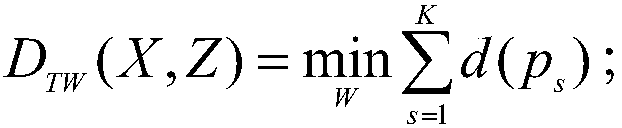Single-phase ground fault line selection method and device
A single-phase-to-ground fault and line selection method, applied in fault location, measurement device, fault detection by conductor type, etc. Line accuracy, avoidance of indeterminate lines, and the effect of reducing computation time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
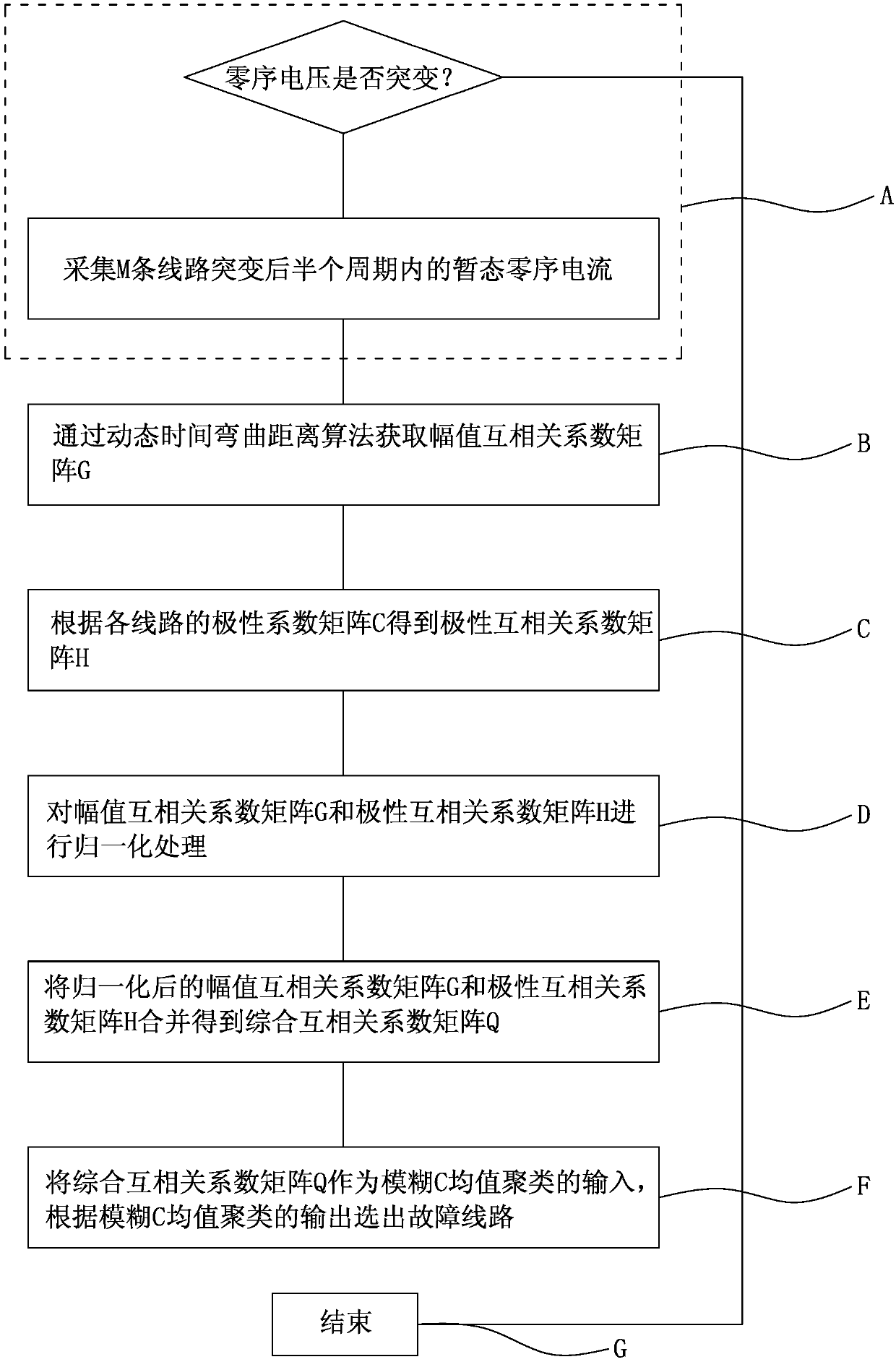
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown, a single-phase ground fault line selection method includes the following steps:
[0045] A. Determine whether the zero-sequence voltage has a sudden change. If so, collect the transient zero-sequence currents of the M lines in the half period after the sudden change, and enter step B; otherwise, enter step G;
[0046] Among them, judging the sudden change of zero-sequence voltage includes the following steps:
[0047] Perform db4 wavelet decomposition on the zero-sequence voltage signal, and perform single-branch reconstruction on the decomposed d3 detail coefficients. When the modulus maximum value of a sampling point in the single-branch reconstruction signal is greater than or equal to 0.1, it is determined that the zero-sequence voltage signal has occurred mutation;
[0048] After judging that the zero-sequence voltage signal has a sudden change, the transient zero-sequence current transformer of each line is collected by the transient z...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com