Device and method for detecting brain waves
A brain wave, non-instantaneous technology, applied in the field of physiological signal analysis, can solve the problems of large amount and complexity of brain wave data, interference, and anatomical structure obstruction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0126] Example 1: Functional Electroencephalotopography (fEEToPG)
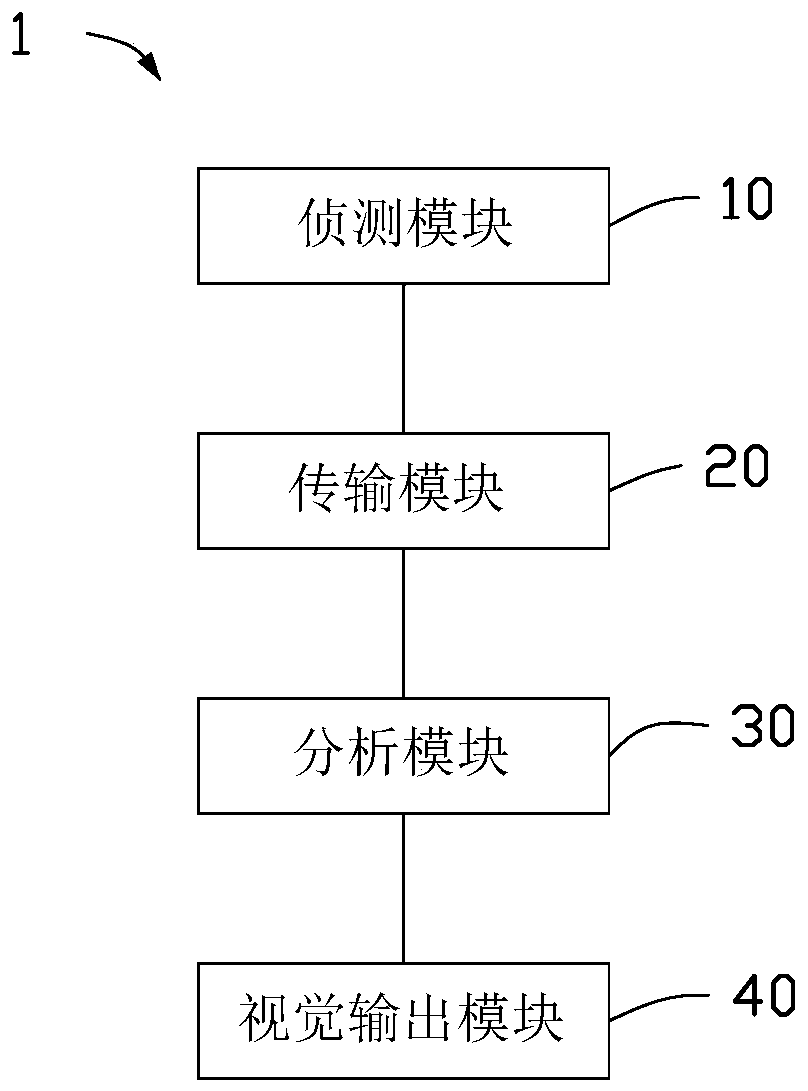
[0127] please see Figure 11 and Figure 12 , one or more embodiments of the present application provide several visual outputs of functional brain wave topography. In a system for generating functional brain wave surface topography, the detection module includes a detection unit array capable of simultaneously detecting brain electrical activities in different regions of the skull. The detection unit array can be a plurality of electrodes with a special arrangement, wherein each electrode can obtain a detected signal of a corresponding area.
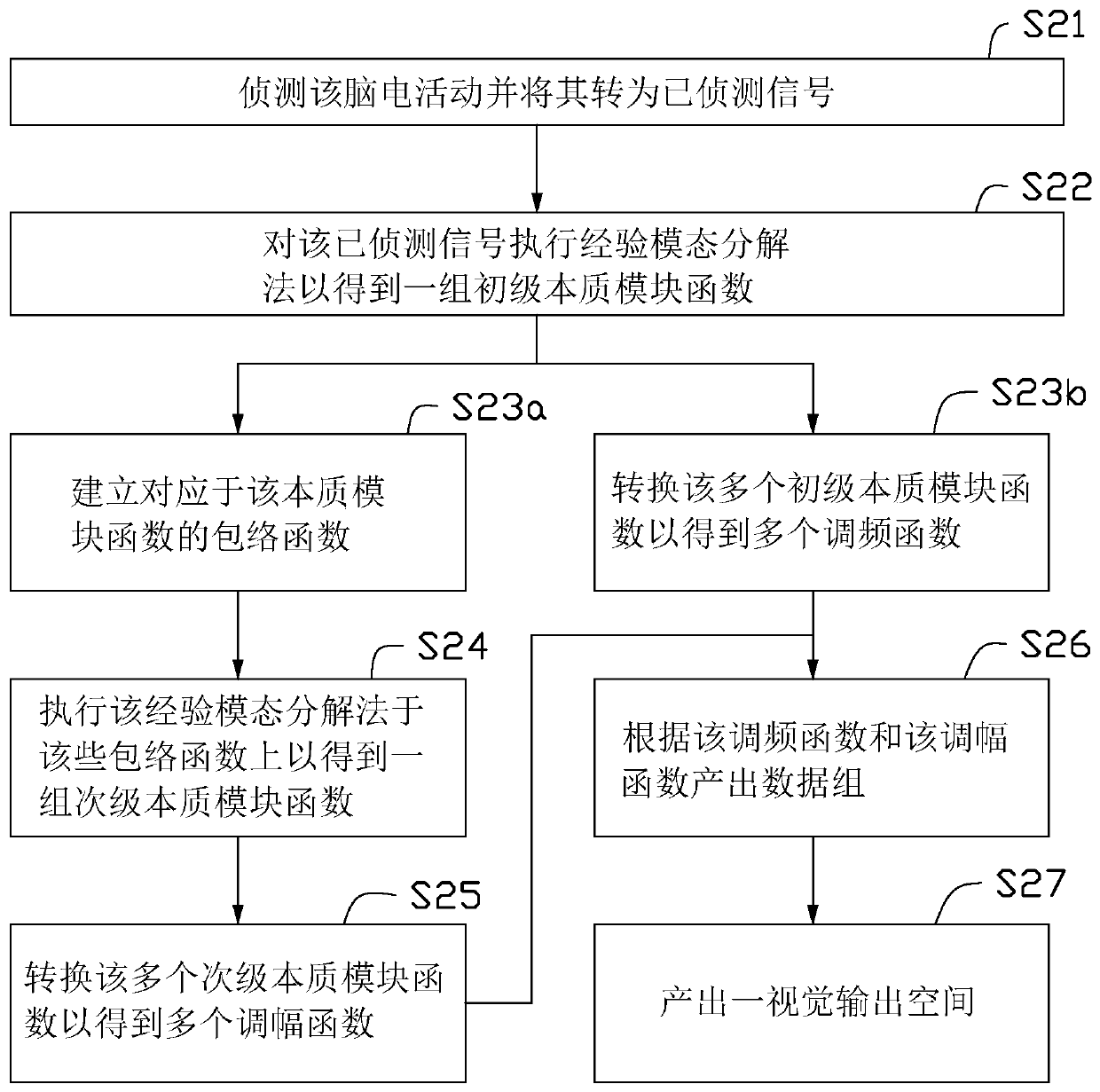
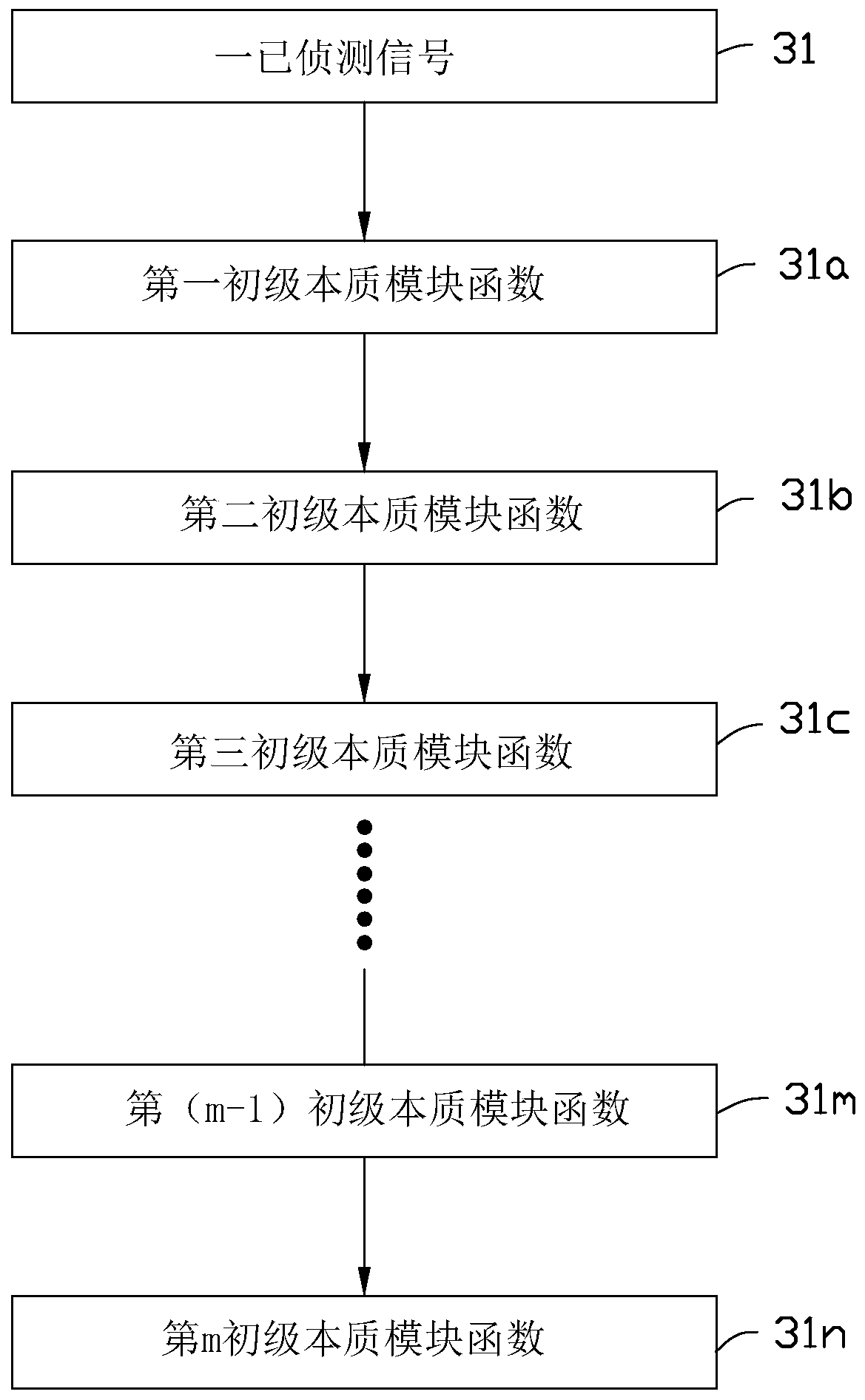
[0128] The method for visualizing functional brain wave surface topography includes: using the detection module to detect the brain electrical activity; generating multiple analyzed data sets by multiple detection units, and each analyzed data set includes multiple analysis data units, and each analyzed data unit further includes a detection unit ID; within the bound...
example 2
[0132] Example 2: Functional Electroencephalotomography (fEEToMG)
[0133] please see Figure 13 to Figure 16 , one or more embodiments of the present application provide several visual outputs of functional brainwave tomograms. In a system for generating functional brain wave tomograms, the detection module includes a detection unit array capable of simultaneously detecting brain electrical activities in different regions of the skull. The detection unit array can be a plurality of electrodes with a special arrangement, wherein each electrode can obtain a detected signal of a corresponding area.
[0134]The method for visualizing a functional brain wave tomogram includes: using the detection module to detect the brain electrical activity; generating a plurality of analyzed data groups by a plurality of detection units, and each analyzed data group includes a plurality of analyzed data units, and each unit of analyzed data further includes a detection unit ID; within the bou...
example 3
[0140] Example 3: Clinical Application of Functional Electroencephalography (fEEG)
[0141] The clinical use of functional EEG will be illustrated by the following figures to identify specific visual output patterns in various neuropsychiatric states, such as: cognitive impairment, Alzheimer's disease , Huntington's disease, depression, migraine, anesthesia depth, insomnia, Parkinson's disease, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder; ADHD), anesthesia depth monitoring, and drug addiction. The specific visual output forms of the functional electroencephalogram are related to the diagnosis, prognosis, clinical assessment or disease stage of the above diseases. Comparisons between specific visual output modalities of different functional EEGs can also be used to discern differences between two groups of people with different mental states, or differences between two groups of people with the same disease but different stages of the disease , the difference between two groups ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com