Exchange block chain system and corresponding universal block chain interoperation method and network
A blockchain, interoperable technology, applied in the blockchain field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
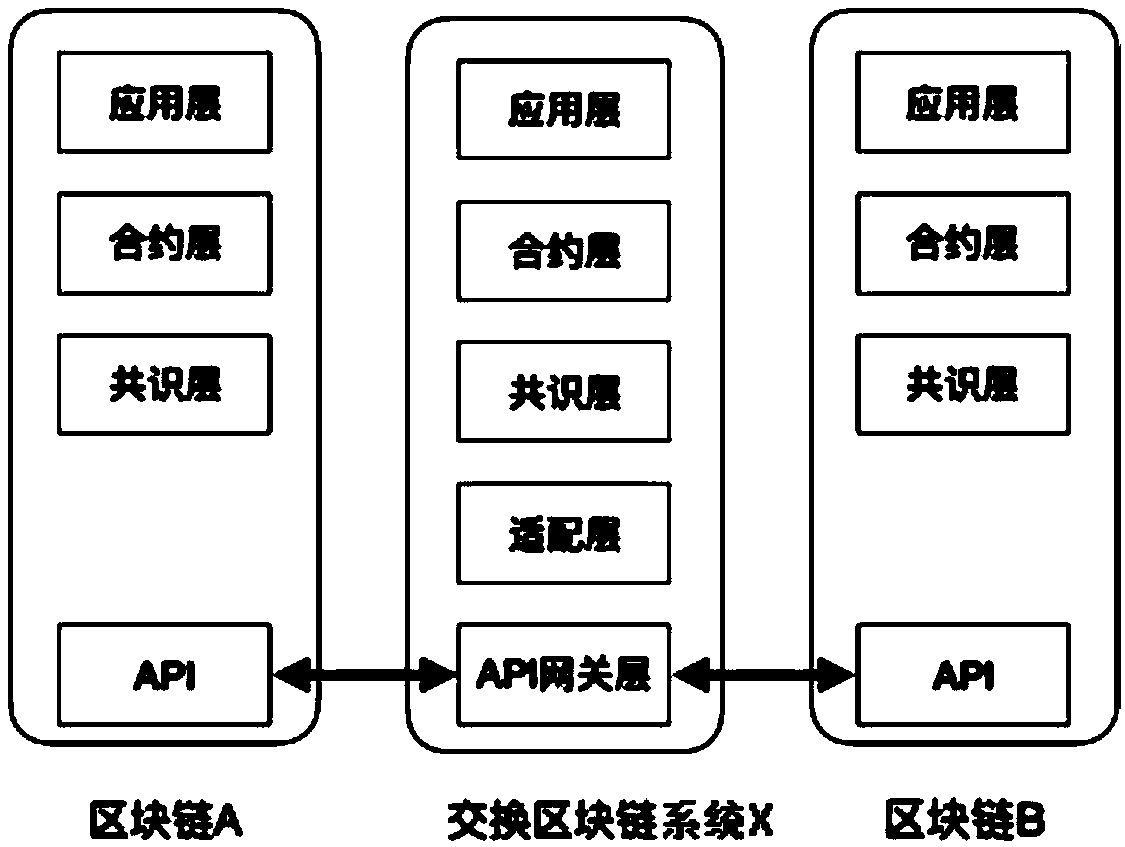
[0069] See figure 1 , which shows a logical layered structure in a general blockchain interoperability system.
[0070] According to the ISO / OSI layered design idea, the exchange blockchain system can be logically divided into: application layer, contract layer, consensus layer and adaptation layer. At the application layer, business logic needs to be described by a unified, permission-based operating primitive; at the contract layer, complete functions are realized by writing operation procedures, taking into account cross-chain data consistency; at the consensus layer, the consensus mechanism ensures that the execution process can The data is transparent and cannot be tampered with; the adaptation layer realizes protocol conversion and message communication of heterogeneous blockchains.
[0071] a. Application layer
[0072] The operating primitives adopted by the application layer mainly focus on the interoperability description at the abstract level, and uniformly identi...
Embodiment 2
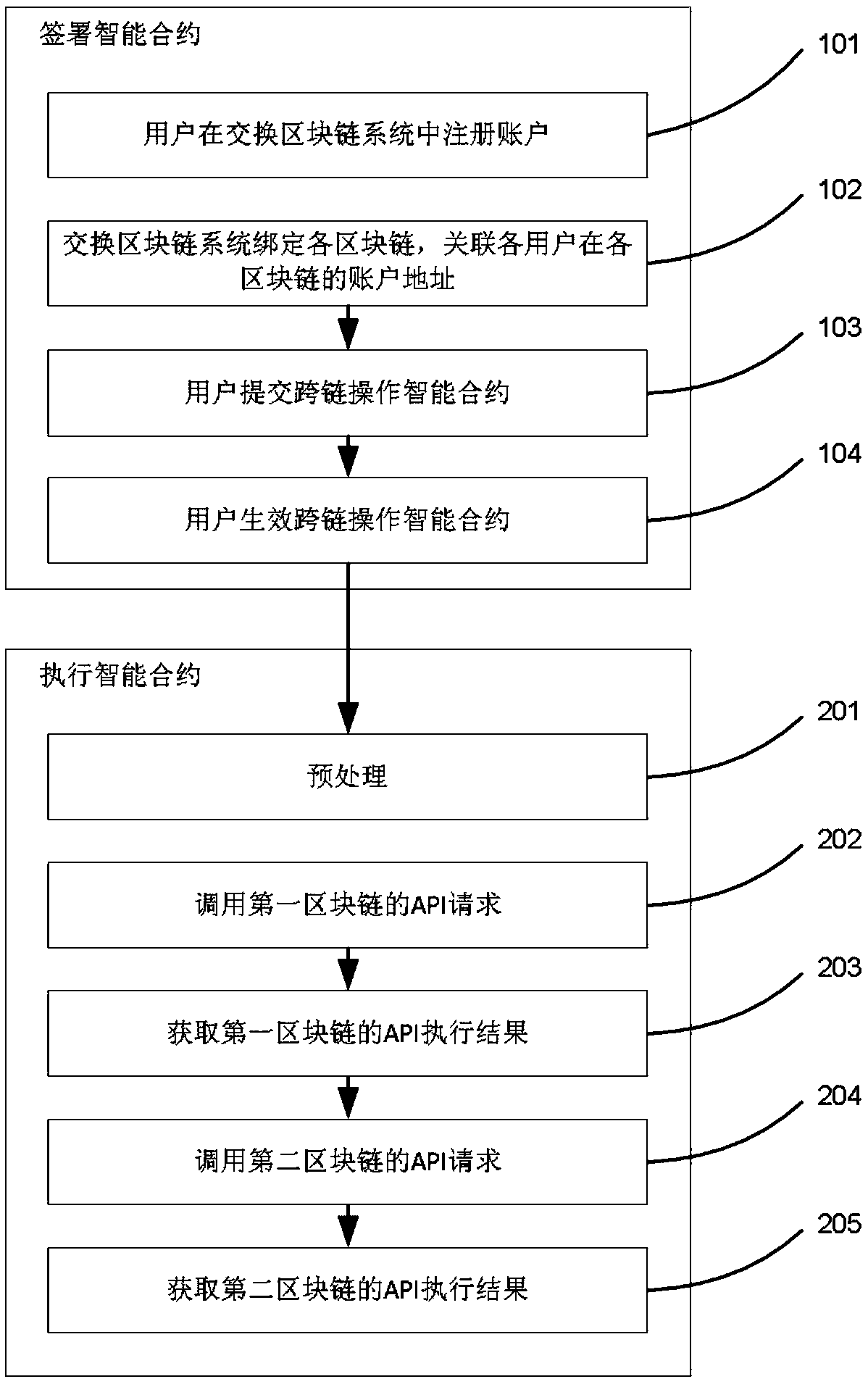
[0088] See figure 2 , which shows a flow chart of a general blockchain interoperability method, which is described as follows.
[0089] The first stage is the contract signing process:
[0090] Step 101, user a and user b register their respective accounts in the exchange blockchain system.
[0091] Step 102, the exchange blockchain system binds the target blockchain systems A, B and the exchange rate center C, and automatically associates the account addresses a@A, a@B, b of users a and b in the blockchain systems A and B @A, b@B.
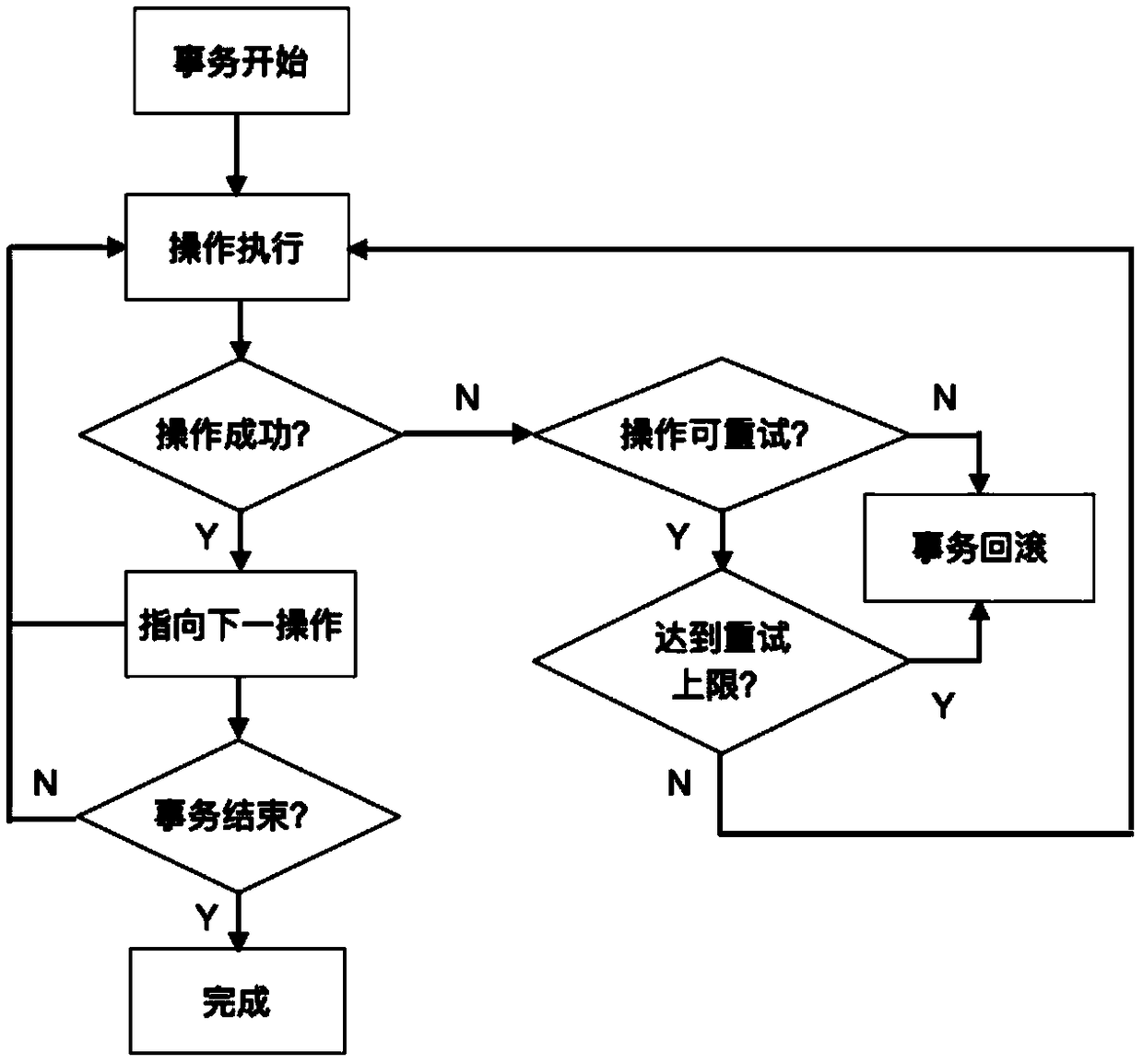
[0092] Step 103, user a or b submits a smart contract to the interactive blockchain, the content is as follows: 1) a transfers m tokens to b on blockchain A, 2) b then transfers m tokens to a on blockchain B Enter n (according to the data of the exchange rate center C, n=m*k, k is the exchange rate) tokens. If 1) execution fails, the process rolls back (no operation) without retrying. If the execution of 2) fails, the completed step 1) is ro...
Embodiment 3
[0109] See Figure 4, which shows a general blockchain interoperability network model. Among them, including exchange blockchain system X, blockchain system A, blockchain system B and non-blockchain system C, where C is a centralized network. The exchange blockchain system X consists of multiple distributed nodes. Exchange blockchain system X is interconnected with blockchain system A and blockchain system B. Because the blockchain system A and the blockchain system B run their own network protocols, the exchange blockchain system X needs to go through the corresponding proxy node when exchanging data with the blockchain system A and the blockchain system B. . The agent node is responsible for converting the general protocol inside the exchange blockchain system X into the unique network protocol of the target blockchain system A or B to realize data interaction. At the same time, the exchange blockchain system X can also interact with the target centralized network C, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com