A filtering method based on an event trigger mechanism
An event-triggered and mechanism-based technology, applied to electrical components, adaptive networks, impedance networks, etc., can solve the problem of large estimation errors in filtering methods, and achieve the effects of reducing estimation errors, easy solution and implementation, and good estimation effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
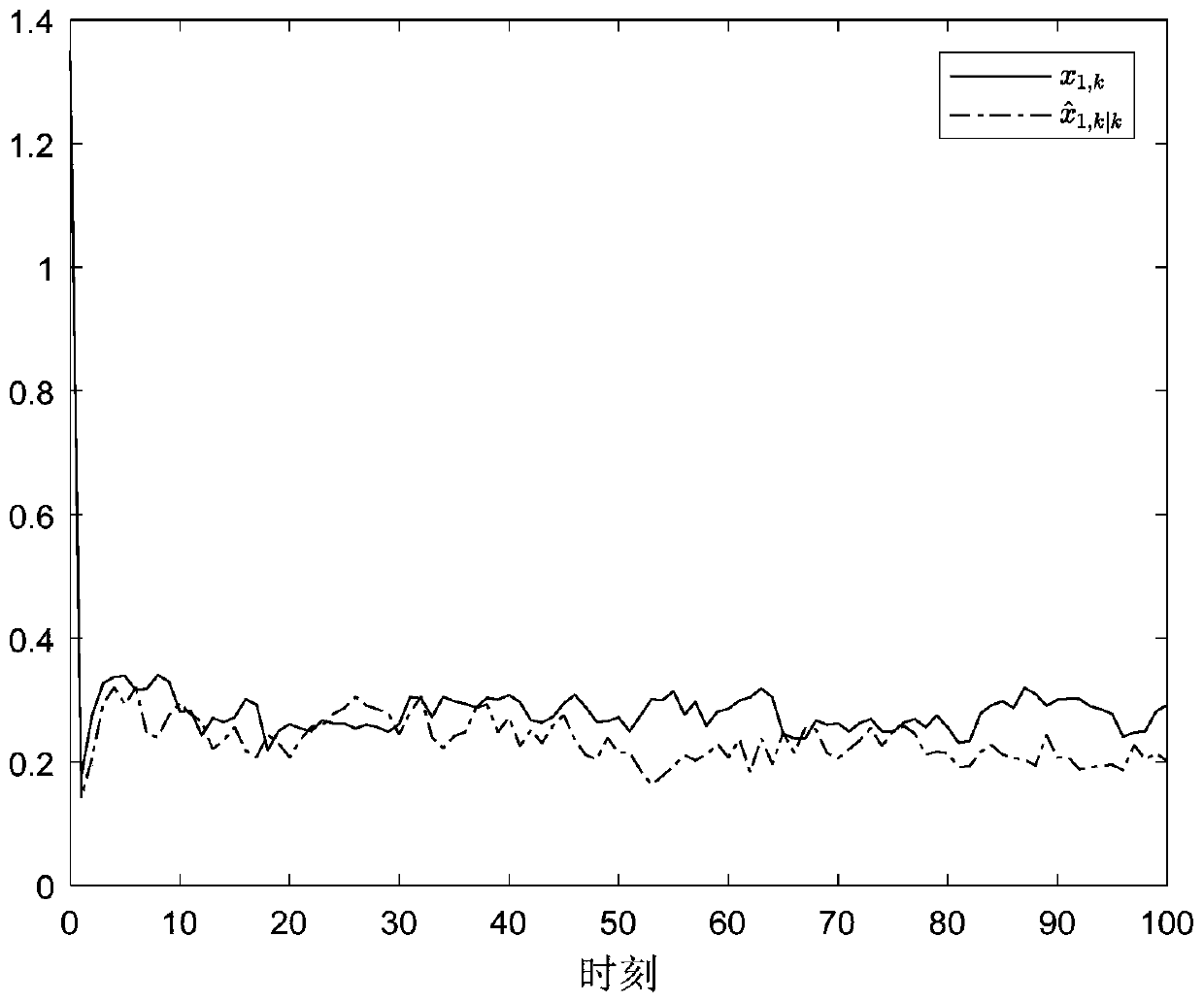
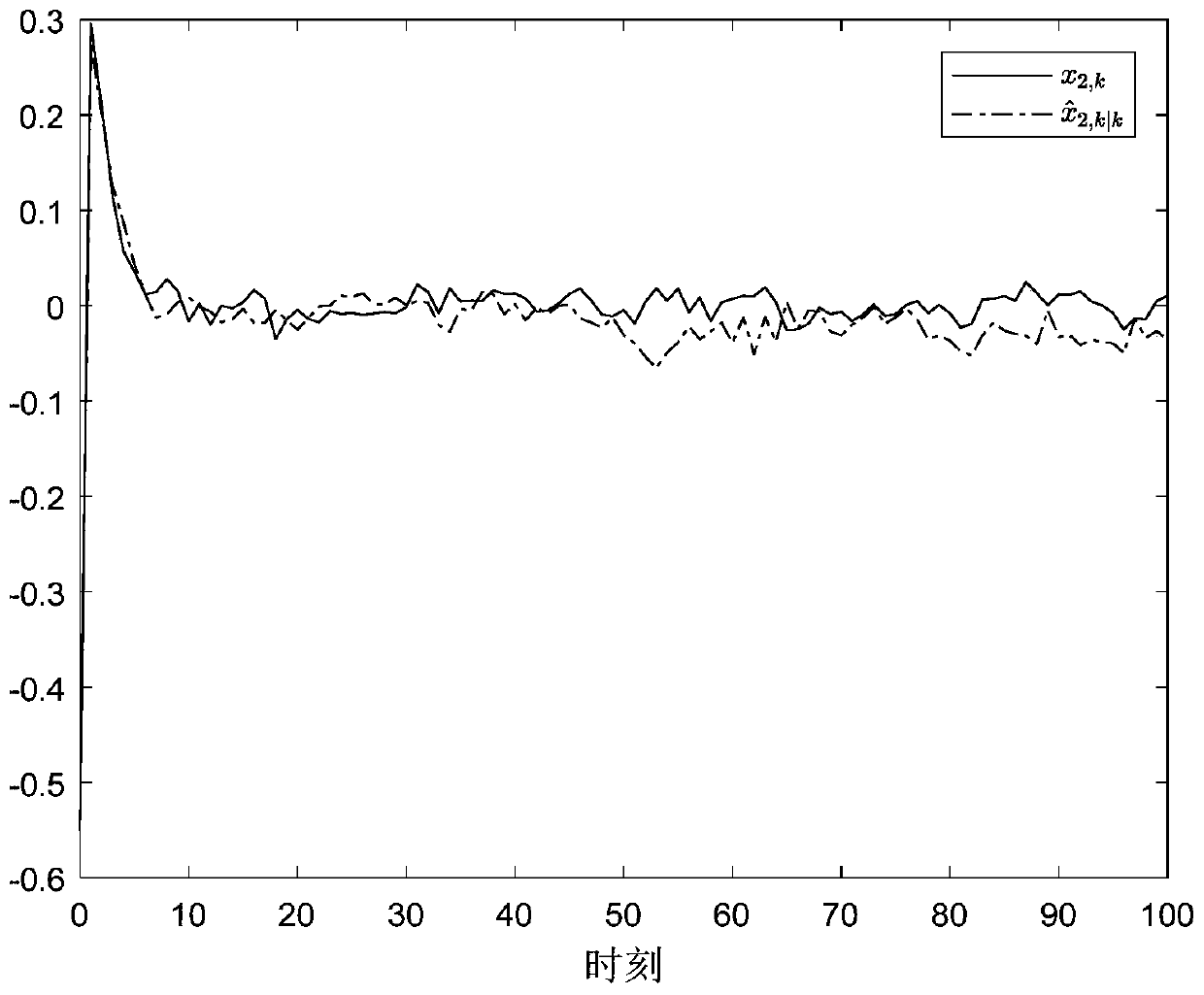
[0022] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination Figure 1 Describe this implementation mode, this implementation mode is a filtering method based on an event trigger mechanism, such as figure 1 As shown, the specific steps of the method are:
[0023] Step 1, establishing a dynamic model of a nonlinear stochastic system with multiple measurement loss phenomena with uncertain loss probability;
[0024] Step 2, under the event trigger mechanism, filter design is performed on the dynamic model of the nonlinear stochastic system with multiple measurement loss phenomenon with uncertain loss probability;
[0025] Step 3. Calculate the upper bound Ω of the one-step forecast error covariance matrix of the filter k+1|k ;
[0026] Step 4. According to the upper bound of the one-step forecast error covariance matrix Ω k+1|k , to calculate the filter gain matrix K k+1 ;
[0027] Step five, the filter gain matrix K calculated in step four k+1 Introduce the state estimation formula...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0031] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that in said step one, a dynamic model of a nonlinear stochastic system with multiple measurement loss phenomena with uncertain loss probability is established; the specific process is:
[0032] The state-space form of the dynamic model for nonlinear stochastic systems with multiple measurement dropout phenomena with uncertain dropout probabilities is:
[0033]
[0034] the y k = Ξ k C k x k +h(x k ,ζ k )+ν k (2)
[0035] In the formula, are the state variables at time k and k+1 respectively; the initial value x 0 The mean is Variance is P 0|0 ; is the real field of the state of the dynamic model of the nonlinear stochastic system, n is the dimension; is the measurement output at the kth moment, is the real field of the state of the dynamic model of the nonlinear stochastic system, m is the dimension; η k with ζ k is Gaussian white noise with zero mean ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0037] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is that the data loss matrix Ξ k =diag{ξ 1,k ,ξ 2,k ,...,ξ m,k}, diag{} is a diagonal matrix; ξ i,k For m variables that are independent of each other with respect to i and k, i=1,2,...,m, obey the Bernoulli distribution with a value of 1 or 0, and satisfy the following conditions:
[0038]
[0039] Where i is the location of data loss, k is the time, is the determined mathematical expectation, Δξ i Describe the uncertainty of probability, i=1,2,...,m, Prob{} is the probability, is the expectation of {};
[0040] The non-linear function g(x k , η k ) and h(x k ,ζ k ) satisfy g(0,η k )=0, h(0,ζ k )=0 and the following conditions:
[0041]
[0042]
[0043]
[0044] Among them, s>0 is a known constant, with Both are nonlinear parameter matrices, r=1,2,...,s; for The transpose of g(x j , η j ), h(x j ,ζ j ) is a nonlinear function, j ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com