Spatial geometric error measurement and identification method for multi-line machine tools based on laser interferometer
A technology of laser interferometer and geometric error, applied in measuring/indicating equipment, metal processing machinery parts, metal processing equipment, etc., can solve problems such as coefficient matrix singularity, limited error identification, difficult to solve production problems, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0057] The present invention will be described in further detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
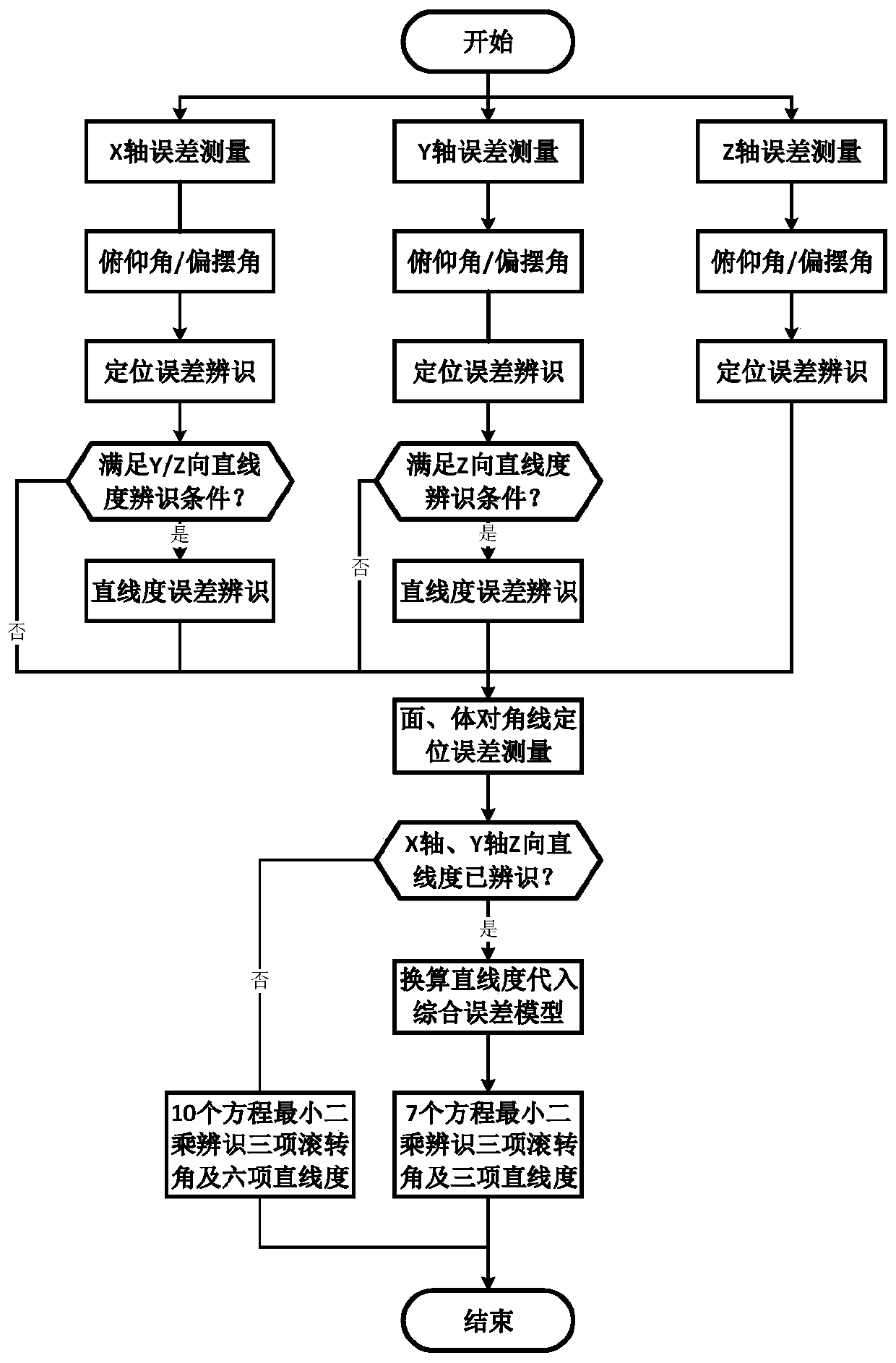
[0058] refer to figure 1 , a method for measuring and identifying spatial geometric errors of multi-line machine tools based on laser interferometers, including the following steps:
[0059] 1) Plan the measurement space in the machine tool stroke space, and design and plan the measurement path in the measurement space;
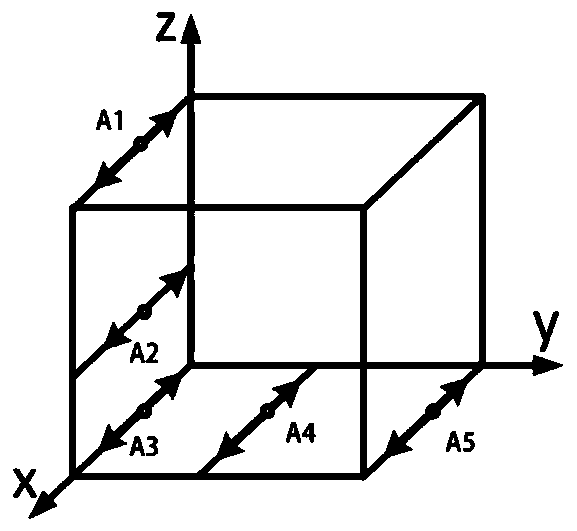
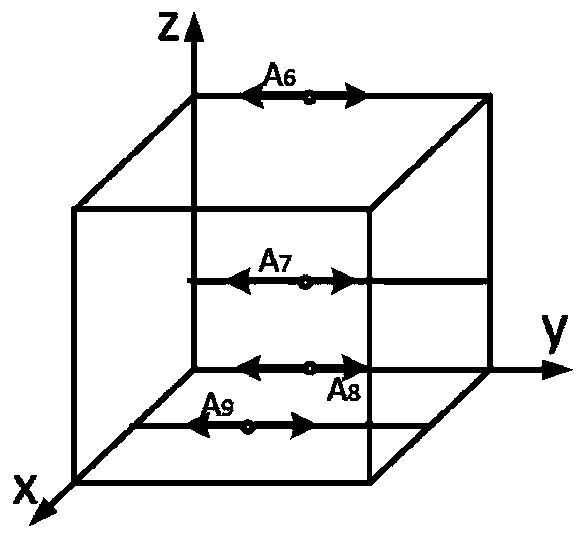
[0060] For the X axis, refer to figure 2 , in the measurement space, the positioning error, two non-roll angle errors and two mutually perpendicular straightness errors are measured. The positions of the measurement lines are all parallel to the X axis, and the positioning error δ x (x) The measurement starting point is A 1 (x 1 ,y 1 ,z 1 ), around the Y-axis angle error ε y (x) Measurement starting point A 2 (x 2 ,y 2 ,z 2 ), around the Z-axis angle error ε z (x) Measurement starting point A 3 (x 3 ,y 3 ,z 3 ), Y-direction straig...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com