Systems and methods for implementing deterministic finite automata (DFAS) via a blockchain
A blockchain, block technology, applied in transmission systems, digital transmission systems, data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as cannot be changed or deleted, hash changes, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0153] Example 1 of the Codification Technique of the Invention - Simple Scenario
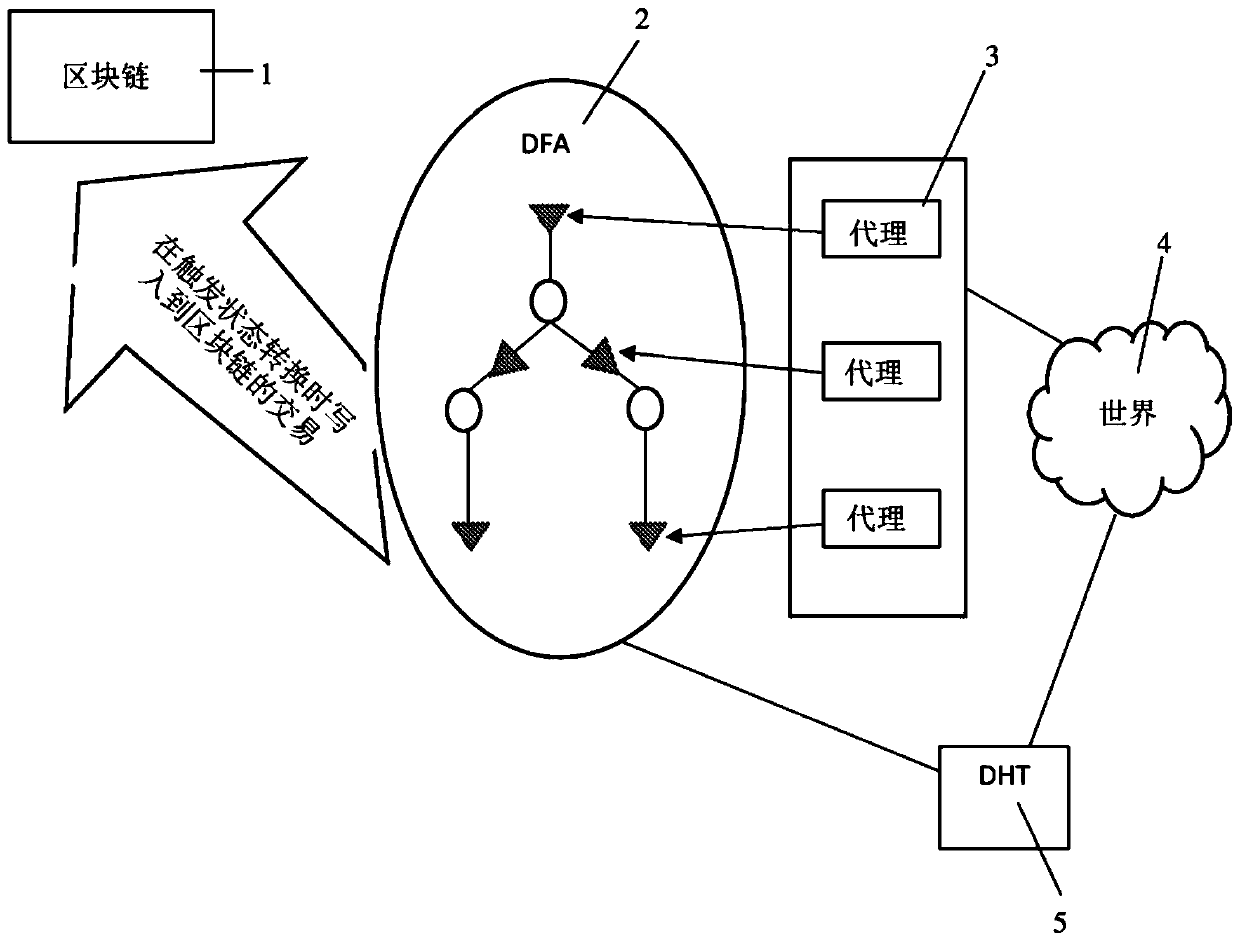
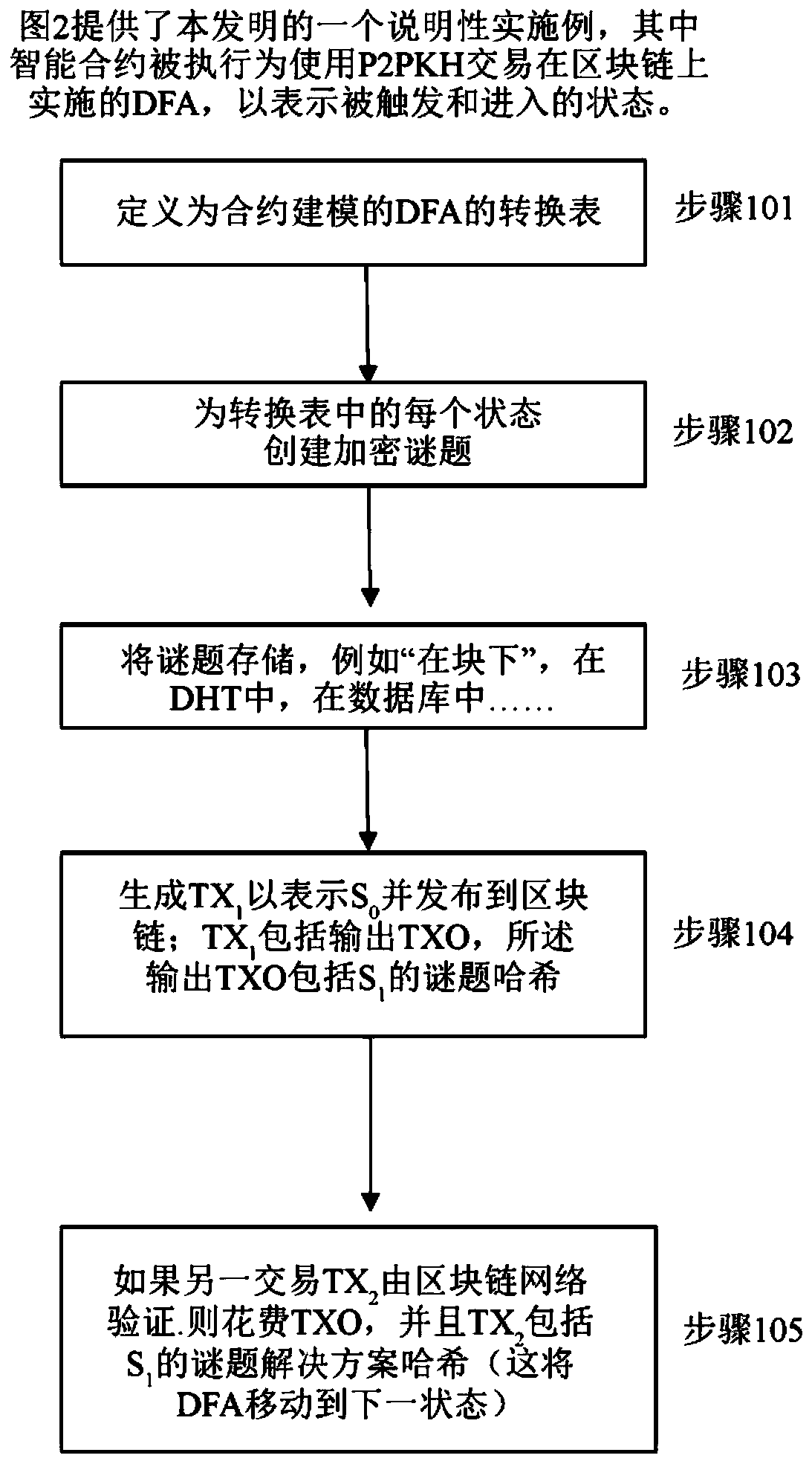
[0154] As already explained, a DFA consists of a finite set {S,I,t,s 0 ,F}, which represent the possible state (S), input (I), transition (t), initial state (S), respectively. 0 ) and a final state (F) (also known as the receiving state). Additionally, a set of actions (a) can be defined that represent the side effects of execution and determine the output of the computation.
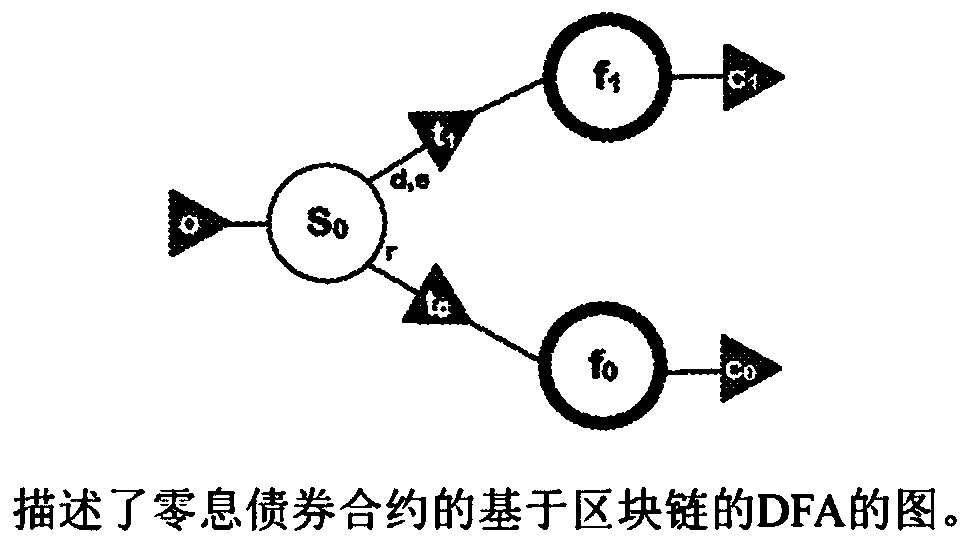
[0155] For the description and illustration of the present invention, we will consider a 3-period coupon bond. The elements (and symbols) of the DFA we consider for such contracts can be statically defined as given in Tables 2 to 4. Note that the initial state is specified by S in our notation, and the accepting state is F 0 and F 1 .
[0156] Table 2: List of Contract Status of Coupon Bonds:
[0157] state describe S The contract is created and signed, the execution has not started. T 1
...
example 2
[0174] Example 2 of the Codification Technique of the Invention - Recurrence State
[0175] As mentioned above, some subset of states or coupon bonds (T i and D i state) correspond to very similar interpretations of state machine states, except that they differ in the number of time periods or coupons (i) they involve; that is, in the sense that they can be viewed as states that are repeated multiple times (eg from i=1 to a given imax, where in our case imax=3). In view of this, it makes sense to simplify the representation of the DFA by including all those states in the recurring state (R) for separate processing. With this simplification, we present below the contract state list (Table 7), state transition table (Table 8), equivalent state diagram (Table 8) of our exemplary coupon bond Figure 11 ) and the state definition table of the DFA (Table 9); note that the other elements of the DFA (inputs and actions) are unchanged from the previous section.
[0176] Table 7: ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com