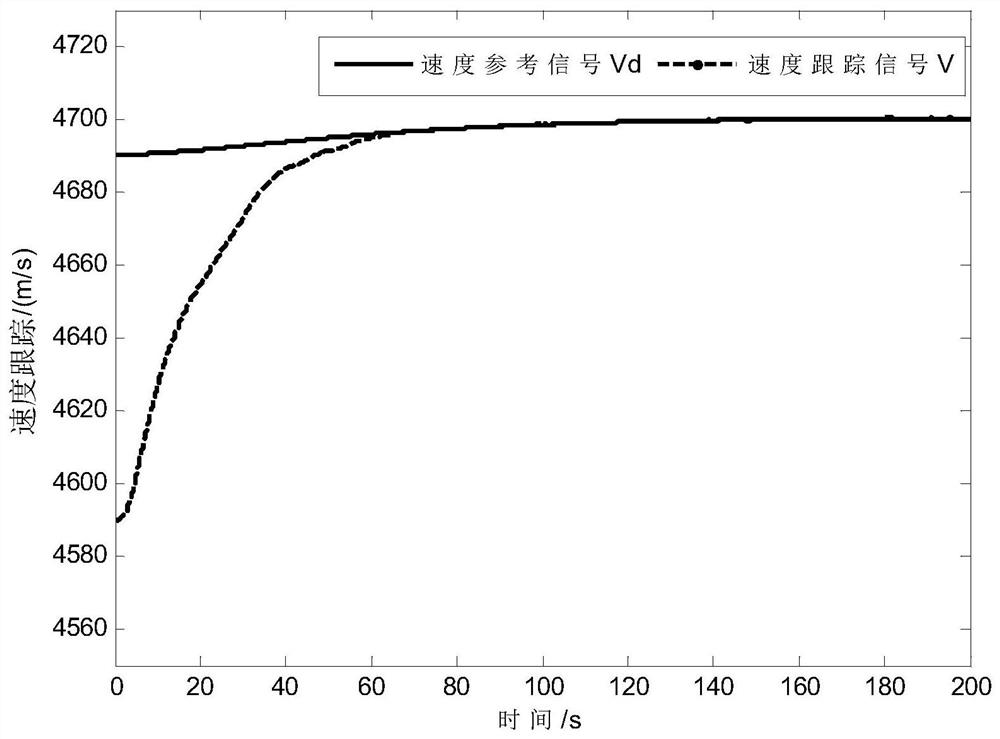
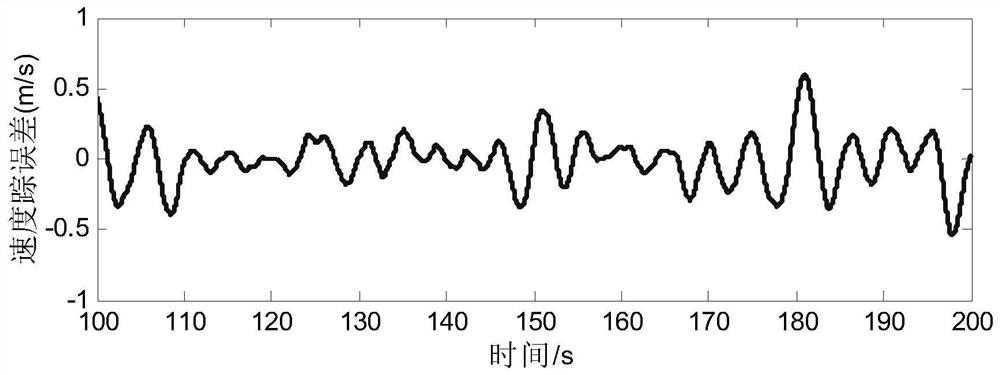
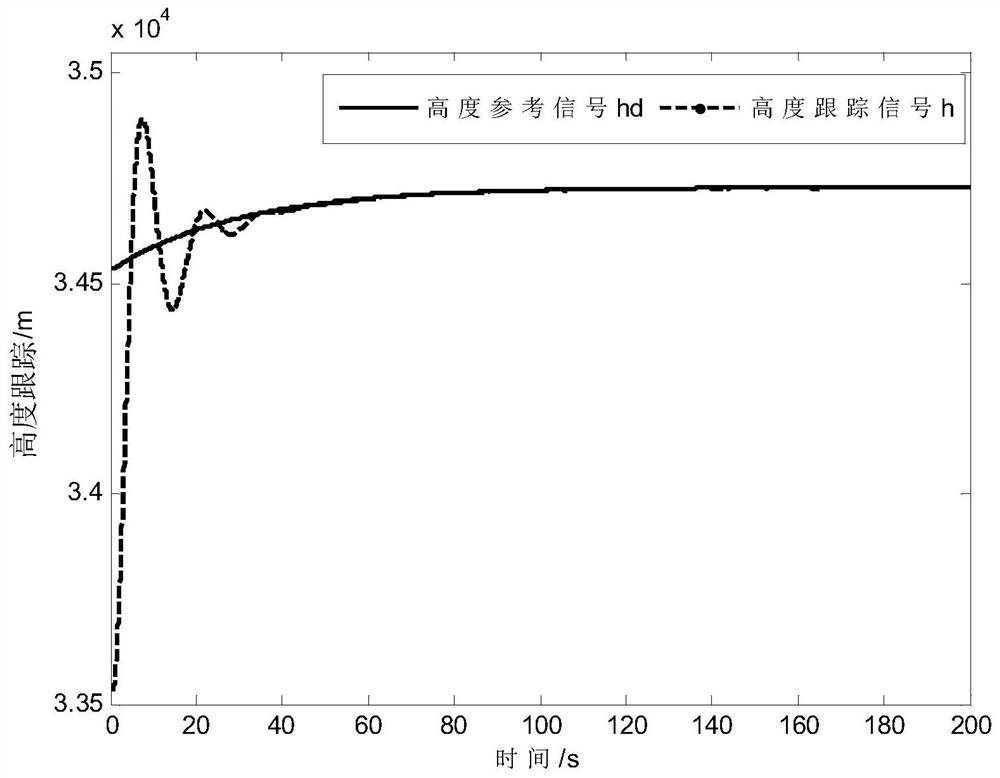
A tracking control method for hypersonic vehicle based on nonlinear function
A non-linear function and hypersonic technology, applied in the direction of adaptive control, general control system, control/regulation system, etc., can solve the problems of complex control model and poor robustness, and achieve strong robustness and improved control accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0047] Specific embodiment one: a hypersonic vehicle tracking control method based on a nonlinear function comprises the following steps:
[0048] Hypersonic Vehicle Model Description
[0049] In order to facilitate the design of hypersonic vehicle control system, the feedback linearization model (Sun H, Li S, Sun C. Finite time integral sliding mode control of hypersonic vehicles [J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2013, 73 (1-2): 229-244.):
[0050]
[0051] where φ c and δ e is the control input, f v , f h , b 11 , b 12 , b 21 and b 22 For specific definitions, see literature (Sun H, Li S, Sun C. Finite time integral sliding mode control of hypersonic vehicles [J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2013, 73(1-2): 229-244.).
[0052] remember Then formula (1) can be rewritten as:
[0053]
[0054] Among them, Δf v , Δf h , Δb 11 , Δb 12 , Δb 21 , Δb 22 is a bounded term resulting from parameter uncertainty and external disturbances. Let Δ 1 =Δf V +Δb 11 δ e +Δb 12 φ c ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0170] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that in the step 1, the hypersonic vehicle model is converted through the state feedback controller, and the specific process of obtaining the transformed hypersonic vehicle model is as follows:
[0171] The hypersonic vehicle model is:
[0172]
[0173] in for σ 1 derivative of for σ 2 derivative of σ 1 and σ 2 is a function with the speed error and height error of the hypersonic vehicle as independent variables, d is the system (hypersonic vehicle model) disturbance, u is the control input, B is the control gain matrix, and F is the intermediate function;
[0174]
[0175]
[0176] B=-b
[0177]
[0178] in is the third derivative of the reference speed signal, is the fourth derivative of the reference height, f V is a nonlinear function with the speed of the hypersonic vehicle as an independent variable, f h is a nonlinear function with the height of the hypersonic vehi...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0184] Specific implementation mode three: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one or two is: the expression of s in the said step two is:
[0185] s = σ 2 +k 2 σ 1
[0186] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com