Method and system for promoting sleep quality through wearable equipment
A sleep-promoting, wearable device technology that is applied in diagnostic recording/measurement, medical science, and telemetry patient monitoring. It can solve problems such as smart wristbands that cannot be reminded, achieve the best sleep effect, and prevent excessive or low exercise.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
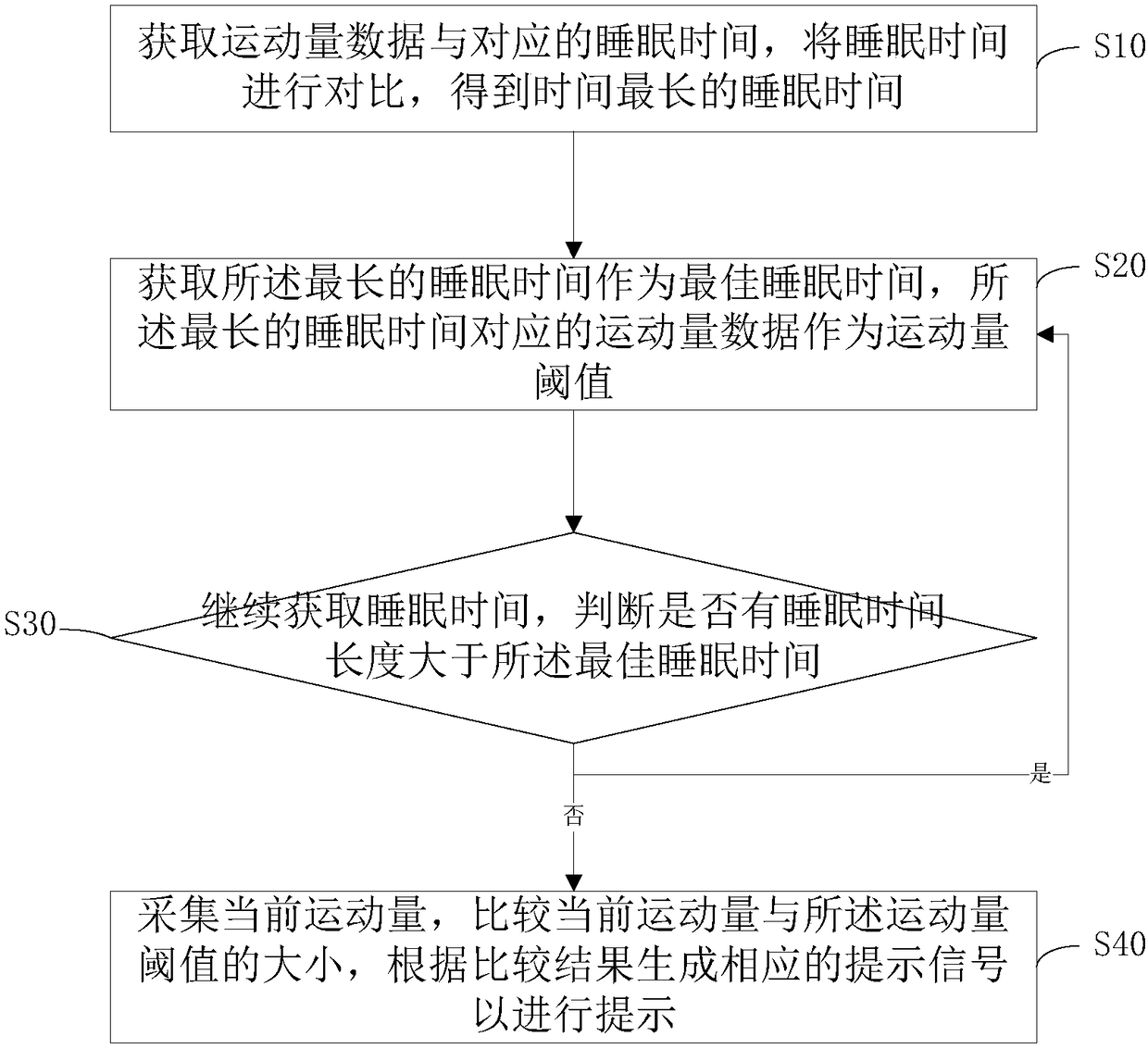
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for a wearable device to promote sleep quality, including steps:
[0046] S10: Obtain the exercise data and the corresponding sleep time, compare the sleep time, and obtain the longest sleep time;
[0047] S20: Obtain the longest sleep time as an optimal sleep time, and the exercise amount data corresponding to the longest sleep time as an exercise amount threshold;
[0048] S30: continue to acquire sleep time, judge whether there is a sleep time longer than the optimal sleep time, if yes, go to step S20, if not, execute step S40;
[0049] S40: Collect the current amount of exercise, compare the current amount of exercise with the threshold of the amount of exercise, and generate a corresponding reminder signal for reminder according to the comparison result.
[0050] In step S10, sleep time and exercise data correspond to each other according to time. The user’s daily sleep time corresponds to the user’s ex...
Embodiment 2
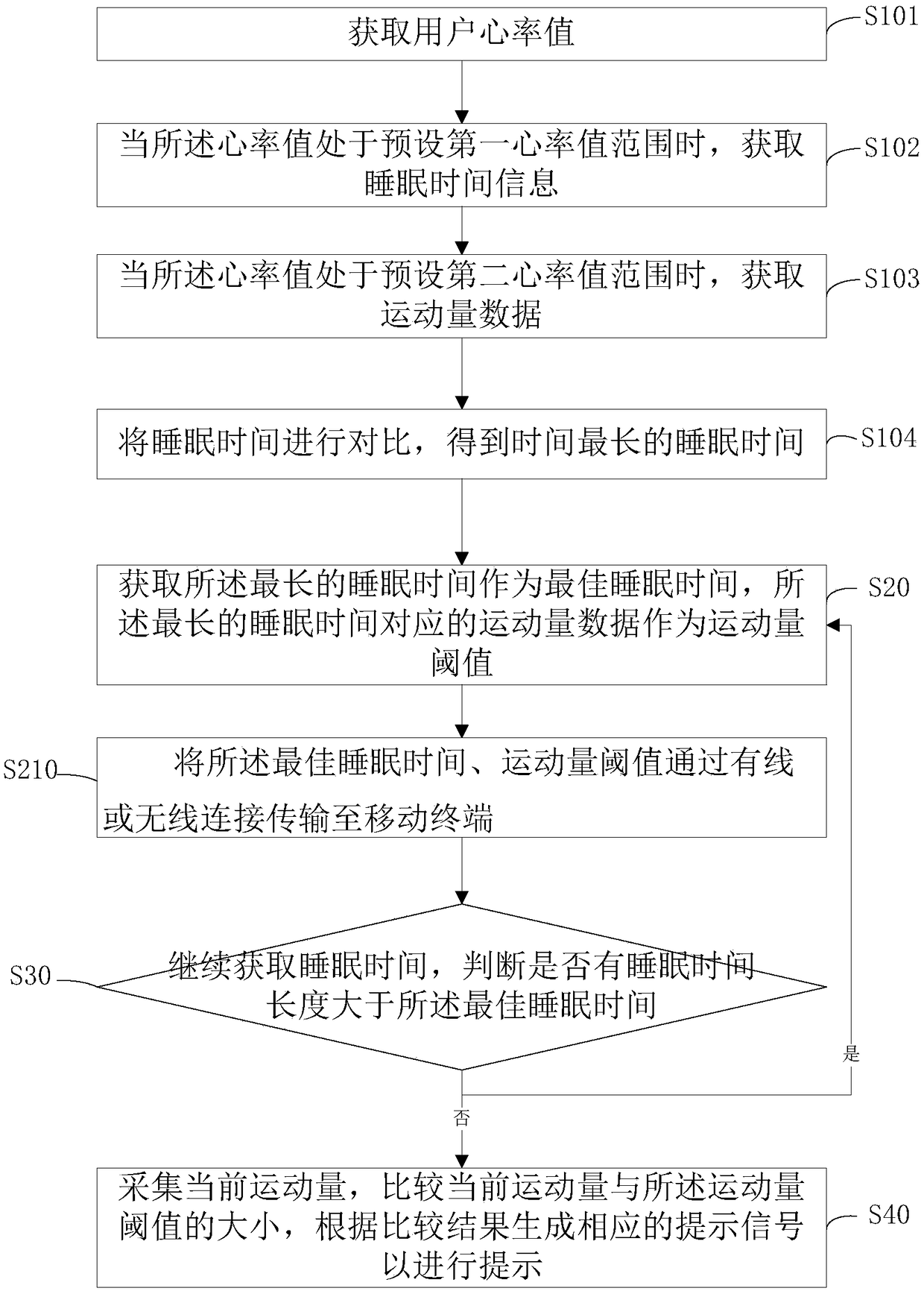
[0056] Such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment provides a method for a wearable device to promote sleep quality. The difference from Embodiment 1 is that step S10 also includes at least the following steps:
[0057] S101: Obtain the user's heart rate value;
[0058] S102: Acquire sleep time information when the heart rate value is within a preset first heart rate value range;
[0059] S103: When the heart rate value is within a preset second heart rate value range, acquire exercise data.
[0060] specifically,
[0061] When the user is exercising, the heartbeat is faster and the heart rate value is larger. When sleeping, the heartbeat frequency becomes lower and the heart rate value is smaller. Under normal circumstances, the heartbeat of a person is between 60 and 100 times per minute. During exercise, the heartbeat frequency Significantly more, the heart rate is between 110 and 140 for moderate and low-intensity exercise, and the heart rate is faster for strenuous exe...
Embodiment 3
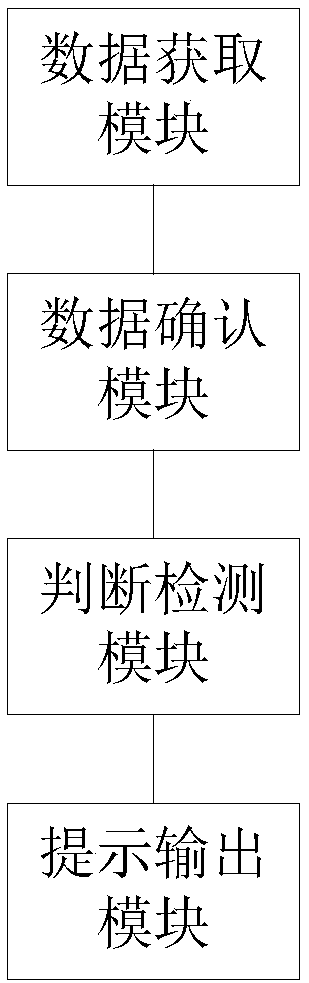
[0071] Such as image 3 As shown, this embodiment provides a system structure diagram of a wearable device promoting sleep quality, including:
[0072] Data acquisition module: used to continuously acquire exercise data and corresponding sleep time, compare the sleep time, and obtain the longest sleep time;
[0073] Data confirmation module: used to obtain the longest sleep time as the optimal sleep time, and the exercise amount data corresponding to the longest sleep time as the exercise amount threshold;
[0074] Judgment detection module: used to continue to obtain sleep time, judge whether there is a sleep time length greater than the optimal sleep time, if so, then go to the data confirmation module, if not, then go to the prompt output module;
[0075] Prompt output module: used to collect the current amount of exercise, compare the current amount of exercise with the threshold value of the exercise amount, and generate a corresponding prompt signal for prompting accord...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com