An auxiliary method for early warning of water inrush disaster in coal mine
A disaster and coal mine technology, applied in the auxiliary field of coal mine water inrush disaster early warning, can solve the problems of different actual water inrush positions of precursor information, difficulty in predicting the position of water inrush points, complicated data preprocessing, etc. The effect of large-scale production application and improving the accuracy of early warning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
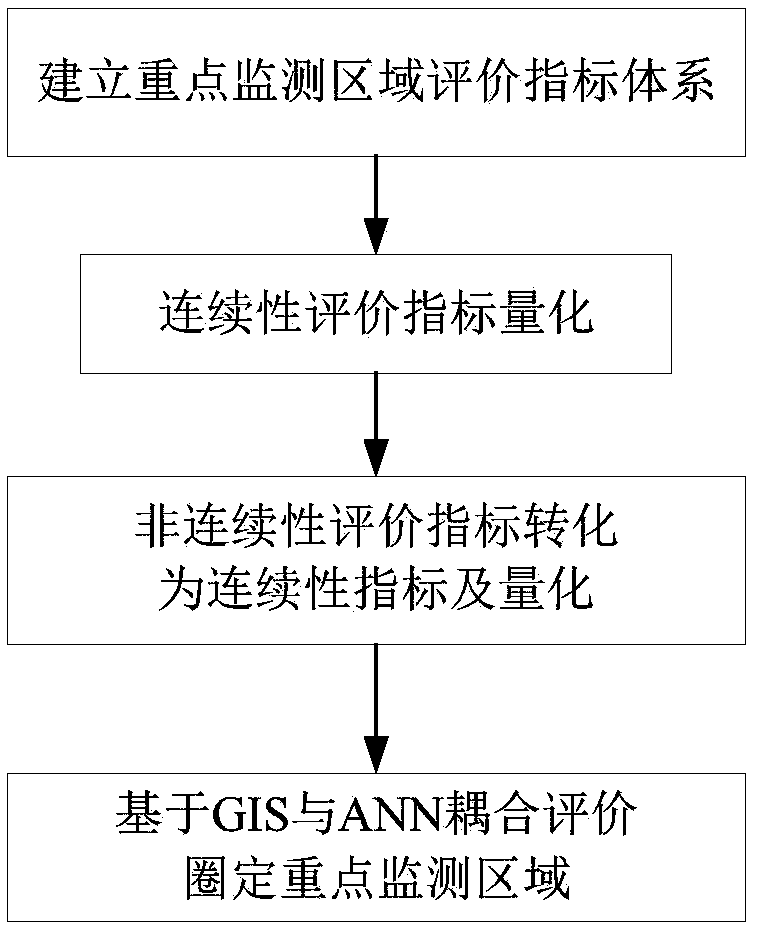
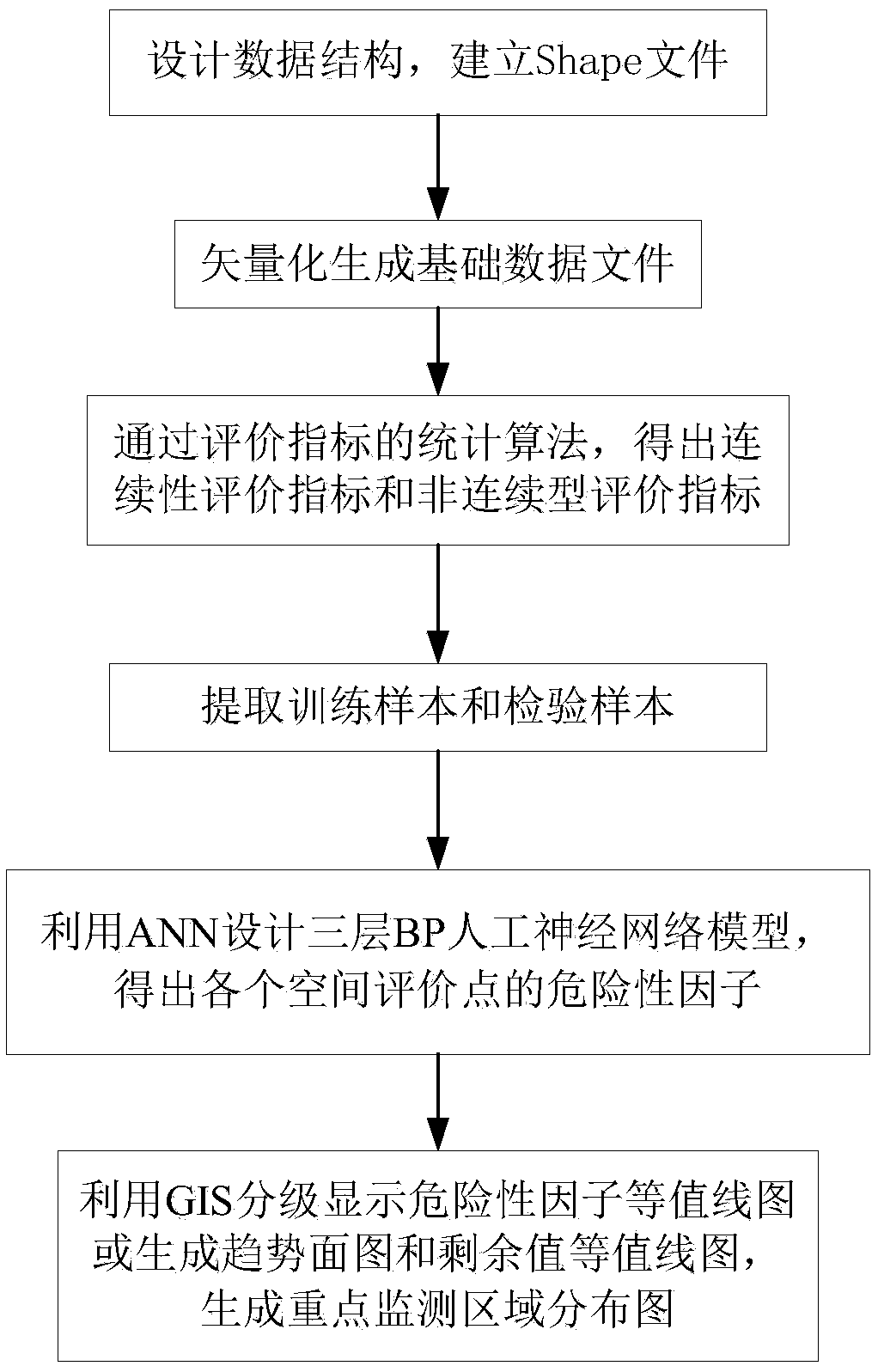
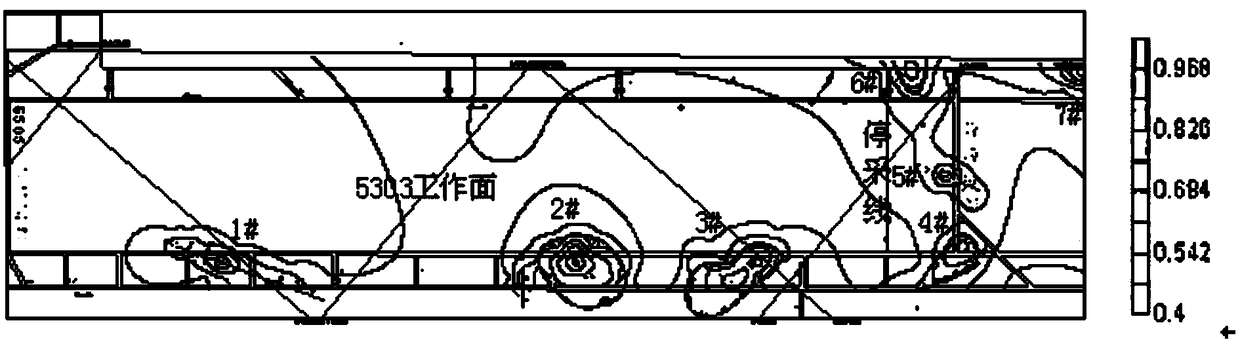
[0086] This specific embodiment takes the monitoring and early warning of the bottom plate of the mining working face as an example. In order to delineate key monitoring areas and optimize the on-site layout of the coal mine water inrush disaster early warning system, the auxiliary method for coal mine water inrush disaster early warning provided by the present invention is used to monitor a certain working face. The area was evaluated.
[0087] The mining of this working face is mainly affected by the aquifer and collapse column, and there is not enough data on the water-richness of the aquifer. Therefore, only the water pressure of the aquifer, the water-resistant coal pillar of the aquifer, the fault risk index, and the subsidence column are selected in the evaluation process. Column risk index four evaluation indicators.
[0088] According to the main borehole data in and around the working face (see Table 3 for details) and the CAD format maps of the study area, according...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com