A kind of anti-theft tumbler lock and graphene anti-theft tumbler lock
A tumbler lock and graphene technology, applied in the field of anti-theft locks, can solve the problems of rough detection logic and false detection of tumbler locks, and achieve the effect of meticulous detection logic, less false alarms, and accurate detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
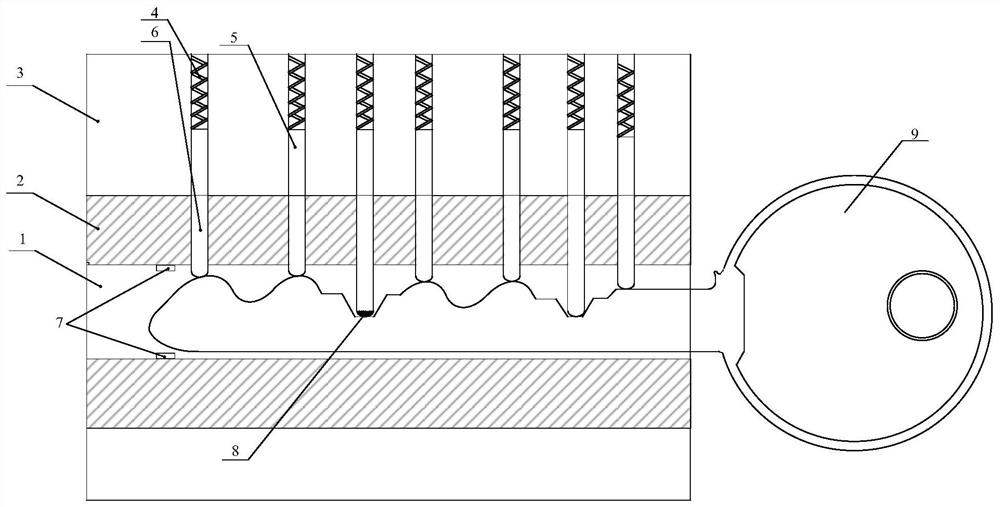
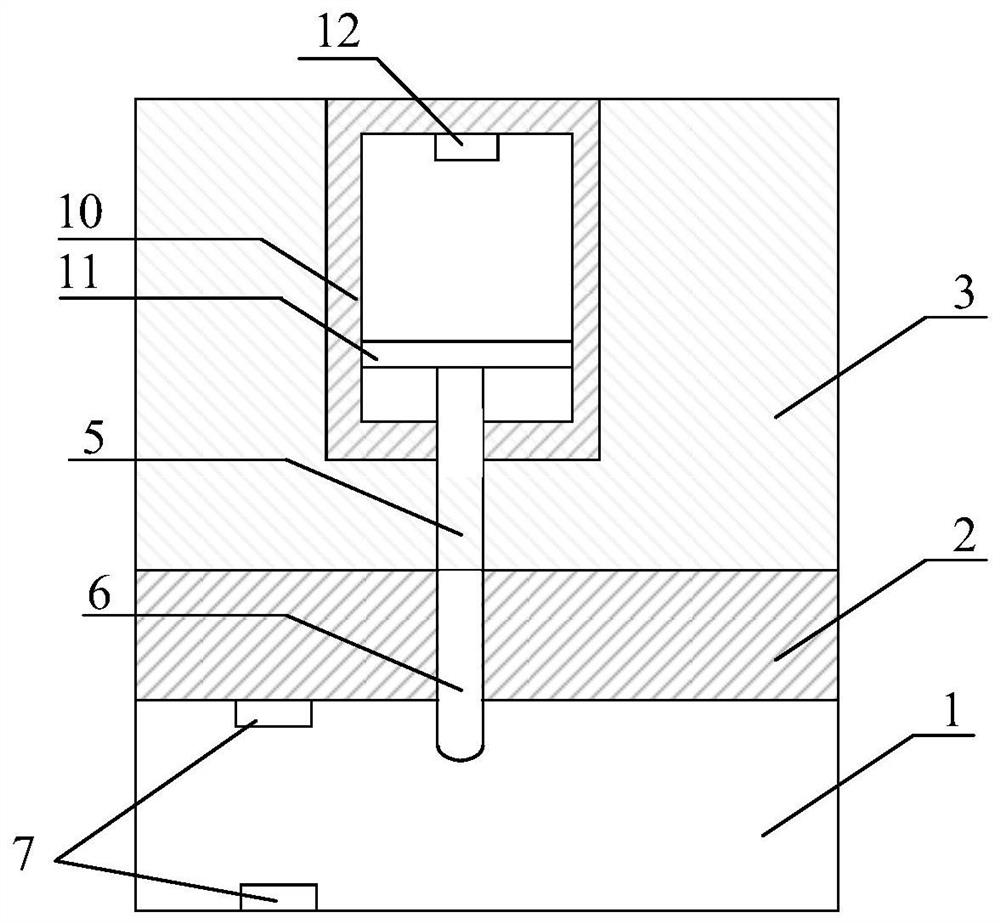
[0013] Embodiment 1: The anti-theft tumbler lock of this embodiment, wherein at least one outer tumbler 6 is provided with a pressure sensor 8, and at least one photoelectric sensor 7 is arranged around any one of the inner outer tumblers 6, and the outside of the lock cylinder is provided with a The processor (not shown) connected to the pressure sensor 8 and the photoelectric sensor 7, the processor is used to judge the Whether there is an illegal unlocking behavior.
[0014] Specifically, the present invention judges whether illegal unlocking occurs through the pressure sensor arranged at the lower part of the outer tumbler and the photoelectric sensor of the inner lock cylinder. The pins include an inner pin and an outer pin in contact with each other, the outer pin refers to a part in contact with the key, and the inner pin is a part in contact with the spring in the magazine groove. The "surrounding" of "any one of the outer pins" can be the position of the outer pins, ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0020] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: the number of photoelectric sensors 7 is 1, and the preset position is the position where the innermost pin of the inner lock cylinder 2 is located.
[0021] The beneficial effect of this embodiment is: the purpose of detecting illegal unlocking can be achieved by using a group of photoelectric sensors, which saves costs, and the setting of the preset position in this way can accurately determine the position where the key has reached the end of the lock cylinder. It should be noted that "the position of the pin at the deepest part of the inner lock cylinder" should ensure that the pin does not block the receiving part of the photoelectric sensor.
[0022] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0023] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the quantity of pressure sensor 8 is 1, the quantity of photoelectric sensor 7 is 1, and pressure sensor 8 is arranged on the pin 6 of inner lock core 2 deepest. At the bottom, the photoelectric sensor 7 sets the deepest position where the end of the key 9 can be inserted;
[0024] Processors include:
[0025] The first detection unit is used to determine whether the receiving end of the photoelectric sensor detects a light signal within a preset time threshold when the pressure received by the pressure sensor is greater than the gravity of the marble, and if so, the processor sends out a warning message.
[0026] It can be seen from the principle of the normal unlocking process in the specific embodiment 1 that when the pin 6 is lifted during the normal unlocking process, the key 9 should have been fully inserted, so when the pressure sensor 8 detects a pressure cha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com