Coding unit (CU) division method applied to high efficiency video coding (HEVC)
A technology for encoding frame and depth, applied in the field of video encoding, can solve the problems of slow encoding speed and high computational complexity of HEVC encoding, and achieve the effect of improving encoding speed, realizing CU division, and achieving obvious acceleration effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
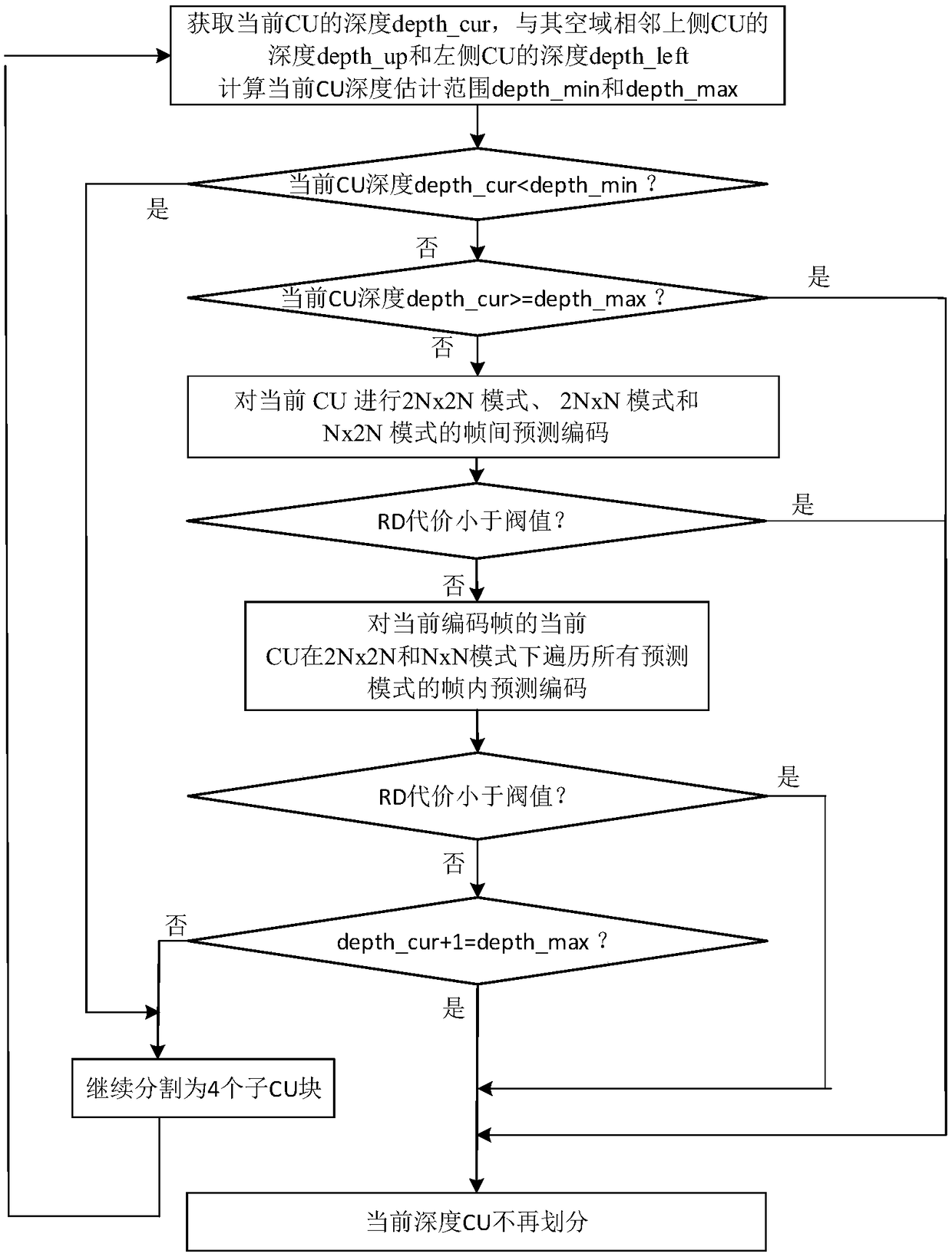
[0039] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the specific process of a CU division method for HEVC in this embodiment is:
[0040] Step 1. The size of the current CU of the current coded frame is 2Nx2N, obtain the depth_cur of the current CU of the current coded frame, and obtain the space adjacent to the current CU of the current coded frame (only consider the upper and left sides of the same frame) The depth of the side CU and the left CU, so as to estimate the current CU depth minimum depth_min and maximum depth_max of the current coded frame;
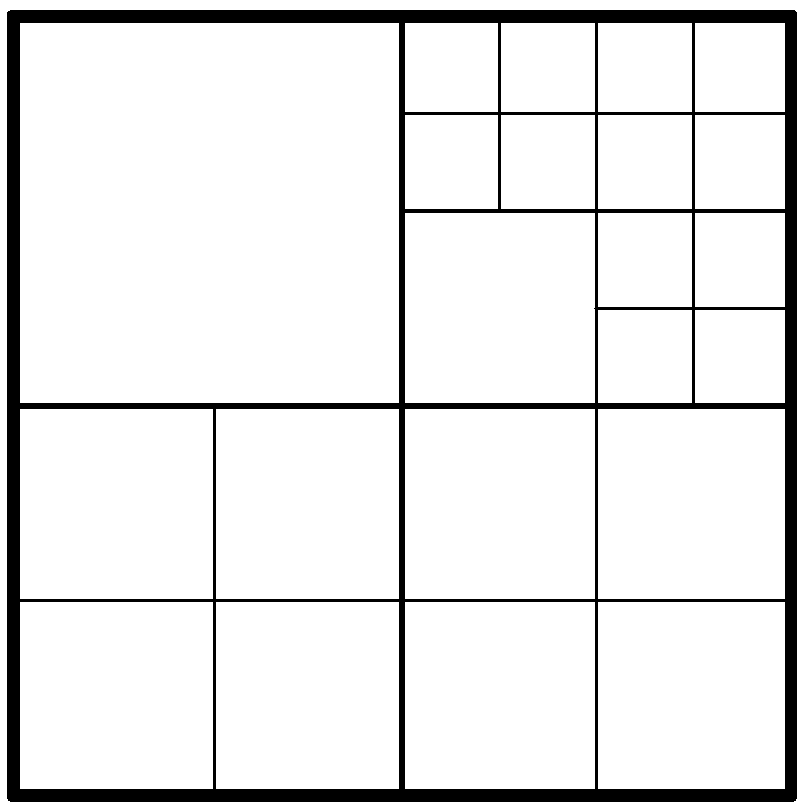
[0041] The left and upper CUs of a CU refer to the left and upper CUs immediately adjacent to the upper left corner of the CU (such as Figure 7 shown).
[0042] That is, |depth_cur-depth_up|≤1 and |depth_cur-depth_left|≤1;
[0043] In this formula, the depths of the adjacent upper CU and left CU are known. By combining the two equations, the minimum depth_min and maximum depth_max of the cu...
specific Embodiment approach 2
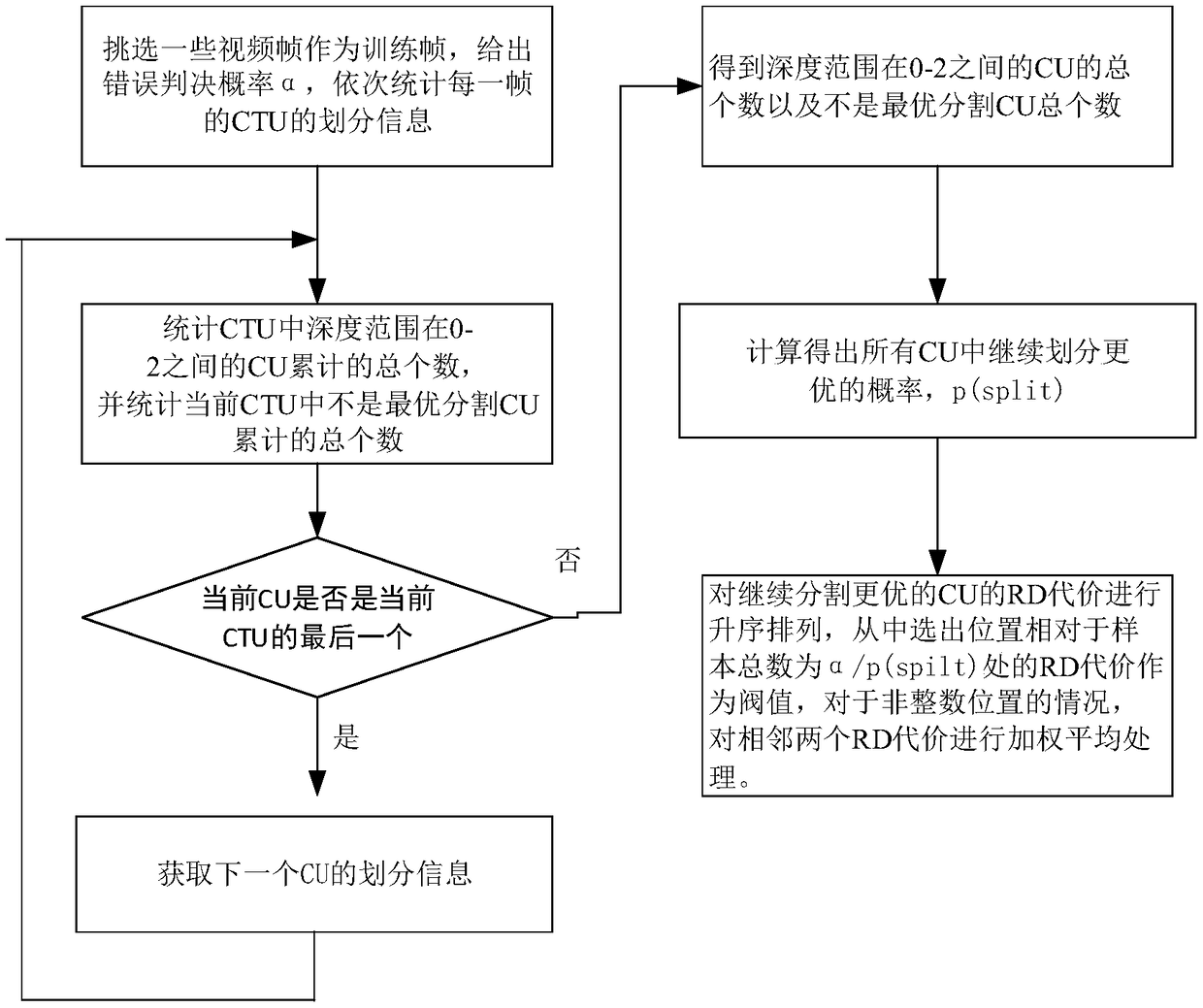
[0054] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the specific calculation formula of the rate-distortion cost in the steps 2 and 3 is as follows:
[0055] J(s,c,QP,λ m )=SSD(s,c)+λ m B(s,c,QP)
[0056] Among them, J is the rate-distortion cost, λ m Represents the Lagrangian multiplier, QP represents the quantization coefficient, B is the number of bits required for encoding, s is the original CU, c is the reconstructed CU obtained by performing inter-frame prediction or intra-frame prediction on the original CU, SSD(s,c ) represents the difference sum of squares of s and c;
[0057] The bit rate B required for encoding is obtained by quantizing and encoding the prediction residuals of the original CUs and the reconstructed CUc by the HEVC encoder.
[0058] By quantizing and encoding the residuals of s and c, the number of bits is obtained as B(s,c,QP), and the size of QP affects B(s,c,QP);
[0059] The specific calculation method of SSD...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0063] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 2 This embodiment is described. The difference between this embodiment and the first or second embodiment is that the quantization coefficient QP takes an integer between 0 and 51 (only one QP value is taken each time).
[0064] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or Embodiment 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com