Spinal minimally invasive surgery navigation method and system based on augmented reality
A minimally invasive surgery and augmented reality technology, applied in the field of surgical navigation, can solve the problems of invisible surgery scenes, visual fatigue of doctors, and increase the difficulty of surgery, so as to avoid surgery errors, enhance comfort, and improve the effect of surgery success rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
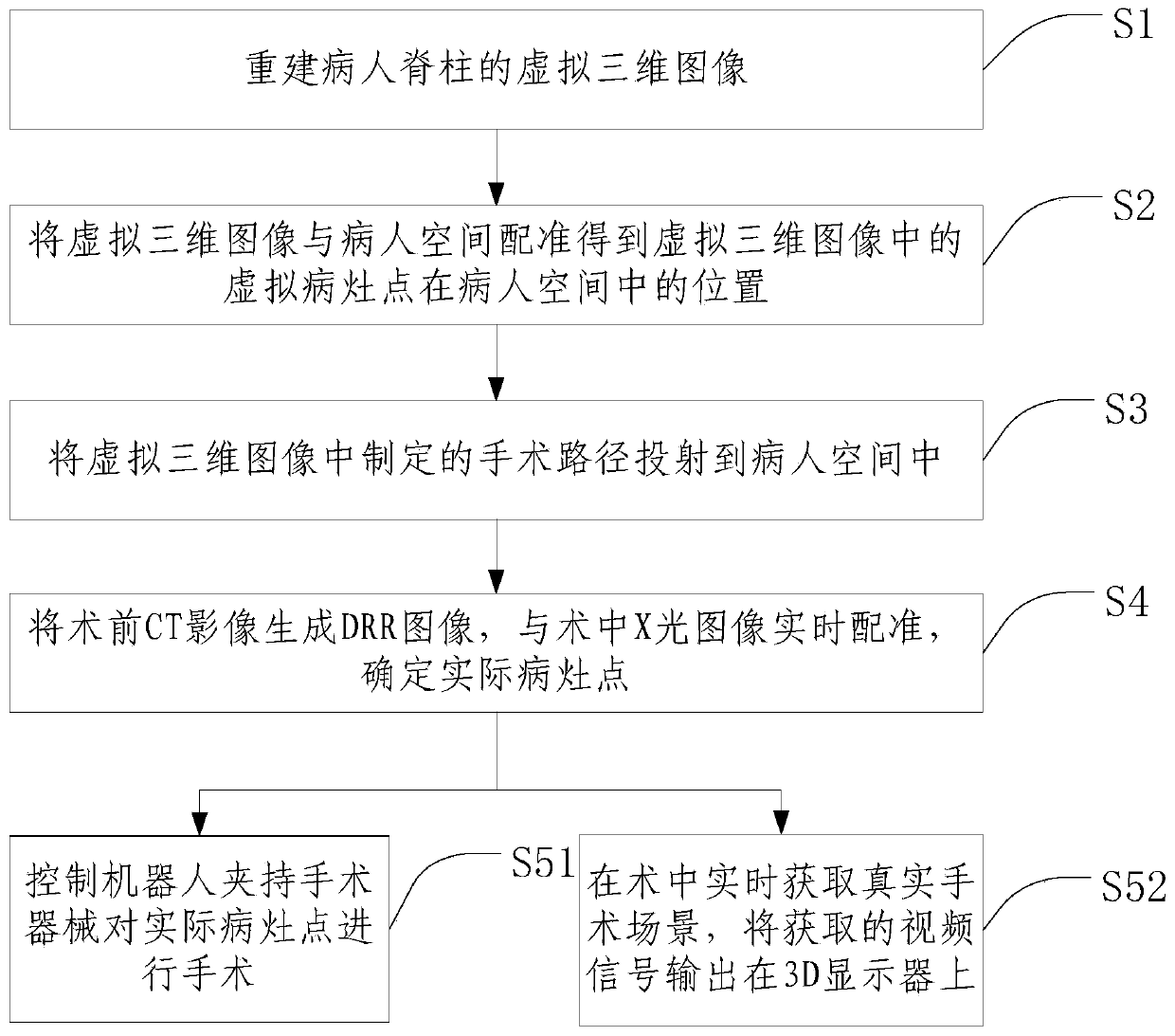
[0041] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is an augmented reality-based navigation method for spinal minimally invasive surgery in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. The method includes the following steps:
[0042] S1. Reconstructing a virtual three-dimensional image of the patient's spine.
[0043] It specifically includes: reconstructing a virtual three-dimensional image of the patient's spine based on a set of CT images.
[0044] S2. Registering the virtual three-dimensional image with the patient space to obtain the position of the virtual lesion point in the virtual three-dimensional image in the patient space.
[0045] Wherein, registering the virtual 3D image with the patient space specifically includes: respectively setting 4 non-coplanar marker points in the virtual 3D image and the patient space, and aligning the 4 marker points in the virtual 3D image with the 4 marker points in the patient space. The two marker points coincide respectively, that is, the registrat...
Embodiment 2
[0052] A navigation system for spinal minimally invasive surgery based on augmented reality, which includes:
[0053] The image reconstruction module is used to reconstruct the virtual three-dimensional image of the patient's spine;
[0054] It specifically includes: reconstructing a virtual three-dimensional image of the patient's spine based on a set of CT images.
[0055] The first registration module is used to register the virtual three-dimensional image with the patient space to obtain the position of the virtual lesion point in the virtual three-dimensional image in the patient space;
[0056] Wherein, registering the virtual 3D image with the patient space specifically includes: respectively setting 4 non-coplanar marker points in the virtual 3D image and the patient space, and aligning the 4 marker points in the virtual 3D image with the 4 marker points in the patient space. The two marker points coincide respectively, that is, the registration is realized.
[0057]...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com