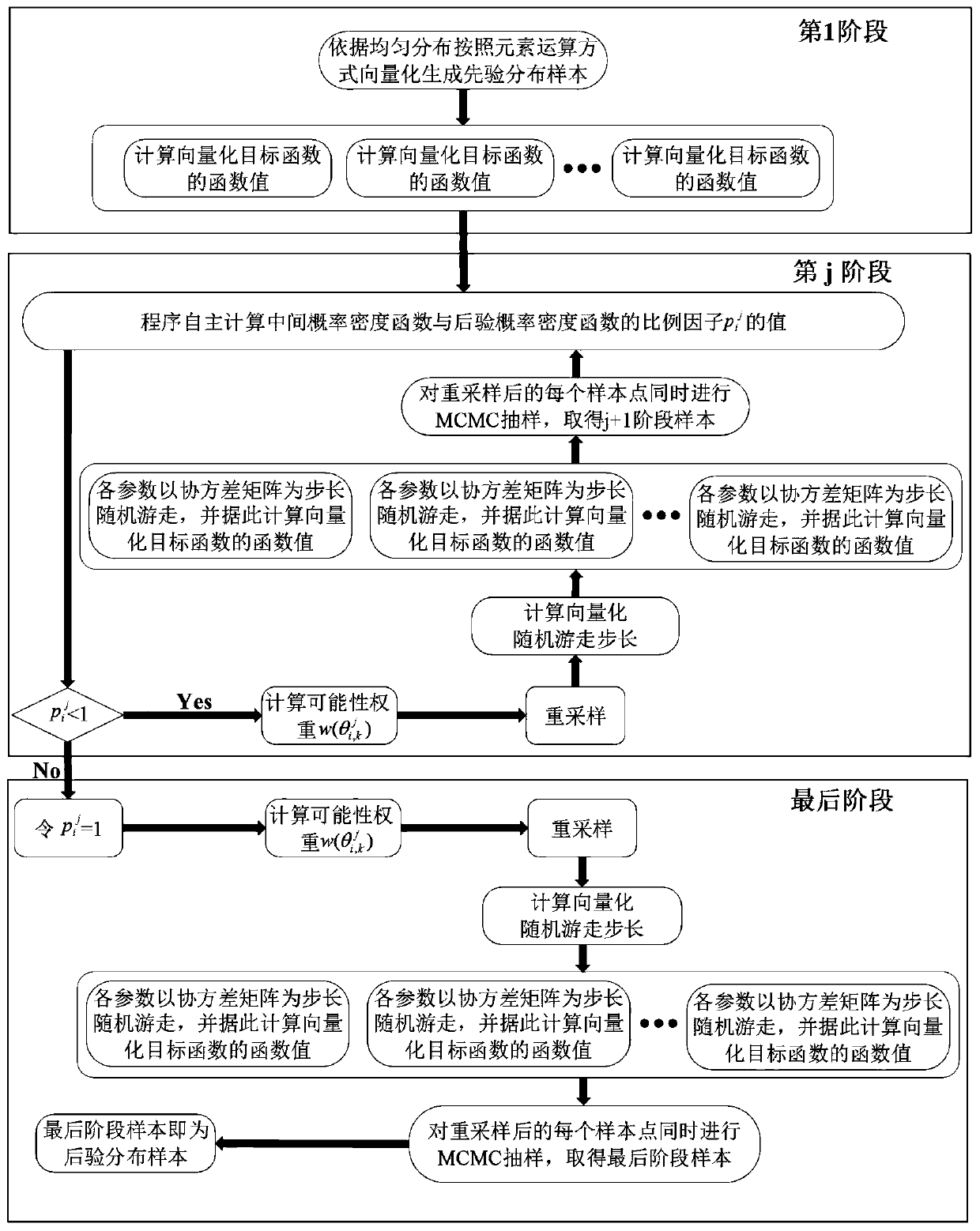
A vectorized distributed parallel TMCMC random sampling algorithm
A random sampling and distributed computing technology, applied in the direction of complex mathematical operations, can solve the problems of astonishing time-consuming calculation, slow calculation speed, and limited application of Bayesian sampling correction method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
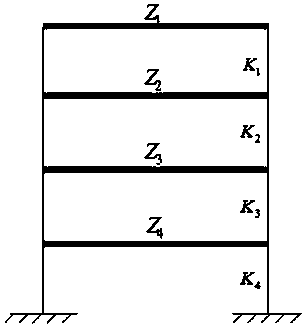
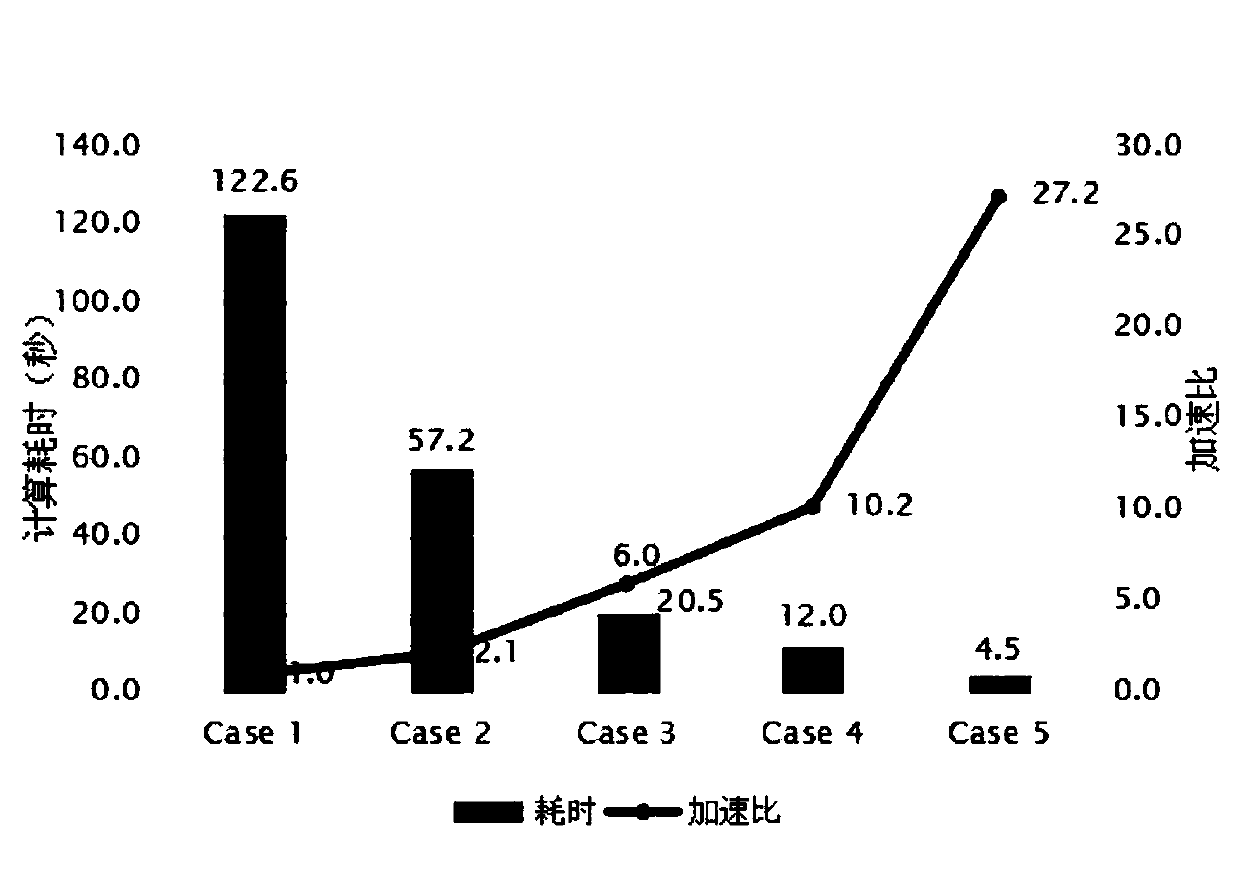
[0090] This embodiment is a correction of the numerical simulation of a four-layer shear-type frame model, the four-layer shear-type frame model is as follows figure 2 shown. Therefore, the system model in this case is a four-layer shear frame model, and the quality of each layer of the frame is assumed to be the same, that is, Z 1 = Z 2 = Z 3 = Z 4 =200kg, the interlayer stiffness of each layer is also the same, that is, K 1 = K 2 = K 3 = K 4 =4×10 3 N / m. The damping of the model adopts the form of Rayleigh damping, assuming that the damping ratios of the first two orders are both 0.02, that is, ξ 1 = ξ 2 = 0.02. input using the K 2 point on the form of a single point excitation. The excitation form is Gaussian white noise excitation, and then the input white noise signal and the corresponding linear time domain response output signal of each layer of the structure are used as the original monitoring data. Perform FFT transformation on the input and output sign...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com