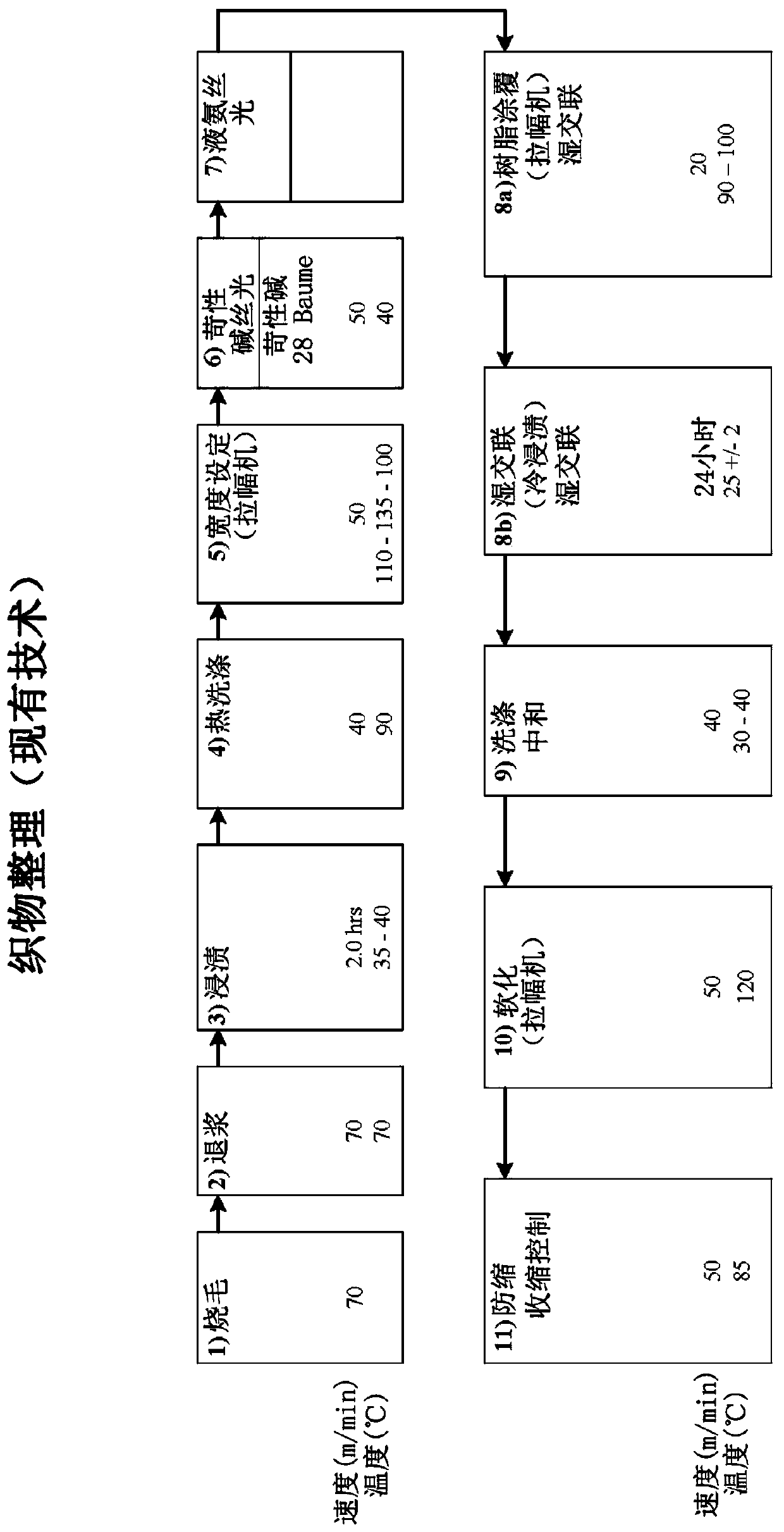
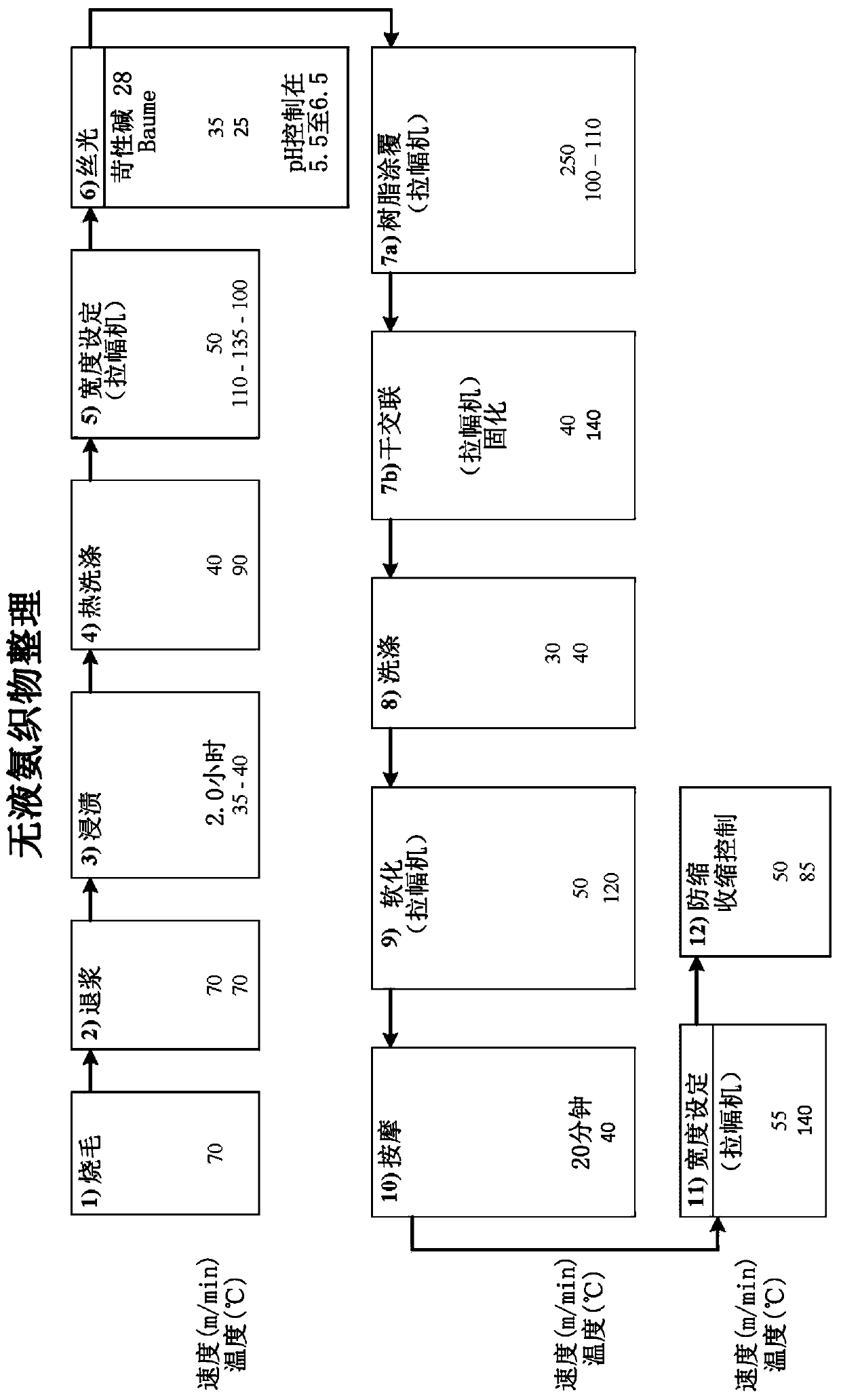
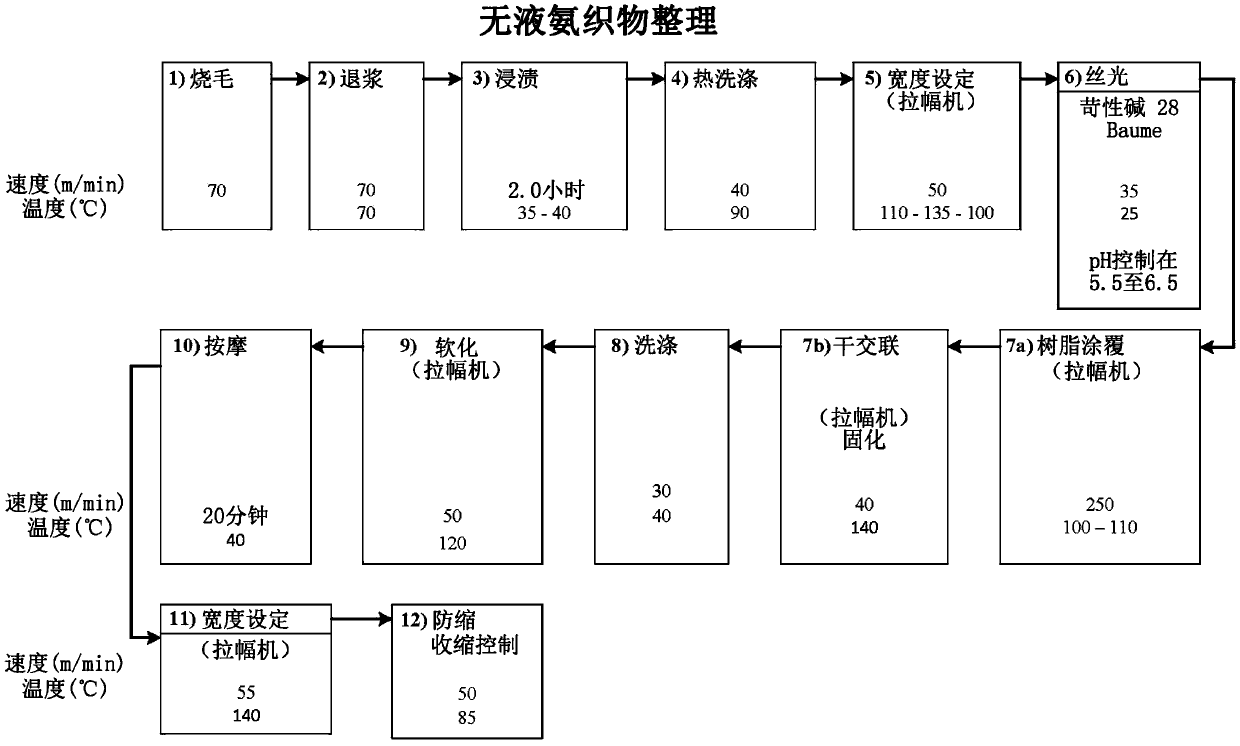
Non-iron fabrics and garments, and a method of finishing the same
A technology of non-ironing fabrics and fabrics, which is applied in the field of non-ironing fabrics and clothing and their finishing, and can solve the problems of fabric or clothing losing strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0099] Durable Press Grade
[0100] Tested to compare via eg figure 2 Shown are the Durable Press (DP) ratings of six different fabrics produced by the process of the invention after three and five washes. Fabrics will vary in construction, weave, weight and color. Wash with Tide detergent on a regular cycle at 41°C, then dry on a 4-pound tumble-drying medium. Durable Press Rating tested according to AATCC-124.
[0101] Table 1: Smooth Appearance (DP) Report
[0102]
[0103]
[0104] As shown in Table 1, the durable press rating of each fabric remained at 3.5 after three washes and after five washes.
[0105] Formaldehyde content
[0106] A test was performed to compare the formaldehyde content of fabrics treated according to the present invention with the formaldehyde content of fabrics treated according to conventional liquid ammonia moisture curing methods. The fabrics are all 100% cotton.
[0107] Table 2: Comparison of formaldehyde content in finished fabri...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com