Common phase error compensation
A phase error, associated technology, applied in the field of error compensation, to achieve the effect of improving resource utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
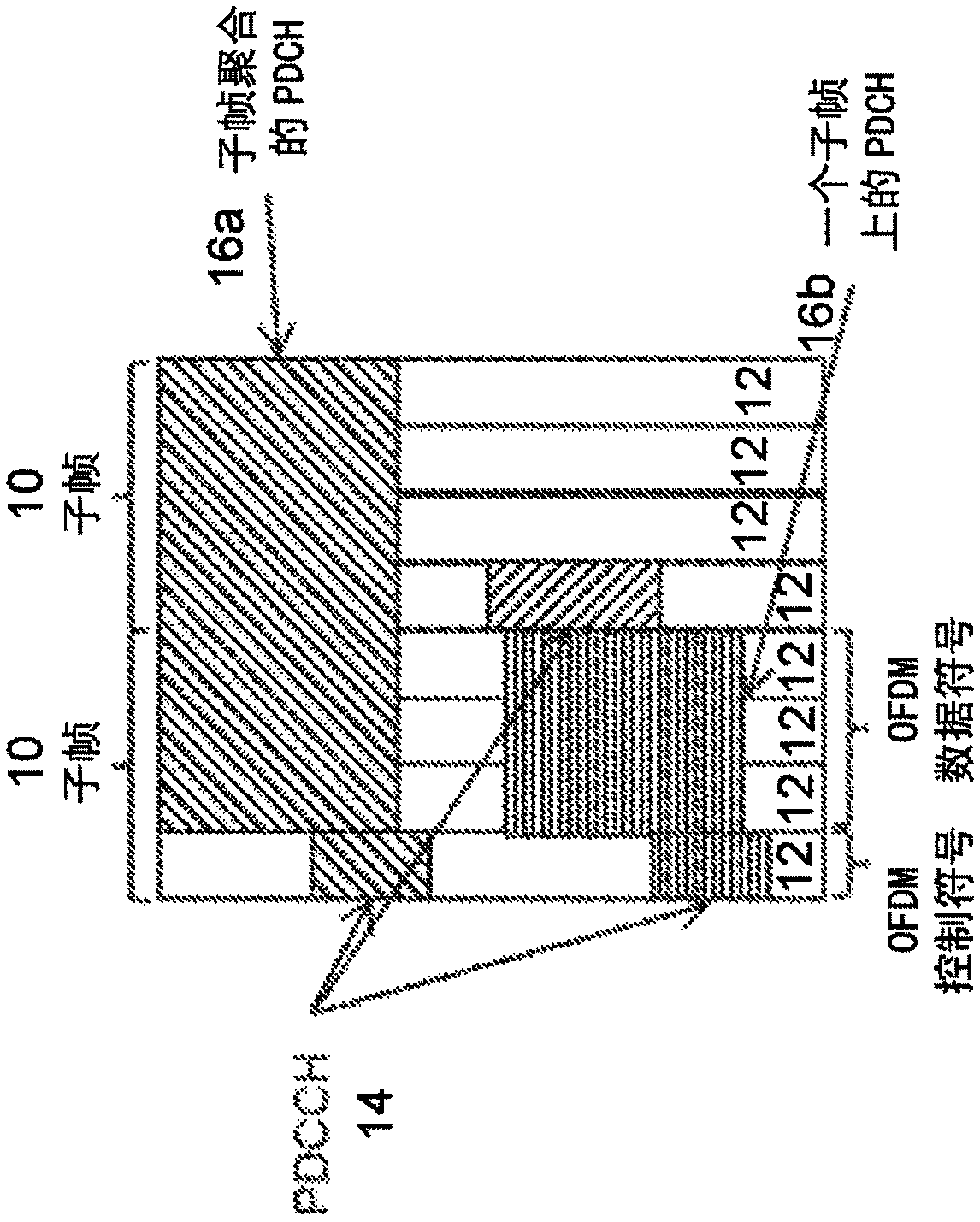
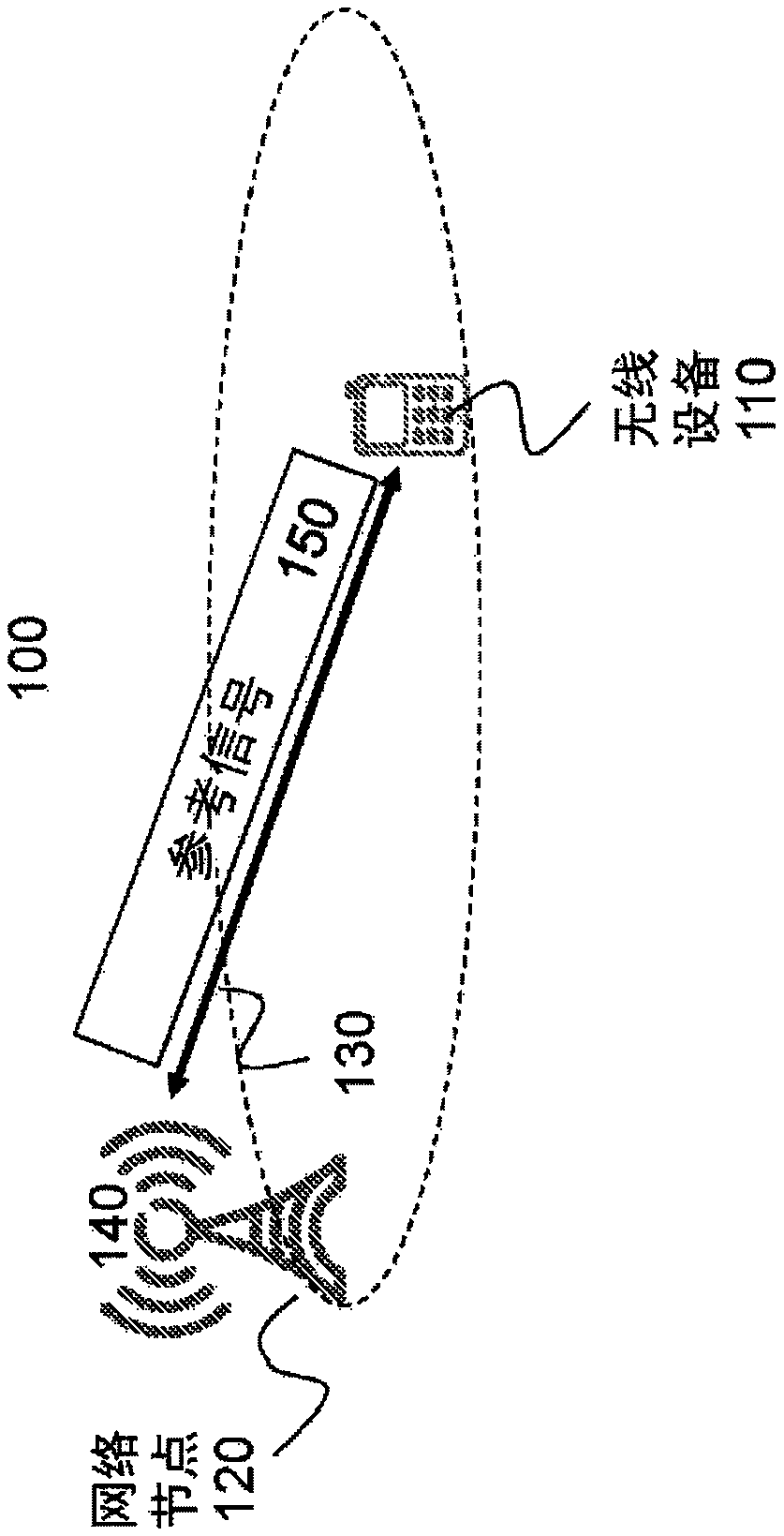
[0046] A conventional synchronous radio system includes an always-on downlink signal (eg, PSS / SSS / CRS in LTE) that enables the UE to track the time-frequency synchronization of the base station without communicating with the network. This design simplifies time-frequency synchronization, but at the cost of poor energy performance and constant interference from always-on signals.
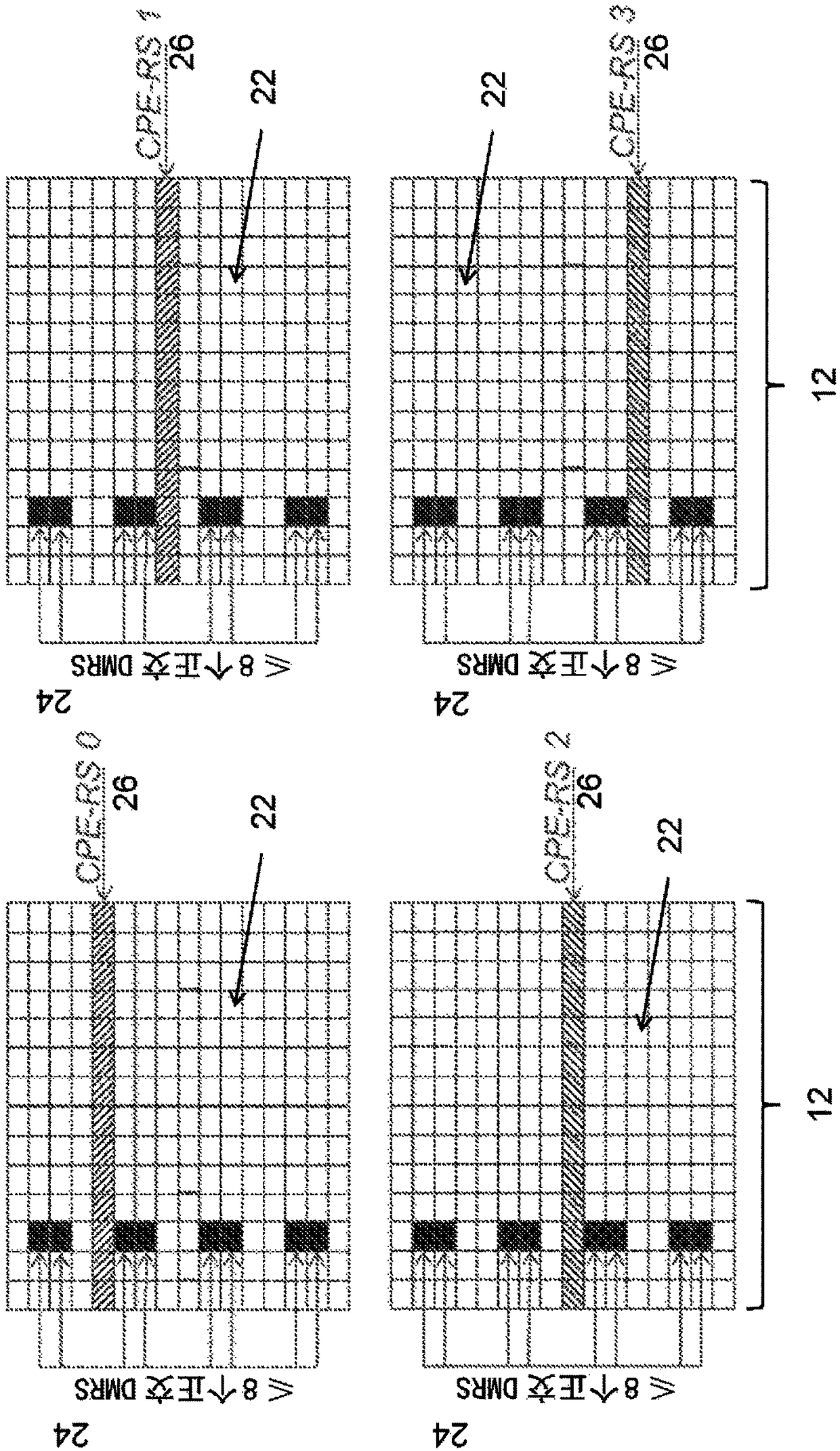
[0047] A thin system design that eliminates signals that are always present is another option. However, the consequence of eliminating an ever-present signal such as CRS is that tracking and fine-tuning of time-frequency synchronization becomes more complicated. Relying on DM-RS for time-frequency synchronization will incur significant overhead as it uses most of the spectrum for synchronization at the expense of reduced data rates. For example, using DM-RS to track common phase errors is inefficient because the required time density is high for accurate common phase error tracking. DM-RS is design...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com