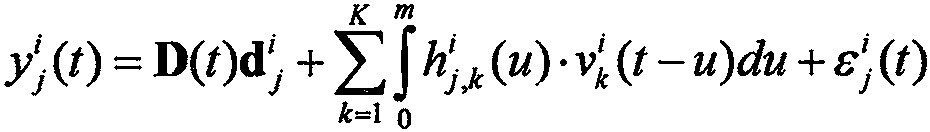Brain reaction comparison method based on low-order multielement generalized linear model
A generalized linear model and multivariate technology, applied in the field of biomedical image analysis, can solve problems such as unrecognizable, ignoring the spatial characteristics of fMRI data, and low signal-to-noise ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
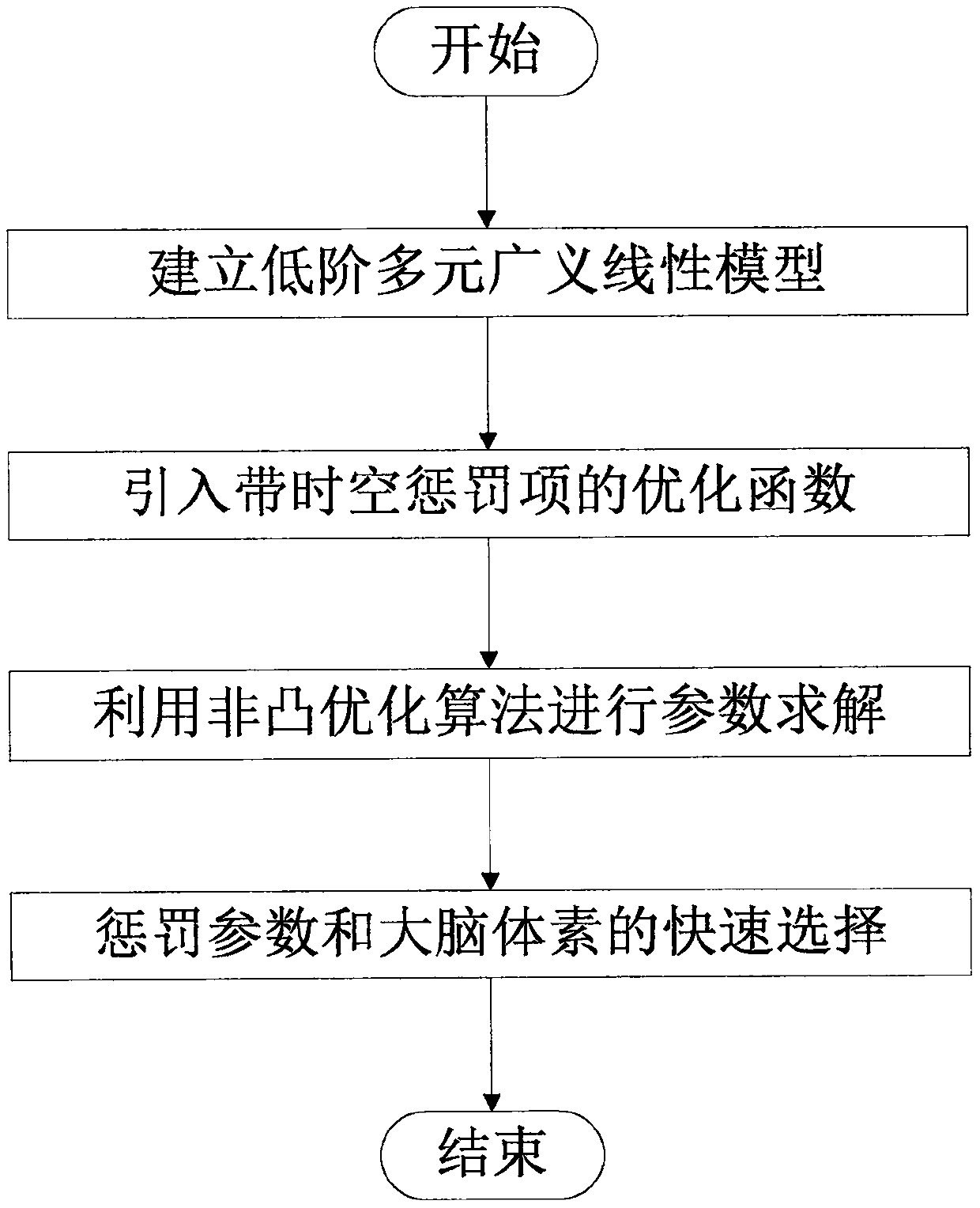
[0046] refer to figure 1 , the present invention includes establishing a low-order multivariate generalized linear model for fMRI data of all brain voxels, introducing an optimization function with a penalty term, using an iterative algorithm to solve the model parameters, and performing penalty coefficients and responses to different brains through the proposed fast selection strategy. Quick selection of voxels. Specific steps are as follows:
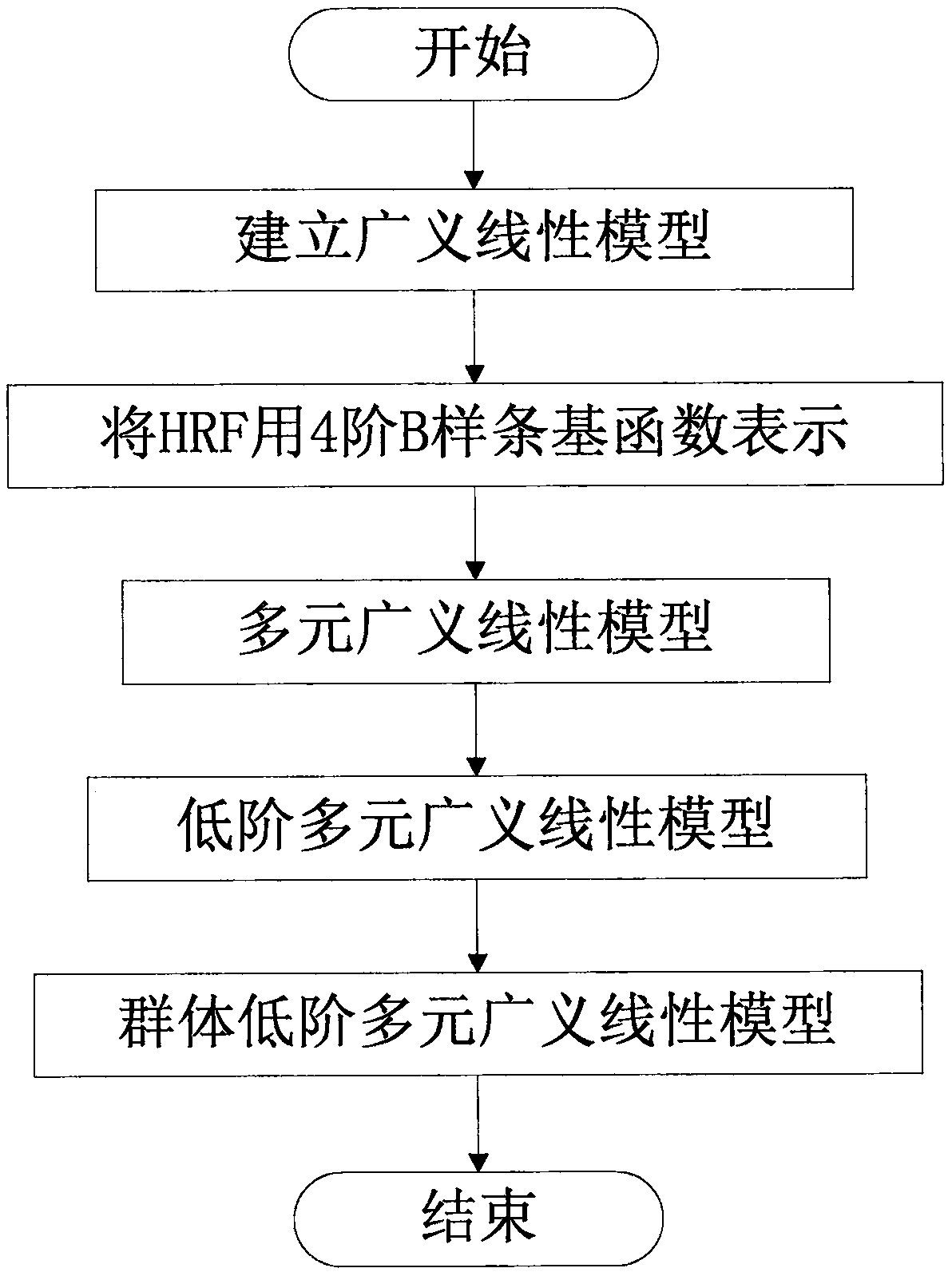
[0047] 1. Building a low-order multivariate generalized linear model for fMRI data
[0048] Step 1: Build the following GLM model for the fMRI time series of each brain voxel
[0049]
[0050] in Indicates the fMRI time series observed by subject i at brain voxel j, K is the number of stimuli in the fMRI experiment, m is the domain of definition of HRF, and is assigned a value of 15 to 25. r=1 T RT / 128+1=7, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com