A Differentially Variable Pitch Blade and Helicopter Rotor System
A variable-pitch blade and rotor shaft technology, applied in rotorcraft, motor vehicles, aircraft, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the lift of the tip part, the overall weight of the rotor device, and the sticking of the blades, so as to reduce the power transmission link. , Improve the efficiency of energy transfer and avoid friction loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
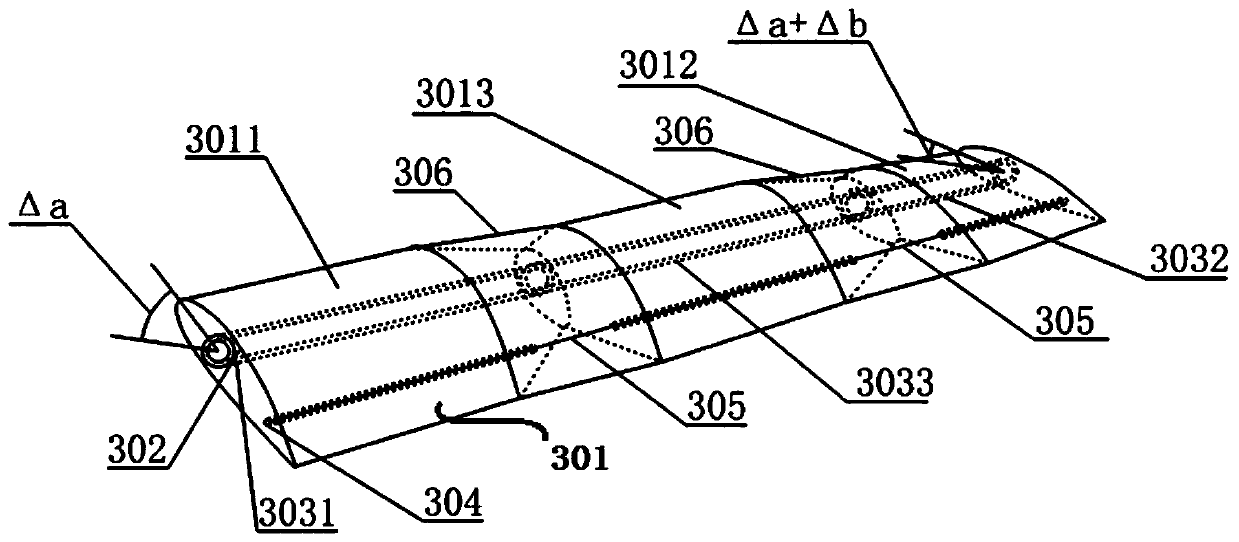
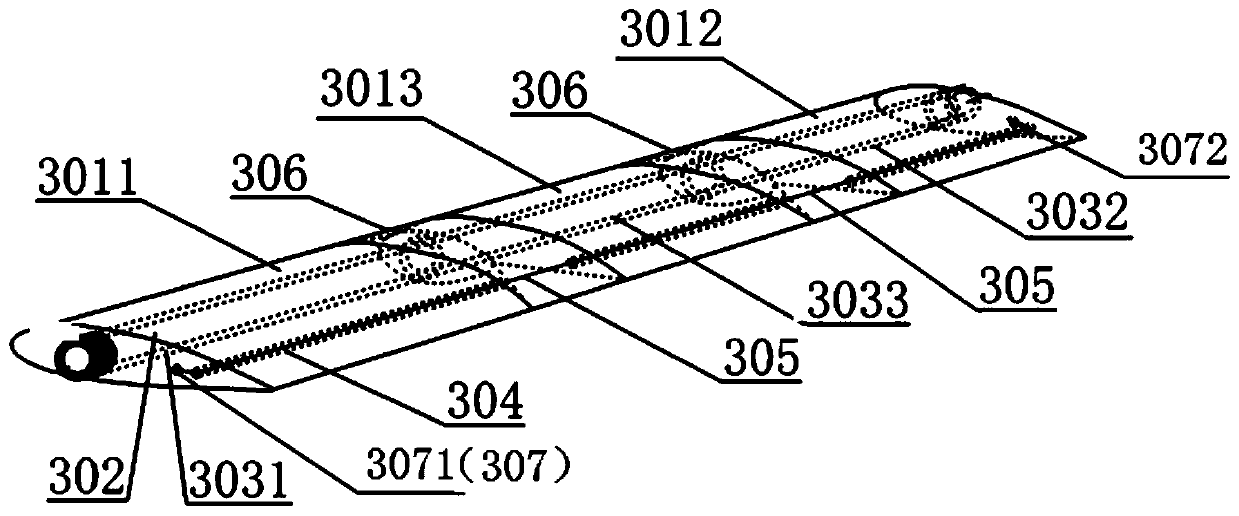
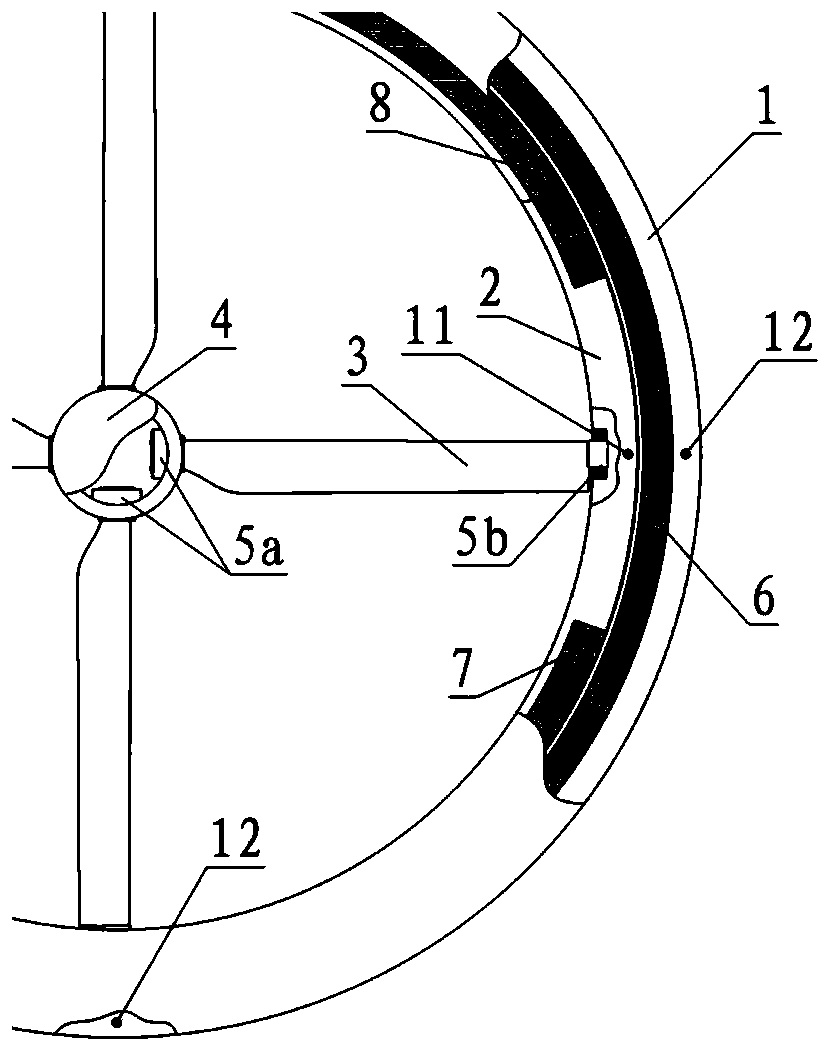
[0034] The first aspect of the present application provides a differentially variable pitch blade, such as figure 1 As shown, a first embodiment is provided, which includes:
[0035] At least two airfoil sections 301 are rotationally connected between adjacent airfoil sections, and each airfoil section has a first through hole and a second through hole;
[0036] The torsion rod 302 is penetrated and rotatably arranged in the first through holes of all the airfoil sections; and
[0037]The variable-pitch control cable 305 runs through the second through holes of all the airfoil sections, and the two ends of the variable-pitch control cable 305 are respectively fixed on the airfoil sections at the blade root and the blade tip;
[0038] Wherein, the first airfoil section at the root of the blade is connected with a first torsion mechanism for driving the first airfoil section to twist a first angle, and the second airfoil section at the tip of the blade is connected with a secon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com