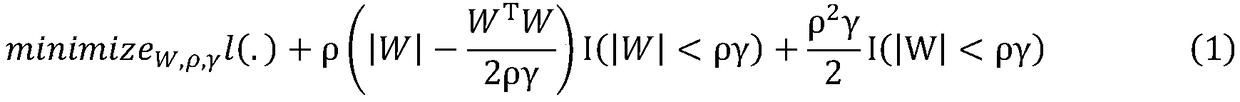Gene-gene interaction recognition method based on sparsity factor analysis
An interaction and gene technology, applied in the field of genetics, can solve the problem of insufficient recognition ability of gene-gene interaction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
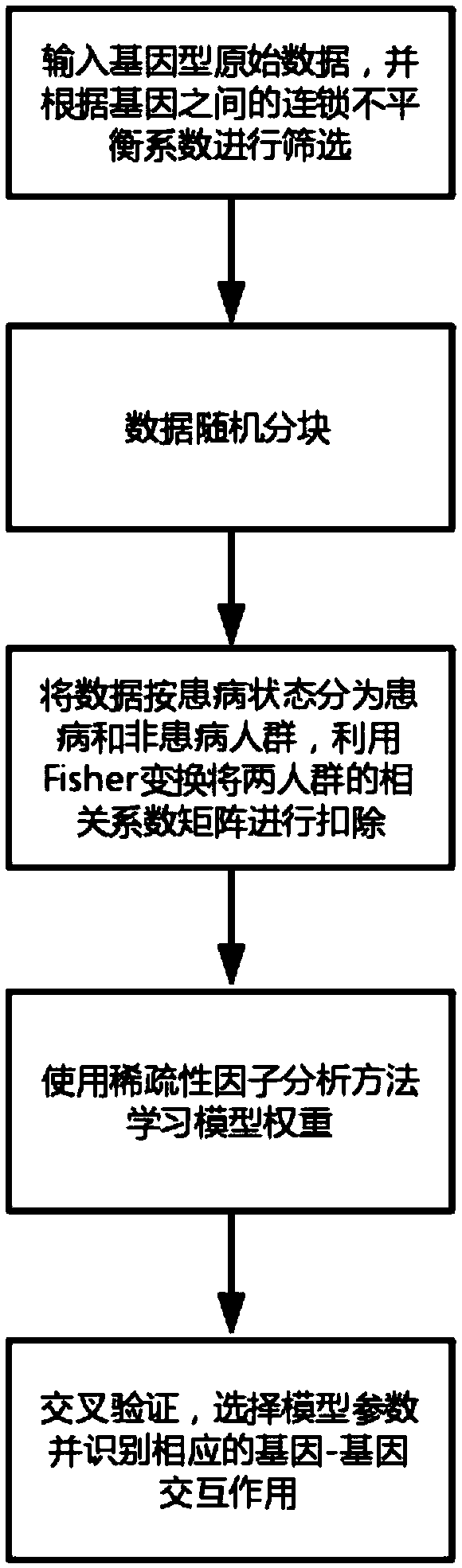
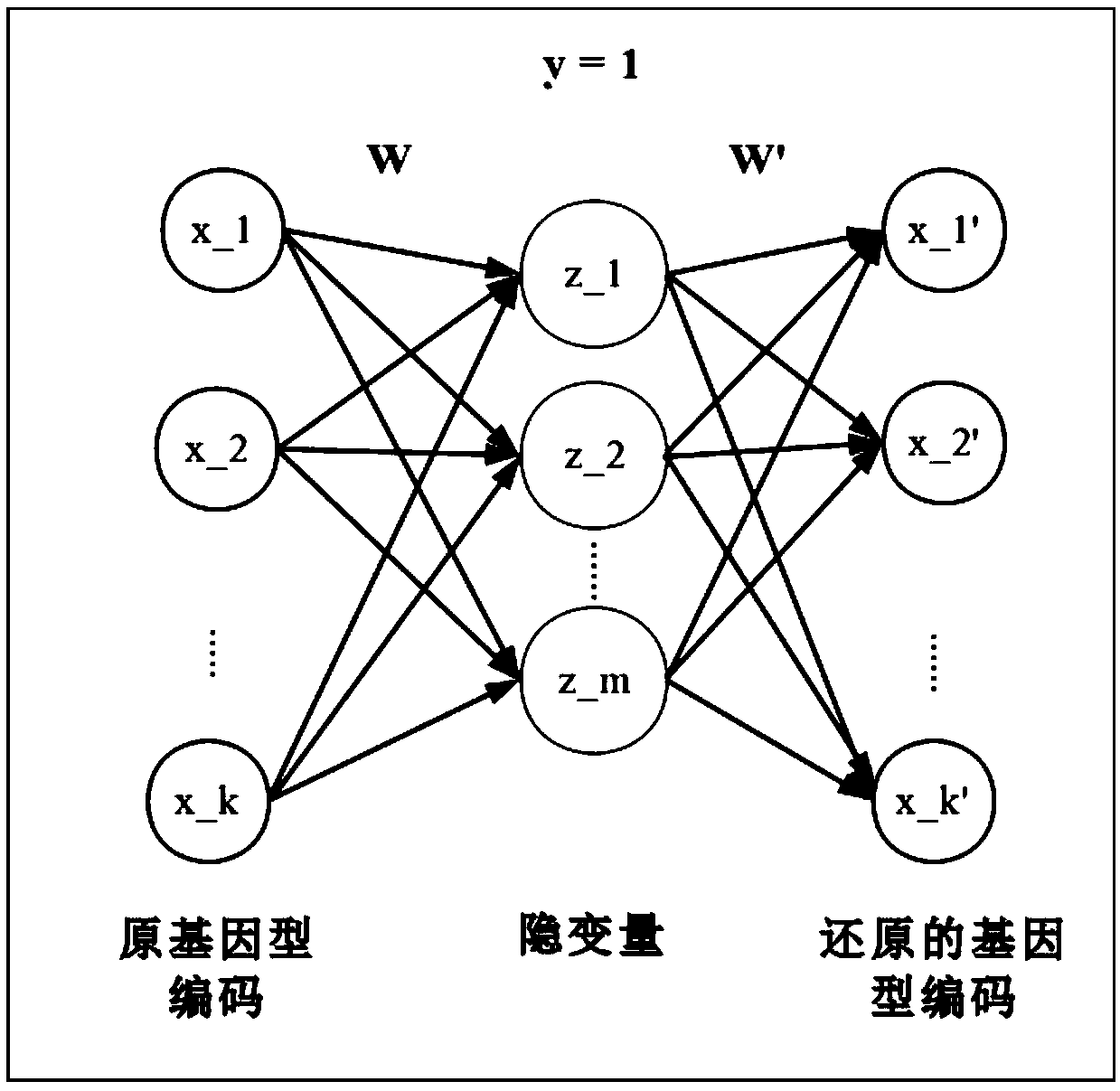
[0014] Suppose K={1,2,...,k} is a set of SNP sites, code x k ={-1,0,1}, k∈K; y={0,1} is a binary quality trait, define M={1,2,...,m}, mm , m∈M; n×k matrix X is the standardized genotype coding matrix, and n×m matrix Z is the hidden variable matrix. Define a linear transformation W with dimension k×m, which satisfies Z=XW and X′=ZW T , and define the residual matrix as Ψ=X-X′.
[0015] The model structure is as figure 2 As shown, the genotype coding matrix X is projected onto the latent variable matrix Z through the linear mapping W, and then through the linear transformation ZW T Restore to X', and minimize the error term Ψ. Among them, according to the sparsity assumption, the dimension m<<k of Z, and most elements of W are 0.
[0016] Assuming that the error function of data X and X′ is l, the model can be expressed as:
[0017]
[0018] Among them, ρ and γ are both adjustment parameters. When γ approaches +∞, the model approaches LASSO, and when γ approaches 1, the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com