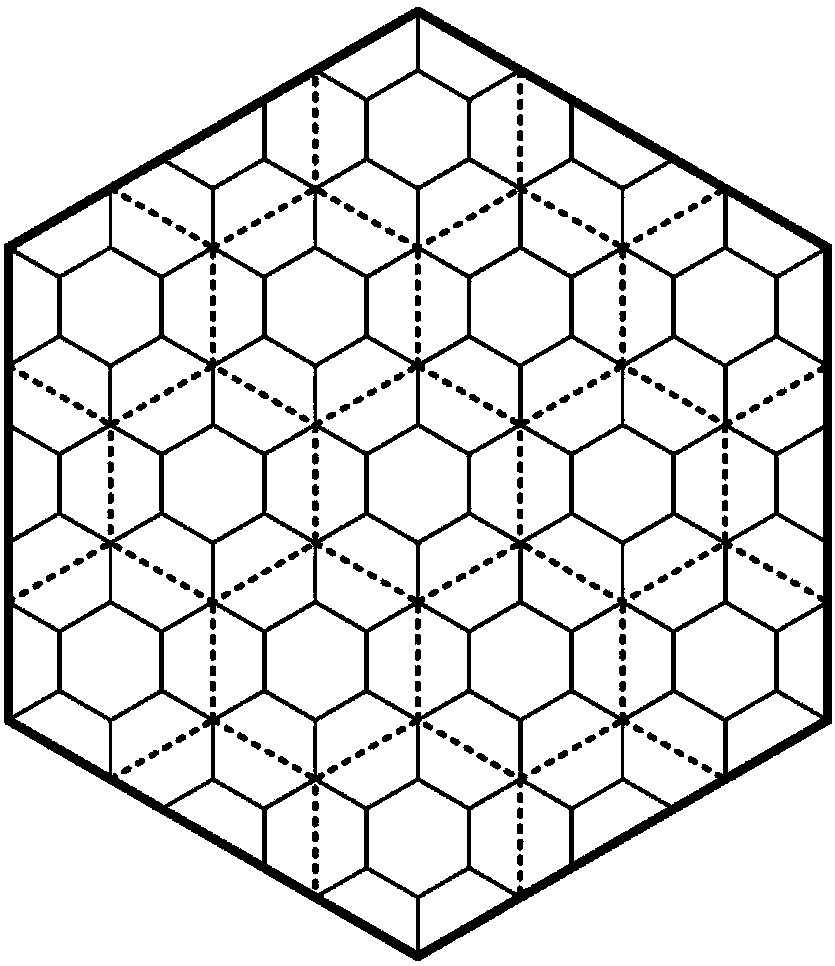
Coding method and device for layered grid
A coding method and grid technology, applied in the field of spatial information, can solve the problems of difficult hierarchical relationship of multi-resolution hexagonal grid cells, complex spatial data processing process, and lack of self-similarity of hexagons, achieving strong Spatial connectivity and spatial scalability, good spatial data representation, and the effect of reducing processing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] An embodiment of the present application provides a coding method for a hierarchical grid, including the following steps:
[0047] Step 101:
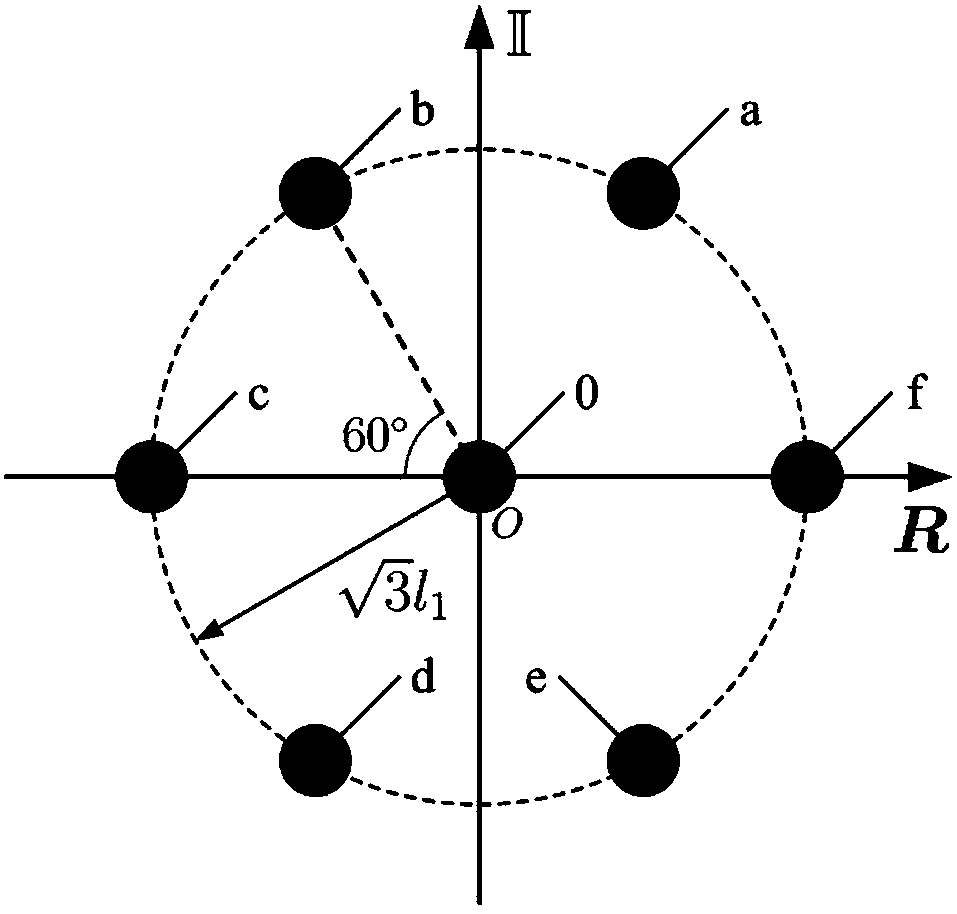
[0048]In a plane, the first layer of grid points is established, and the first layer of grid points includes a central grid point and six first layer vertices surrounding the central grid point, and the first layer of vertices are located at the The center grid point is the center of the circle, with is on a circle with a radius, and the included angle between every two adjacent vertices of the first layer and the line connecting the center grid point is 60°.
[0049] In the above steps, l 1 is the unit length, figure 2 It is the position relationship diagram of the first-level grid points in the complex plane coordinate axis. The first-level grid points include a central grid point o and six vertices a, b, c, d, e, and f surrounding the central grid point o. The 6 vertices around the center grid point o are located at the ...
Embodiment 2
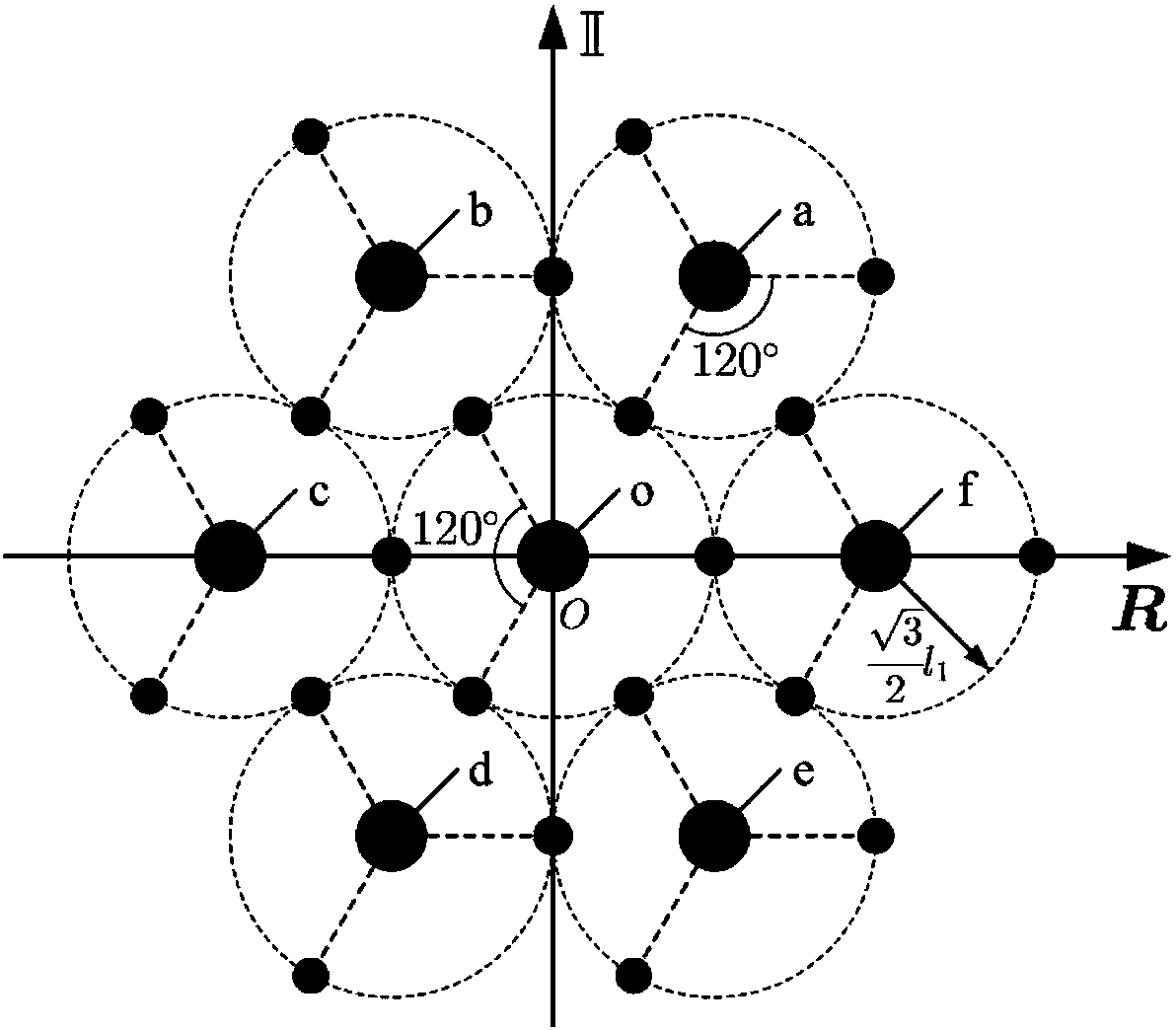
[0069] Based on the above-mentioned embodiments, this embodiment of the present application provides a coding method for a hierarchical grid. When n is less than N, the position of the n+1th layer vertex relative to the nth layer grid point is the same as the position of the nth layer vertex relative to the nth layer The positions of the -1 level grid points are the same.
[0070] Wherein, N is an integer greater than 1, which may refer to the total number of layers of the hierarchical grid. For example, it is limited that there are 10 layers of grids, that is, N=10. The position of the 5th level vertex relative to the 4th level grid is the same as the position of the 4th level vertex relative to the 3rd level grid. The newly added vertices of each layer are selected according to the extension direction of the existing grid points. According to the above selection rules, the extension direction of the newly added grid points can be guaranteed to be uniform. Six new vertices...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Based on the above embodiments, an embodiment of the present application further provides a method for encoding a hierarchical grid, which is used for calculating the grid encoding provided by the above embodiments.
[0123] Denote the set of grid points encoded by code elements as for The code element encoding algorithm in includes:
[0124] The coded addition operation follows the parallelogram rule; the coded subtraction operation follows the parallelogram rule and is inverse to the coded addition operation; the coded multiplication operation follows the rotation and scaling of vectors in polar coordinates.
[0125] Through the above coded addition, subtraction, and multiplication operations, the position of the grid point coded by the symbol can be moved. Specifically, the rotation and scaling of the grid point relative to the origin position, or the switching between multiple grid point positions can be realized. In this way, the positioning of grid points, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com