Robot dynamics parameter identification method and device, terminal device and storage medium
A technology of dynamic parameters and identification methods, applied in manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve the problems of low identification accuracy of dynamic parameters, achieve the effect of improving identification accuracy and avoiding error accumulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
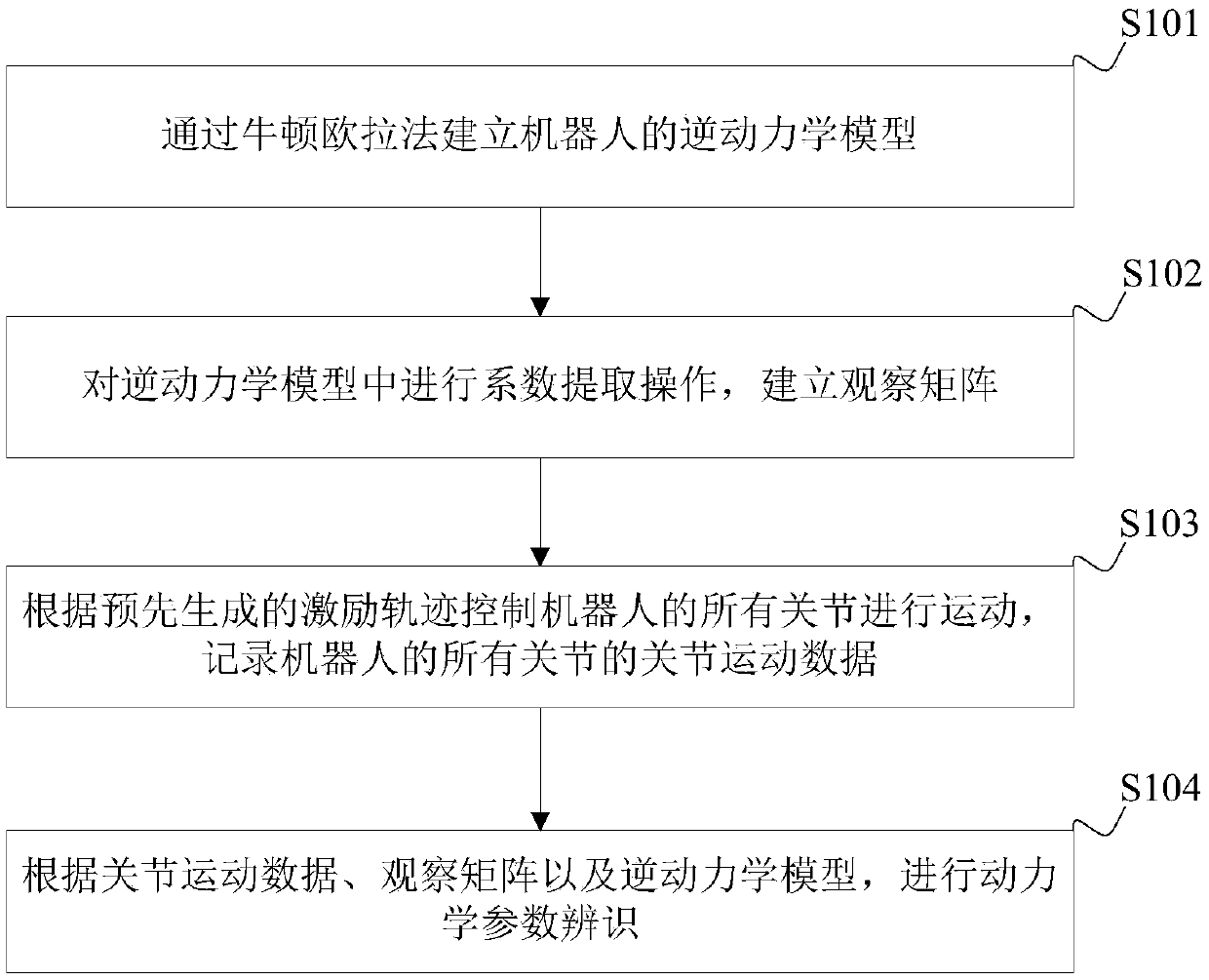
[0073] See figure 1 , is a schematic flow diagram of a method for identifying robot dynamics parameters provided in an embodiment of the present application, and the method may include the following steps:
[0074] Step S101, establishing an inverse dynamics model of the robot through the Newton-Euler method.
[0075] Specifically, the above inverse dynamics model can be specified as Among them, τ j =τ m -τ ext , τ m is the torque of the robot joint servo motor, τ ext is the external moment, M is the robot inertia matrix, C is the Coriolis centrifugal force matrix, G is the gravity, F is the friction force, q is the joint position, is the joint velocity, is the joint acceleration.
[0076] It can be understood that the process of establishing the inverse dynamics model by the Newton-Euler method is well known to those skilled in the art, and will not be repeated here.
[0077] Step S102 , extracting coefficients from the inverse dynamics model to establish an obs...
Embodiment 2
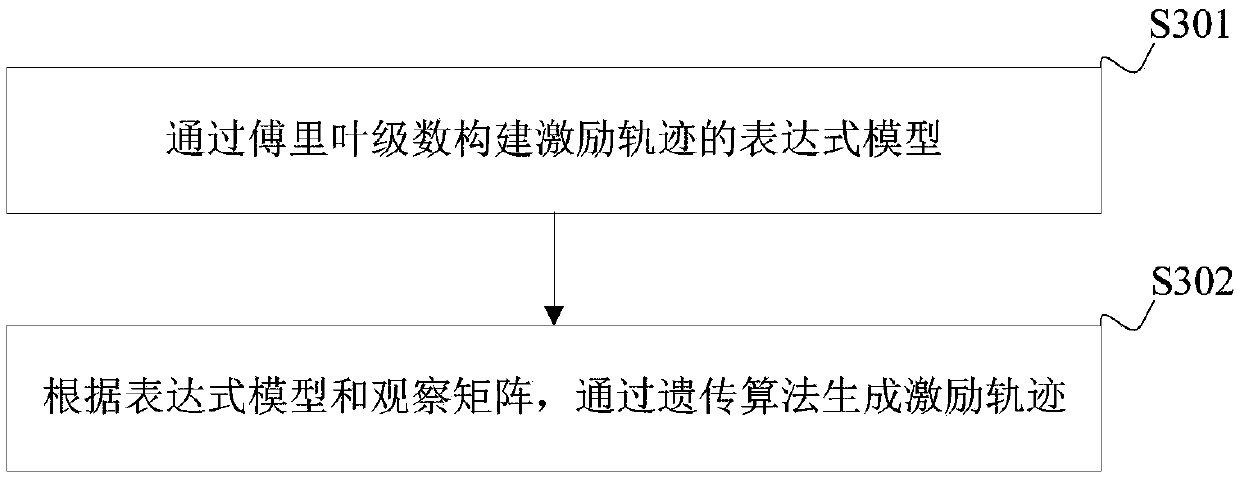
[0102] The excitation trajectory in the first embodiment above may be pre-generated, and the generation method of the excitation trajectory may be any existing method. However, in the process of identifying the parameters of the excitation trajectory generated by the existing method, the problem of the universality of the identification data will be encountered. For example, if the data used in the identification process only includes velocities within the range of 30° / s, then the dynamic model derived from the identified parameters will perform poorly for velocity data above 30° / s. At present, most of the excitation trajectories used in the dynamic parameter identification of robots are constructed by Fourier series, and the acceleration and velocity of the excitation trajectories are generally very small, which cannot cover high acceleration and high velocity areas.
[0103] In order to enable the identified dynamic model to cover areas of high acceleration and high speed, t...
Embodiment 3
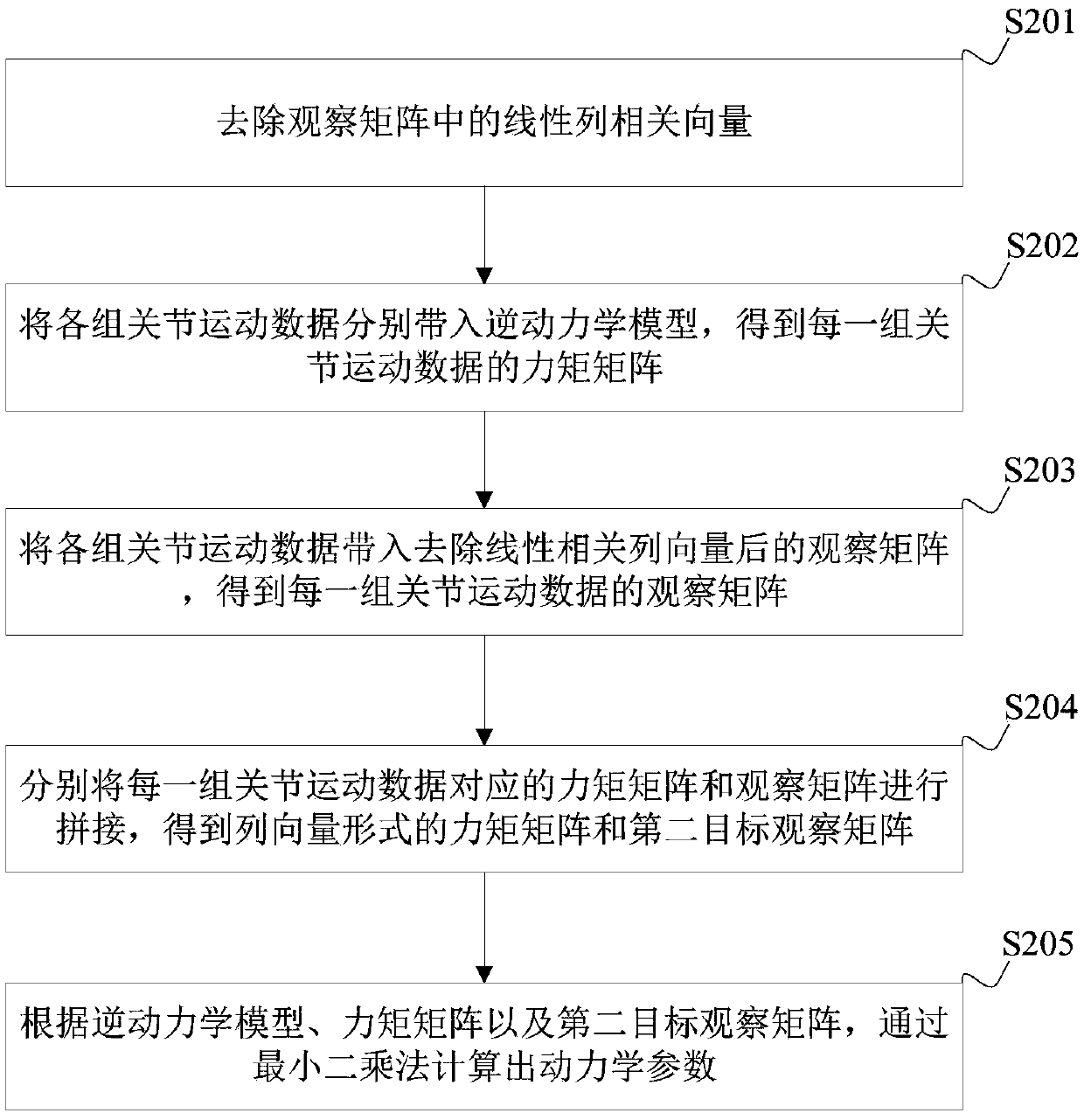
[0136] See Figure 5 , which is a schematic structural block diagram of a robot dynamic parameter identification device provided in an embodiment of the present application, the device may include:
[0137] The inverse dynamics model building block 51 is used to establish the inverse dynamics model of the robot by the Newton Euler method;
[0138] The observation matrix building module 52 is used to perform coefficient extraction operations in the inverse dynamics model to establish an observation matrix;
[0139] The joint motion data recording module 53 is used to control all joints of the robot to move according to the pre-generated excitation trajectory, and record the joint motion data of all joints of the robot;
[0140] The identification module 54 is configured to perform dynamic parameter identification according to the joint motion data, the observation matrix and the inverse dynamic model.
[0141] In a feasible implementation manner, the above-mentioned device ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com