Passenger congestion detection method based on convolution neural network for urban rail transit
A convolutional neural network and urban rail transit technology, applied in neural learning methods, biological neural network models, neural architectures, etc., can solve problems such as large measurement errors and poor real-time performance, reduce workload and improve safety and service quality effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
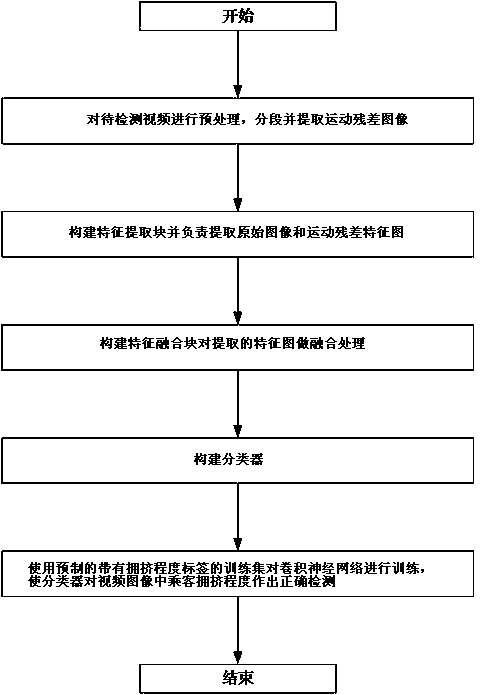
[0033] Convolutional neural network-based passenger congestion detection method for urban rail transit, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0034] S1, acquiring traffic monitoring video to be detected, preprocessing the video to be detected, segmenting and extracting motion residual images;
[0035] S11, acquiring traffic monitoring video to be detected;
[0036] S12, set the detection cycle T, divide the video to be detected into video segments with a length T according to the detection cycle T, and the first frame image of the video segment is a reference image, denoted as p 1 ;
[0037] S13, take other images in the video segment, for example take a frame of images at 1 / 3T, 2 / 3T and T in the detection unit respectively, denoted as p 2 ,p 3 ,p 4 , will p 2 ,p 3 ,p 4 Respectively with the reference image p 1 To do the difference, obtain the motion residual image of the crowd in the video segment to be detected, denoted as p 12 ,p 13 ,p 14 .
...
Embodiment 2
[0047] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: in step S5 to train the convolutional neural network, the stochastic gradient descent algorithm is used to correct the parameters in the convolutional neural network, and the formula of the stochastic gradient descent method is as follows :
[0048] g(θ)=∑θx i
[0049]
[0050]
[0051] Among them, g(θ) represents the network hypothesis function, θ represents the parameter weight of the convolutional neural network, h(θ) represents the loss function, and y i Indicates the sample value of the i-th sample, m indicates the total number of algorithm iterations, σ indicates the penalty coefficient, Represents the gradient, η represents the learning rate in gradient descent;
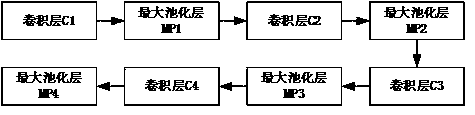
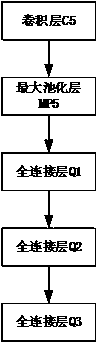
[0052] The convolutional neural network structure parameter update method involved in this method adopts an improved stochastic gradient descent method. Compared with the traditional method, the improved stochastic gradient desce...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Step 1: Set the detection period T. In this embodiment, T=3 sec is taken as an example, and the video to be detected is divided into video segments with a length T according to the detection period T, which is hereinafter referred to as a detection unit. Take the first frame image of the detection unit as the reference image, denoted as p 1 ; Take the images at t=1s, t=2s and t=3s in the detection unit, denoted as p 2 ,p 3 ,p 4 ; put p 2 ,p 3 ,p 4 Respectively with the reference image p 1 Do the difference, get the motion residual image of the crowd in the detection unit, denoted as p 12 ,p 13 ,p 14 ; Set the reference image p 1 and the motion residual image p 12 ,p 13 ,p 14 Combined into a group as the input of the passenger congestion detection algorithm; according to the actual operation of urban rail transit, the congestion is divided into 10 levels: spacious {(0-2 level), comfortable (3-5 level), crowded (5 -8 grades), danger (9-10 grades)}, intercept ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com