Adaptive selection of signal-detection mode
A signal and synchronization signal technology, applied in wireless communication, digital transmission system, electrical components, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the calculation burden of the synchronization process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
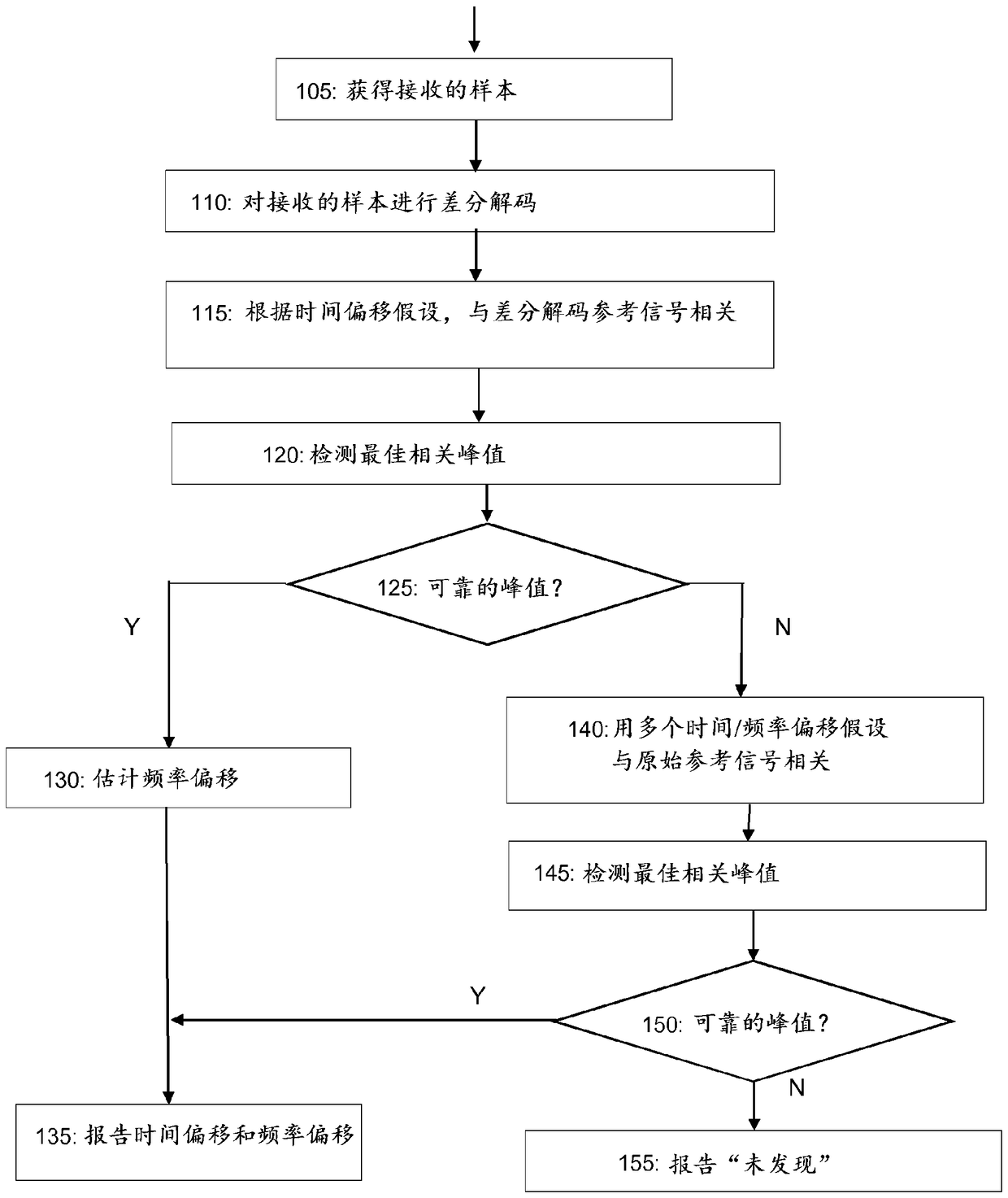
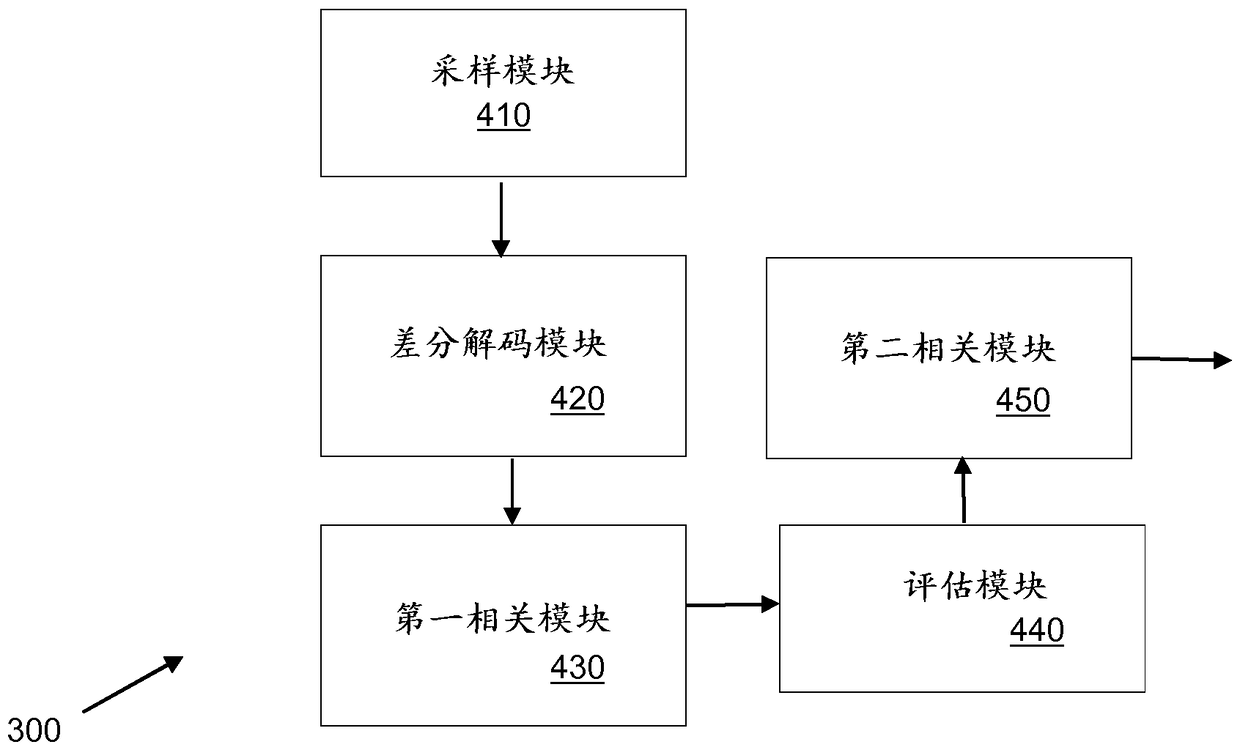
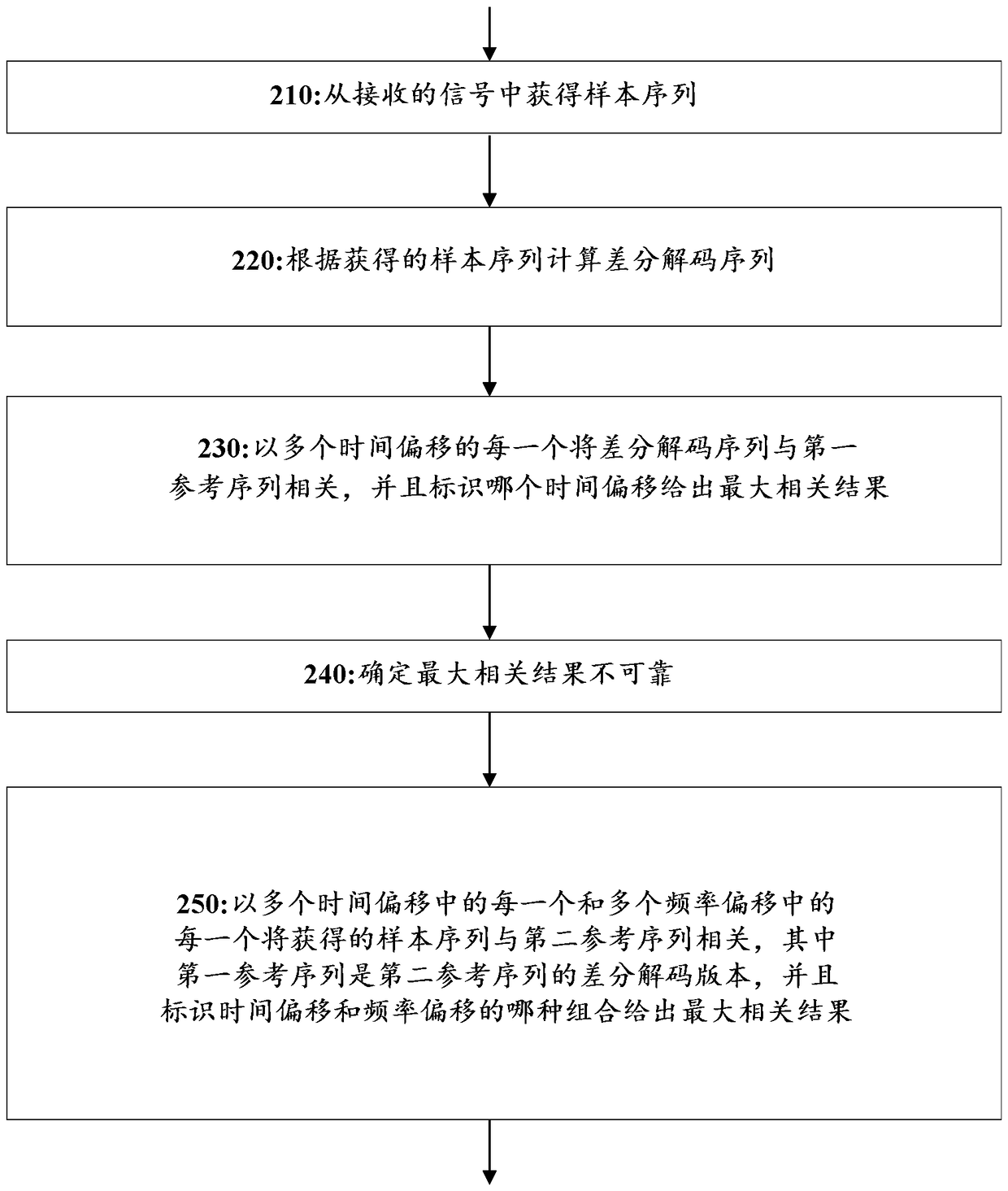
[0019] So-called coherent detection is often used to detect the presence of synchronization signals in the received signal. With coherent detection, the phases of all samples / symbols are considered jointly, since all samples / symbols over a given time period are effectively added constructively / coherently in the received signal processing. For example, coherent detection may be performed by correlating a time series of complex-valued samples taken from the received signal with a reference sequence corresponding to the synchronization signal as represented in the time domain.
[0020] Conventional coherent detection does not tolerate frequency errors well because frequency errors deviate samples in the time-domain sequence, eg over time, from a reference sequence that was initially time-aligned and phase-aligned with the time-domain sequence. Thus, when using coherent detection techniques, it is generally necessary to add a frequency offset search dimension to the synchronizatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com