Methods of encoding and decoding information
A technology for information encoding and information decoding, applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, coding, informatics, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0168] Example 1. Implementation of the encoding method described above for writing the control bits of a logical addition (ab) operation, where the rule is applied modulo a binary addition: if operands (a) and (b) are both "0" in In all other cases, the result is "1":
[0169]
[0170] For ternary addition (X, Y, Z) modulo 2, the rule applies: if no operands are equal to "1" or their even number, the result is "0", and otherwise the result is "0":
[0171]
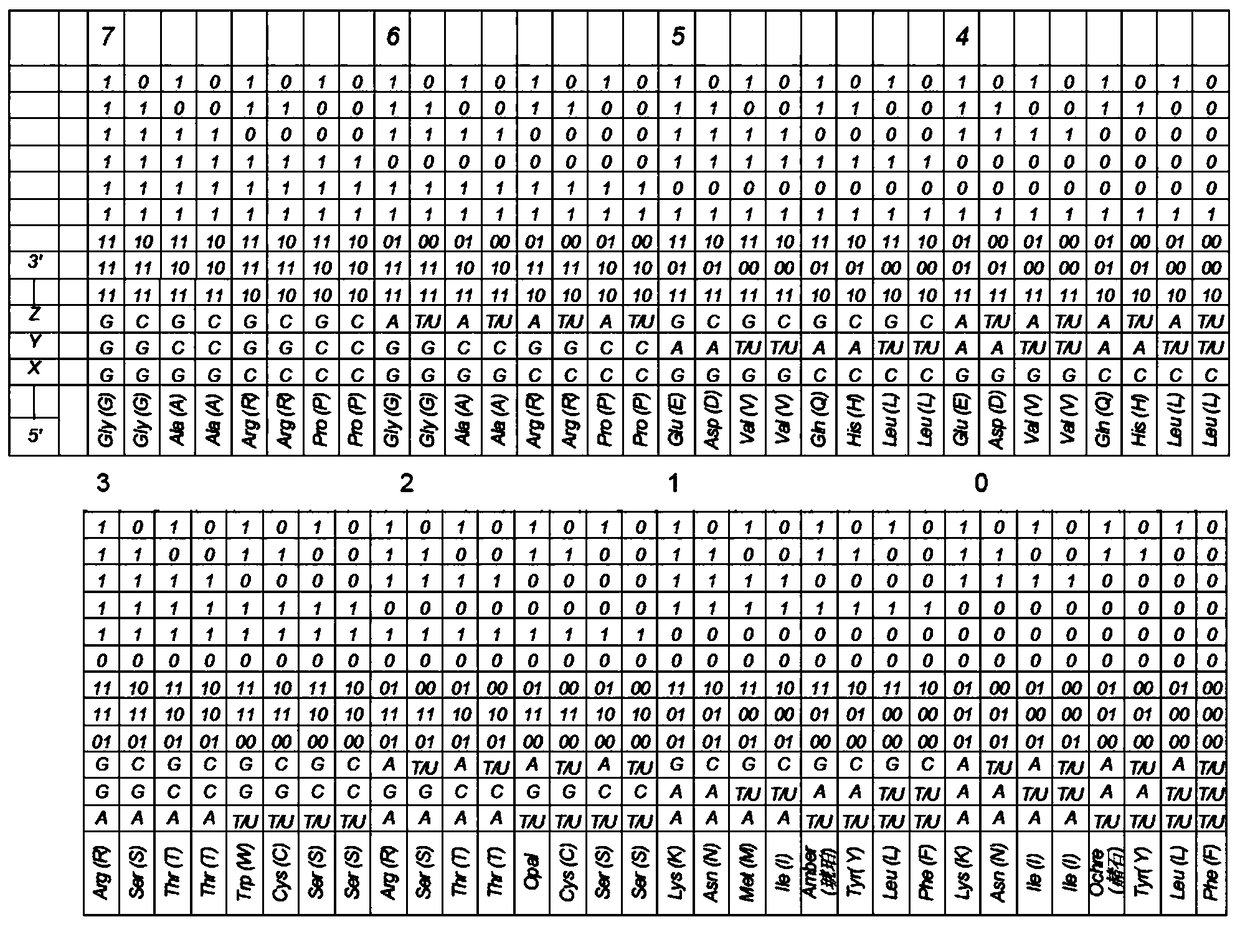
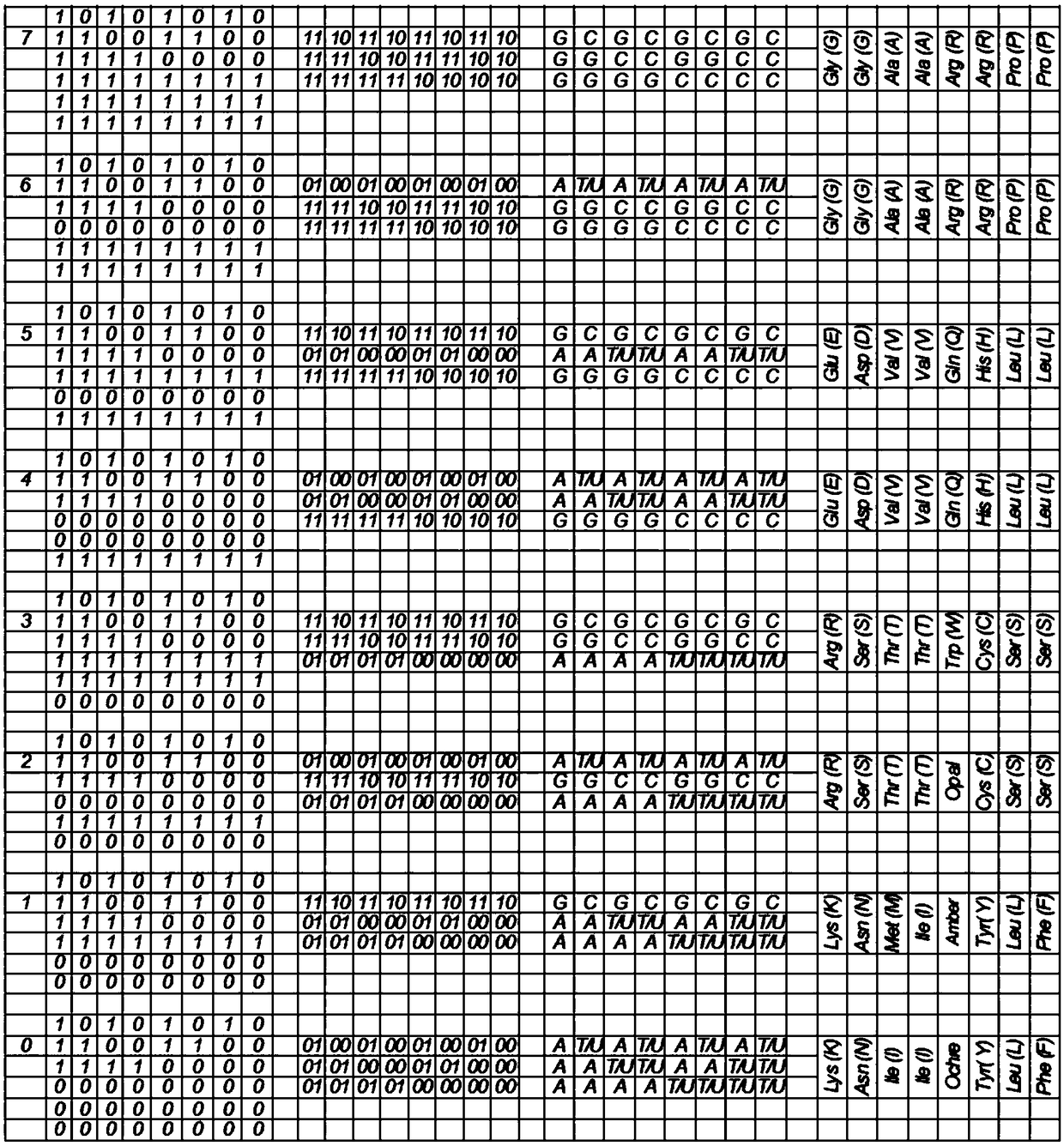
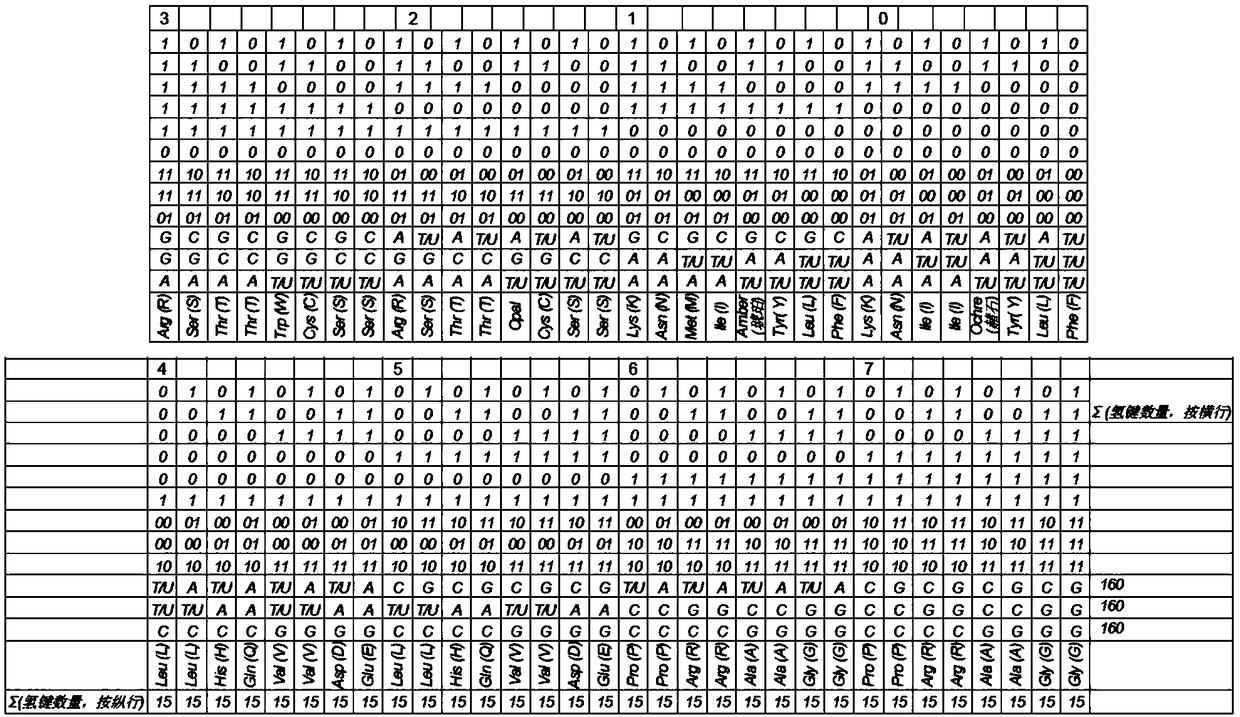
[0172] This method of recording is based on the three-bit decomposition of the major nitrogen bases (A, C, G, T, U) and their minor analogues:
[0173] the bit "p" of the nitrogen-based class (purine or pyrimidine);
[0174] The number "h" of hydrogen bonds at nitrogenous bases (2 or 3);
[0175] • The "e" bit for a nitrogen base (aMino or Keto).
[0176] In this case, the first two information bits ("p" - purine or pyrimidine and "h" - the number of hydrogen bonds) act as variable values, and the third control b...
example 2
[0197] Example 2 Encoding of the word "МИР" (without checking for errors)
[0198] exist Figure 17 The correspondence of the triplet DNA code (RNA) to the symbol values of the Latin and Russian letters is shown in . Recording is performed from the 5' end to the 3' end. In this example, three nitrogenous bases correspond to a logic element.
[0199] Code combinations can be represented in different ways:
[0200] 1) Linear:
[0201]
[0202] 2) Block (vertical):
[0203]
[0204] 3) Block (horizontal):
[0205]
[0206] The word "МИР" is divided into logical elements "М", "И", "Р". Each element constructed according to the above principles is assigned a unique letter symbol compiled according to the triplet molecular genetic system ( Figure 17 ). Each symbol is associated with an element of the system and adds indexing information.
[0207]
[0208]
[0209] Then, the code combination is determined from the value of the addition function modulo 2:
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap