Two-stage slot less cylindrical permanent magnet linear motor
A permanent magnet linear motor, two-stage technology, applied in electrical components, electromechanical devices, electric components, etc., can solve the problems of large space occupied by the magnetic isolation bridge, increase of the effective volume of the motor, discrete motor structure, etc. Average thrust, increased reliability, increased thrust density effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
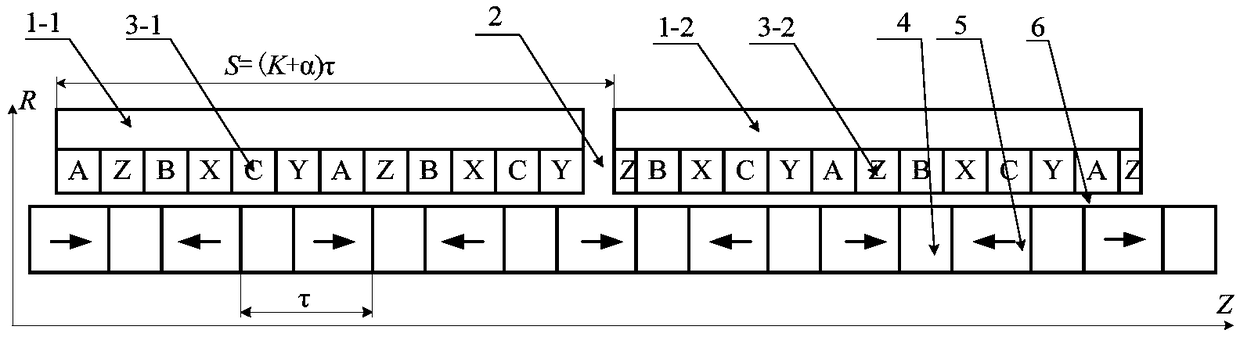
[0024] Such as figure 1 with figure 2 As shown, the present invention provides a two-stage slotless cylindrical permanent magnet linear motor, which includes a two-stage primary assembly and a secondary assembly. The primary assembly is composed of a first section of primary iron core 1-1, a second section of primary iron core 1-2, an armature winding 3-1 and an armature winding 3-2. The primary assembly adopts a slotless structure, and the armature winding 3-1 and the armature winding 3-2 are respectively fixed on the inner circles of the cylindrical primary iron core 1-1 and the cylindrical primary iron core 1-2. The secondary assembly consists of a secondary iron core 4 and a permanent magnet 5 . There is an air gap 6 between the primary and secondary components. A magnetic isolation bridge 2 is arranged between the two primary structures. The sum of the lengths of the first primary iron core and the magnetic isolation bridge is (K+α)*τ (K is a positive integer, τ is t...
Embodiment approach 2
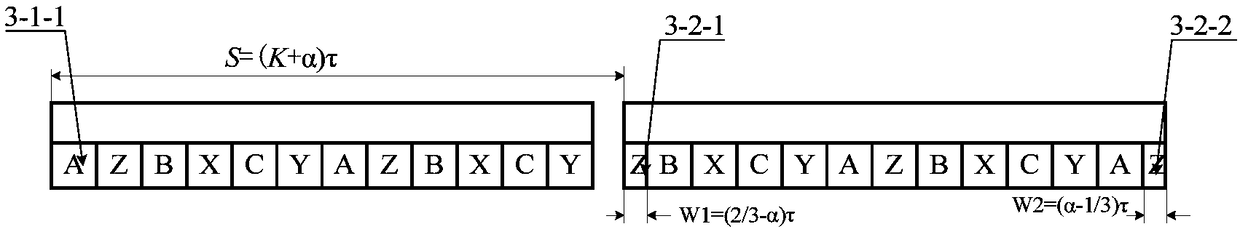
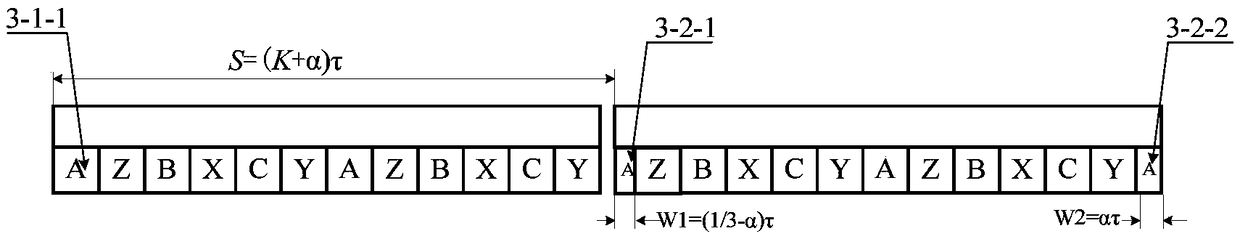
[0027] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: image 3 As shown, the sum of the lengths of the primary iron core and the magnetic isolation bridge of the first section is (K+α)*τ (K is a positive integer, 0<α<1 / 3, τ is the pole pitch of the motor), and the armature of the second section The start and end of the winding are coils of width W1=(1 / 3-α)τ and W2=α*τ, respectively. The phase of the initial-end coil 3-2-1 on the second primary stage is the same as that of the initial-end coil 3-1-1 on the first primary stage.
Embodiment approach 3
[0029] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is: Figure 4 As shown, additional teeth 8 at the ends are added at both ends of the primary assembly of the first stage and the primary assembly of the second stage.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com