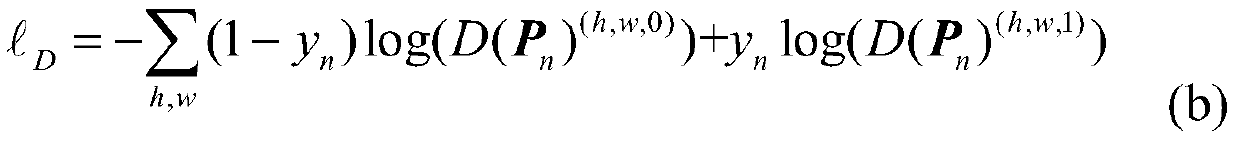Multi-dimensional field weed identification method based on generative adversarial learning
A recognition method and multi-dimensional technology, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer components, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient data labeling, limited performance improvement, threat to field crop yield, etc., and achieve the effect of strong flexibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
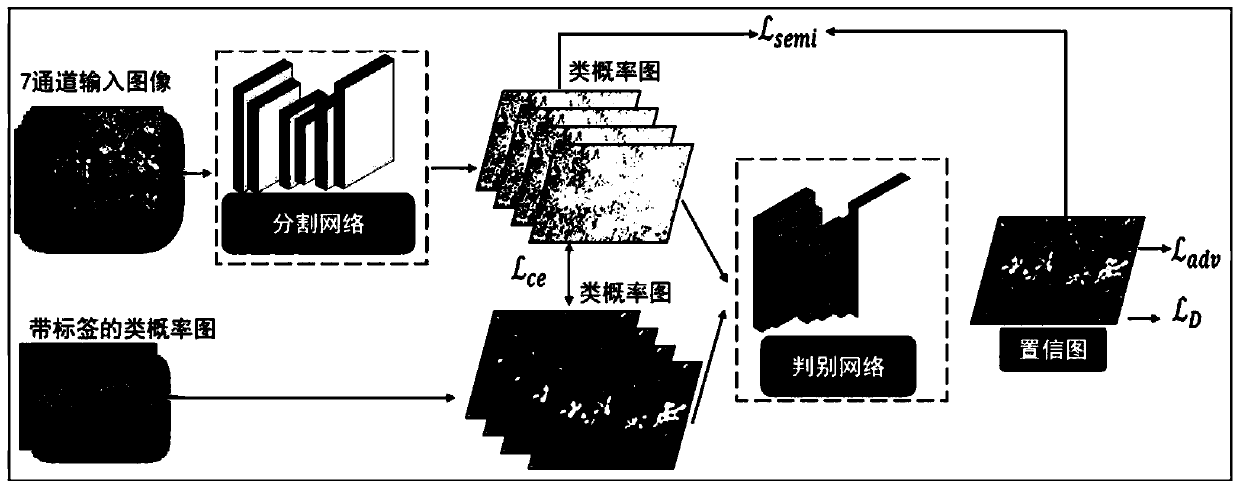
[0043] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention provides a multi-dimensional field weed recognition method based on generative confrontation learning, adopts a semi-supervised learning strategy, uses generative confrontation learning to find the confidence region of unlabeled data, and obtains the final field weed recognition result through self-learning .
[0044] The overall network designed by the present invention includes two networks altogether: segmentation network and discrimination network; segmentation network can be arbitrary depth segmentation network, as figure 1 As shown, the present invention uses a multi-channel image as the input of the segmentation network, and the output is a class probability map; the input of the discriminant network is the above class probability map, and the class probability map can be a labeled class probability map or a segmentation network The output class probability map, the output of the discriminant network is a spatial ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com