Sliding mode control method for networked control system under circumstance of uncertain probability of occurrence
A technology of networked control and probability of occurrence, which is applied in the field of sliding mode control, can solve the problems of not being able to deal with distributed sensor time-delay and bounded time-varying time-delay at the same time, and achieve the effect of ensuring stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
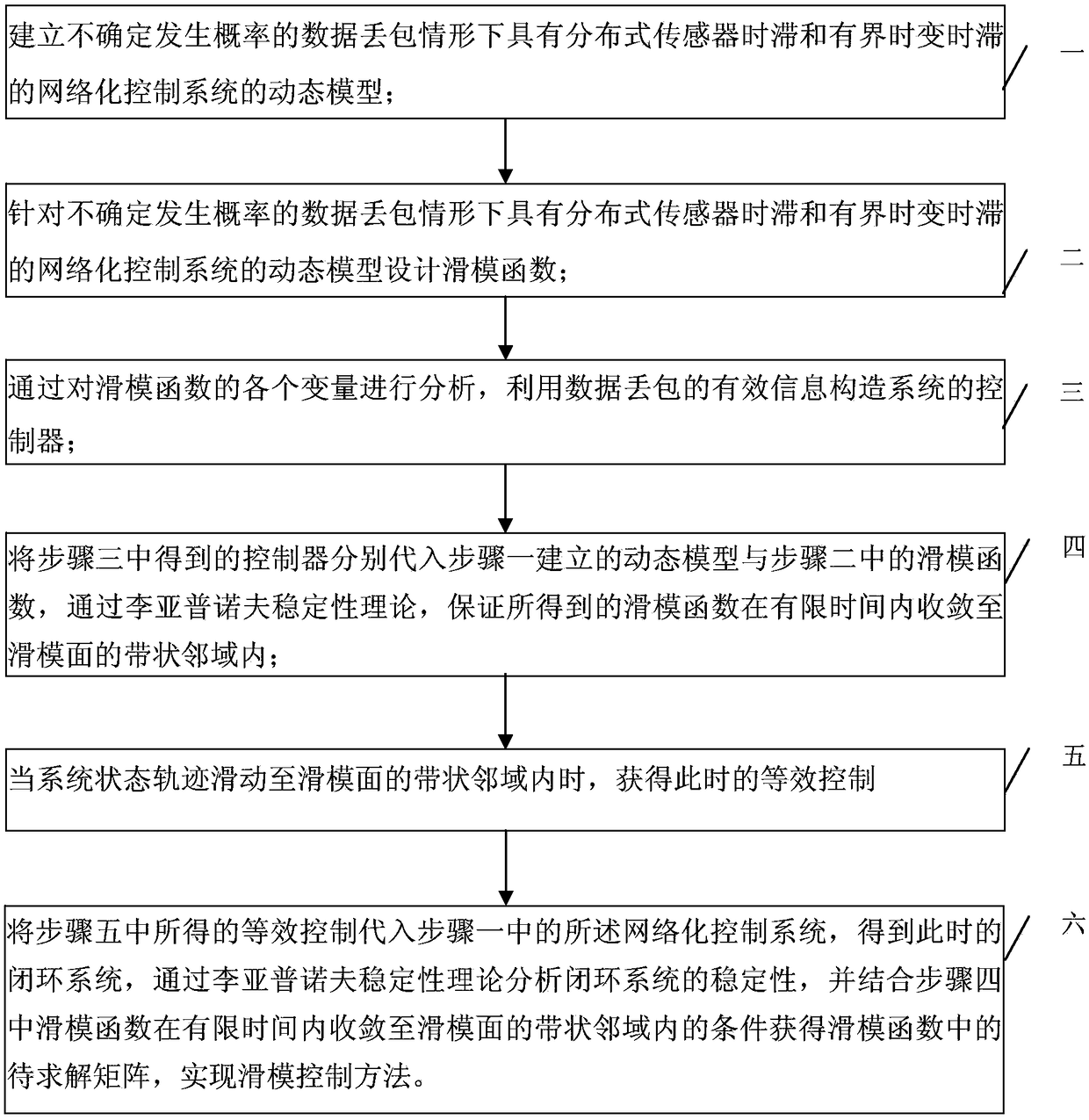
[0019] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 The present embodiment is described. The sliding mode control method of the networked control system under the situation of uncertain occurrence probability given in this embodiment specifically includes the following steps:
[0020] Step 1. Establishing a dynamic model of a networked control system with distributed sensor time-delay and bounded time-varying time-delay in the case of data packet loss with uncertain probability of occurrence;
[0021] Step 2, designing a sliding mode function for the dynamic model of the networked control system with distributed sensor time-delay and bounded time-varying time-delay in the case of data packet loss with uncertain probability of occurrence;
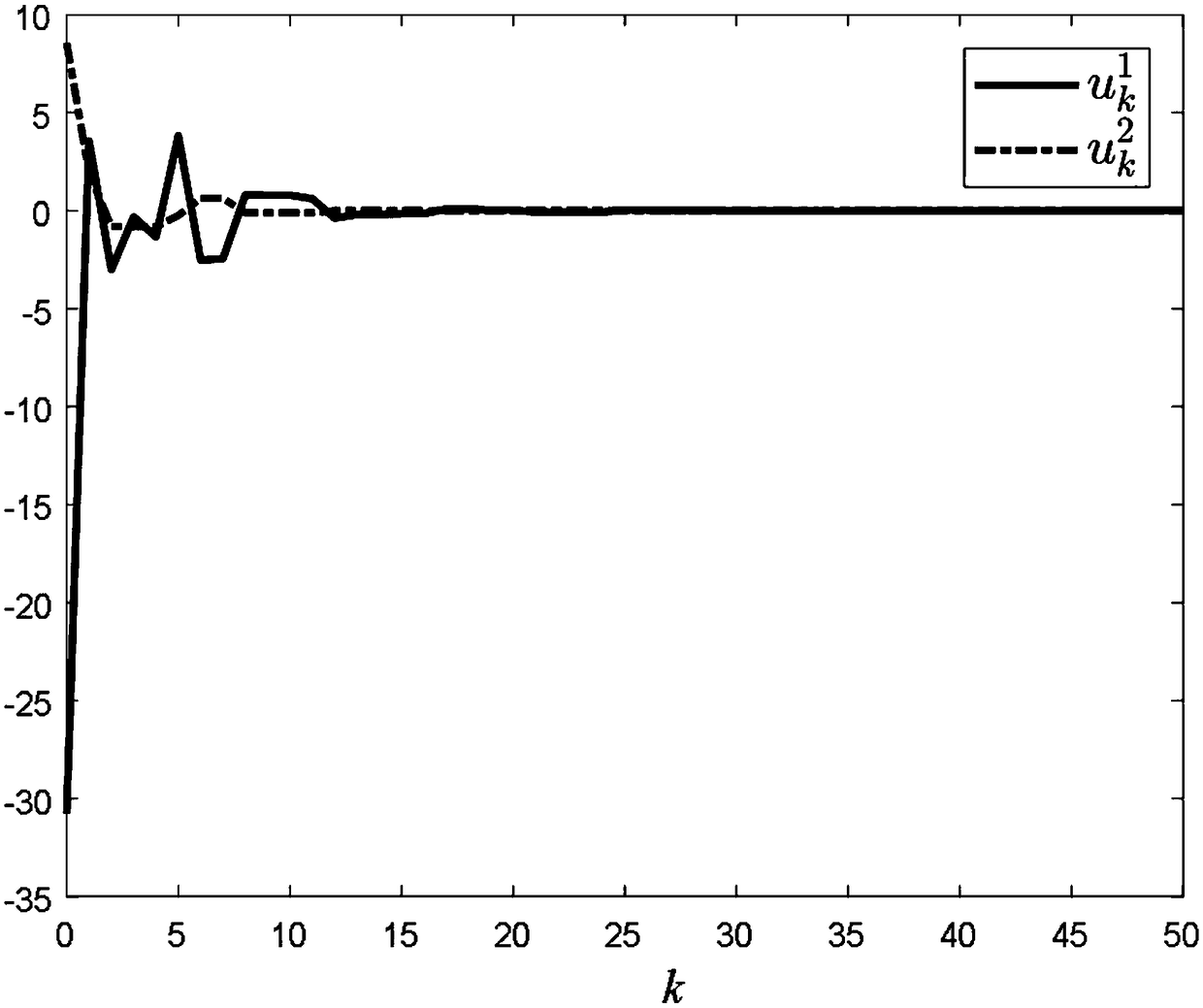
[0022] Step 3. By analyzing the variables of the sliding mode function, use the effective information of data packet loss to construct the controller u of the system k ;
[0023] Step 4, the controller u obtained in step 3 k Substit...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0026] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is that the specific process of step one includes:
[0027] The state space form of the dynamic model is specifically:
[0028]
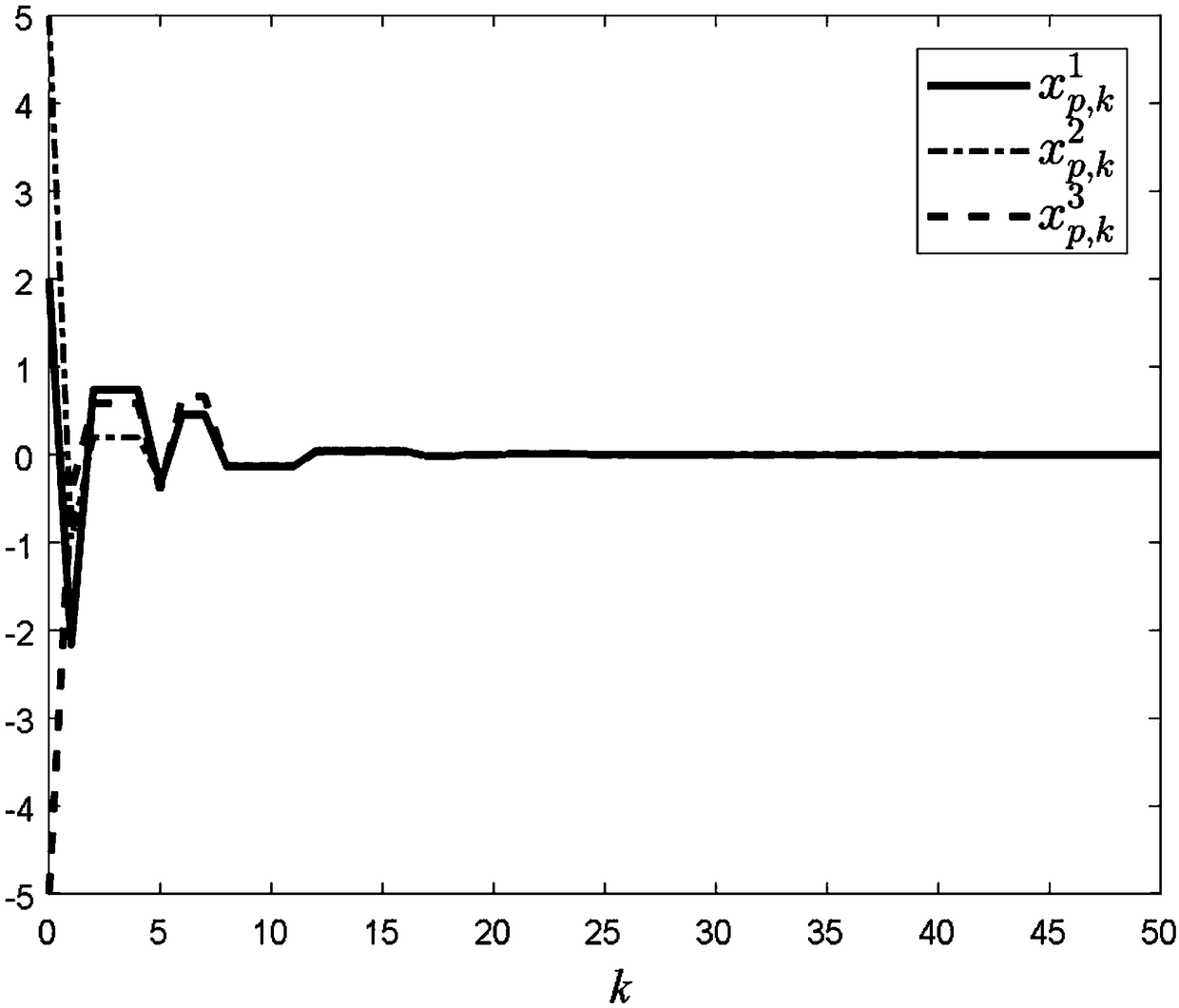
[0029] where x k is the state variable of the dynamic model of the networked control system at time k, x k+1 is the state variable of the dynamic model of the networked control system at time k+1, for k-d k The state variables of the dynamic model of the networked control system at time; d k is a bounded time-varying delay, satisfying d m ≤d k ≤d M , d m 、d M respectively d k The lower and upper bounds of x k-p is the state variable of the dynamic model of the networked control system at time k-p; A is the system matrix, A d is the system delay matrix, B is the system control matrix, C is the delay distribution matrix, and D is the system disturbance matrix; f(x k ) is a bounded nonlinear disturbance function;...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0035] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment two is that the sliding mode function described in step two is specifically:
[0036]
[0037] Among them, G=B T P, B T is the transpose of B, the matrix P to be solved is a symmetric positive definite matrix, satisfying that GB is non-singular and G[CD]=0; x k-2 is the state variable of the dynamic model of the networked control system at time k-2.
[0038] Other steps and parameters are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com