Method and application of femtosecond laser direct writing processing with near 4π solid angle using multiphoton excitation
A femtosecond laser and multi-photon technology, applied in laser welding equipment, metal processing equipment, optics, etc., to achieve the effect of solving the problem of out-of-focus and uniform material properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
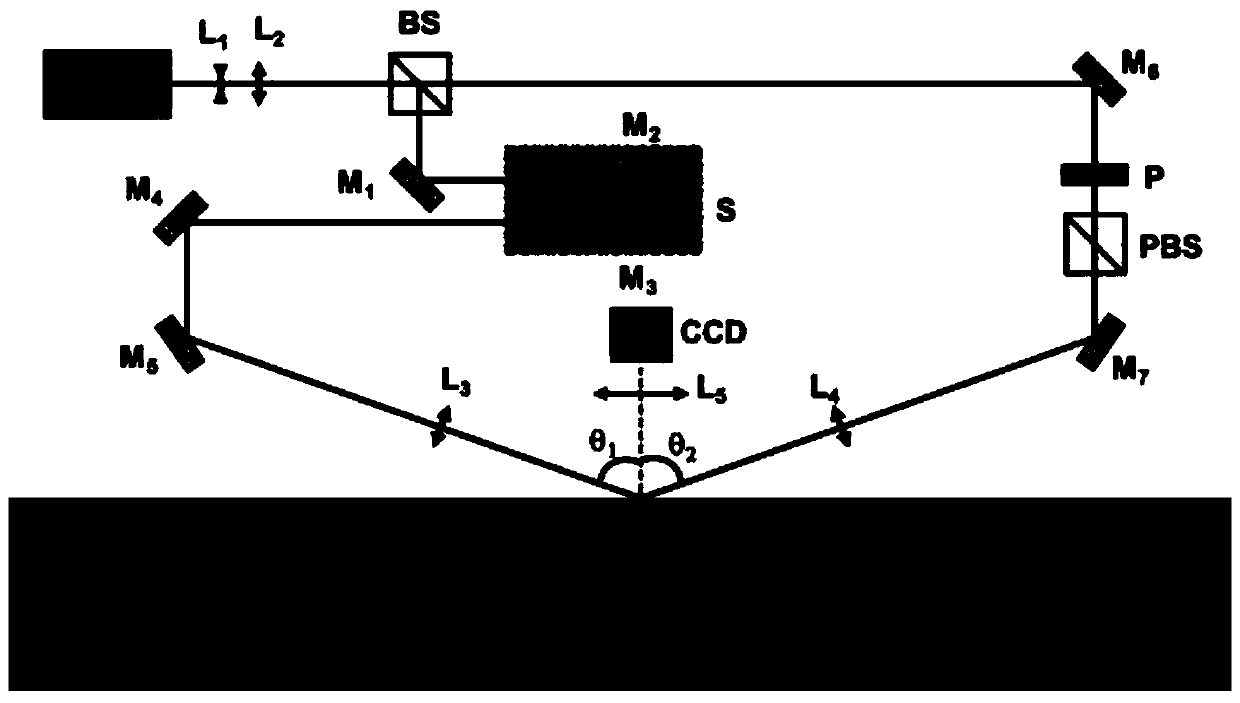
[0027] Multiphoton excitation is achieved by adjusting the time-domain synchronization of sub-beam femtosecond laser pulses.
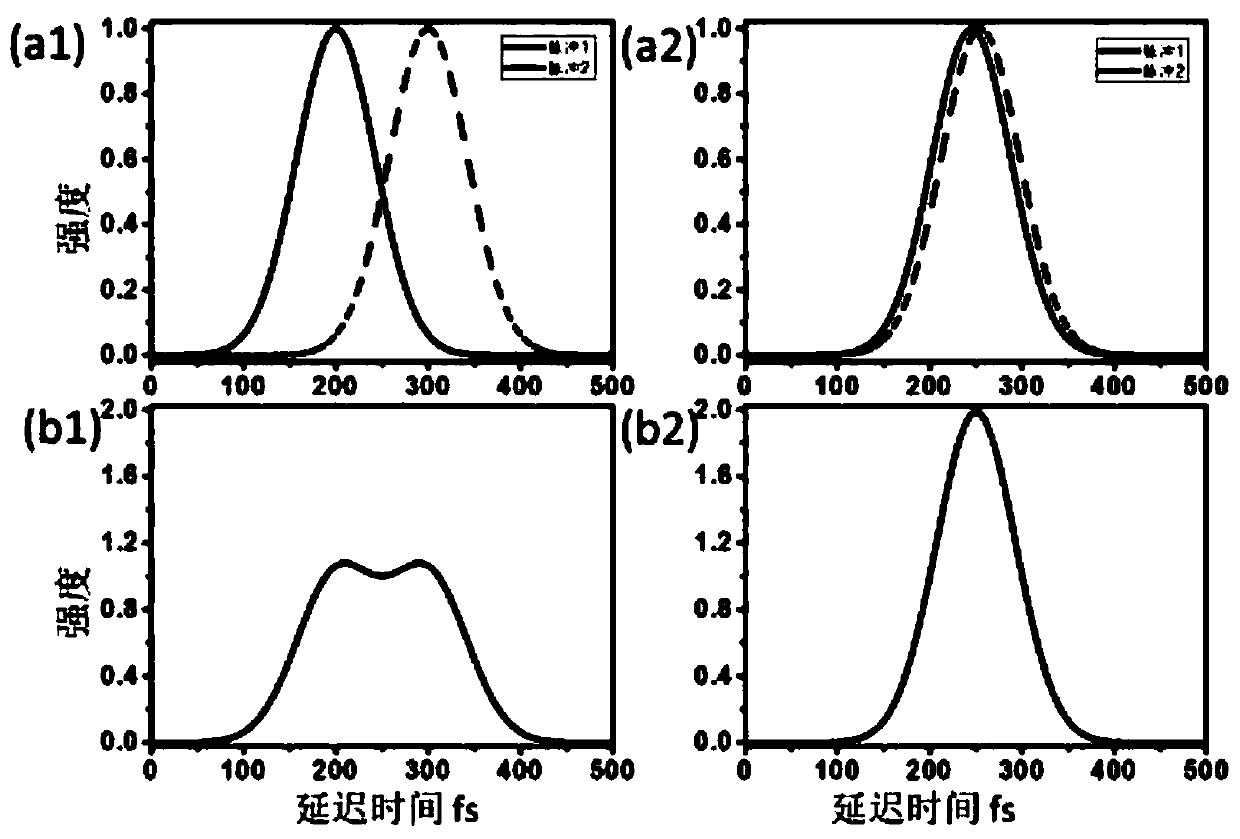
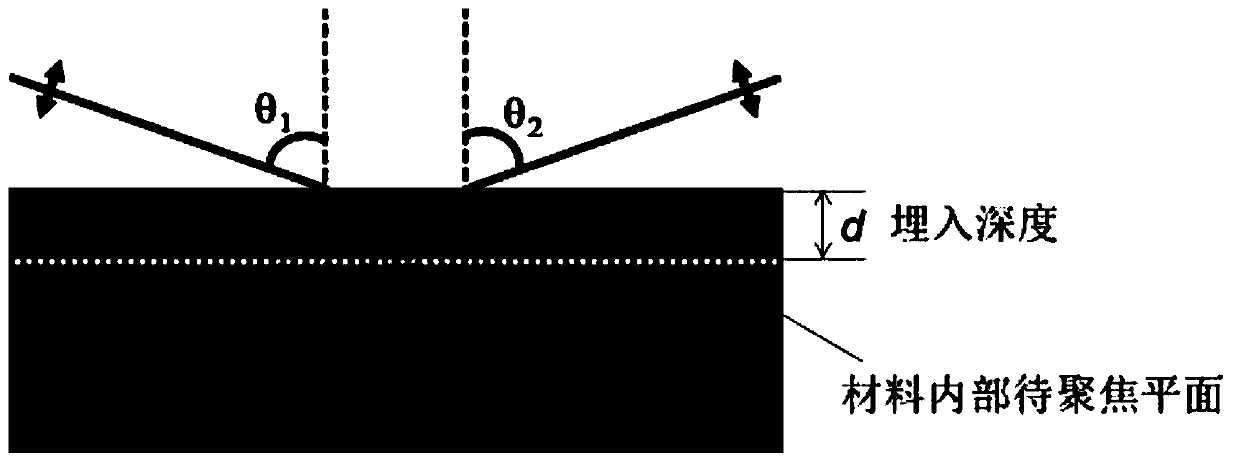
[0028] The way of using multi-photon excitation to "combine" energy can also provide the energy required for material modification. At the same time, the orthogonally converging sub-beam femtosecond laser can form a near-spherical focal spot with a solid angle of nearly 4π, which can correct the serious defocus of a single femtosecond laser in direct writing processing with a large embedding depth. In order to ensure that the energy of multiple photons can be effectively superimposed, it is necessary to adjust the pulse of the sub-beam laser through the optical path to achieve synchronization in time and space, that is, synchronization in the instant domain. Time synchronization adjustment is performed first, even if the sub-beam femtosecond lasers after beam splitting go through the same optical path. Then carry out spatial synchronization adjustment...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Three-dimensional embedded waveguide quantum devices using multiphoton excitation focal spot with near 4π solid angle.
[0036] By adjusting the time-domain synchronization of sub-beam femtosecond laser pulses, a multi-photon excitation focal spot with a solid angle of nearly 4π can be obtained deep inside the material, and its energy distribution has a near-spherical characteristic, thereby effectively correcting the defocus. Three-dimensional embedded quantum devices such as three-dimensional waveguides can be obtained by direct writing processing using multi-photon excitation focal spots with near 4π solid angle.
[0037] Three-dimensional embedded structure processing with multiphoton excitation focal spot with nearly 4π solid angle:
[0038] (1) Generation of time-synchronized pulses: the same as in Embodiment 1, wherein the femtosecond laser beam expands the spot by 4 times.
[0039] (2), pulse space synchronization adjustment: same as embodiment 1.
[0040] (3)...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viewing angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com