Adaptive wide-area damping controller
A wide-area damping and self-adaptive technology, applied in the direction of reducing/preventing power oscillation, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient damping improvement, and achieve the effect of improving self-adaptive ability, suppressing low-frequency oscillation, and increasing damping improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
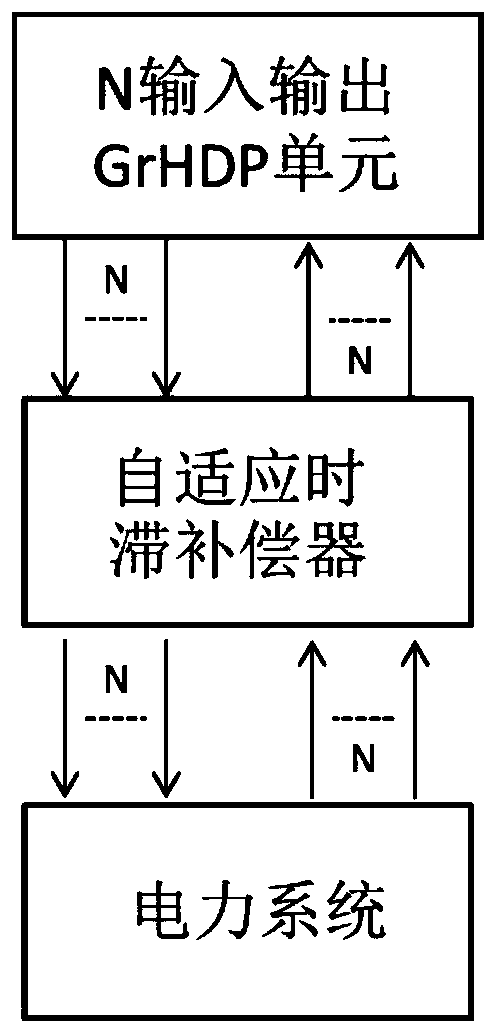
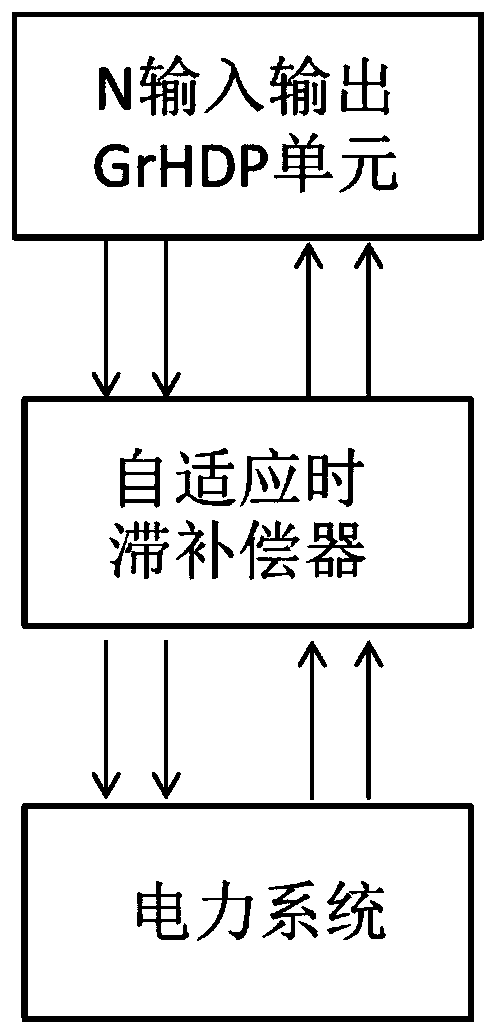
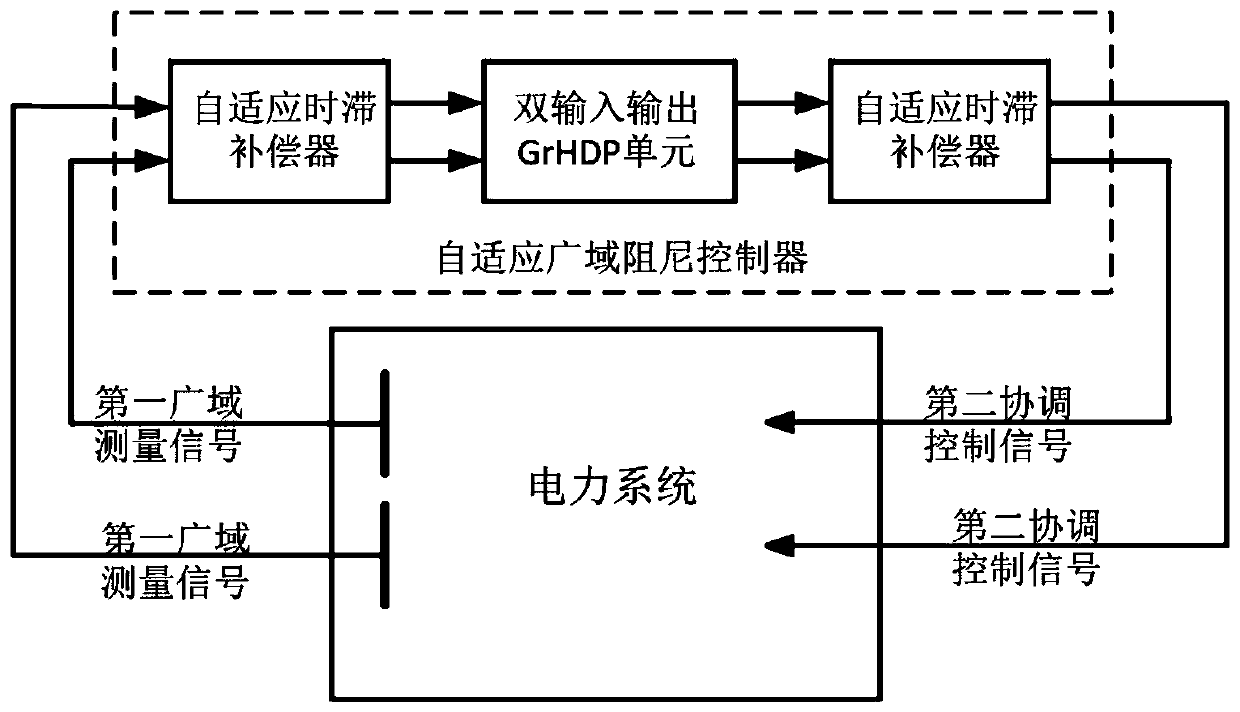
[0051] An adaptive wide-area damping controller such as figure 1 As shown, including: adaptive skew compensator and N-input-output GrHDP unit. Wherein, the adaptive time-delay compensator is used to obtain N first wide-area measurement signals from the power system, perform adaptive time-delay compensation on the N first wide-area measurement signals, and output the N first wide-area measurement signals The N second wide-area measurement signals corresponding to the signals one by one; the N input and output GrHDP unit is used to receive the N second wide-area measurement signals, and based on the GrHDP model algorithm, calculate and obtain the N second wide-area measurement signals A corresponding N first coordinated control signals are output; the adaptive time lag compensator is also used to receive the N first coordinated control signals, and perform adaptive time lag compensation on the N first coordinated control signals to obtain N second coordinated control signals co...
Embodiment 2
[0055] On the basis of Embodiment 1, the adaptive time lag compensator includes: n time lag compensation sub-modules and an additional gain calculation unit. Among them, n delay compensation sub-modules are used to perform adaptive delay compensation on each input signal; the additional gain calculation unit is used to calculate the additional gain value corresponding to the input signal according to the communication delay of each input signal , where the input signal is the first wide-area measurement signal or the first coordinated control signal; then the transfer function of the adaptive time-delay compensator for each input signal is:
[0056]
[0057] Among them, K represents the additional gain value of the input signal, SDC i (s) represents the transfer function of the ith time-delay compensation sub-module, β i (τ) represents the weight of the ith time-delay compensation sub-module, n is the number of time-delay compensation sub-modules, and the value is the orde...
Embodiment 3
[0073] On the basis of Embodiment 2, the simplified input signal delay transfer function is:
[0074] Among them, s represents a complex variable, and τ represents a communication time delay.
[0075] It should be noted that, specifically, the time-delay transfer function G of the input signal using the first-order Pade approximation transform d (s) Approximate simplification, the simplified transfer function is G D (s), its calculation formula is as follows:
[0076]
[0077] to G D (s) is further deformed to obtain the following formula:
[0078] Among them, τ is the communication delay of the input signal, and s is a complex variable.
[0079] This formula is the time-delay transfer function of the input signal in this embodiment. It should be noted that if the time-delay transfer function of the input signal is approximated twice by using different methods, the simplified input signal time-delay transfer function obtained is If they are different, their order w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com