Method for determining light damage on cultural relics based on Raman spectroscopy analysis
A technology of Raman spectroscopy and determination method, which is applied in the interdisciplinary fields of analytical chemistry, lighting technology, and cultural relics protection. It can solve the problems of no new revision, lack of scientific basis for promotion, and lack of effective support for research results, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
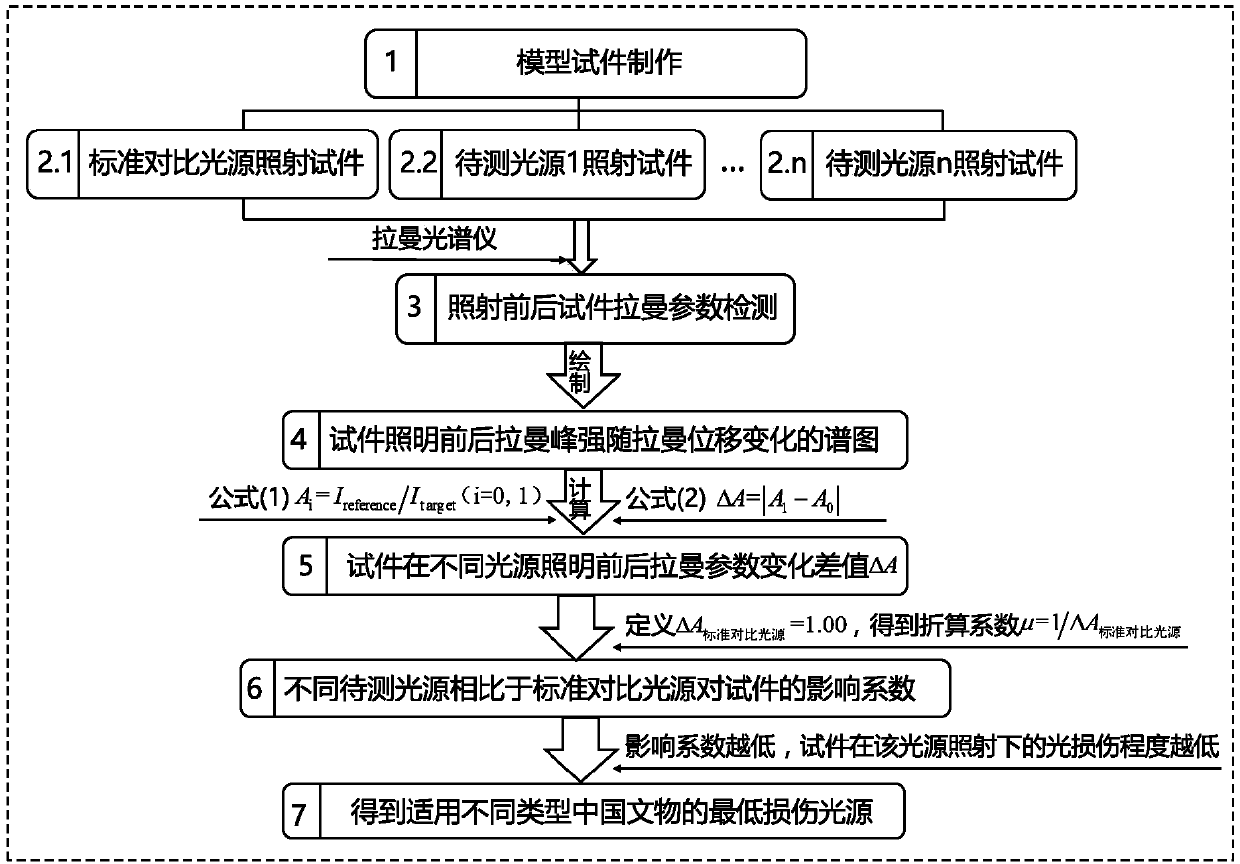
[0083] See the technical solution process figure 1 .
[0084] 1. Model test piece
[0085] (1) For cultural relics composed of a single material: the constituent materials are made into model specimens, such as wood, bamboo, and animal specimens.
[0086] (2) For cultural relics composed of composite materials: the main constituent materials were made into model specimens, such as calligraphy and painting, and the pigments and paper and silk substrates were made into samples.
[0087] 2. Experimental light source
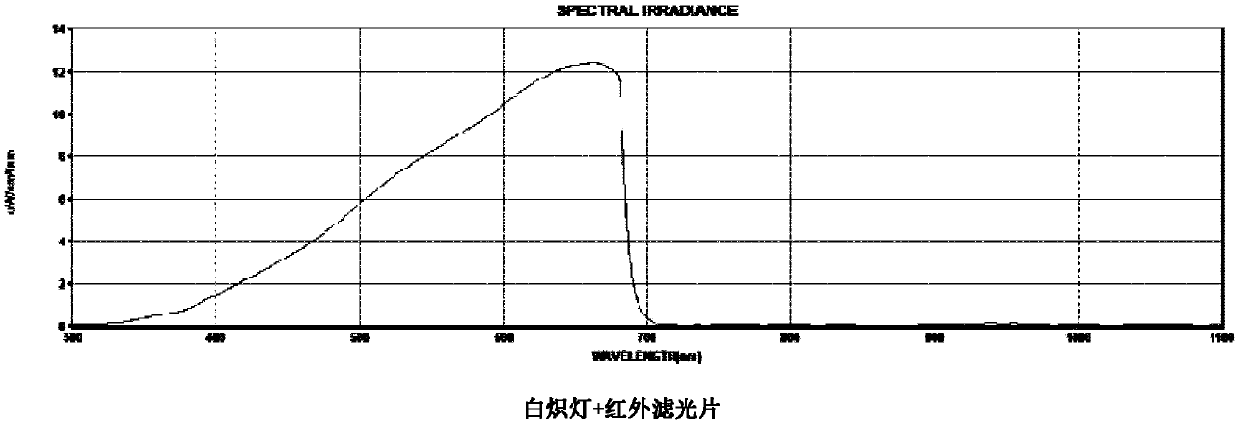
[0088] (1) Standard contrast light source: CIE standard A light source (incandescent lamp, Tc=2700K, Ra=97) is used, and infrared filters are used to filter out the infrared spectrum (only the visible spectrum is included to meet the lighting requirements of cultural relics), As a standard contrast light source. The spectral power distribution of the light source is shown in figure 2 .
[0089] (2) Experimental light source to be tested: other types of metal halide lamps, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com