Multi-domain Optical Network Static Multicast Protection Method Based on Hierarchical PCE and Double Matrix Game
A matrix game, optical network technology, applied in data switching network, selection device of multiplexing system, digital transmission system, etc. capacity, the effect of promoting optimal utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] The invention discloses a multi-domain optical network static multicast protection method based on layered PCE and double-matrix game, which is used to plan the multicast tree and multicast protection tree of each multicast request in the multi-domain optical network. Each multicast request multicast tree is disjoint, and the multicast protection tree of each multicast request is disjoint, including n nodes in the multi-domain optical network, and the nodes include source nodes and leaf nodes , in the multi-domain optical network, the communication requests from each source node to a plurality of leaf nodes corresponding to the source node constitute a multicast request set R={R m |m=1,2,...,k}, where 1≤k≤n, for the mth multicast request R m , whose source node is V sm , the set of multiple leaf nodes is M m ={V Lmi |i=1,2,…,n-1}, V Lmi is the set of leaf nodes M m The i-th leaf node of .
[0050] The multicast tree dedicated protection scheme can be divided into ...
Embodiment 2
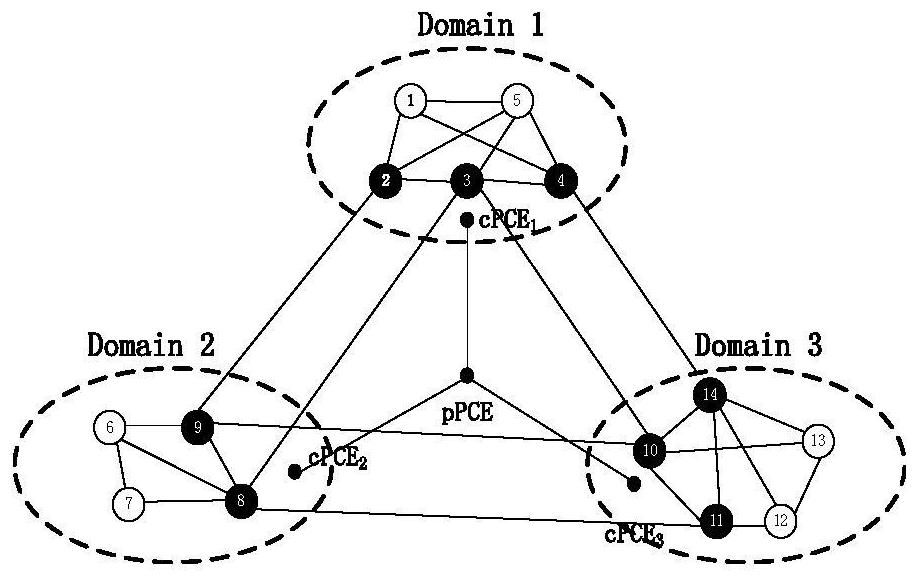
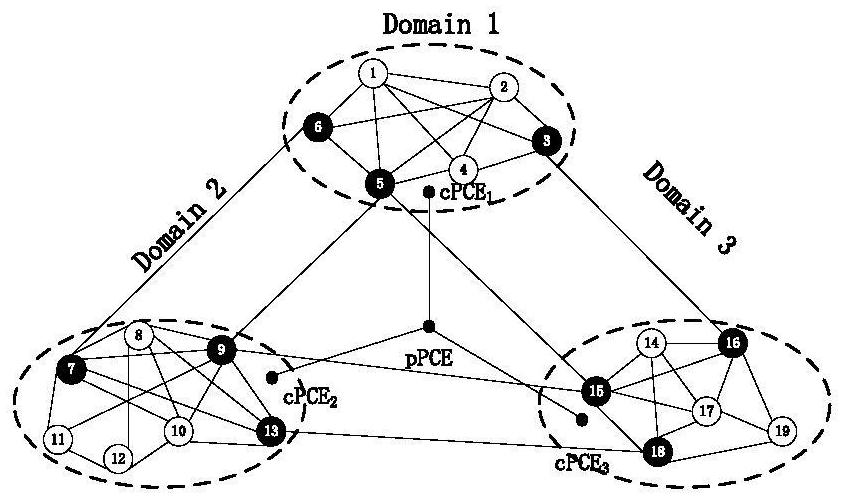
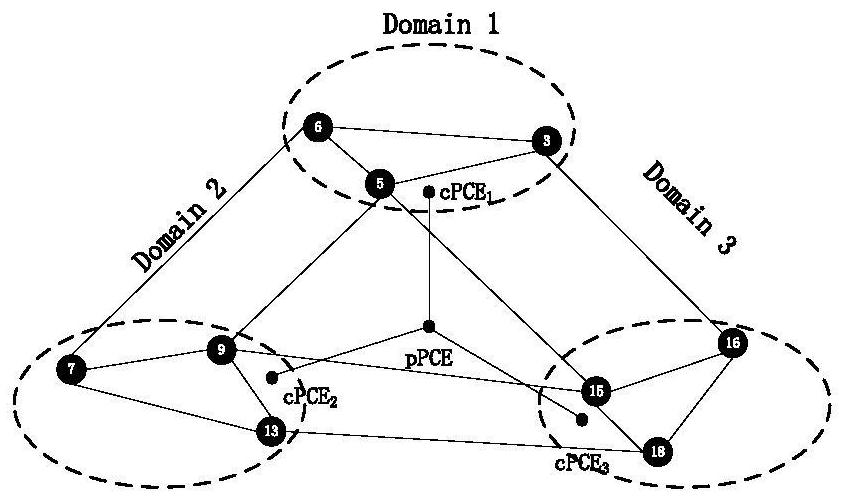
[0101] In this example, given as figure 2 The shown multi-domain optical network G=(19, 50), the topology of the multi-domain optical network after topology aggregation is as follows image 3 shown. In a static environment, it uses the multicast tree protection scheme gained by the method provided by the present invention to give an example, given the multicast request R 1 ={1;5,7,12},R 2 ={2;10,12,18},R 3 ={16;1,2,7,8,10,19}. First process the multicast request R 1 , to determine whether the leaf node {5,7,12} is in domain 1, if so, the sub-path computing unit cPCE1 directly calculates the path and starts the game; if not, the sub-path computing unit cPCE1 sends a request to the parent path computing unit pPCE, in the virtual In the topology graph, inter-domain paths are uniformly calculated and instructions are sent to the sub-path calculation units cPCE of each domain. The sub-path calculation units cPCE of each domain calculate the paths in their respective domains, ...
Embodiment 3
[0103] In this embodiment, a multi-domain optical network system with two-way connection is set up, a multi-domain optical network of three domains, wherein nodes 3, 5 and 6 are in domain 1, nodes 7, 9 and 13 are in domain 2, and nodes 7, 9 and 13 are in domain 2, and nodes 7, 9 and 13 are in domain 3 Inside are nodes 15, 16 and 18. The two-way connection between nodes increases the available paths of the protection mechanism. The system uses TxExtModLaser, FiberNLS, WDM_MUX_N_1_Ideal, Fork, Powermeter, AmpSysOpt, SignalAnalyzer, Const and other modules. Since this embodiment studies multicast service distribution in a static environment, the PCE-related structure is not displayed in the system, but a part of its functions are replaced by nodes. In this paper, the fault module is set and the attenuation value is set. When the attenuation value exceeds 30dB, the link of this section is considered to be faulty. In addition, the length of the optical fiber in the system is not ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com