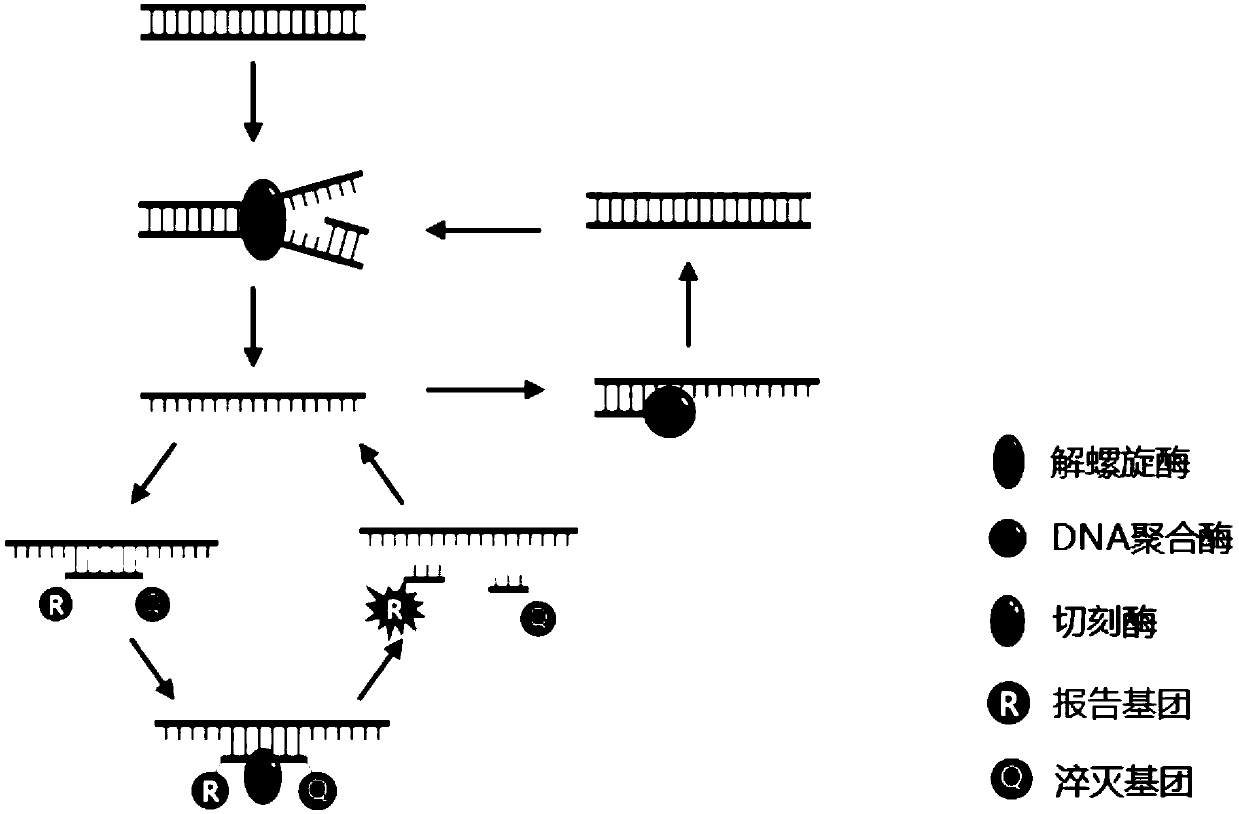
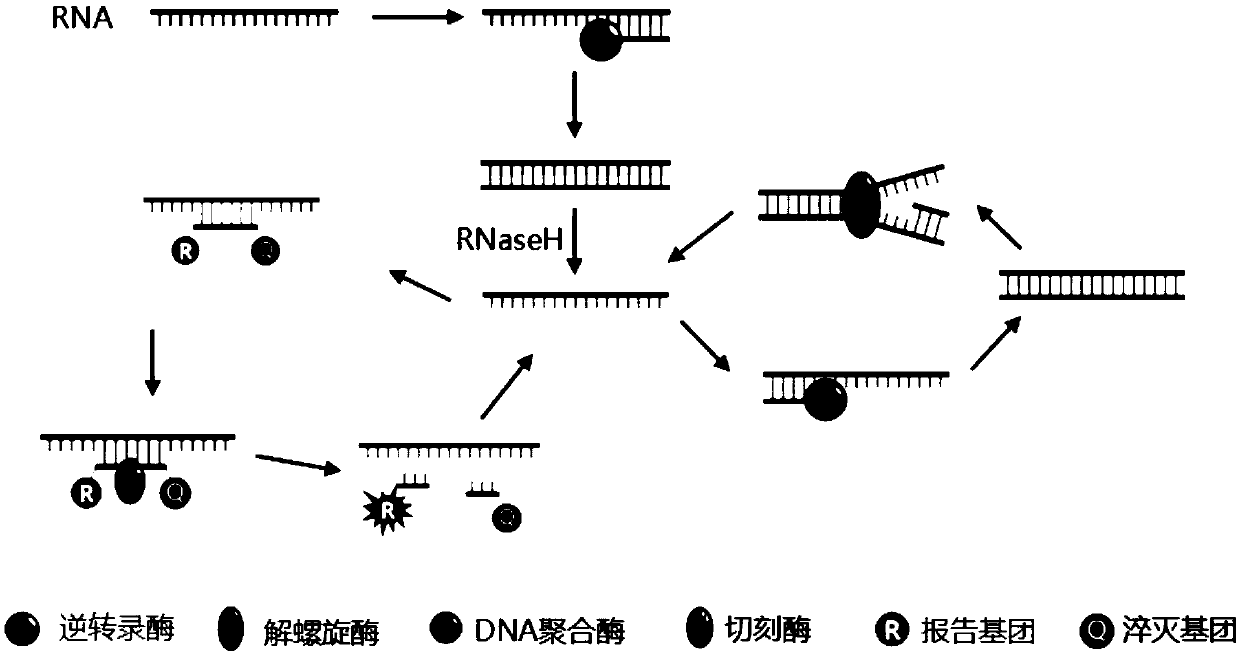
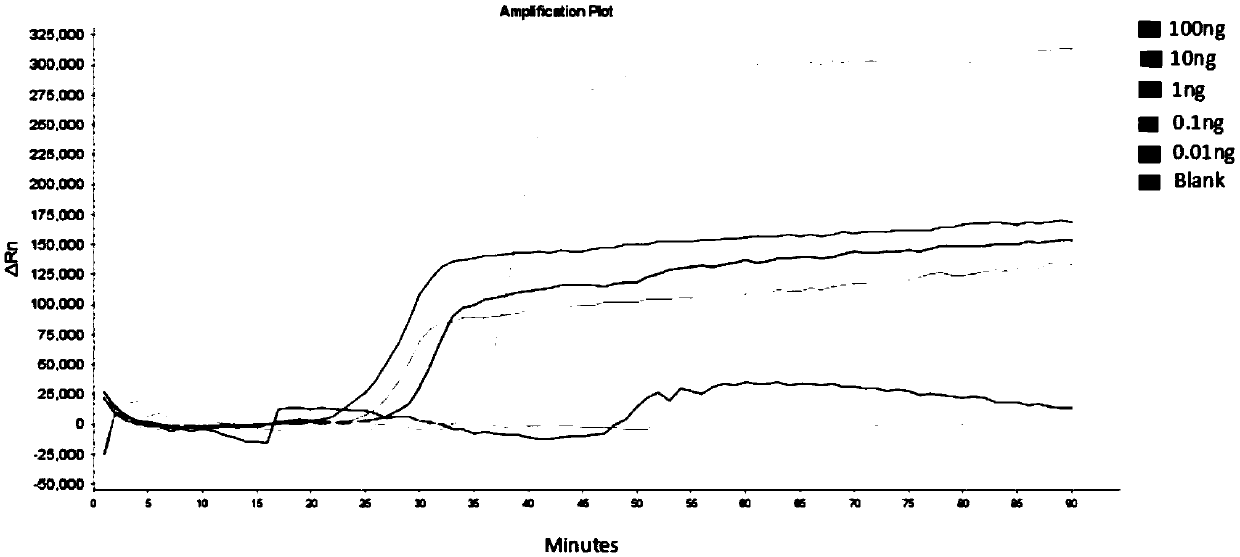
Isothermal amplification nucleic acid detection method based on helicase and nicking enzyme and kit
A detection kit, isothermal amplification technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as laboratory contamination, and achieve the effect of convenient operation, reduced possibility, and real-time detection of fluorescent signals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Embodiment 1 human genome GAPDH gene detection
[0039] 1. Detection kit preparation
[0040] (1) Specific primer design
[0041] For the GAPDH gene of the human genome, multiple parameters such as melting temperature, GC content, primer length, primer structure, and primer-dimer were comprehensively considered to design specific primer pairs, as shown below.
[0042] Amplified fragment (SEQ ID NO:1):
[0043] CGGGTGATGCTTTTCCTAGATTATTCTCTGGTAAATCAAAGAAGTGGGTTTATGGAGGTCCTCTTGTGTCCCCTCCCCGCAGAGGTGTGGTGGCTGTGGCATGGTGCCAAGCCGGGAGAAGCTGAGTCATGGGTAGTTGGAAAAGGACATTTCCACCGCAAAATGGCCCCTCTG
[0044] Upstream primer Primer F (SEQ ID NO:2): 5'-CGGGTGATGCTTTTCCTAGATT-3'
[0045] Downstream primer Primer R (SEQ ID NO:3): 5'-CAGAGGGGCCATTTTGCGG-3'
[0046] (2) Specific Taqman probe design
[0047] Design specific Taqman probes based on single-stranded target nucleic acid templates, and the probe sequences contain nicking enzyme recognition sites. A fluorescent group is attached...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2 Clostridium difficile toxin-producing gene TcdB detection
[0058] 1. Detection kit preparation
[0059] (1) Design of specific primers and probes
[0060] Design specific primers and probes for the detection target sequence Clostridium difficile toxin-producing gene TcdB, as shown below.
[0061] Amplified fragment (SEQ ID NO:5):
[0062] CACAAGTGGTAGAAGAAAGGATTGAAGAAGCTAAAAGCTTAACTTCTGACTCTATTAATTATATAAAGAATGAATTTAAACTAATAGAATCTATTTCTGATGCACTATACGATTTAAAACAACAGAATGAATTAGAAGAGTCTCATTTATATCTTTTGAGGATATATCGGAGACTGATGAAGGCT
[0063] Upstream primer Primer F (SEQ ID NO:6): 5'-CACAAGTGGTAGAAGAAAGGATTG-3'
[0064] Downstream primer Primer R (SEQ ID NO:7): 5'-AGCCTTCATCAGTCTCCGATA-3'
[0065] Probe sequence probe (SEQ ID NO:8): 5'-FAM-AAGAGTCTCATTTTATATCTTTT-BHQ-3'
[0066] (2) Reaction system preparation
[0067] Each 20 μL amplification reaction system contains 4 μL 5× buffer, 2 μL 10 mM dNTP, 1 μL 8U / μL BST polymerase, 0.5 μL 200ng / μL UvrD helicase, 0.5 μL ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Embodiment 3 pathogenic bacteria detection specificity analysis
[0075] Using the kit and detection method described in Example 2, select Escherichia coli, Salmonella, Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella baumannii, Shigella dysenteriae, Clostridium bienzyme, Clostridium perfringens and Non-toxin-producing Clostridium difficile was used as the test sample to detect the toxin-producing gene TcdB of Clostridium difficile, and the specificity of the kit and detection method described in Example 2 in the detection of pathogenic bacteria was analyzed. The specific experimental settings are shown in Table 1.
[0076] Table 1 Pathogen detection specificity analysis experiment settings
[0077] test group
pathogenic bacteria
concentration
1
Toxigenic Clostridium difficile
5000CFU / mL
2
Toxigenic Clostridium difficile
500CFU / mL
3
Escherichia coli, Salmonella
10 6 CFU / mL
4
Staphylococcus aureus, Shigella baumannii ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com