Motorcycle engine electrical starting structure
An engine, electric starting technology, applied in the direction of motor starting, engine starting, engine components, etc., can solve problems such as damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
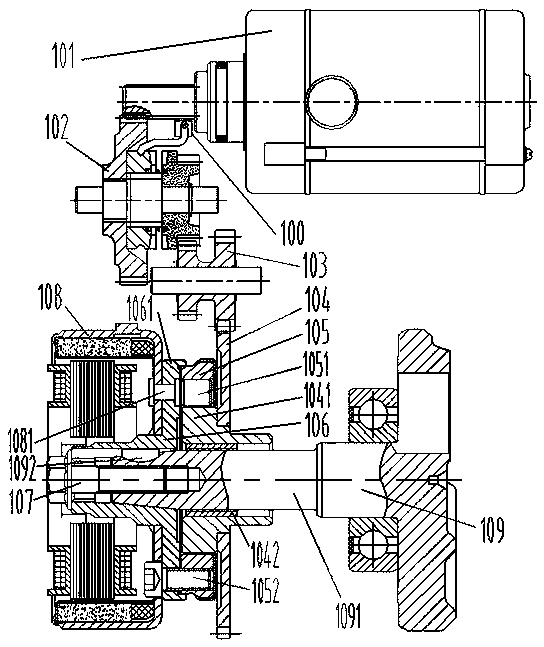
[0041] see Figure 1-3 , a kind of motorcycle engine electric starting structure of specific embodiment 1, comprise starter motor 101, described starter motor 101 is connected crankshaft 109 through transmission mechanism, and described transmission mechanism comprises big double gear 102, small double gear 103, clutch Start the gear 104 and the overrunning clutch 105, the large double gear 102 includes a rotating shaft 1, and the rotating shaft 1 is provided with a large gear 2, a transmission gear 3 and a pinion 4, and the large gear 2 and the rotating shaft 1 pass through a straight tooth flower key fit to ensure synchronous rotation, the pinion 4 is rotatable relative to the shaft 1, and a number of external helical splines 11 are processed on the section 1 of the shaft between the bull gear 2 and the pinion 4 to form an external helical spline section, so The transmission gear 3 is connected with the outer helical spline segment on the rotating shaft 1 through the corresp...
Embodiment 2
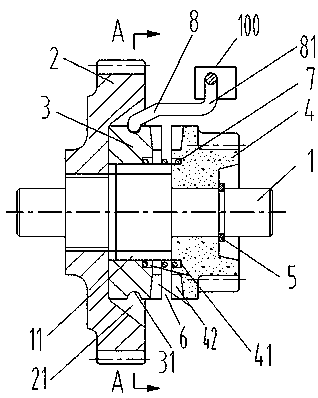
[0049] see figure 2 , 5 , The difference between the second embodiment and the first embodiment is that the return elastic mechanism and the elastic brake mechanism are set in different forms. The end face of the top is provided with a plug installation blind hole 32, and the plug installation blind hole 32 has a built-in spring 33. The corresponding position is the annular plane 43, and the end of the plug 34 facing the pinion 4 is higher than the end tooth 42 of the transmission gear 3 and abuts against the annular plane 43. In terms of positional relationship, the plug installation blind hole 32 and the annular plane 43 are respectively Located on the inner edge of the opposite end surfaces of the transmission gear 3 and the pinion gear 4 , the end surface teeth 42 are respectively located on the outer edges of the opposite end surfaces of the transmission gear 3 and the pinion gear 4 .
[0050] The elastic braking mechanism of the second embodiment is a spring piece 9, ...
Embodiment 3
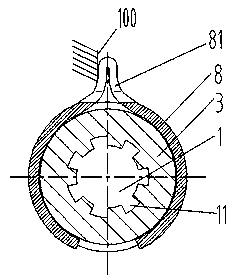
[0054] see figure 2 , 6 The difference between the third embodiment and the first embodiment is that the free end of the elastic section 81 is fixedly arranged, that is, it is fixedly connected with the assembled housing 100, because the axial movement stroke of the transmission gear 3 is not long, so You can also choose to fix the free end of the elastic section 81, so that the transmission gear 3 moves closer to the pinion 4, and when the helical compression spring is compressed, since the free end of the elastic section 81 is fixed, a certain amount of spring ring 8 will also occur. A certain amount of elastic deformation can also provide a certain return auxiliary force for the return of the transmission gear 3; of course, the fixing of the elastic coil 8 mainly restricts it from rotating with the transmission gear 3 to provide the necessary friction braking force.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com