Patents
Literature
106 results about "Posterior probability density function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Linear array SAR imaging method based on iterative minimization sparse Bayesian reconstitution
InactiveCN103713288AImproving Performance for Sparse ImagingRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHypothesisRadar
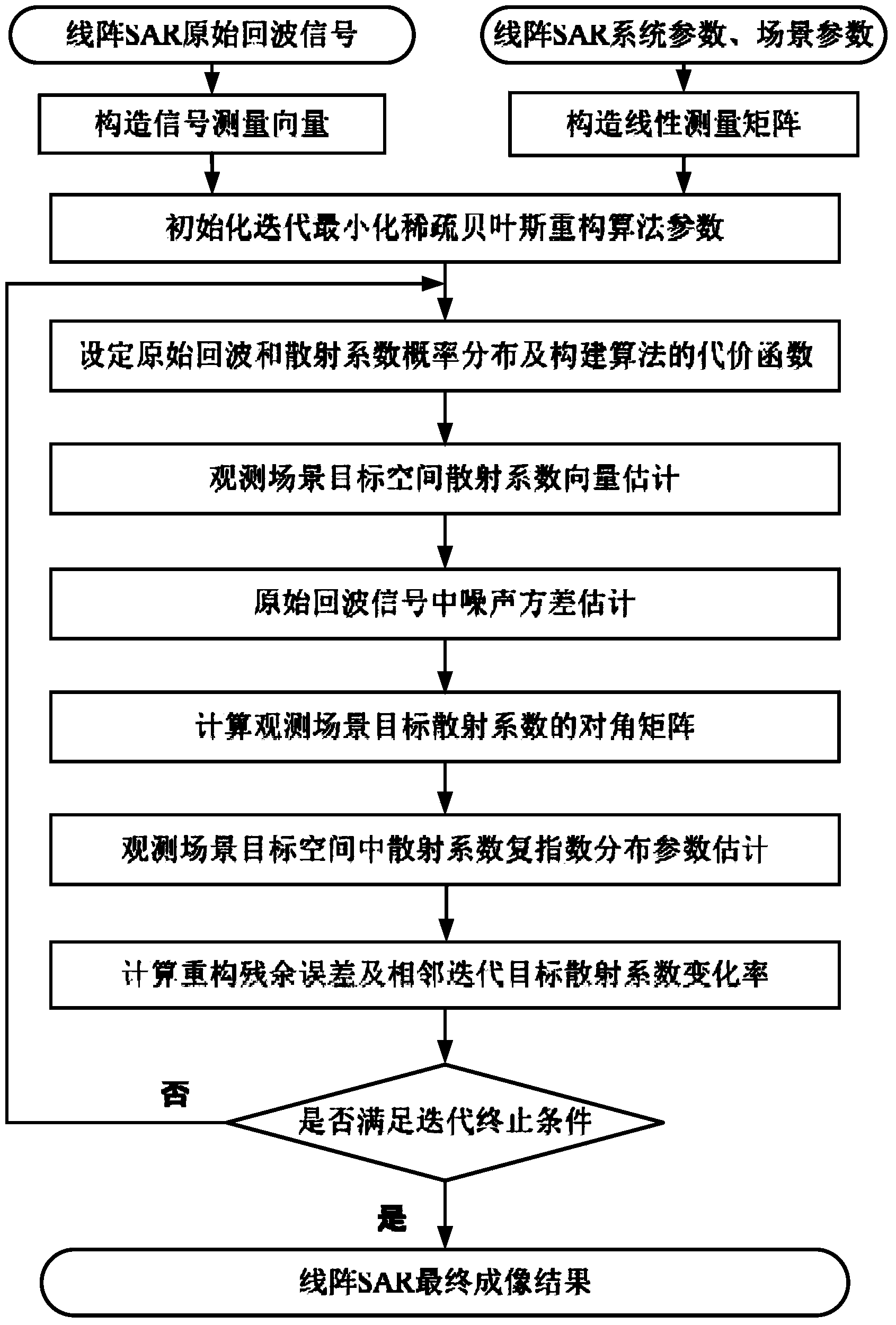
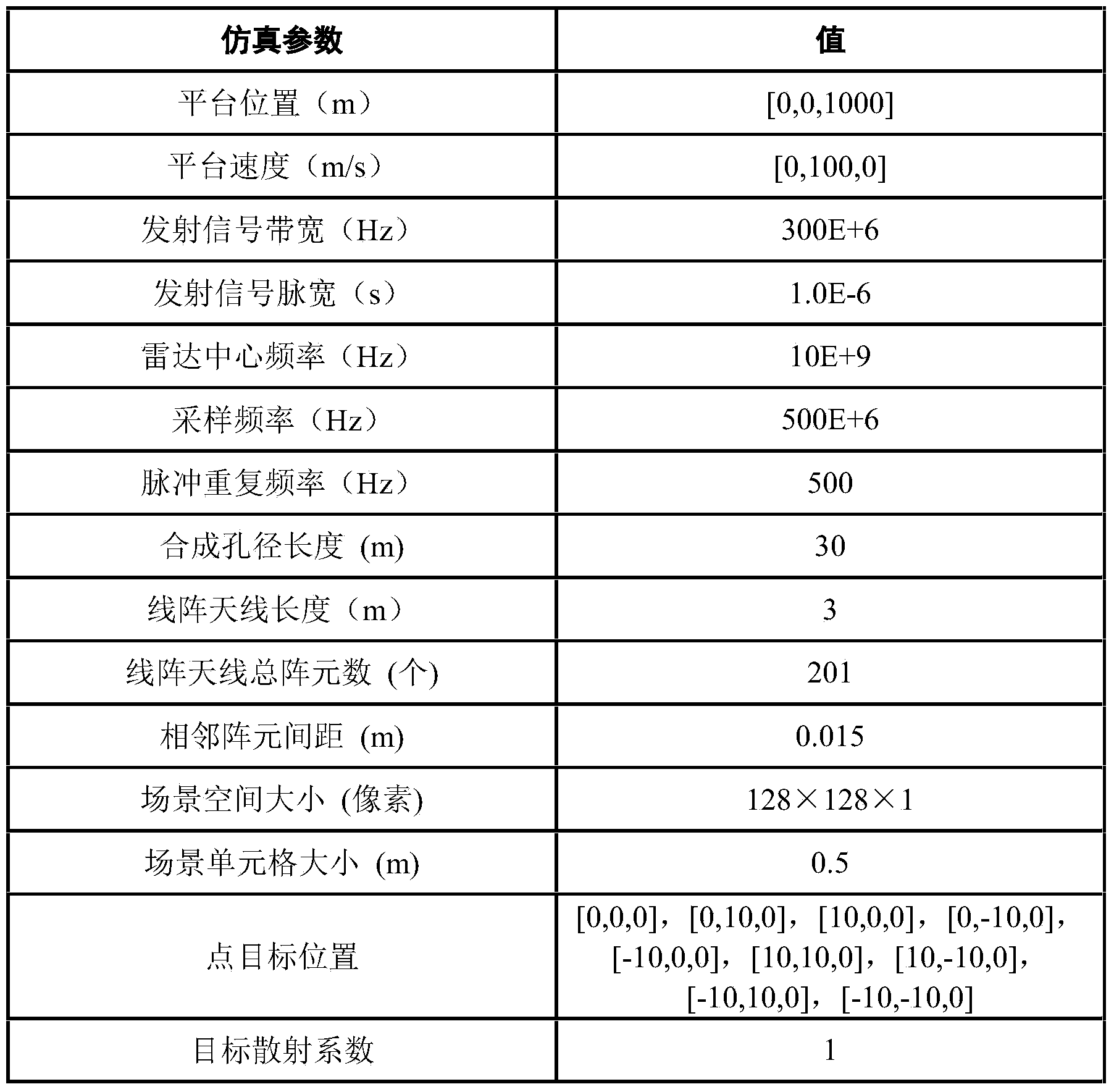
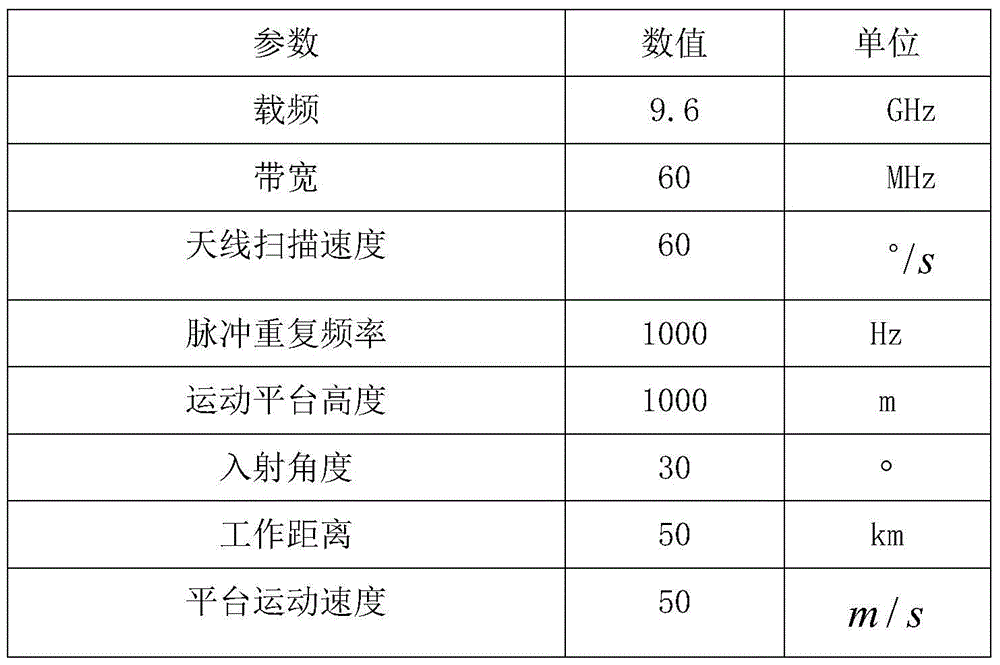
The invention provides a linear array SAR imaging method based on iterative minimization sparse Bayesian reconstitution. The method is prior distributional hypothesis based on a linear array SAR original echo signal measurement model, it is assumed that a prior probability density function of a scattering coefficient in a linear array SAR observation scene target space complies with complex exponential prior distribution, it is also assumed that a posterior probability density function of a linear array SAR original echo signal complies with Gaussian stochastic distribution, a reconstitution cost function of the scattering coefficient in the linear array SAR observation scene target space is set up through the Bayesian criterion, sparse reconstitution of the scattering coefficient in the linear array SAR observation scene target space is achieved through complex exponential distribution parametric optimization estimation and the iterative minimization constitution cost function, and therefore performance of linear array SAR sparse imaging is improved. The linear array SAR imaging method can be applied to the synthetic aperture radar imaging field, the global remote sensing field and other fields.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method for estimating hidden channel parameters of a received GNNS navigation signal
ActiveUS20090074038A1Reduce complexityImprove reliabilityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSatellite radio beaconingPosterior probability densityDynamic channel
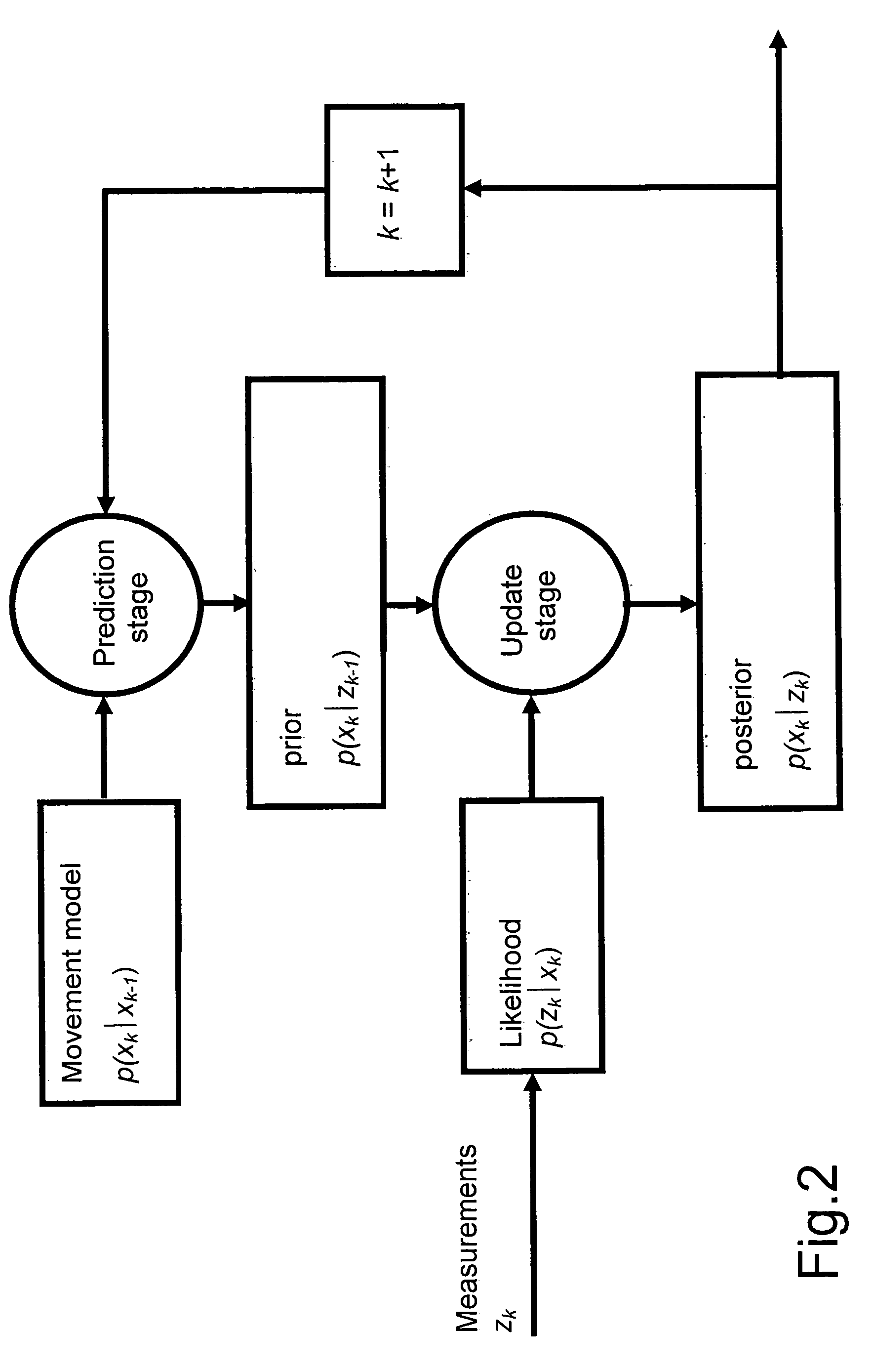
For the reduction of the multipath error of received GNSS navigation signals, a sequential Bayesian estimation is used, with a movement model underlying this estimation, which model is particularly designed for dynamic channel situations. Sequential Monte Carlo methods are used to calculate the posterior probability density functions of the signal parameters. To facilitate an efficient integration in received signal tracking loops, the invention builds on complexity reduction concepts that have previously been used in maximum likelihood (ML) estimators.Applicable with GNSS satellite navigation receivers, e.g. GPS and Galileo.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
Method and System for Image-Based Estimation of Multi-Physics Parameters and Their Uncertainty for Patient-Specific Simulation of Organ Function
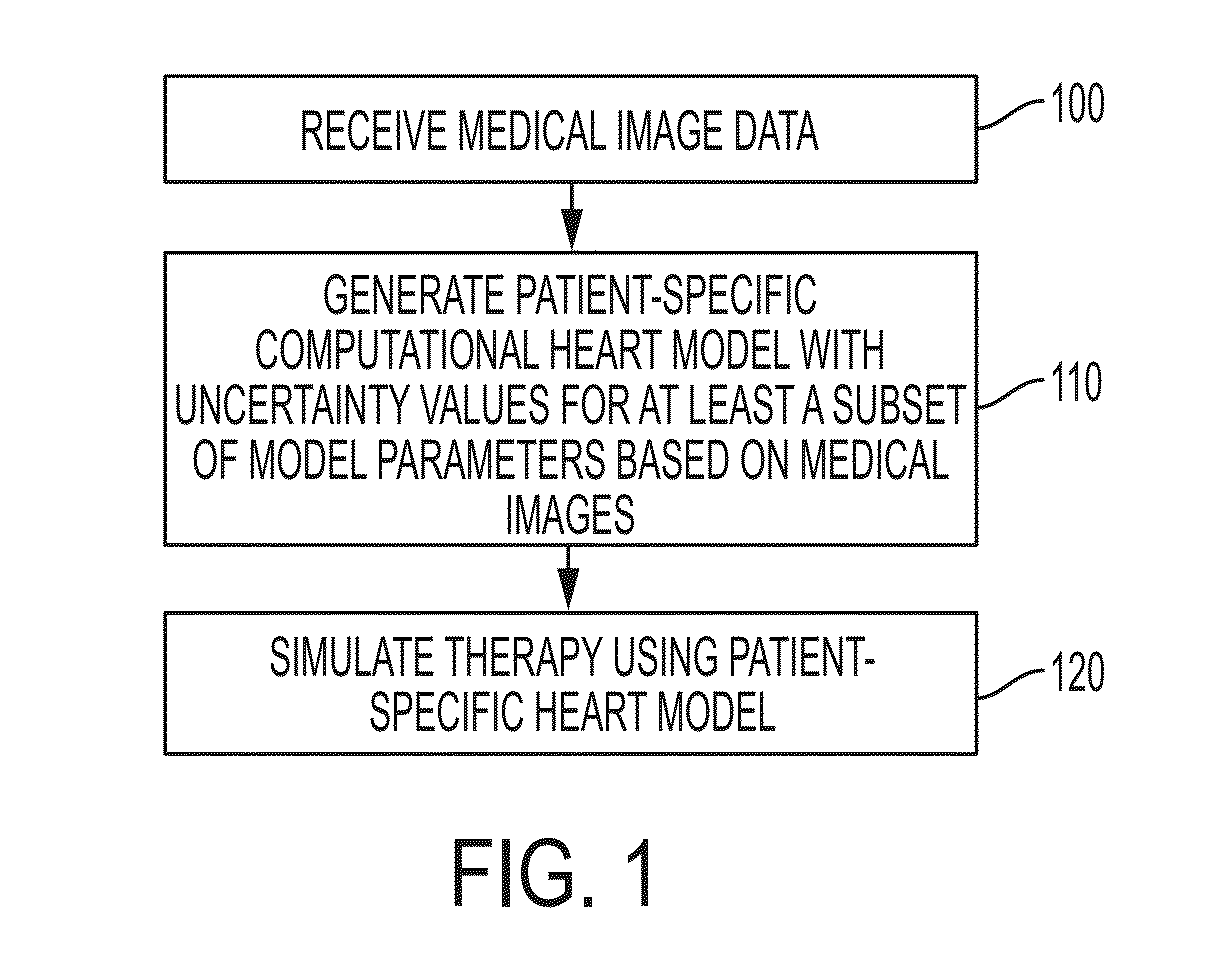
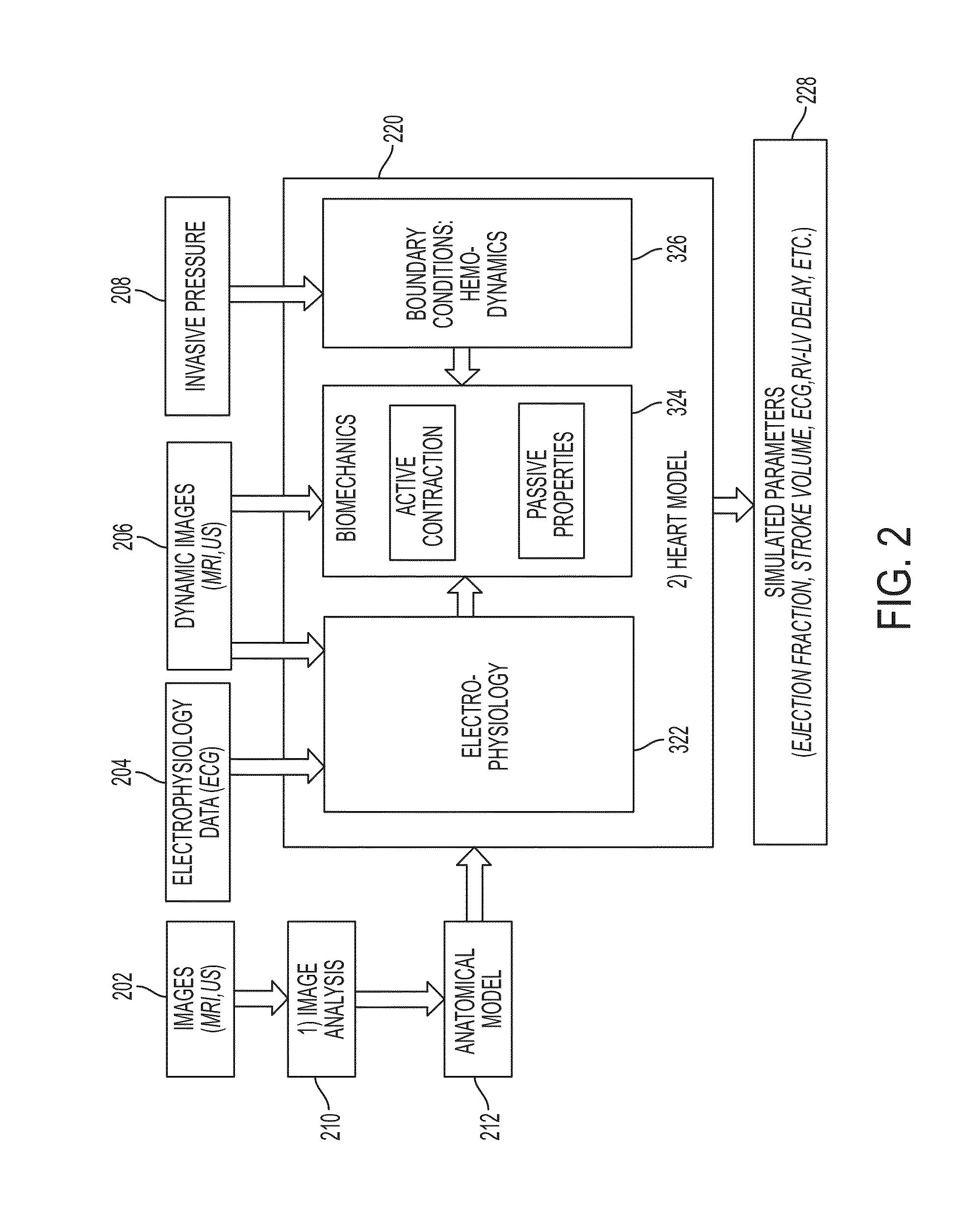
A method and system for estimating tissue parameters of a computational model of organ function and their uncertainty due to model assumptions, data noise and optimization limitations is disclosed. As applied to a cardiac use-case, a patient-specific anatomical heart model is generated from medical image data of a patient. A patient-specific computational heart model is generated based on the patient-specific anatomical heart model. Patient-specific parameters and corresponding uncertainty values are estimated for at least a subset of parameters of the patient-specific computational heart model. A surrogate model is estimated for a forward model of cardiac function, and the surrogate model is applied within Bayesian inference to estimate the posterior probability density function of the parameter space of the forward model. Cardiac function for the patient is simulated using the patient-specific computational heart model. The estimated parameters, their uncertainty, and the computed cardiac function are displayed to the user.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
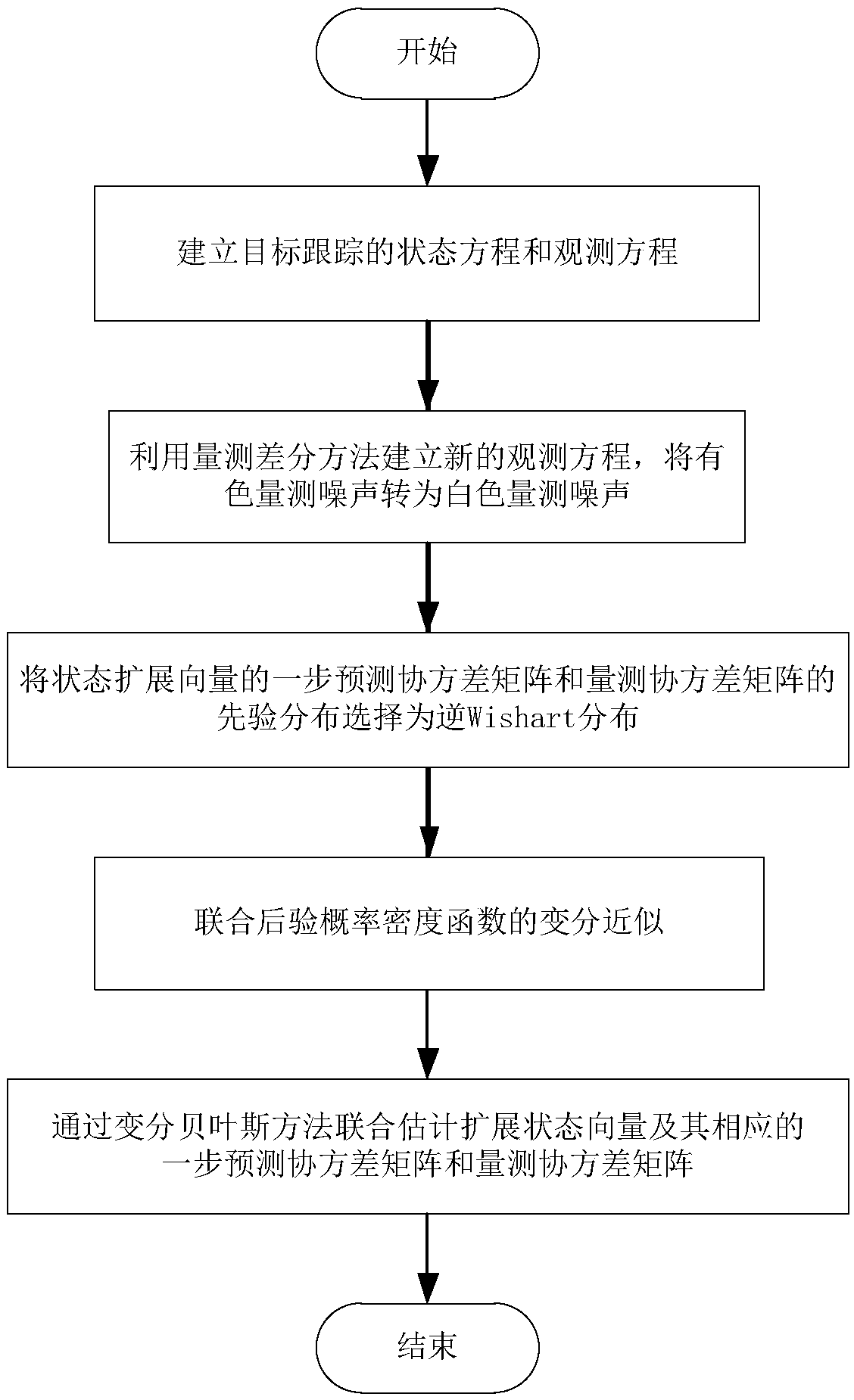
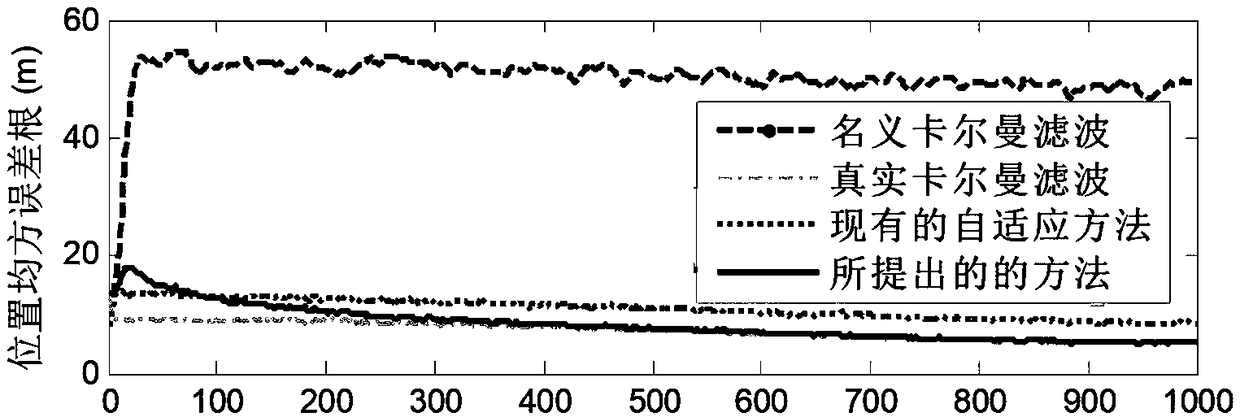
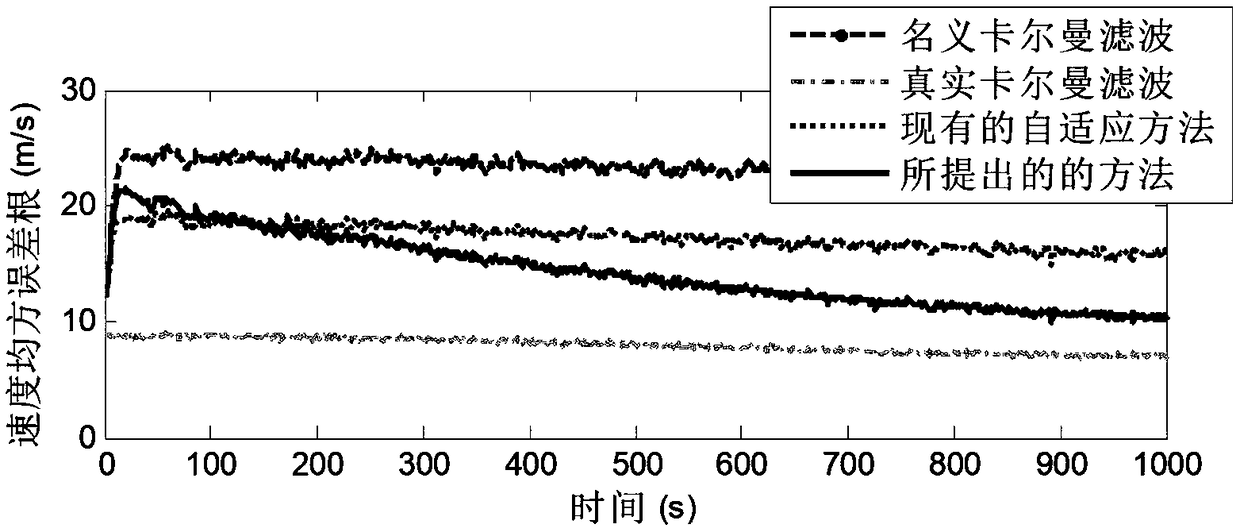
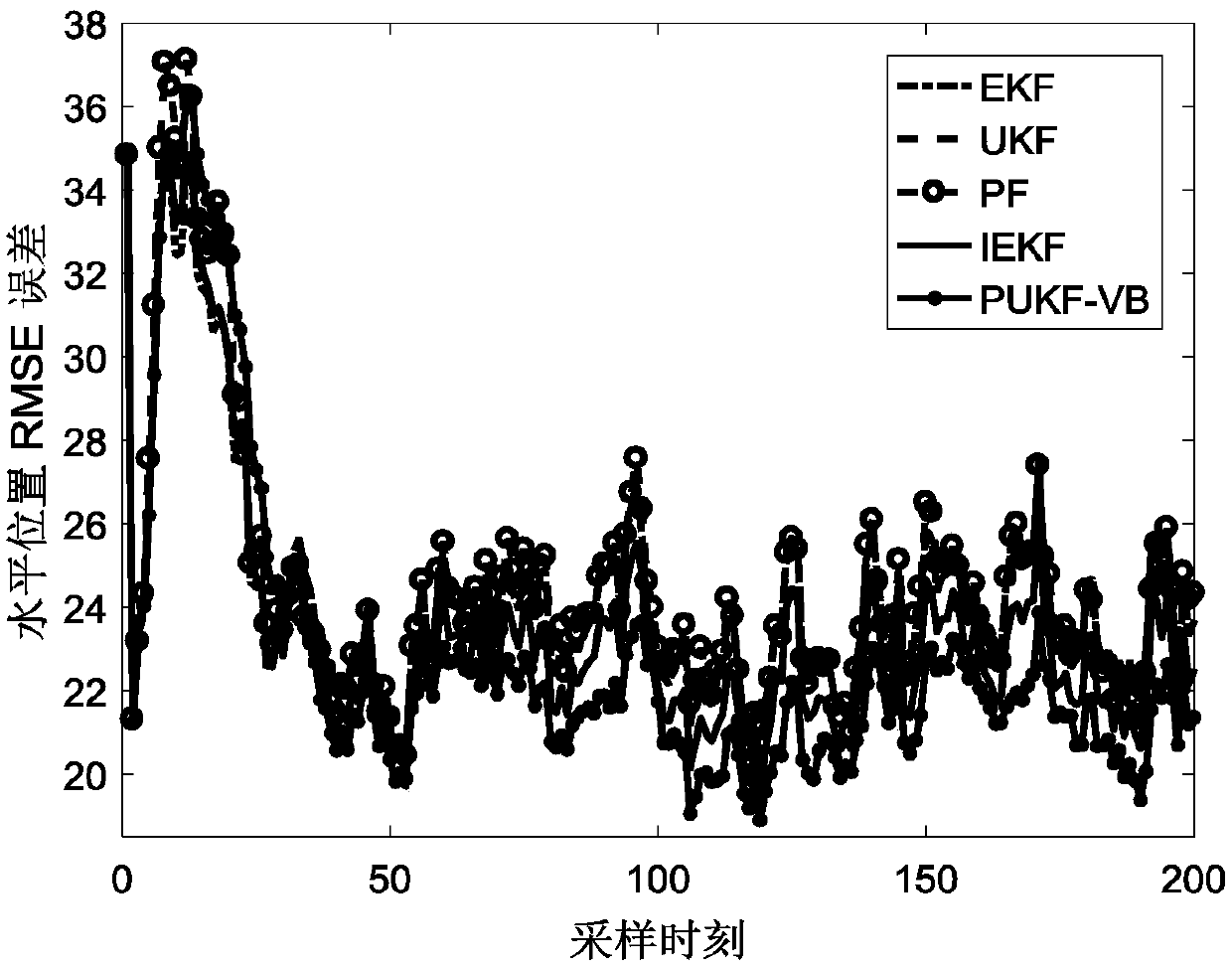
A target tracking method with colored measurement noise and variational Bayesian adaptive Kalman filter
ActiveCN109508445AImprove the accuracy of adaptive filteringNavigational calculation instrumentsComplex mathematical operationsOne step predictionColor measurement
The invention belongs to the technical field of carrier navigation of ships, aircraft, vehicles and the like, in particular to a target tracking method with colored measurement noise and variational Bayesian adaptive Kalman filter. Including: 1. Establishing the state equation and measurement equation of target tracking. 2. converting that color measurement noisento white measurement noise by themeasurement difference method. 3. SelectingThe prior distribution of the one-step prediction covariance matrix and the measurement covariance matrix of the state spread vectors the inverse Wishart distribution. 4. Performing Variational approximation of joint posterior probability density function. 5. Estimating The extended state vector and its one-step prediction covariance matrix and measurement covariance matrix by variational Bayesian method. The method of the invention completes the state estimation task in the target tracking process under the condition of imprecise noise covariance matrix and colored measurement noise, and the tracking accuracy is higher than the existing target tracking method based on other filters.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
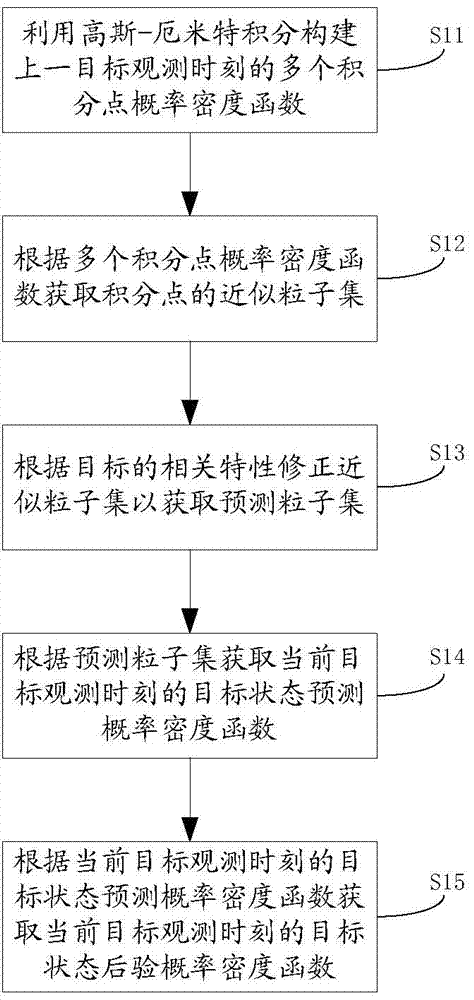
Method and device of particle filtering and target tracking
InactiveCN103902812AIncrease diversityImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsNormal densityComputer science
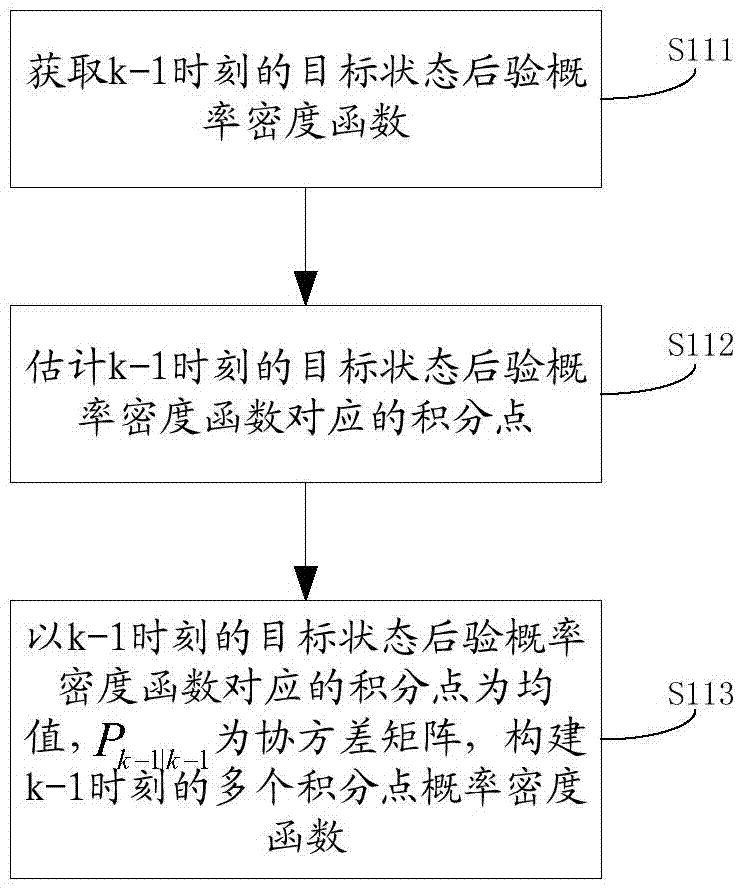
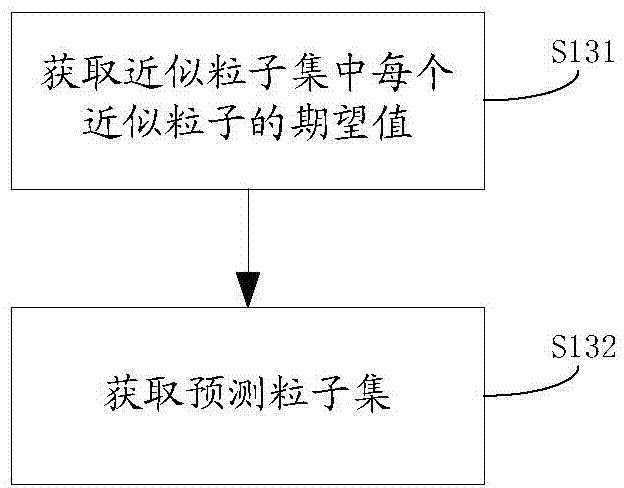
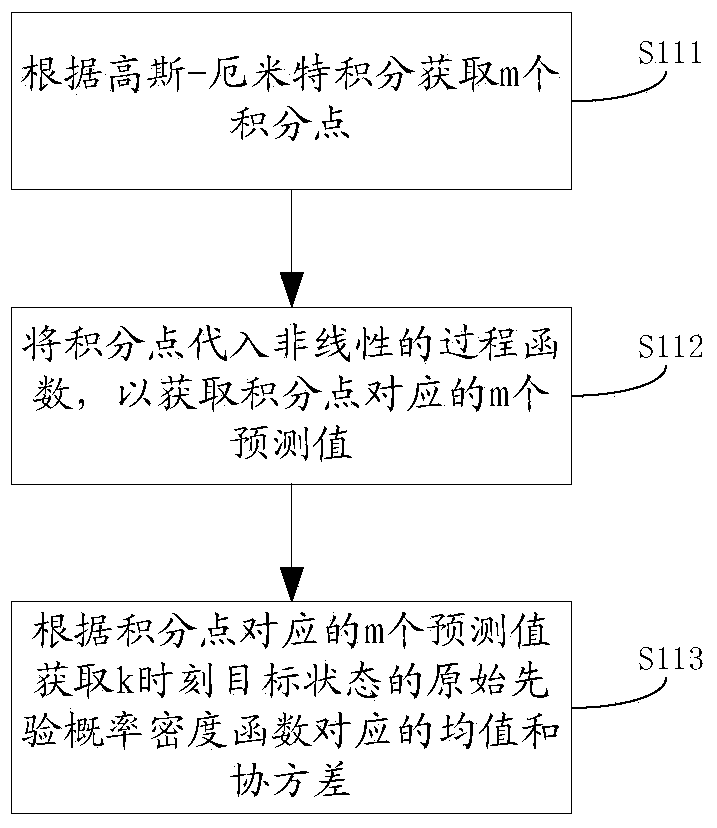
The invention discloses a method and device of particle filtering and target tracking. The method of particle filtering comprises the following steps that a probability density function of multiple integral points at the observation time of the last target is built by the adoption of the Gauss-Hermite integral point, an approximate particle set of the integral points is acquired according to the probability density function of the integral points, a predicted particle set is acquired by amending the approximate particle set according to relative features of the target, a predicted probability density function of a target state at the observation time of the current target is acquired according to the predicted particle set, and a posterior probability density function of the target state at the observation time of the current target is acquired according to the predicted probability density function of the target state at the observation time of the current target. According to the method, diversity and accuracy of particles are enhanced, and filtering accuracy and target state estimation performance are improved greatly.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Underwater multi-target tracking method
InactiveCN103645487AOvercoming the Constraints of ManeuveringIncrease flexibilitySatellite radio beaconingComputation complexityMulti target tracking
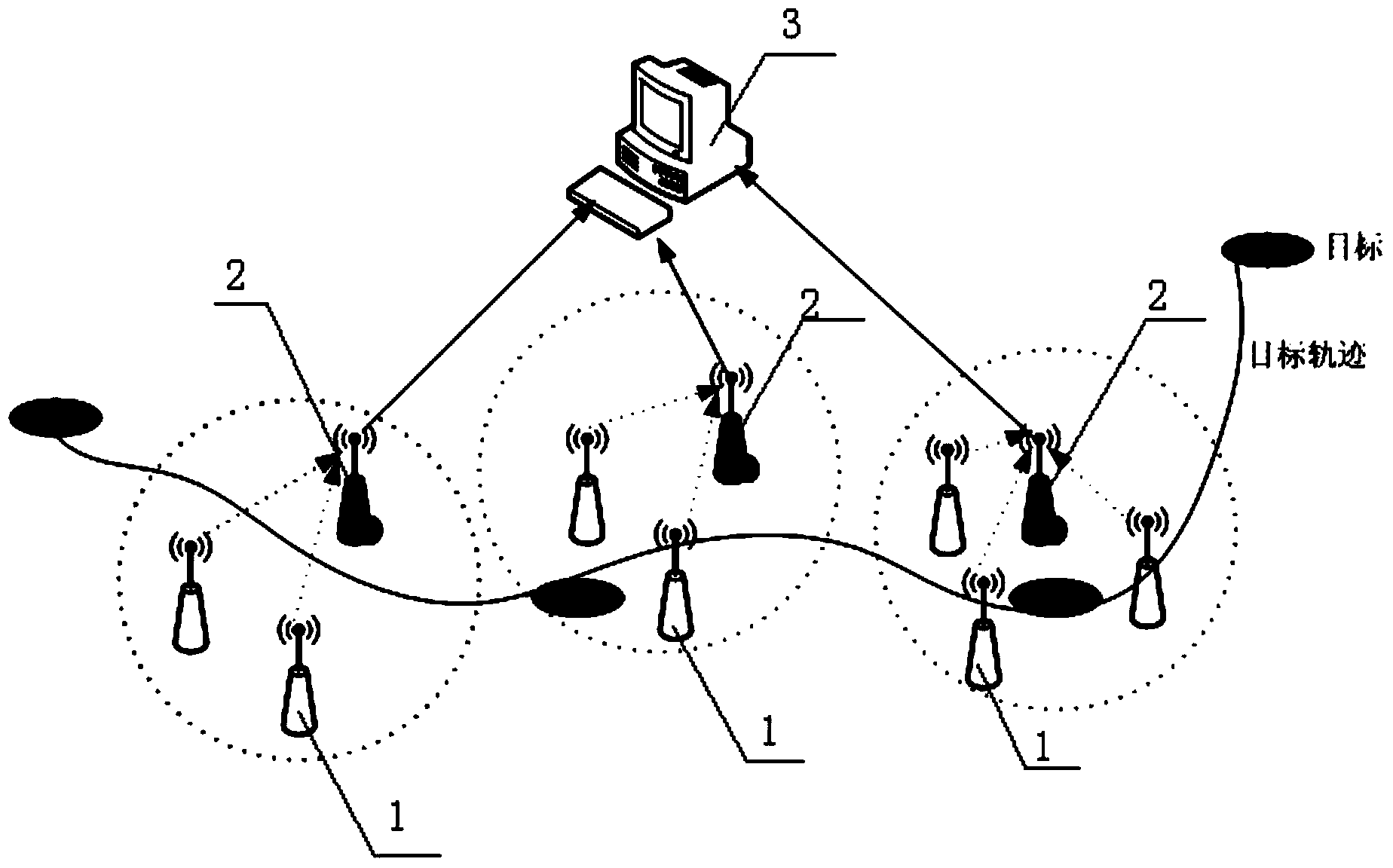
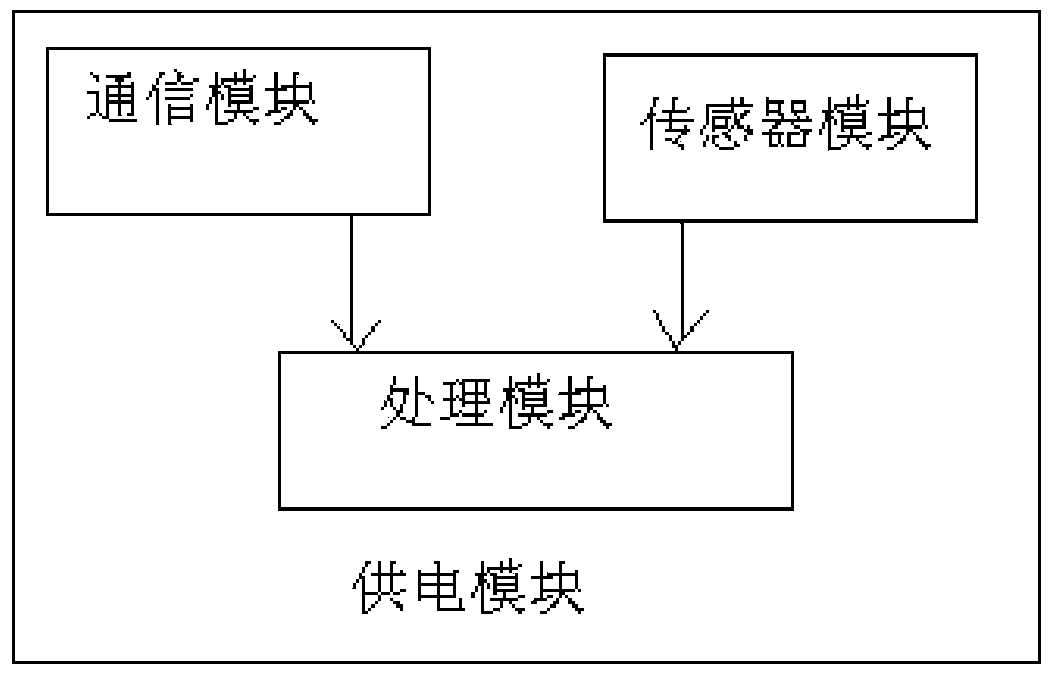
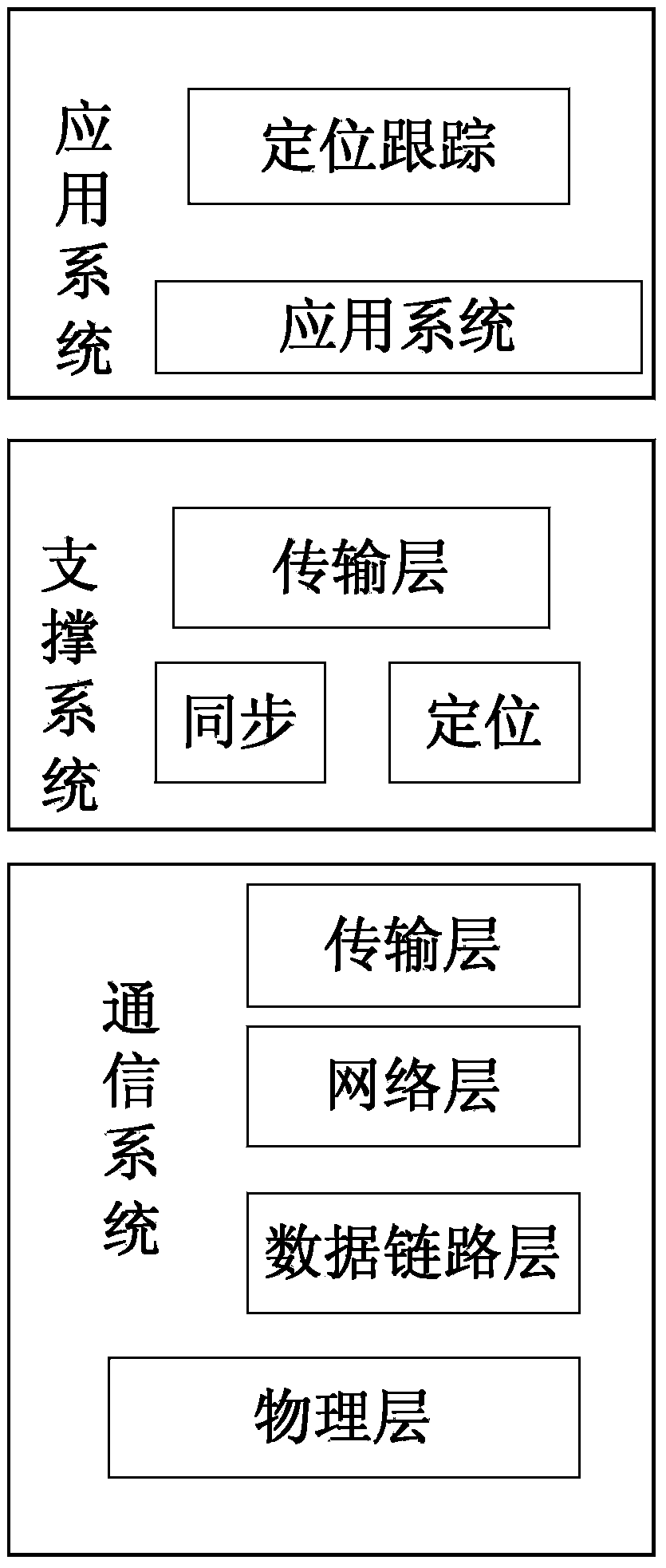
Disclosed in the invention is an underwater multi-target tracking method. A wireless sensor network positioning system comprises a plurality of sensor nodes, a cluster head node and a control system. For the system positioning, an improved resampling non-augmented tasteless particle filtering algorithm is used to realize target positioning based on sensor network configuration. Because the algorithm fully utilizes information measured at current time at the current orientation to estimate a particle posterior probability density function, a defect that particle selection has blindness according to a PF algorithm is overcome, so that the approximate and better positioning precision can be realized under the circumstances that a few particles exist. Moreover, there is no need to expand the state dimension in a vector, so that the calculation complexity can be substantially reduced, the calculation time is improved, and the system can be realized in real time.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multiple vehicle acoustic signal based on particle filtering in wireless sensor network
InactiveCN101256715ASeparation succeededEasy to handleDetection of traffic movementSpecial data processing applicationsValue setWireless sensor networking
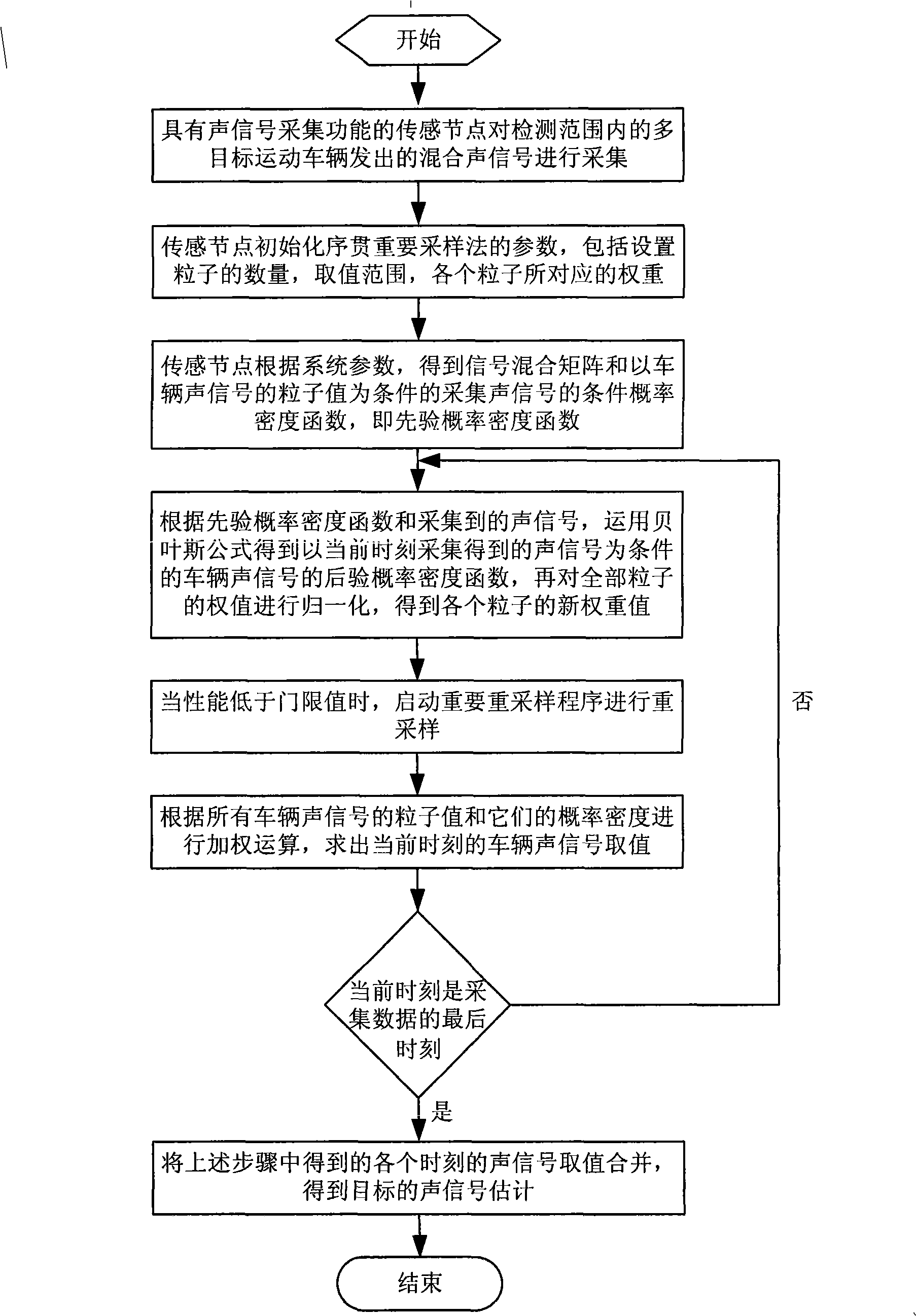
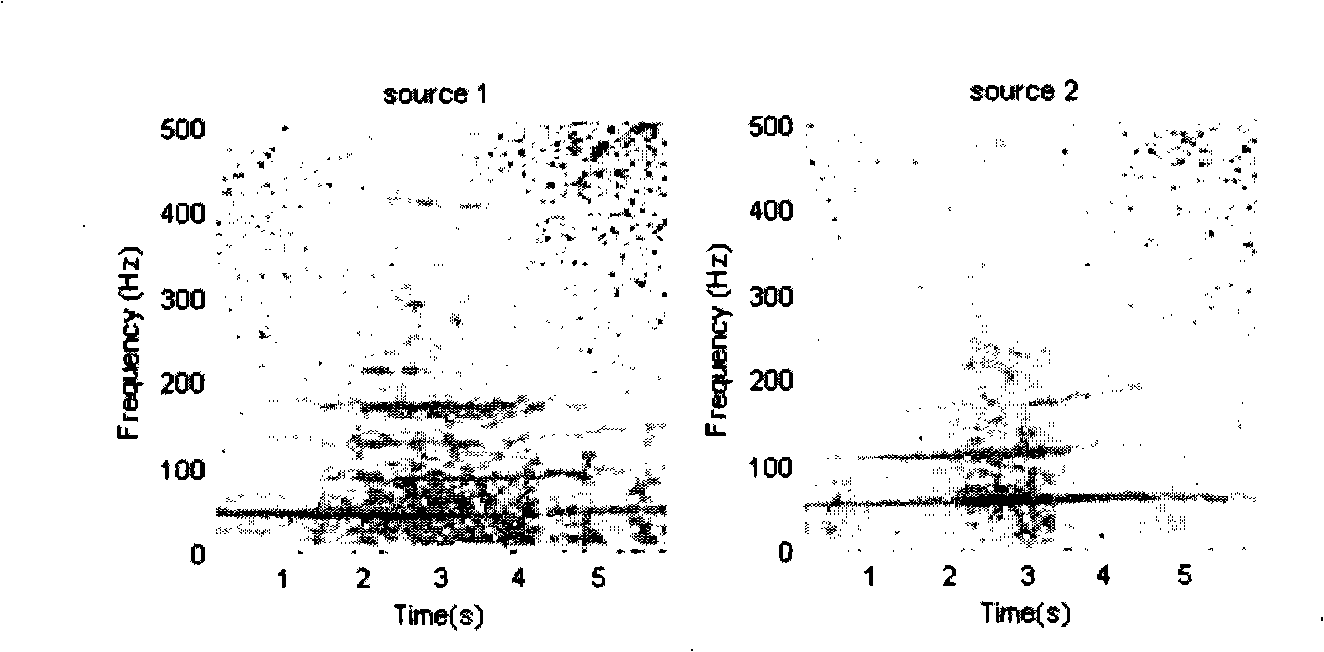
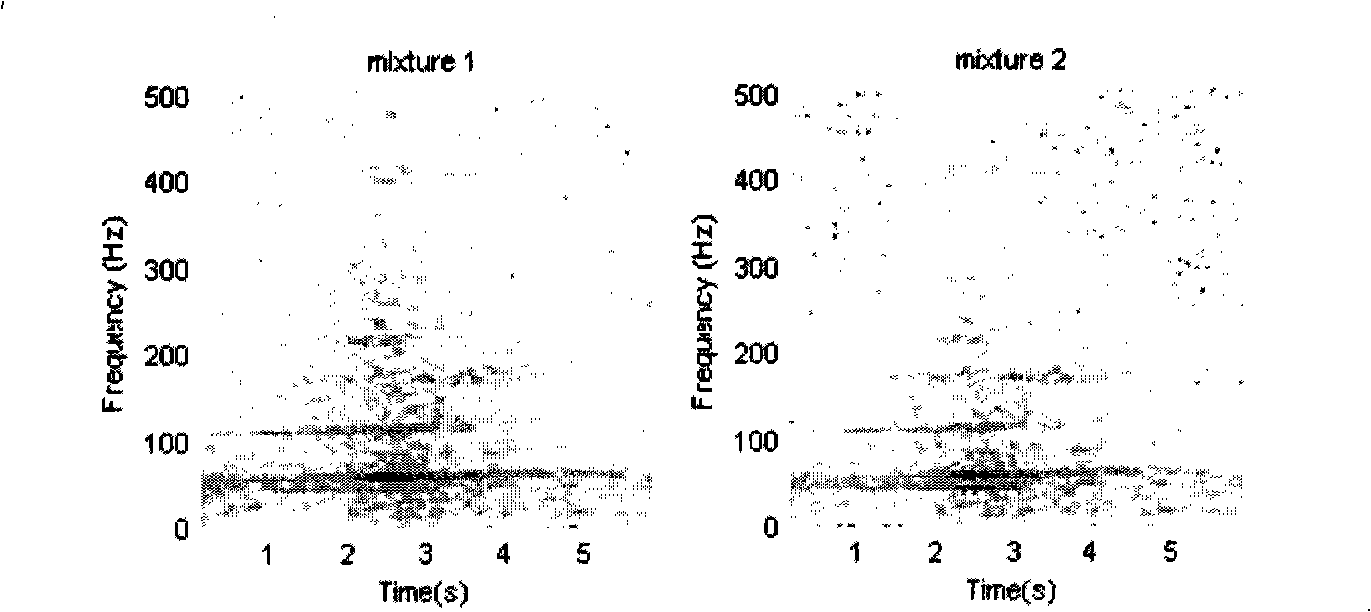
The invention discloses a multi-vehicle signal separation method of wireless sensor network based on particle filter, comprising the steps of: collecting and detecting a sound mixing signal sent by the multi-target motion vehicle in scale by the sensing node, then initializing parameters of sequence important sampling method including particle number, span and weight of each particle and determining signal mixing matrix and prior probability function according to the system parameters, then obtaining the posterior probability function by Bayesian theory, calculating weight of each particle and normalizing to obtain normalized weight of each particle, then re-sampling the particle according to threshold value set, calculating a sound signal value of present time by weighing of all particles, repeating, finally obtaining estimation value of the sound value of all times to separate the multi-vehicle sound signal. The method of the invention is capable of processing non-Gaussian, non-linear mode and sound signal of non-stationary vehicle, which is easy to accomplish.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
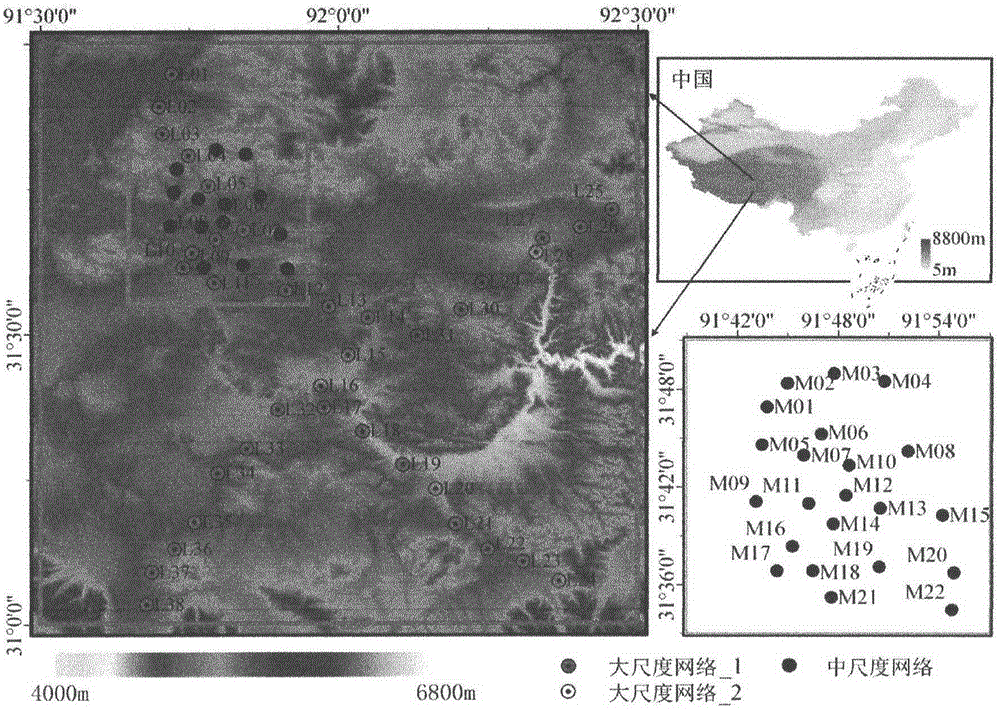
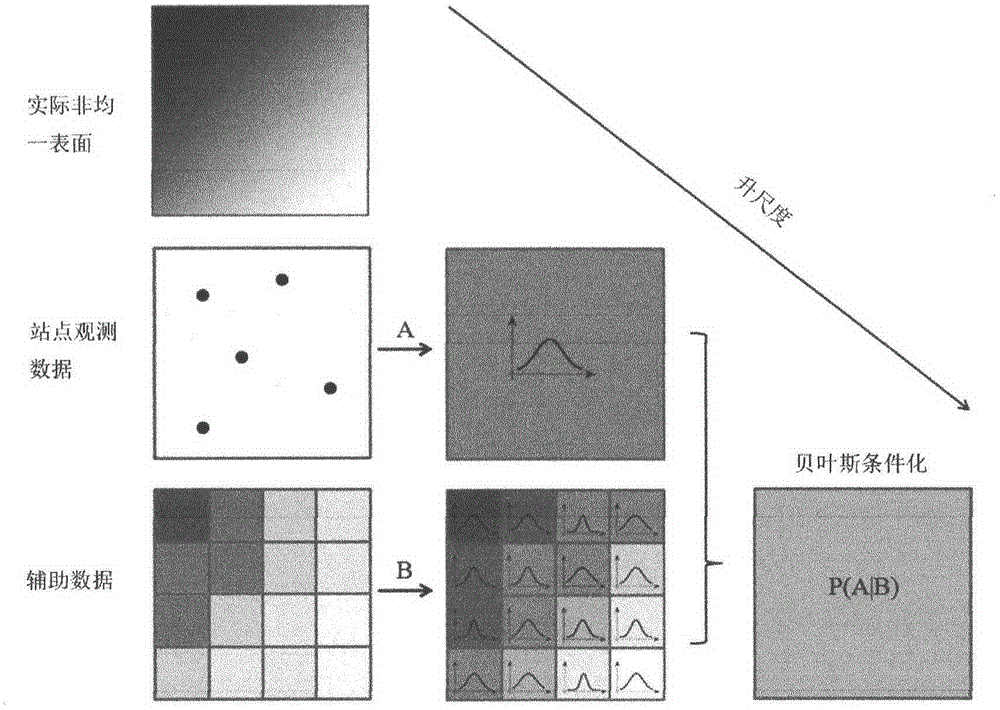
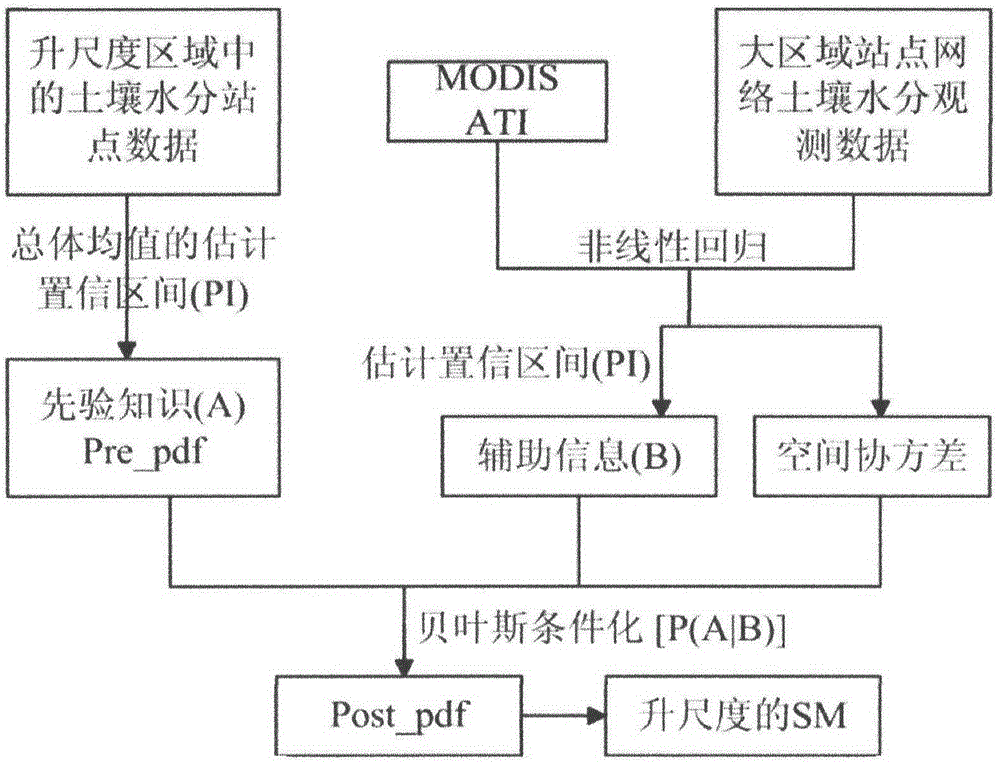
Soil moisture site data upscaling method based on Bayesian theory
InactiveCN104573393AReduce uncertaintySpecial data processing applicationsConfidence intervalSoft data
The invention discloses a soil moisture site data upscaling method based on the Bayesian theory. The soil moisture site data upscaling method includes steps of estimating prior probability density distribution function pre_pdf of a target variable on the basis of sparse site observation data in an upscaling area; inversing MODIS ATI into SM by establishing nonlinear regression relation between the SM and the MODIS ATI, estimating an estimated confidence interval of the soil moisture nonlinear regression and probability distribution as soft data in a probability form; integrating the prior distribution of the target variable and auxiliary information of the probability form from the MODIS ATI through the Bayesian theory, and acquiring posterior probability density distribution function post_pdf of the target variable; calculating the value of the target variable in the maximum probability through maximization of the posterior probability distribution function. By the soil moisture site data upscaling method, uncertainties caused by scale difference between soil moisture remote sensing products and ground site authentication data are effectively reduced. The soil moisture site data upscaling method can be applied to upscaling application of other ground surface parameters.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
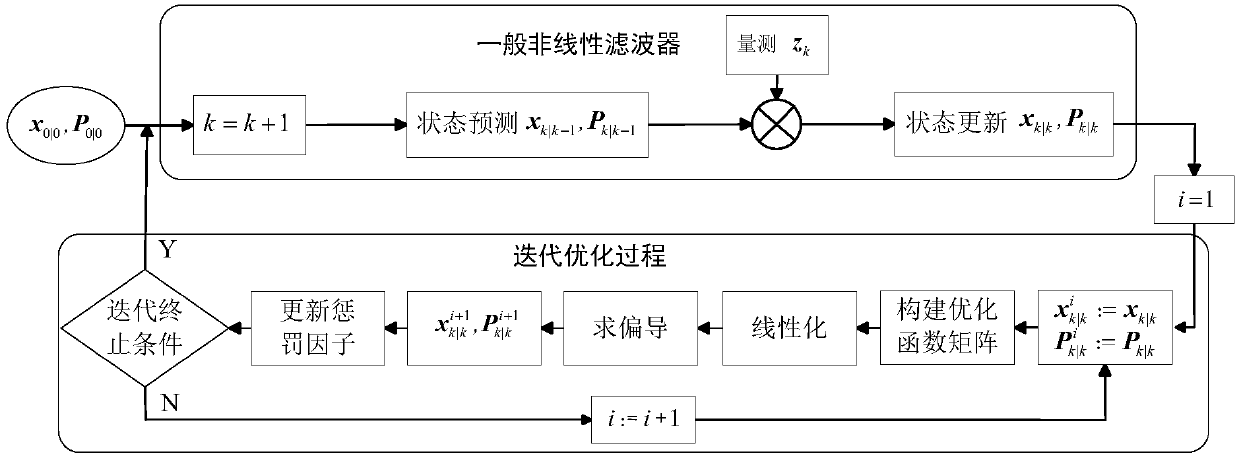
Design method for PNKF-VB
ActiveCN108599737AImprove State Estimation AccuracyIncrease flexibilityDigital technique networkDigital adaptive filtersKaiman filterAdaptive weighting
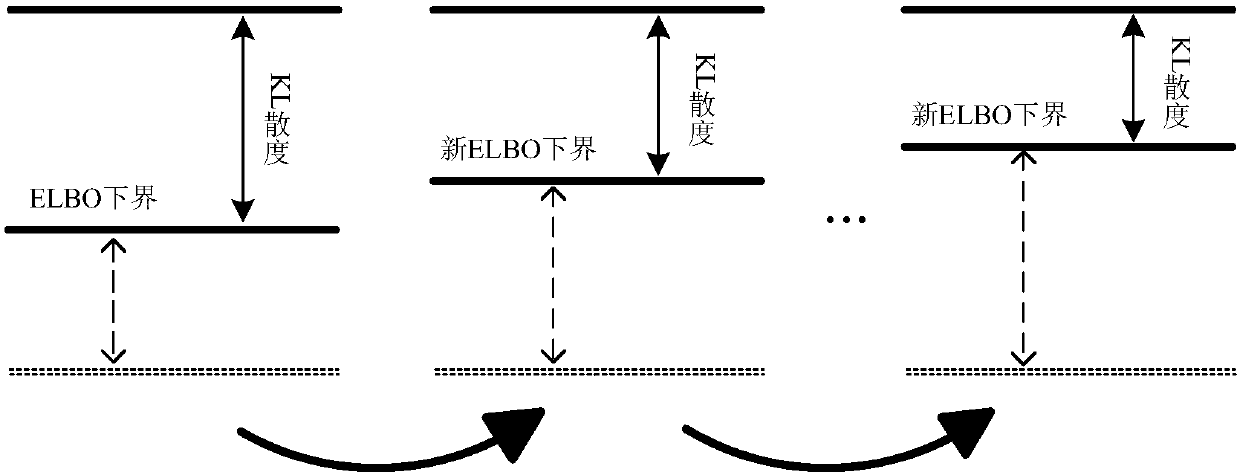
The invention provides a design method for PNKF-VB and relates to the field of a filter. According to the method, variational distribution approximate to a posterior probability density function is constructed under a Gaussian assumption condition; iteration approximation of state estimation is realized by taking KL (Kullback-Leibler) divergence as a penalty function; and the PNKF-VB is derived bytaking confidence lower bound maximization as a target function according to a variational Bayesian frame. According to the method, a relatively tight approximation form of the nonlinear state posterior probability density function can be obtained, so the state estimation precision is improved. The difficult solution problem of the integral of the posterior probability density function in a system state estimation process can be transformed into the problem of optimizing ELBO lower bound. The adaptive weighted KL divergence is taken as the penalty function, so the optimization flexibility isimproved and the state estimation precision is improved. The method has very high significance to nonlinear state estimation theory and practical engineering application.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
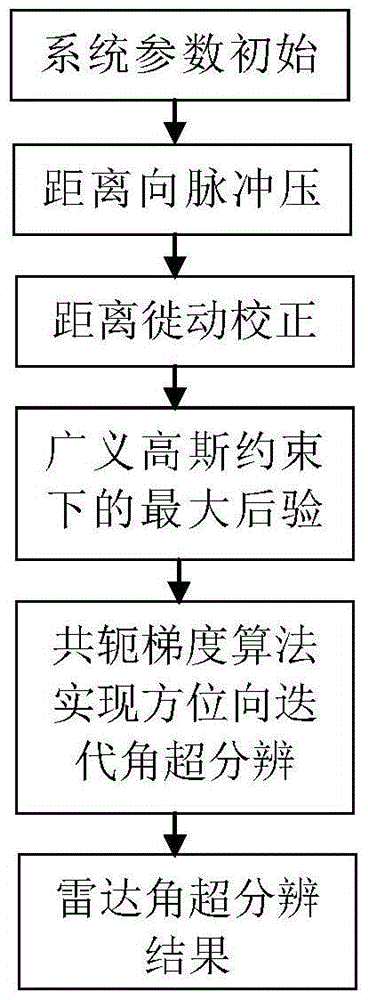
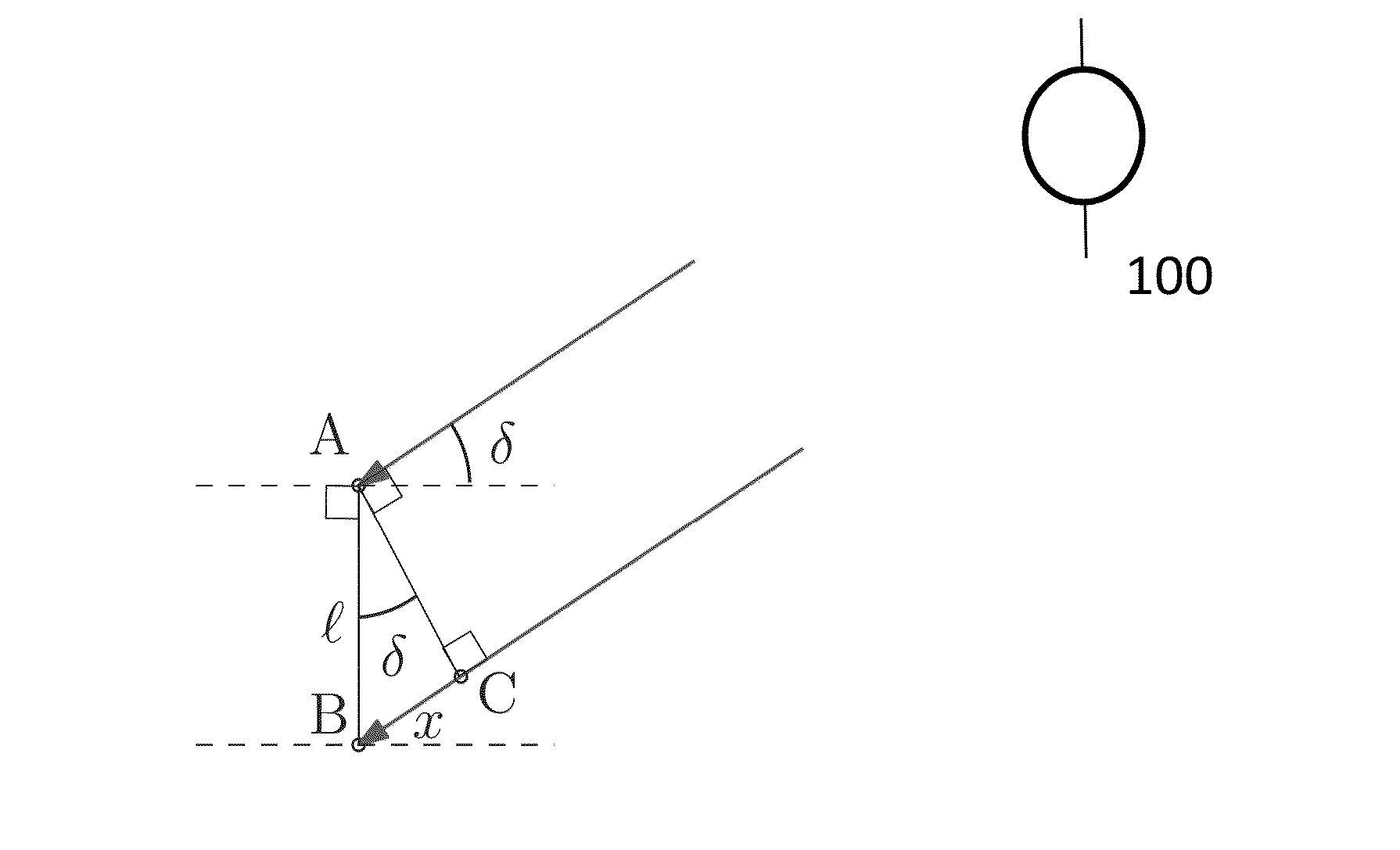
A maximum posterior estimated angle super-resolution imaging method based on generalized Gaussian constraints
ActiveCN105699969APrevent morbidityImproved azimuth resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPrior informationImage resolution
The invention discloses a maximum posterior estimated angle super-resolution imaging method based on generalized Gaussian constraints. Targeted at problems of low resolution of real wave beam radar azimuths in the prior art, the method provided by the invention regards maximum posterior probability density function values of target scattering coefficients as estimation for the target scattering coefficients; under different discrete parameters, different target statistical characteristics and noise statistical characteristics are constraint by generalized Gaussian distribution and regarded as prior information; further, a deconvolution problem of calculating the target scattering coefficients is converted into a regularization estimation problem with variable regularization items; and finally, solving of a regularization estimation problem is realized through utilization of a conjugate gradient algorithm; the solving method is converted into an iterative operation; subsequently, radar angle super-resolution imaging is realized; and problems of low resolution of the azimuths in a scan imaging mode are solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Estimating Anisotropic Parameters
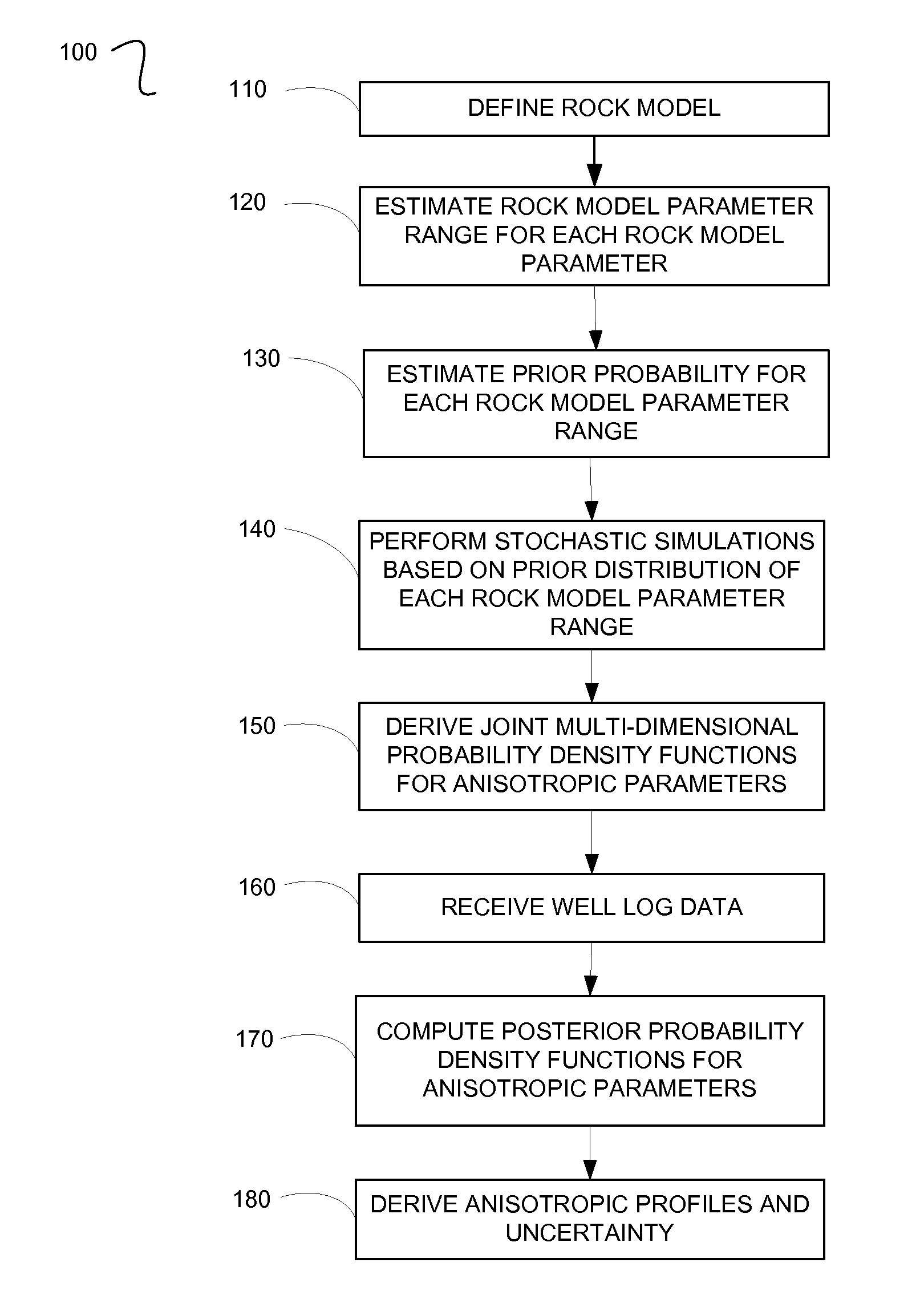
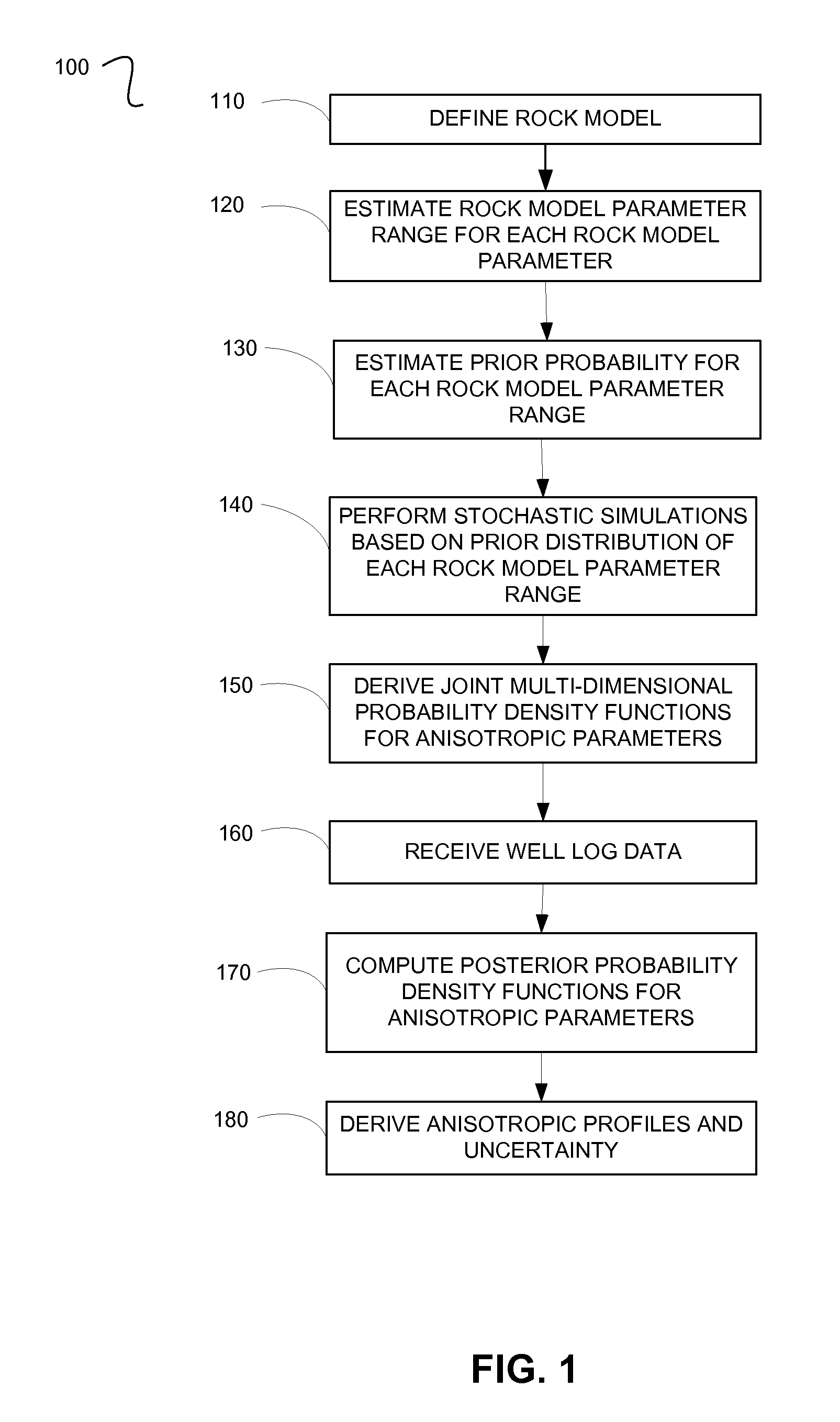
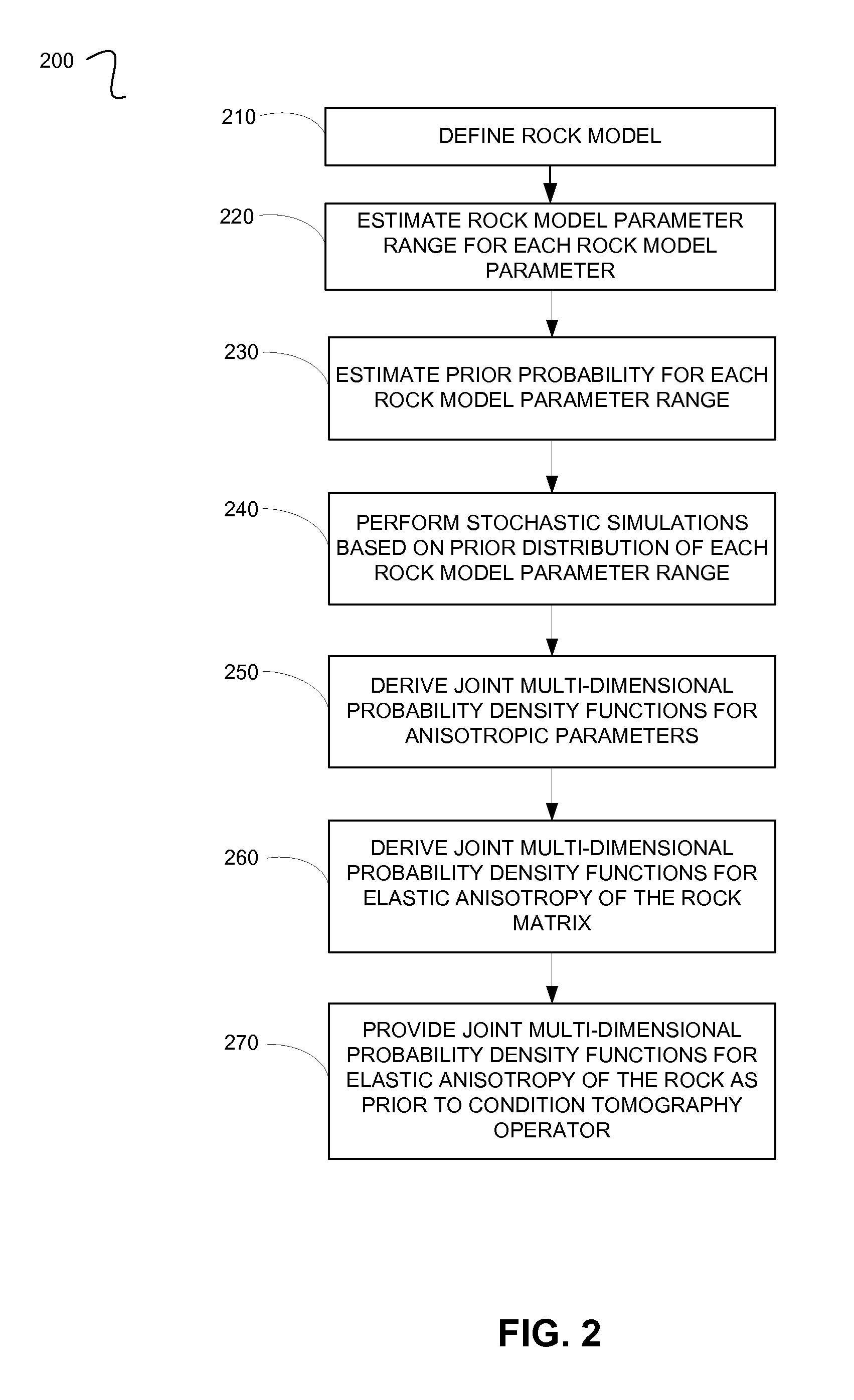
A method for processing seismic data. The method includes performing a plurality of stochastic simulations for one or more rock model parameters to generate one or more anisotropic parameters for a subsurface area of the earth. The method then derives one or more joint multi-dimensional probability density functions for the anisotropic parameters. Using the joint multi-dimensional probability density functions and measured well log data, the method computes one or more posterior probability density functions. The method then includes deriving one or more anisotropic profiles from the posterior probability density functions and generating a seismic image from the anisotropic profiles.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
System and method for interferometrically tracking objects using a low-antenna-count antenna array
InactiveUS20150220488A1Direction finders using radio wavesDigital computer detailsPhase differenceMotion parameter
A radio-frequency interferometry method for determining parameters of motion of a moving object from phase difference information from an antenna baseline formed of two antennas. At each of a plurality of observation events, compute a posterior probability density function from the phase differences from the baseline, separate the modes with a threshold value of probability density, and compute a probability of each mode. For each possible sequence of modes, determine a mode sequence probability as the product of the probabilities of each mode in that sequence, estimate a χ2 goodness of fit function based on an assumed type of motion. Determine the net probability of each possible sequence of modes as the product of a relative probability derived from the χ2 and the mode sequence probability. Alternately, two or more parallel or colinear baselines are used, and the posterior PDF is a combined PDF over each of the baselines.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
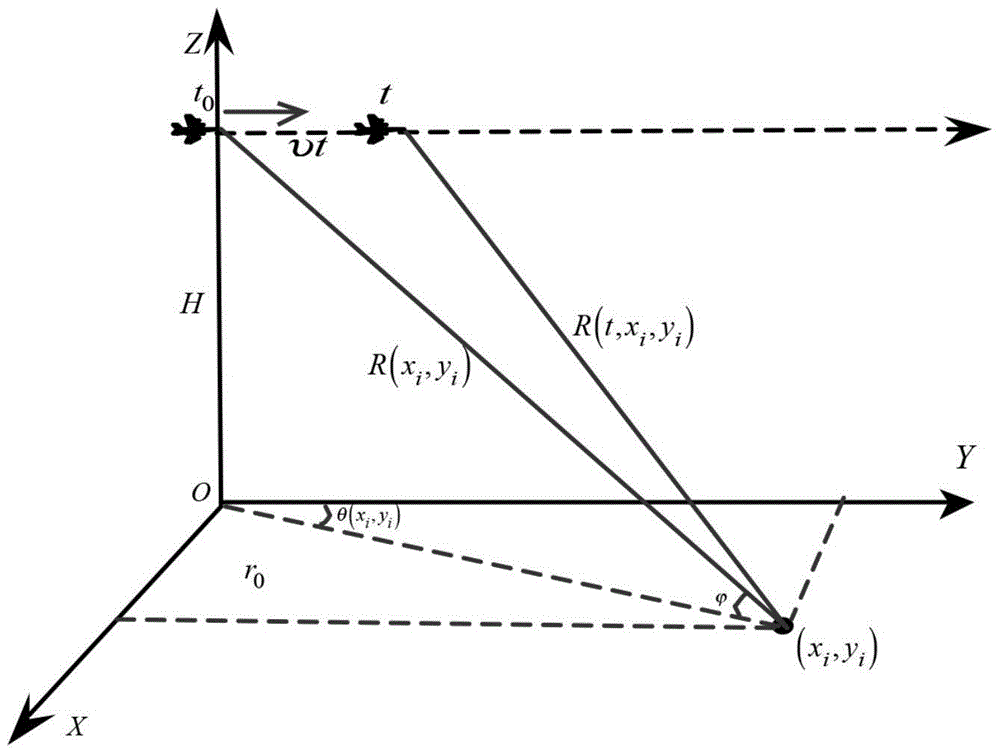
Motion platform scan radar super-resolution imaging method
InactiveCN106291543ARealization of super-resolution imagingAchieving angular super-resolutionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarImage resolution
The invention discloses a motion platform scan radar super-resolution imaging method. Targeted at problems of low resolution of real wave beam radar azimuths in the prior art, the method provided by the invention regards maximum posterior probability density function values of target scattering coefficients as estimation for the target scattering coefficients; under different discrete parameters, different target statistical characteristics and noise statistical characteristics are constraint by generalized Gaussian distribution; further, a deconvolution problem of calculating the target scattering coefficients is converted into a regularization estimation problem with variable regularization items; and finally, solving of a regularization estimation problem is realized through utilization of a conjugate gradient algorithm; the solving method is converted into an iterative operation; subsequently, radar angle super-resolution imaging is realized; and problems of low resolution of the azimuths in a scan imaging mode are solved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
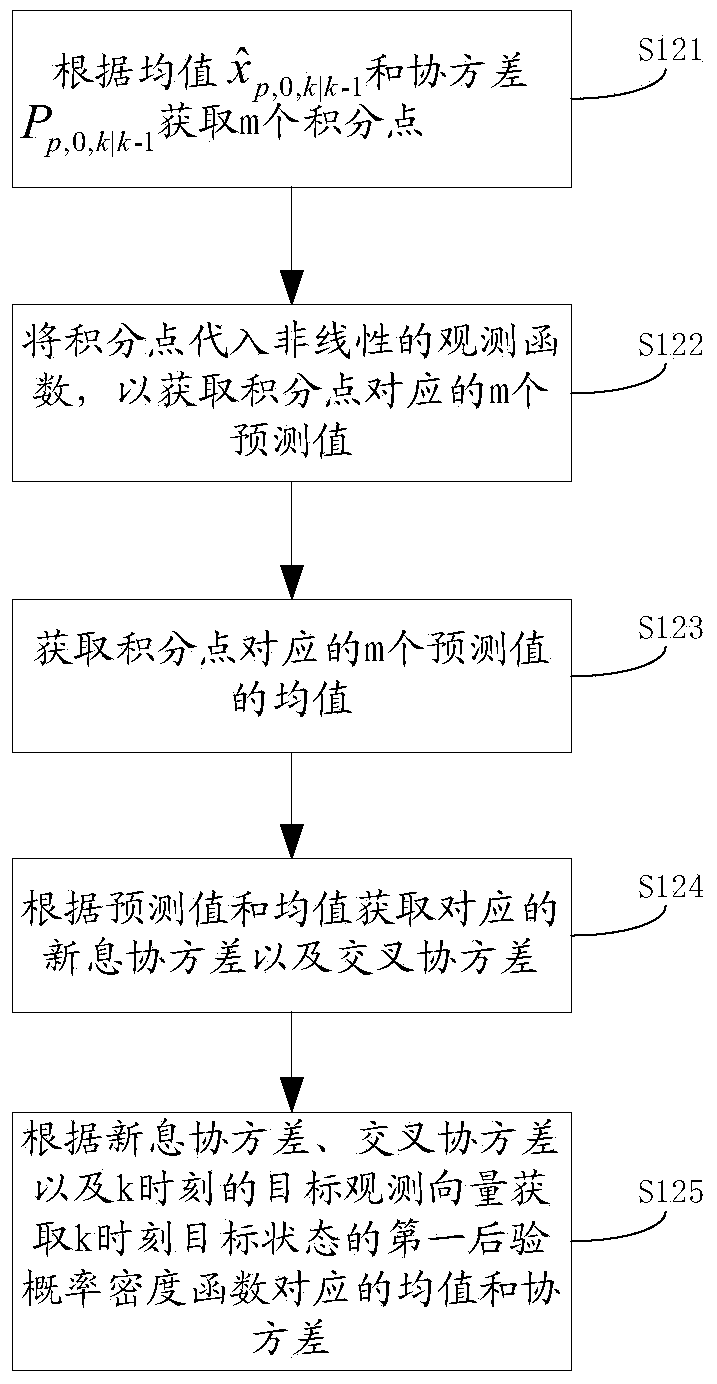
Target tracking method and expansion truncation no-trace Kalman filtering method and device
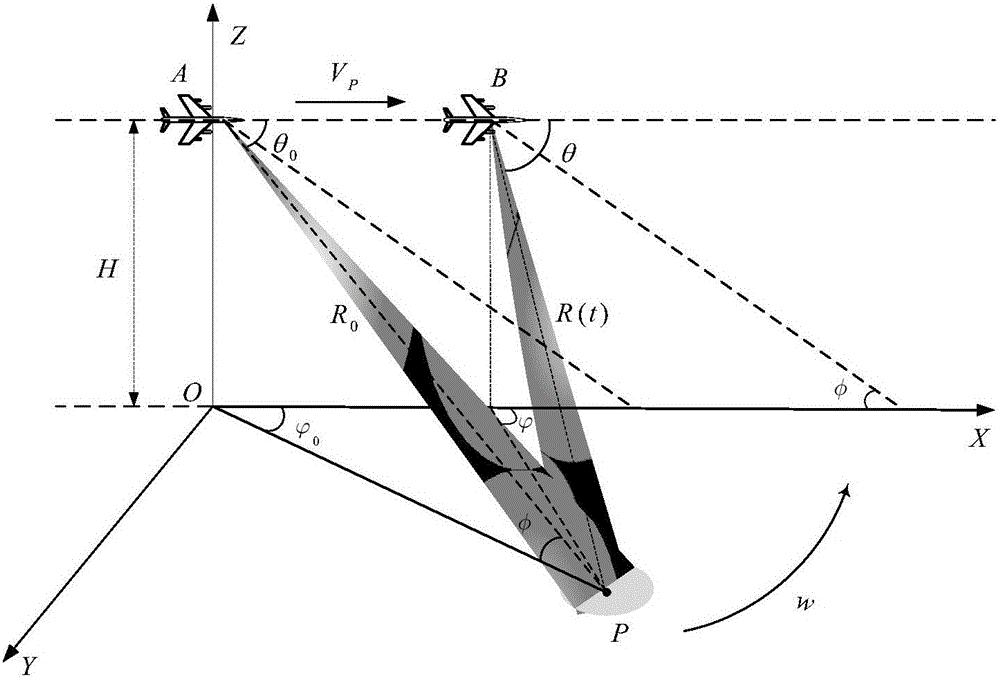
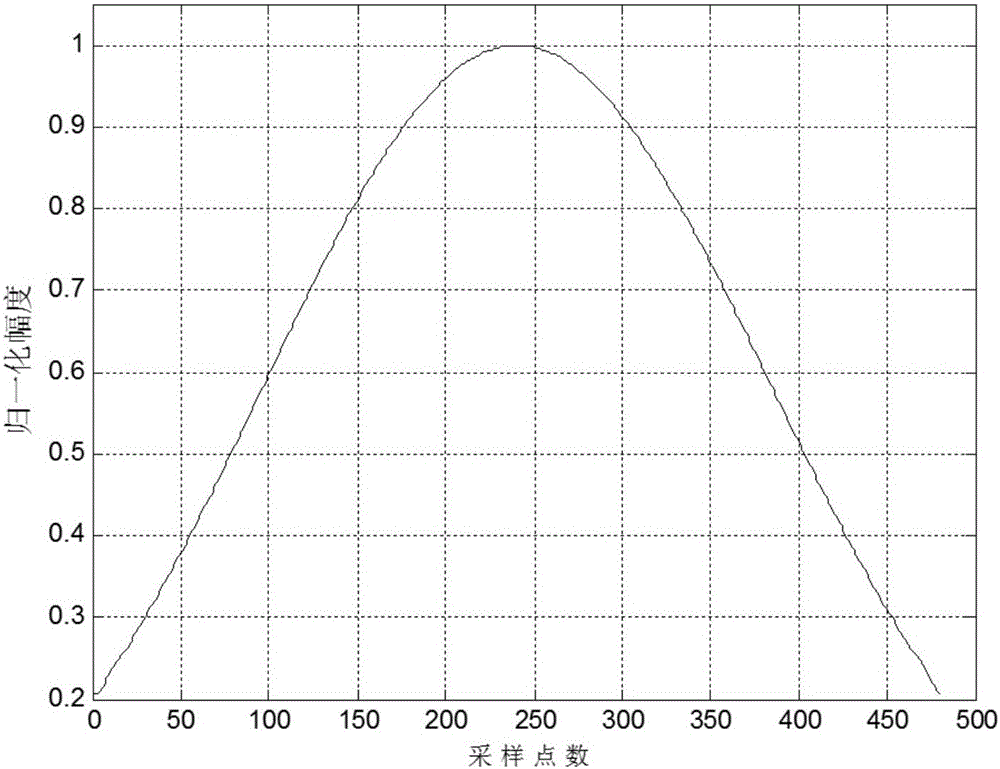
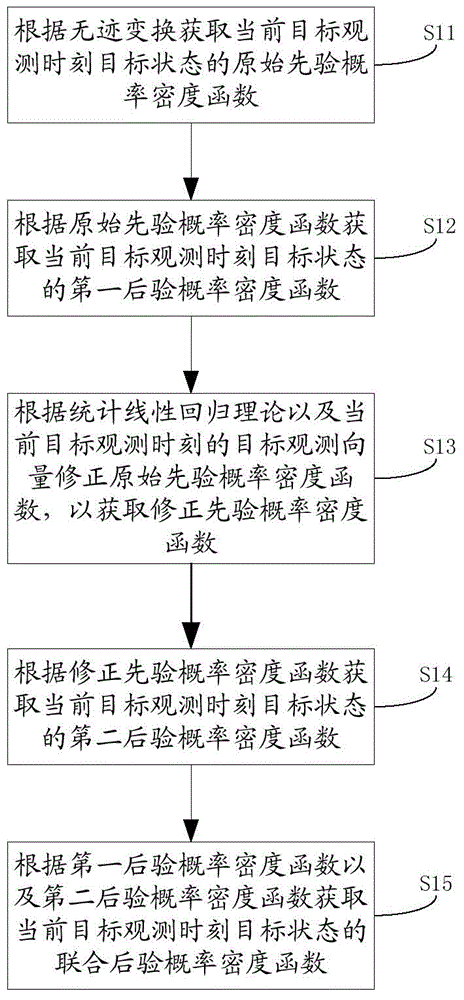
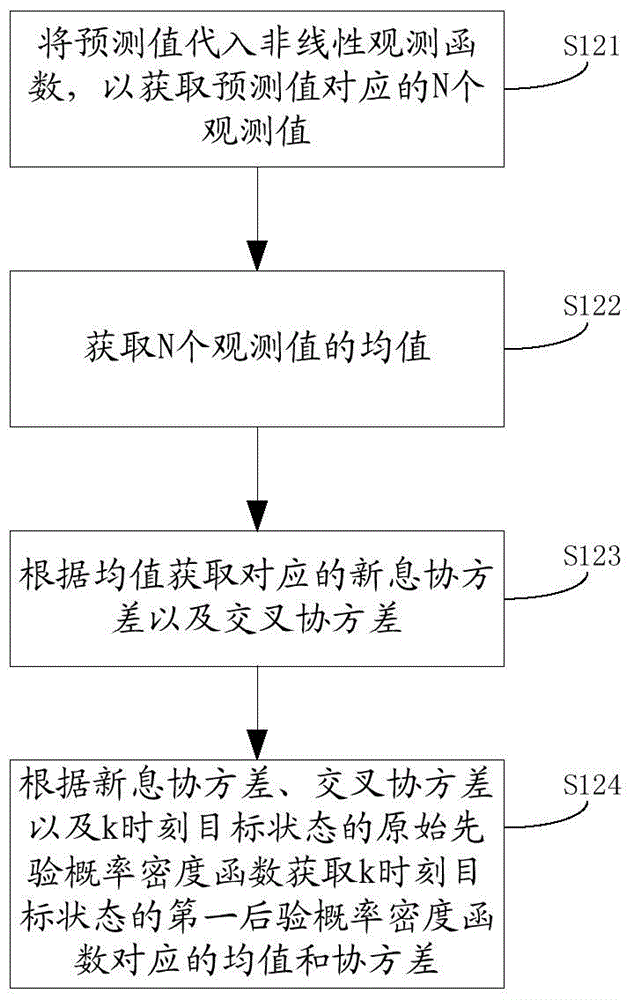
InactiveCN103955892AReduce prior distribution varianceSolve problems that do not have a unique inverseImage enhancementImage analysisLinear regressionSelf adaptive
The invention discloses a target tracking method and system and an expansion truncation no-trace Kalman filtering method and device. The expansion truncation no-trace Kalman filtering method comprises the steps that an original prior probability density function is obtained according to no-trace conversion; a first posterior probability density function is obtained according to the original prior probability density function; the original prior probability density function is corrected according to the statistics linear regression theory and a target observation vector of the current target observation moment so that the corrected prior probability density function can be obtained; a second posterior probability density function is obtained according to the corrected prior probability density function; a combined posterior probability density function is obtained according to the original prior probability density function and the second posterior probability density function. According to the Kalman filtering method, the problem that the observation function does not have the only inverse function can be solved, prior distribution variances of target states are effectively reduced, state upgrading is carried out in a self-adaptation mode according to the precision of the observation information, the filtering precision is effectively improved, and the practicality is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
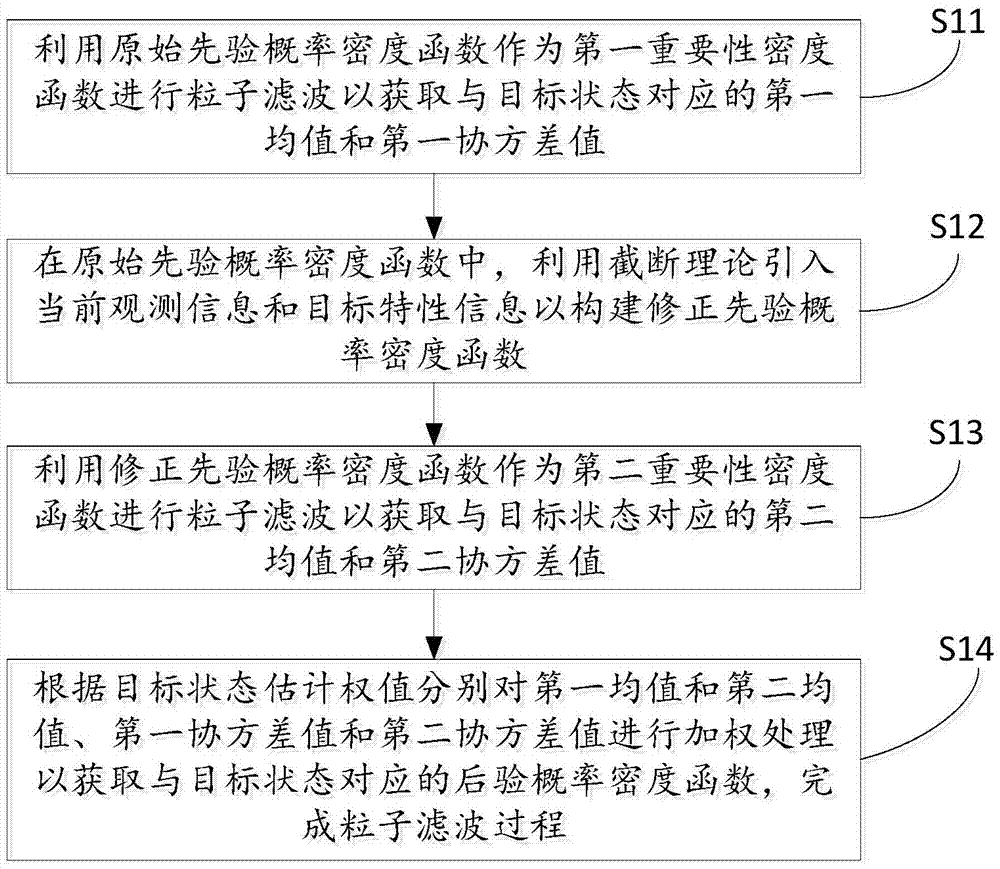
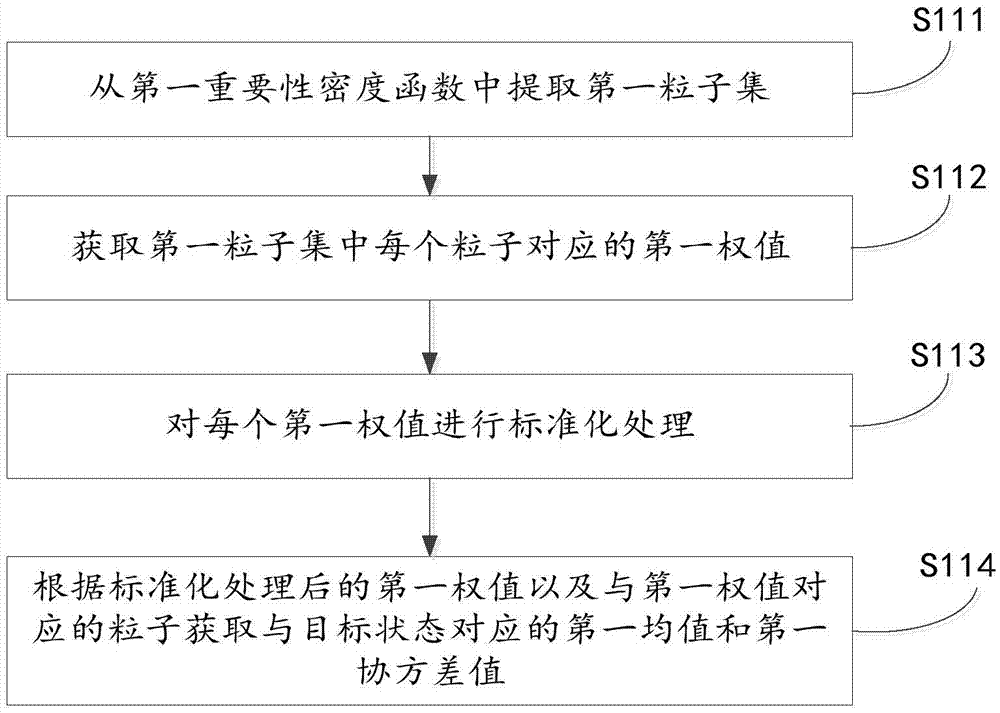
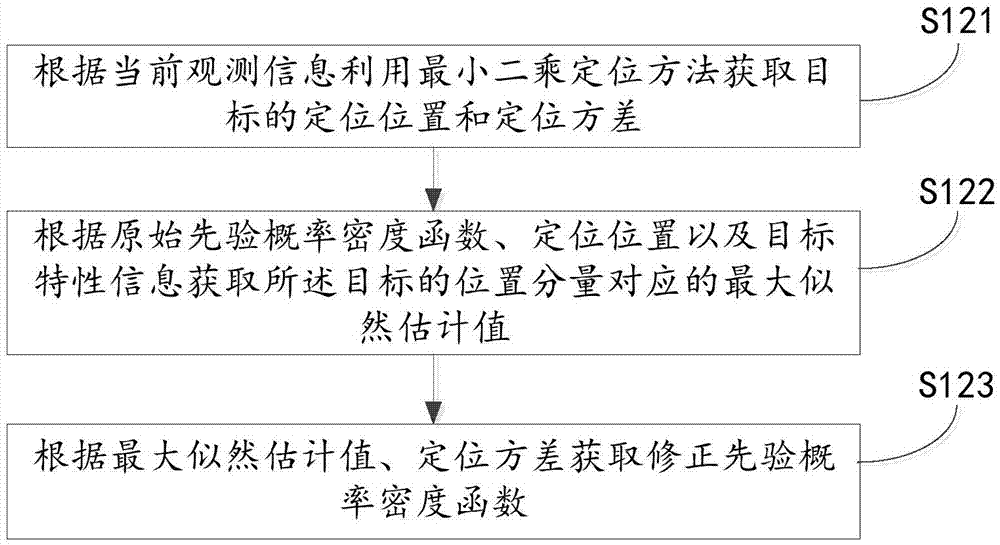
Auxiliary truncation particle filtering method, device, target tracking method and device
ActiveCN105447574AImprove accuracyImprove real-time performanceMathematical modelsEstimated WeightCovariance
The invention discloses an auxiliary truncation particle filtering method, a device, a target tracking method and a device. The auxiliary truncation particle filtering method comprises the steps of adopting an original prior probability density function as a first importance density function for filtering particles to obtain a first mean value and a first covariance value corresponding to a target state; in the original prior probability density function, importing the current observation information and the target characteristic information based on the truncation theory to construct a corrected prior probability density function; adopting the corrected prior probability density function as a second importance density function for filtering particles so as to obtain a second mean value and a second covariance value corresponding to the target state; respectively conducting the weighted treatment on first mean value, the first covariance value, the second mean value and the second covariance value according to the estimated weight of the target state so as to obtain a posterior probability density function corresponding to the target state, and completing the particle filtering process. In this way, the particle filtering accuracy and the particle filtering real-time performance are improved. Meanwhile, the rapid target-tracking problem of a target model in the uncertainty condition caused by the target maneuvering condition in the non-linear and non-gaussian environment can be solved.
Owner:KUNSHAN RUIXIANG XUNTONG COMM TECHCO
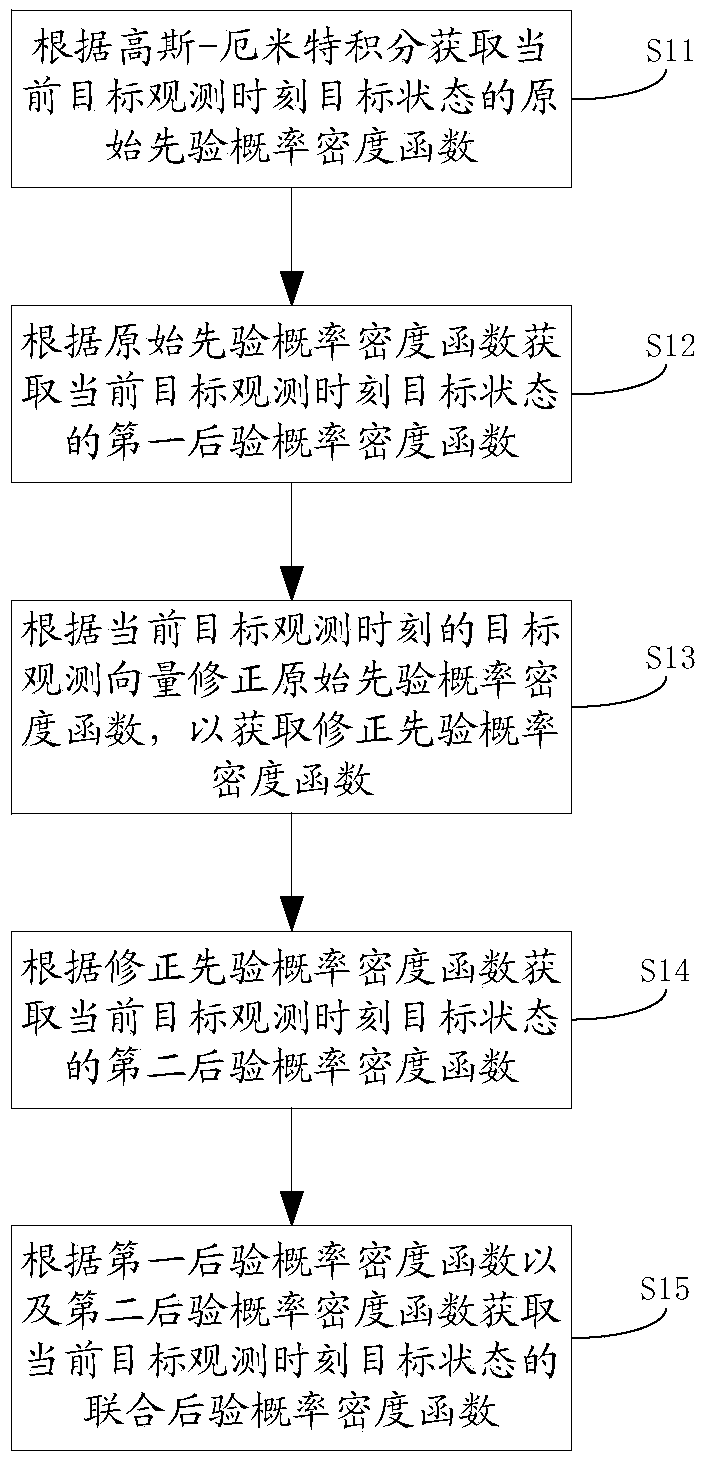
Target tracking method and truncated integral Kalman filtering method and device
InactiveCN103955600AImprove practicalityReduce prior distribution varianceSpecial data processing applicationsComputer scienceTracking system
The invention discloses a target tracking method, a target tracking system, a truncated integral Kalman filtering method and a truncated integral Kalman filtering device. The truncated integral Kalman filtering method comprises the following steps of obtaining an original prior probability density function in a target state according to a Gauss-Hermite integral; obtaining a first posterior probability density function in the target state according to the original prior probability density function; correcting the original prior probability density function according to a target observation vector at a current target observation moment to obtain a corrected prior probability density function; obtaining a second posterior probability density function in the target state according to the corrected prior probability density function; obtaining a joint posterior probability density function in the target state according to the first posterior probability density function and the second posterior probability density function. By applying the target tracking method, the target tracking system, the truncated integral Kalman filtering method and the truncated integral Kalman filtering device, the prior distribution variance in the target state can be effectively reduced; the state update is implemented in a self-adapting way according to the precision of observation information; the filtering precision is effectively improved; the practicability is higher.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
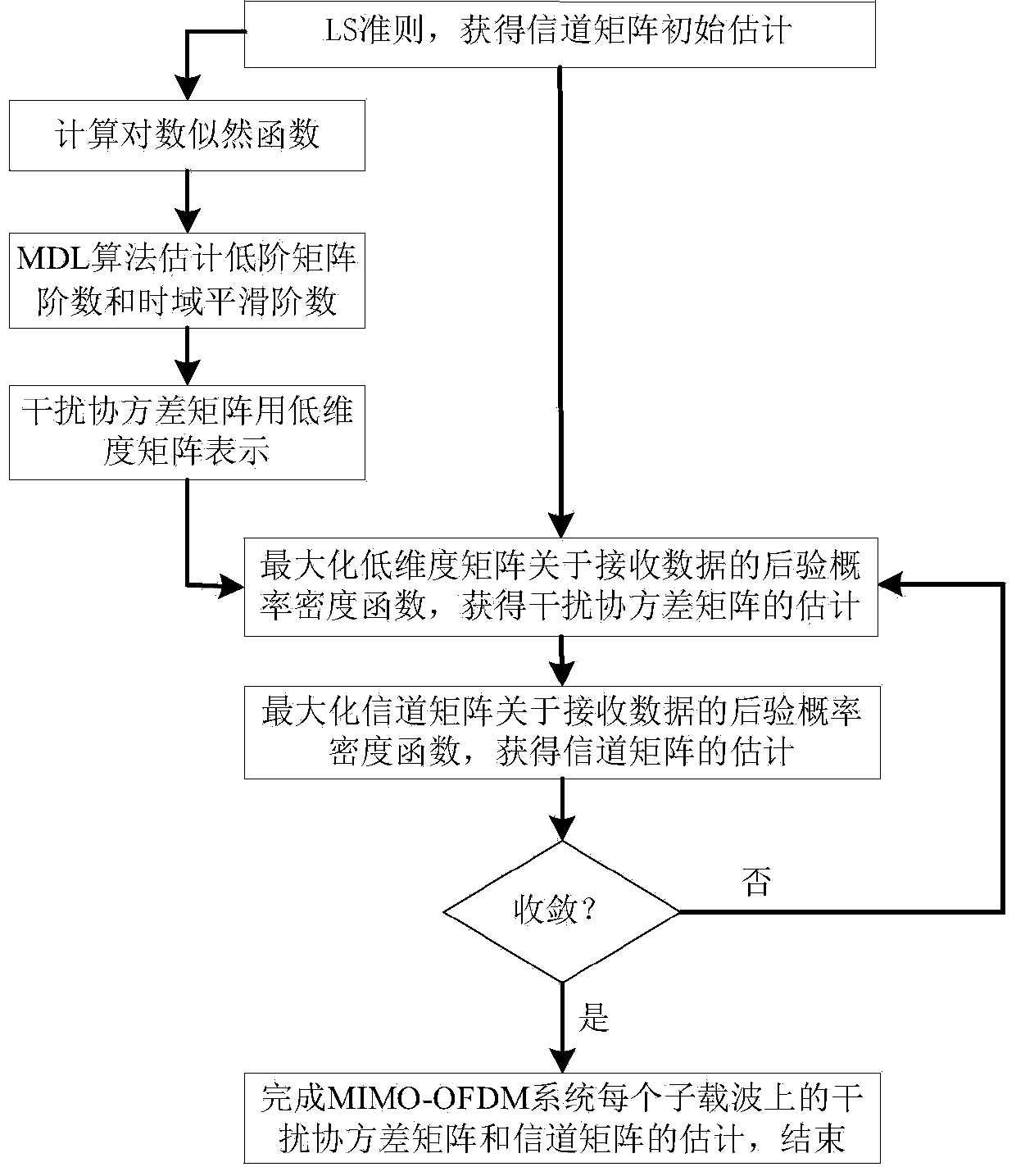
Channel matrix and interference covariance matrix estimation method suitable for MIMO-OFDM system
ActiveCN104022977AExcellent channel resultHigh precisionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksEstimation methodsMaximum a posteriori estimation
The invention provides a channel matrix and interference covariance matrix estimation method suitable for an MIMO-OFDM system. The method is characterized in that based on a maximum posterior probability rule, channel matrixes and interference covariance matrixes on all sub-carriers are estimated in a combined mode. In detail, the method includes the steps that (1), by the adoption of a least square (LS) rule, the initial estimation of the channel matrixes is obtained; (2), each interference covariance matrix is expressed as a low-dimension matrix, by the utilization of the current estimation value of the channel matrixes, the posterior probability density function, about receive data, of the low-dimension matrixes is obtained, and the posterior probability density function is maximized to obtain the estimation of the interference covariance matrix; (3), by the utilization of the estimation value of the interference covariance matrixes, the posterior probability density function, about receive data, of the channel matrixes is obtained, and the posterior probability density function is maximized to obtain the estimation of the channel matrixes; (4), the step2 and the step3 are performed in an iterative mode until convergence is performed. The method has the advantage that according to the scheme, the estimation precision of the channel matrixes and the interference covariance matrixes can be effectively improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Particle filter multi-crack growth prediction method based on dynamic crack number
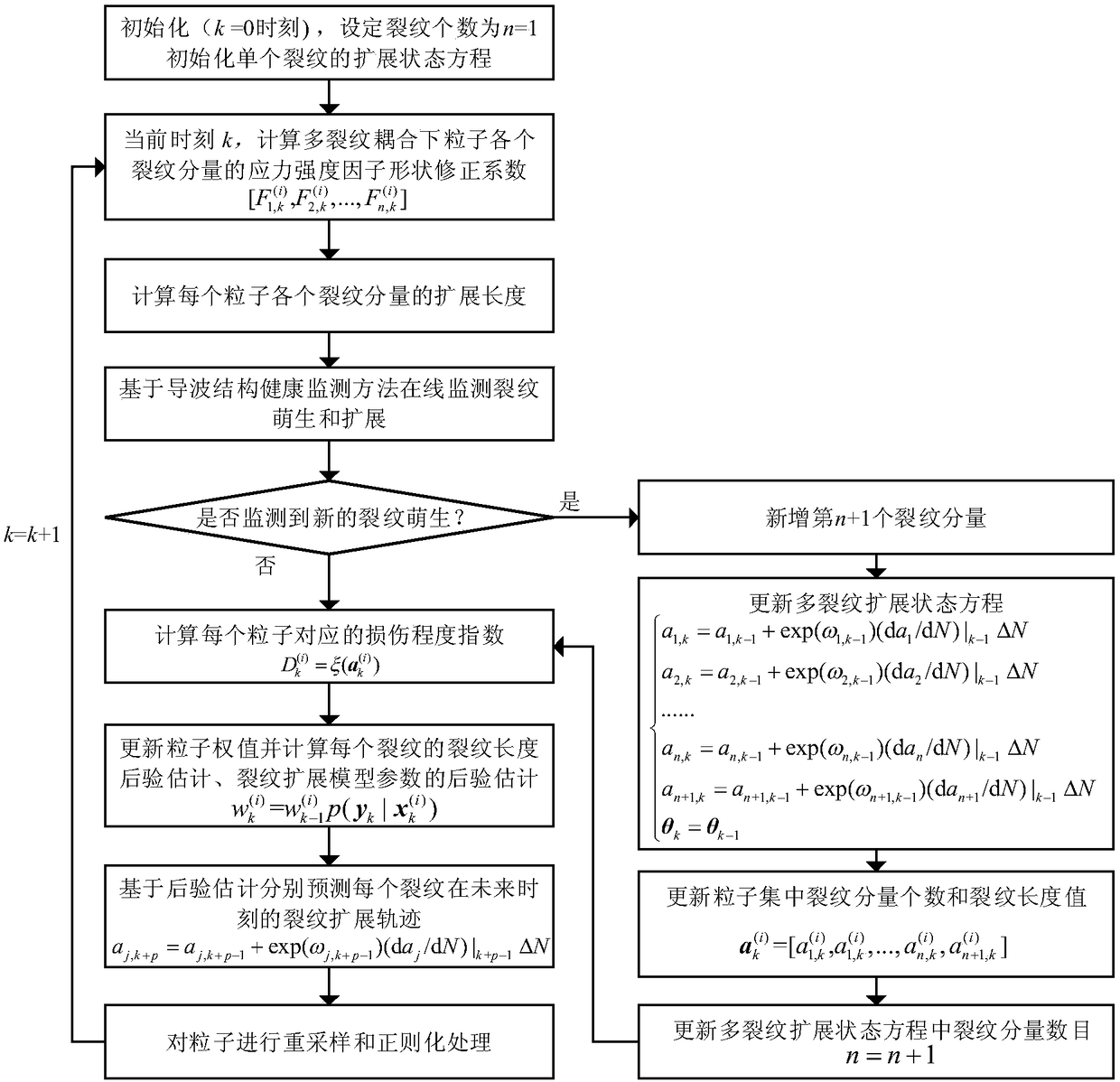
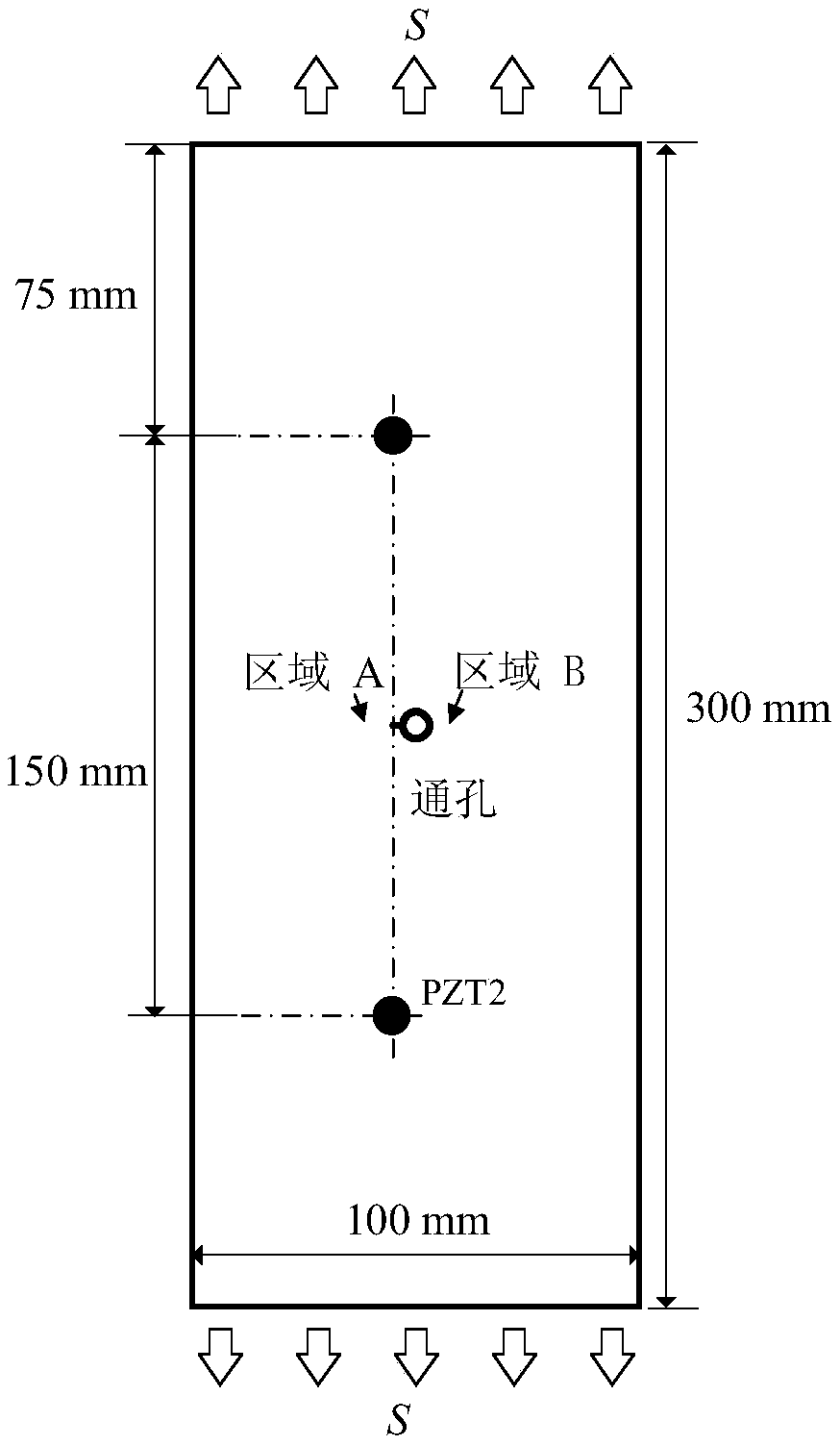
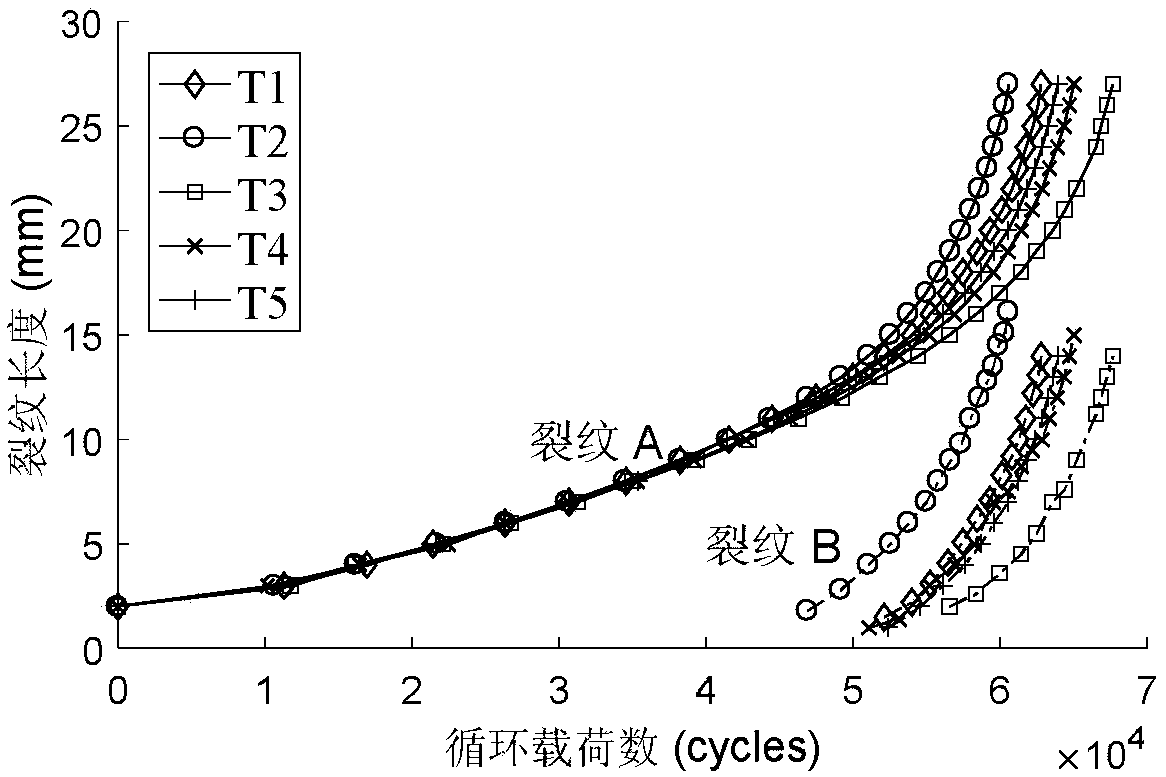
The invention discloses a particle filter multi-crack growth prediction method based on dynamic crack number, belonging to the technical field of fault prediction and health management. The inventionadopts the on-line guided wave structure health monitoring method to on-line monitor the initiation and expansion of cracks in the structure, when the new crack initiation is detected, the crack component and the crack propagation equation number in the multi-crack propagation state equation are updated, the crack propagation law under the multi-crack coupling is constructed, and the particle setis updated. Combined with the on-line observations obtained from guided wave structure health monitoring method, the posterior probability density function of multi-crack propagation state vector is estimated on-line by regularized particle filter. The crack propagation model is updated by posterior estimation of model parameters, and the crack propagation trajectories at future time are predictedby posterior estimation of crack length. The invention can effectively realize on-line monitoring and prediction of multiple cracks in a structure, and has wide application prospect in prediction ofmultiple cracks in a structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Methods and arrangements for detecting weak signals
ActiveUS20120183035A1Increase probabilityDigital computer detailsTransmission monitoringModel selectionInstrument Data
Owner:RADAREAL
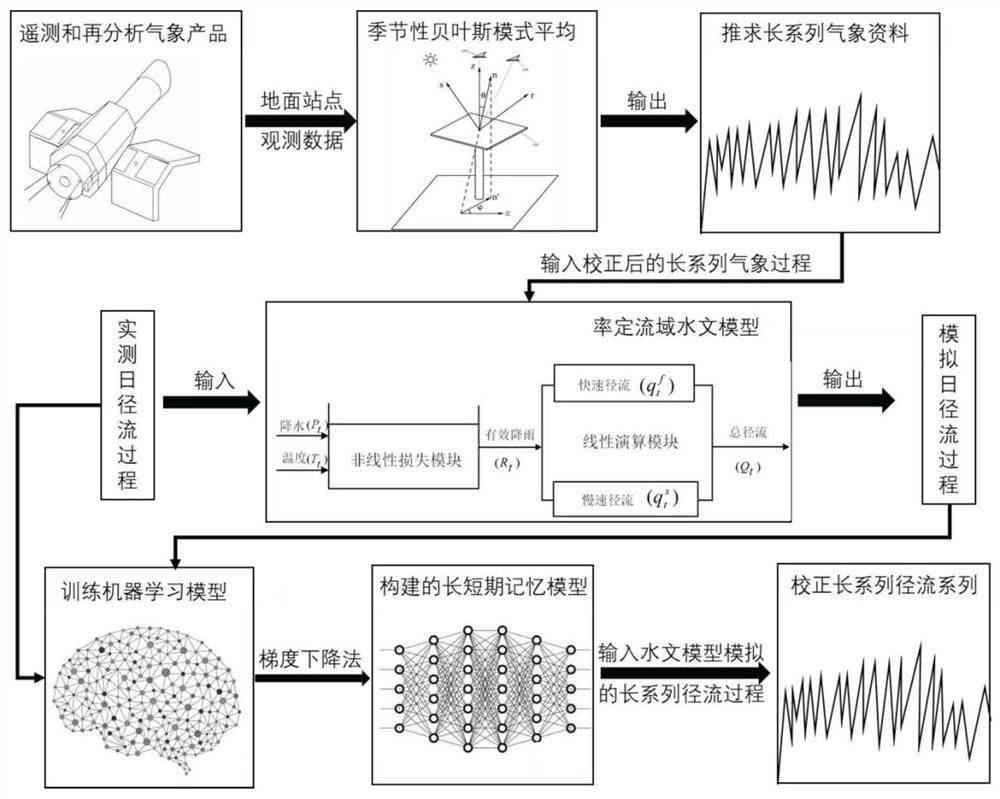
Hydrological simulation method for averagely fusing multi-source data based on Bayesian mode
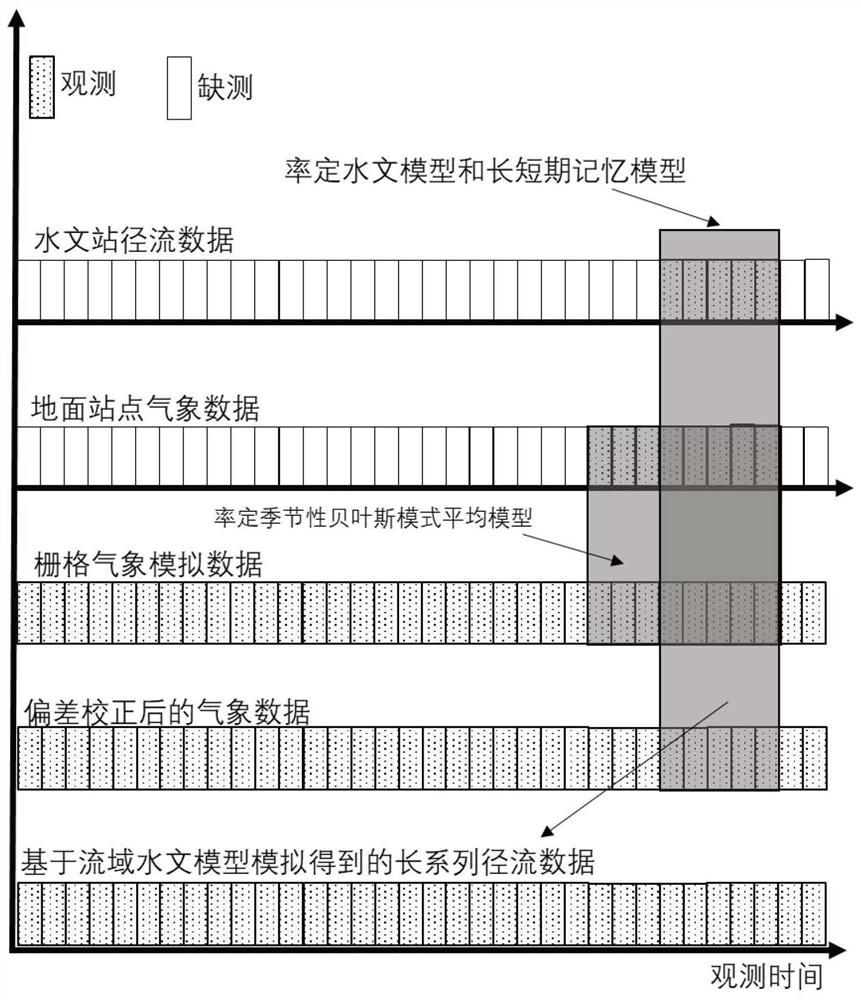
ActiveCN111898660AImprove the simulation effectEasy to operateCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningHydrometryData set
The invention discloses a hydrological simulation method based on Bayesian mode average fusion multi-source data. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, collecting meteorological data, hydrological series, satellite inversion rainfall and a reanalysis air temperature data set of a ground station in a scarce data area; respectively establishing correction models of ground observationdata and a simultaneous simulation meteorological data set in different months by adopting a quantile mapping-based daily deviation correction method, a regression correction method and an equal ratecorrection method; then adopting a seasonal Bayesian mode averaging method, optimizing the weight of each deviation correction scene through a posterior probability density function to acquire a corrected long-series meteorological data set; and calibrating a basin hydrological model and a long-short-term memory neural network model according to actual measurement data, and finally inputting the corrected long-series meteorological data set to realize runoff process simulation. Long-series runoff simulation of regions with scarce data can be realized, and an important reference basis with highoperability can be provided for basin water resource management and planning.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
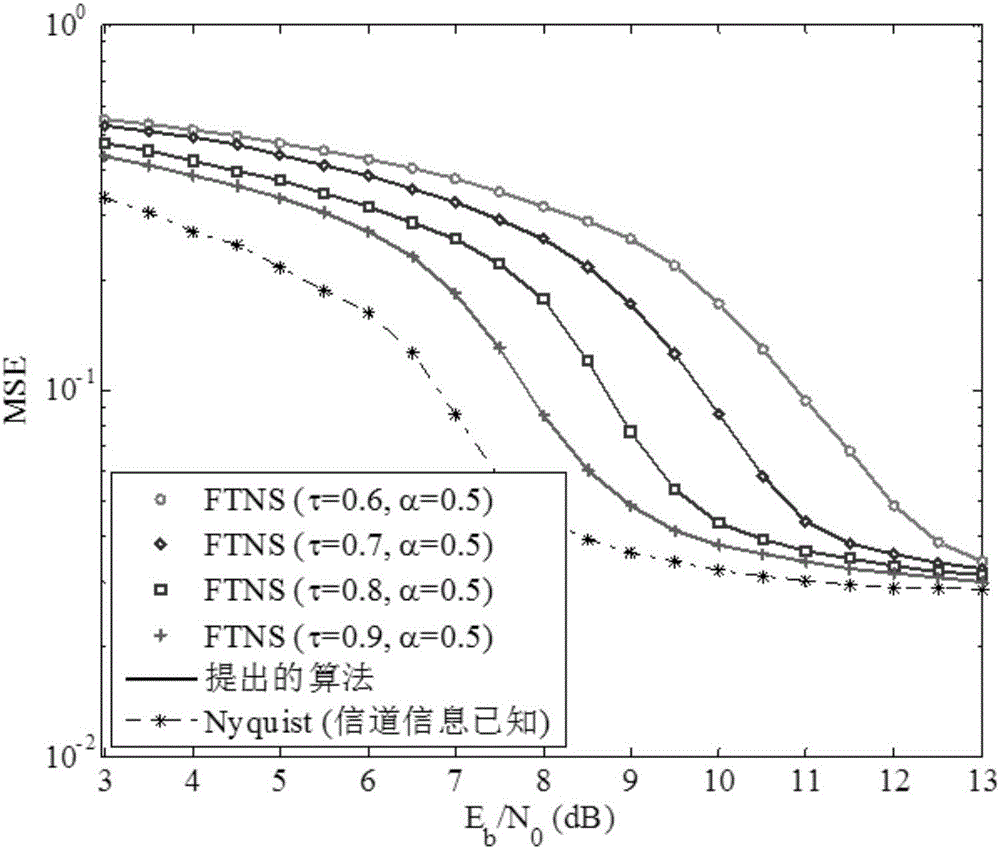
Joint time-frequency doubly selective channels (DSCs) estimation and faster-than-Nyquist signaling (FTNS) detection method
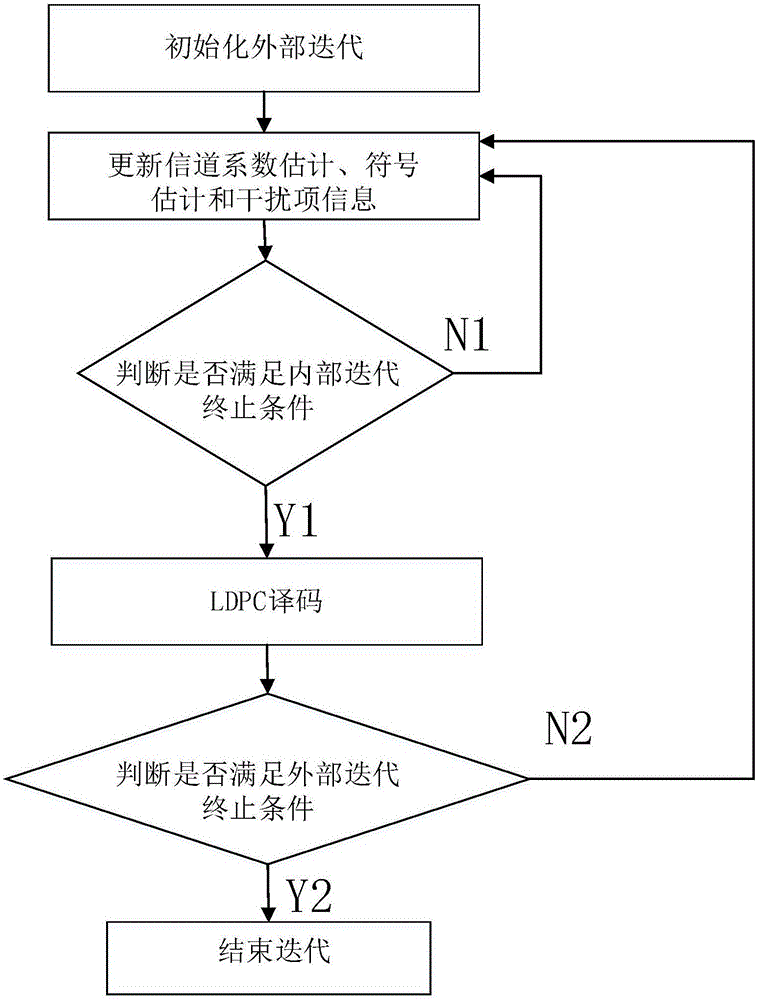
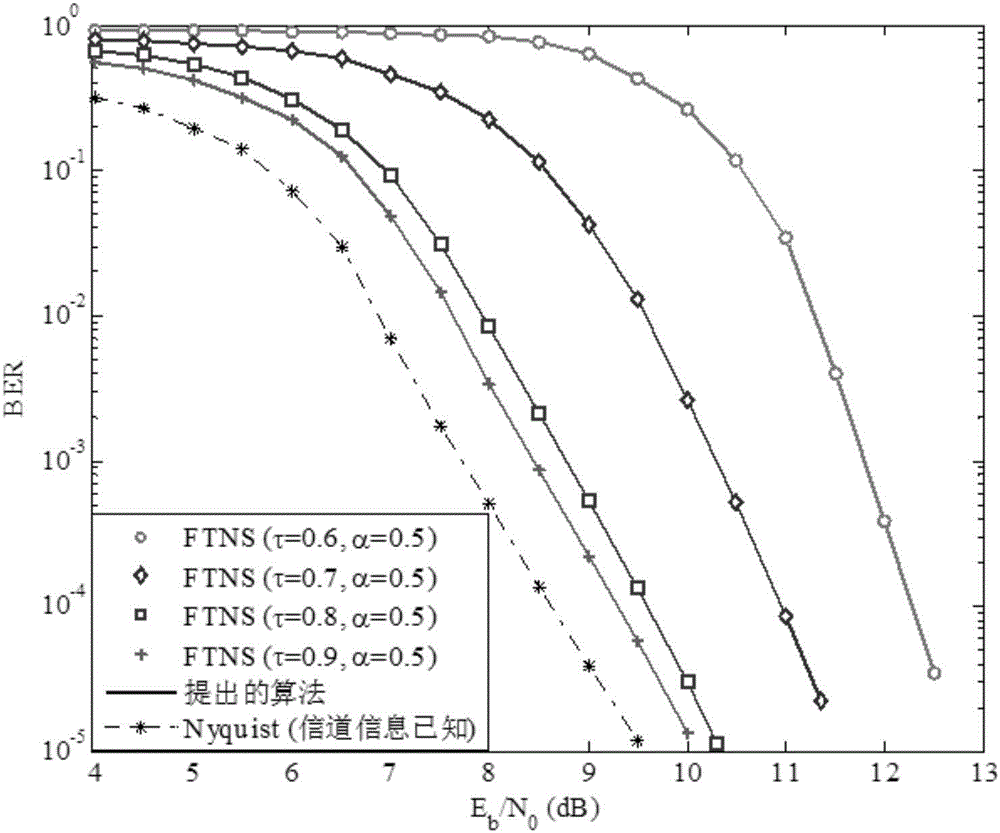
InactiveCN106549892AReduce complexityImprove spectral efficiencyTransmitter/receiver shaping networksPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a joint time-frequency doubly selective channels (DSCs) estimation and faster-than-Nyquist signaling (FTNS) detection method, and belongs to the technical field of design of iterative receivers. The method has a core idea comprising the steps of dividing a transmission data block into a plurality of data sub-blocks, assuming that a channel coefficient in each data sub-block is invariable, using a first-order autoregression model to model channel variations between the different data sub-blocks, and performing channel estimation by fully using a time-varying channel statistical property with the aid of a forward-backward algorithm; constructing a reasonable frequency domain sub-system model to simultaneously cover interference between the data sub-blocks introduced without cyclic prefix (CP) and color noise interference introduced by the FTNS; and further acquiring an approximated posterior probability density function of the channel coefficients and data symbols by using a VB method based on the frequency domain sub-system model and iteratively updating parameter of the function. According to the method, the color noise interference and the interference between the data sub-blocks introduced without the CP are gradually eliminated during an iteration process, and the method has the advantages of low algorithm complexity, high system spectral efficiency, high reliable channel estimation and high symbol detection performance.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
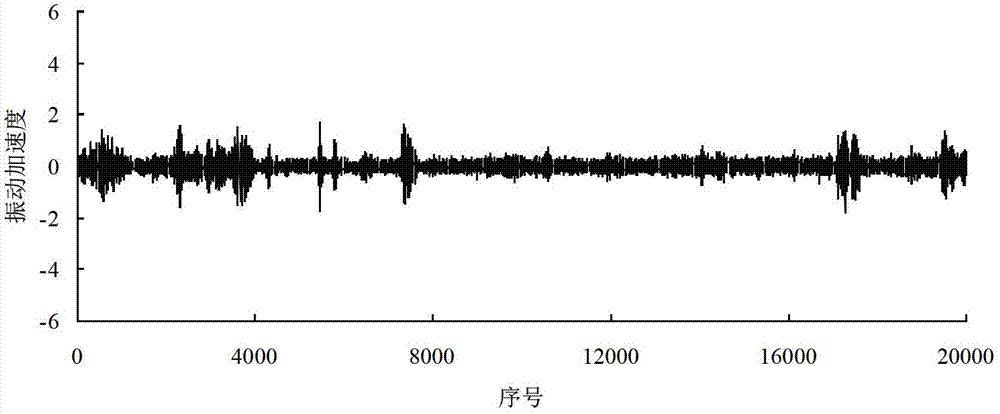
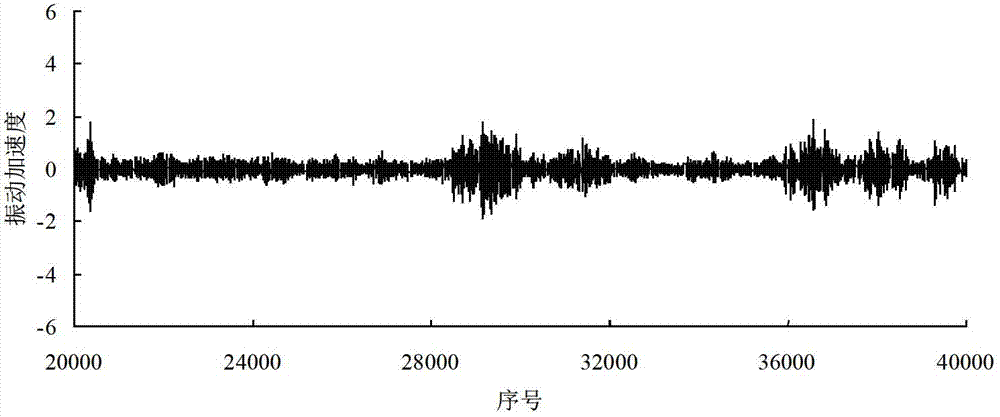
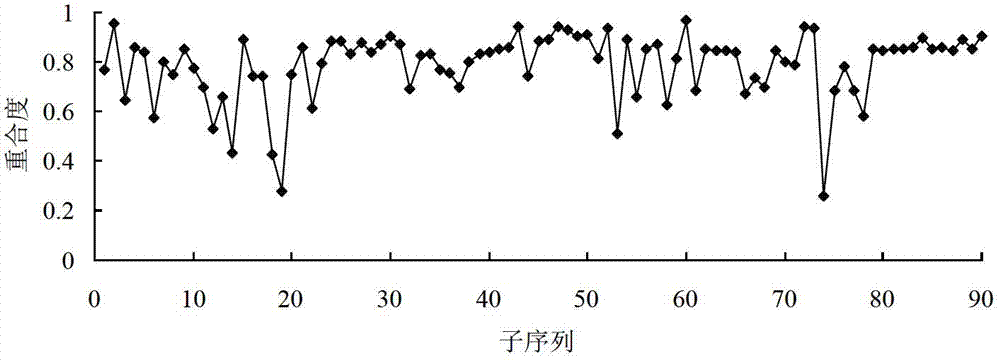
Significance testing method for rolling bearing performance variation process
InactiveCN103246803AAvoid nasty accidentsSpecial data processing applicationsPrior informationNormal density
The invention discloses a significance testing method for a rolling bearing performance variation process. The method includes: regularly sampling the performance of a rolling bearing during service to obtain an r-th time sequence, equally dividing the r-th time sequence into D subsequences, and setting a d-th subsequence data as Xrd; processing the subsequences by bootstrapping to obtain origin moments of all orders of each subsequence; establishing a probability density function of each subsequence according to the principle of maximum entropy; selecting a reference time sequence; establishing a posterior probability density function; establishing contact ratio; giving a significance level alpha; if the contact ratio is smaller than 1-alpha, determining the d-th subsequence Xrd in the r-th time sequence varies significantly; if not, determining no significant variation occurs. By the method under the condition that probability distribution and trend prior information is absent, variation information of the performance of the rolling bearing during service can be checked timely, failure risk of the bearing is found so that measures can be taken as soon as possible, and serious accidents are avoided.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
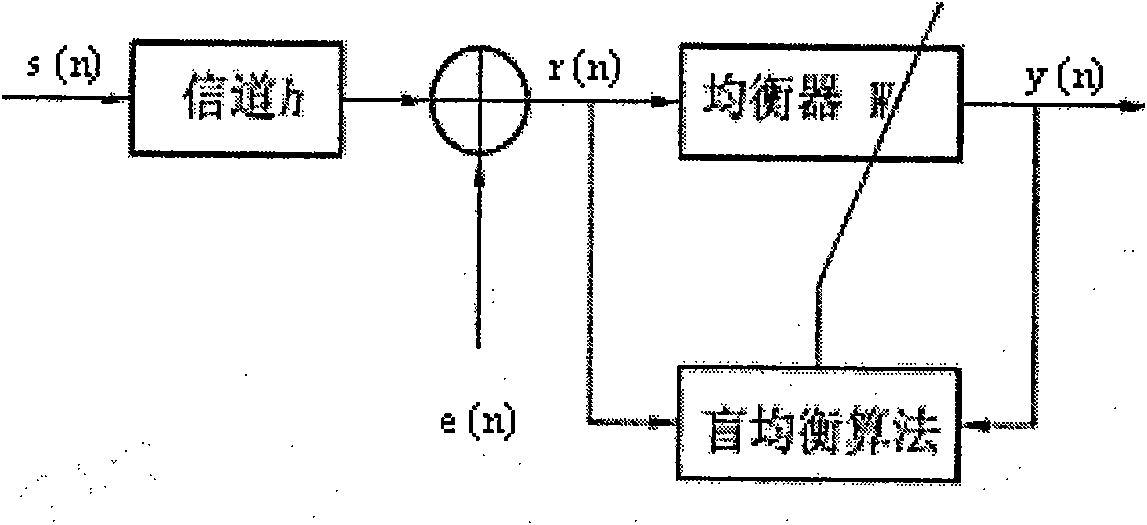
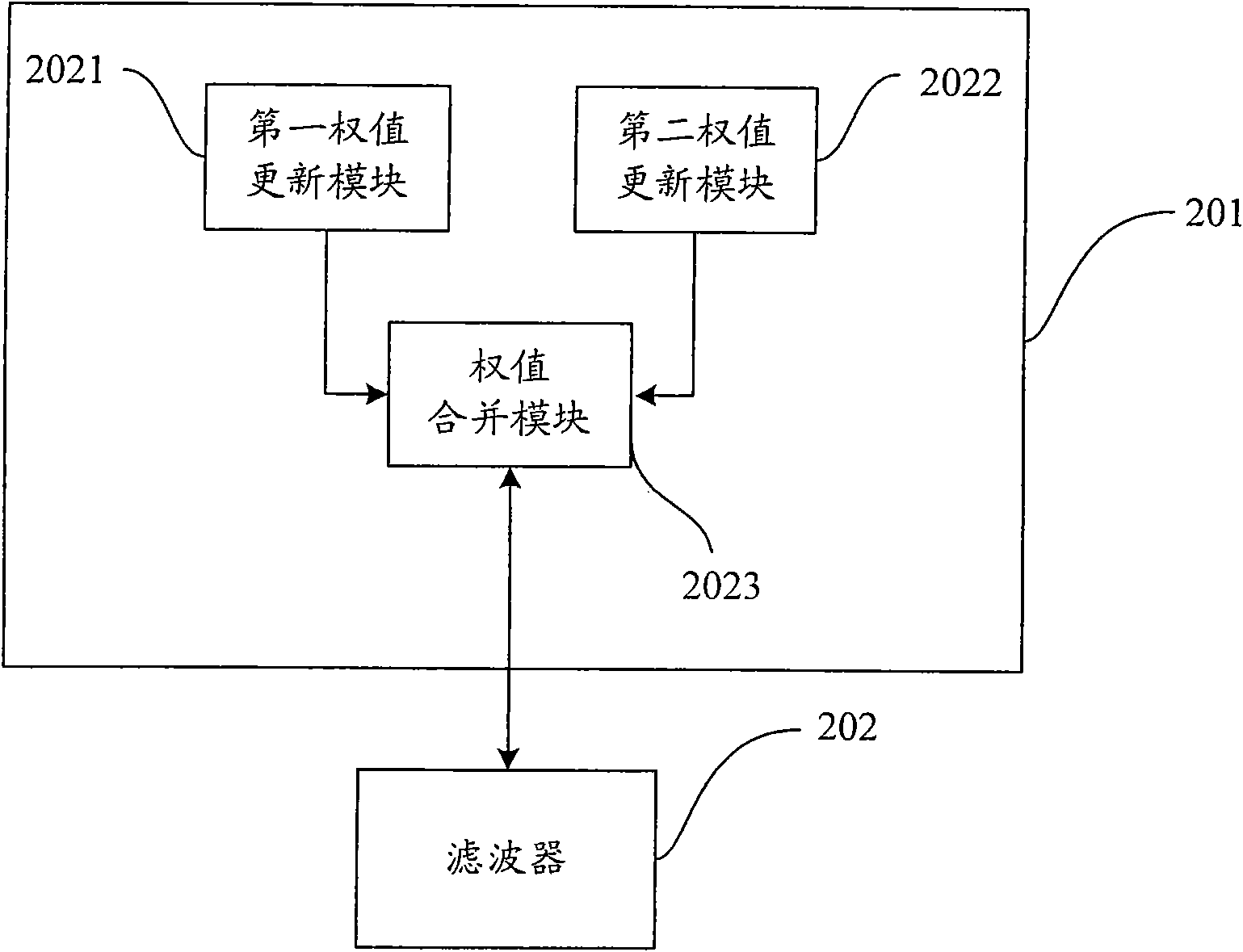
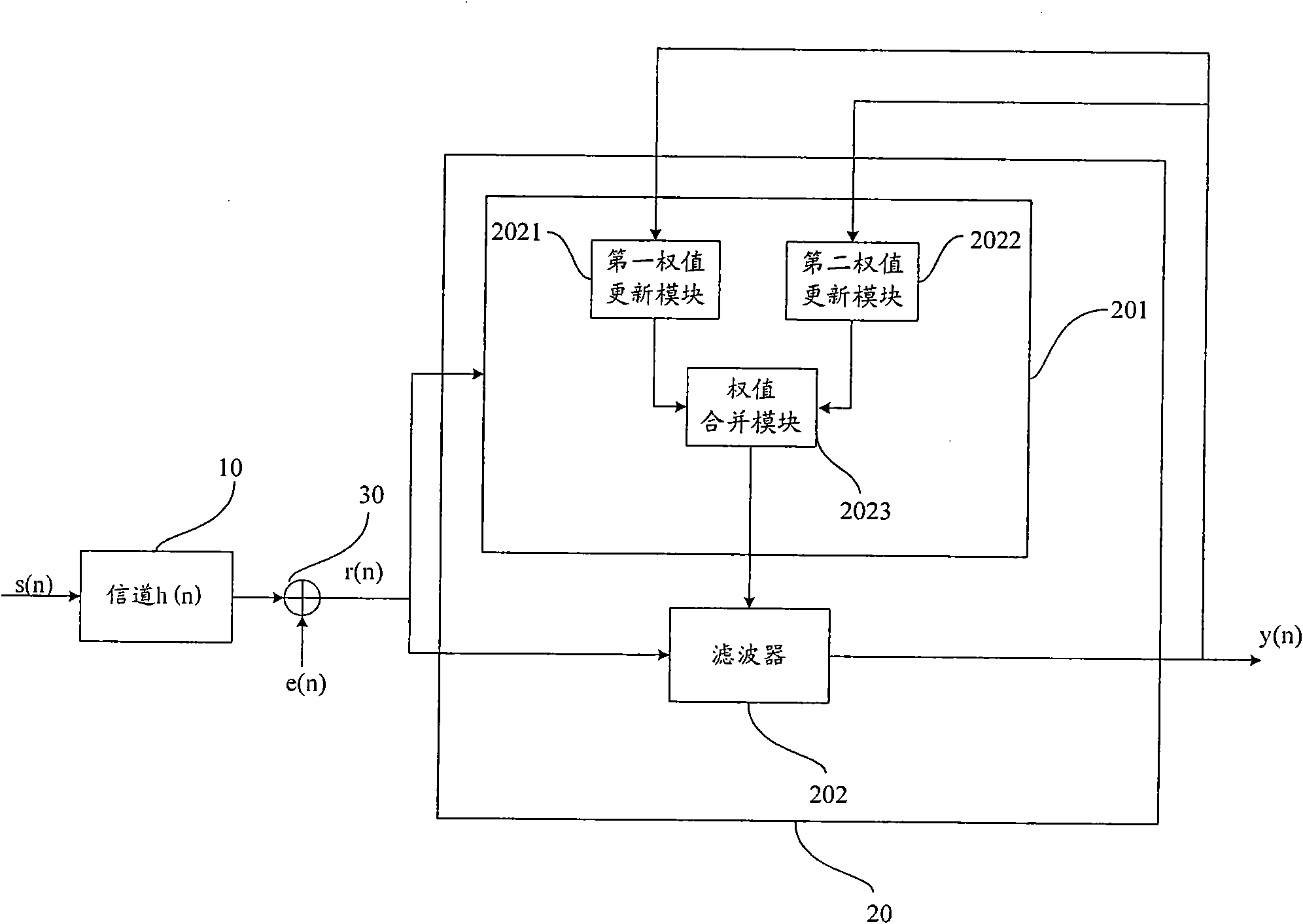
Blind equalizer and blind equalization processing method
InactiveCN101854317AFast convergenceImprove steady state performanceTransmitter/receiver shaping networksBlind equalizerEqualization
The invention provides a blind equalizer and a blind equalization processing method, which are suitable for the field of communication. The blind equalizer comprises a weight updating unit and a wave filter, wherein the weight updating unit comprises a first weight updating module, a second weight updating module and a weight merging module. In the blind equalizer and the blind equalization processing method, a weight vector is updated by making the error items of the first weight updating module minimum and making the logarithmic value of a local posterior probability density function adopted by the second weight updating module maximum, and a received signal vector is output after the received signal vector is subjected to the equalization processing according to the updated weight vector, so the blind equalizer which can increase velocity of convergence and improve steady-state performance is implemented.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV +1
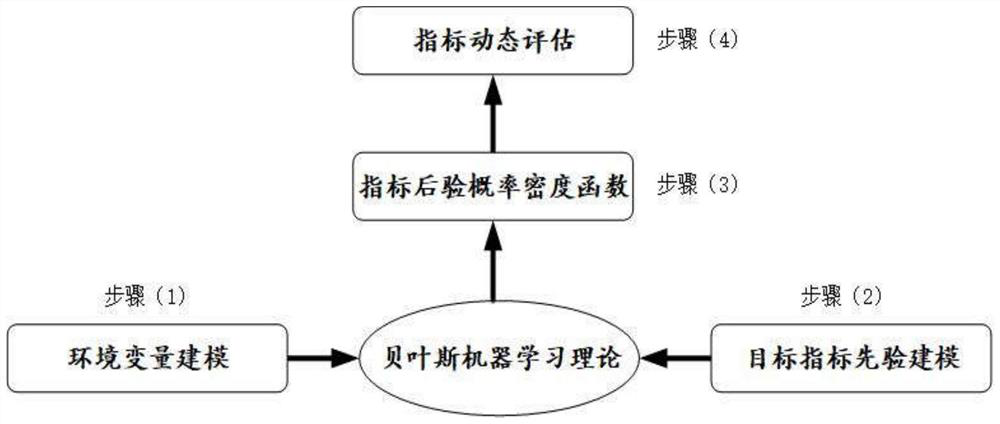
Radar system performance index dynamic evaluation method based on Bayesian machine learning
PendingCN112163373AReduce the number of trialsReduce experiment costWave based measurement systemsDesign optimisation/simulationProbit modelRadar systems
The invention discloses a radar system performance index dynamic evaluation method based on Bayesian machine learning. The method comprises the following steps: modeling a likelihood function of radartarget detection data into Gaussian distribution; modeling the prior distribution of the target performance index to be evaluated into Laplace distribution; performing hierarchical modeling on the target to-be-evaluated performance index by utilizing the Bayesian hierarchical probability model; and performing approximate solution on the posterior distribution of the to-be-evaluated performance indexes of each target by using a variational Bayesian expectation maximization method, thereby obtaining a posterior probability density function and the like. The Bayesian machine learning method is adopted to realize the dynamic evaluation of the radar performance indexes, the biggest advantage is that under the model assumption condition, the analyzed dynamic indication result can be obtained only by observing the data once, the test frequency can be obviously reduced, the test cost and period are reduced, the analyzed index dynamic change range is provided, and the availability and the robustness are obviously improved. Therefore, the applicability for the dynamic evaluation of the radar system performance indexes is good.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
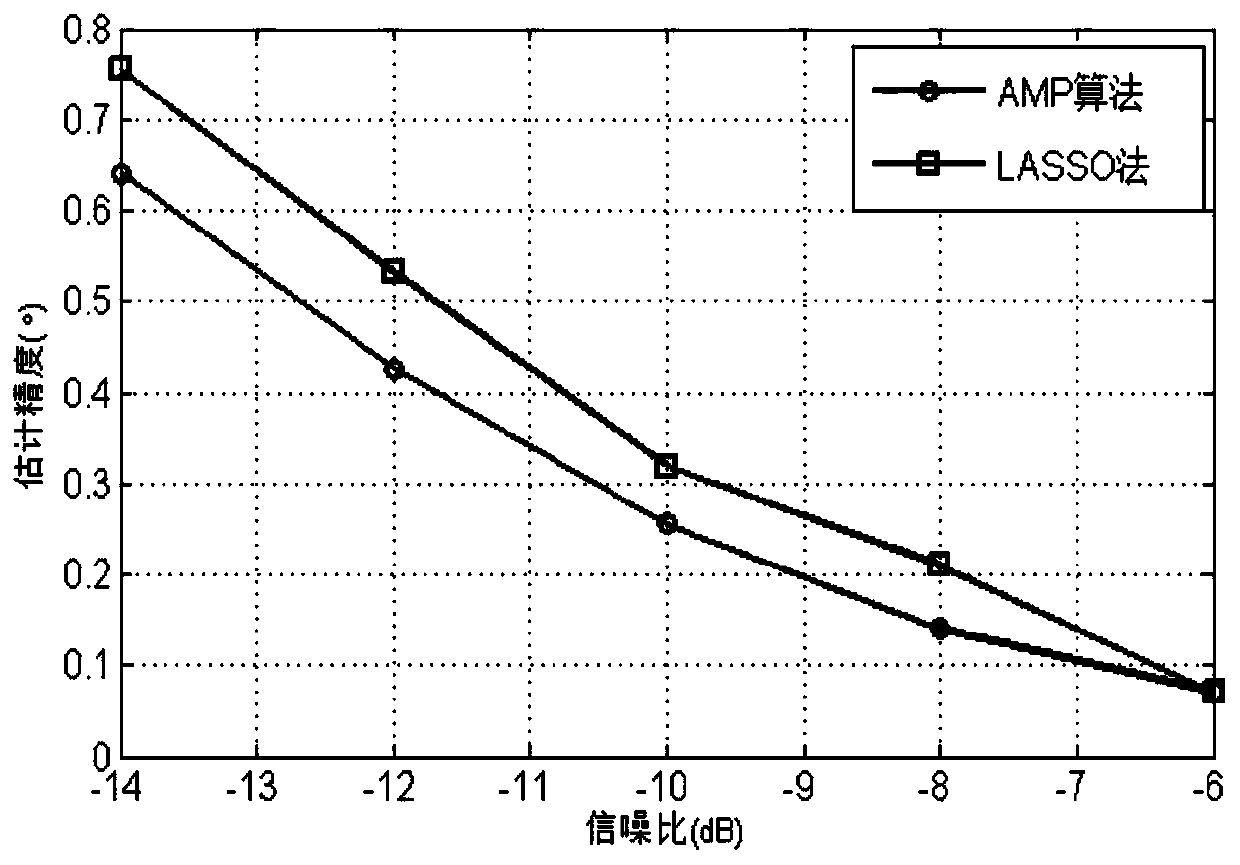
Fast target angle estimation method based on sparse Bayesian learning
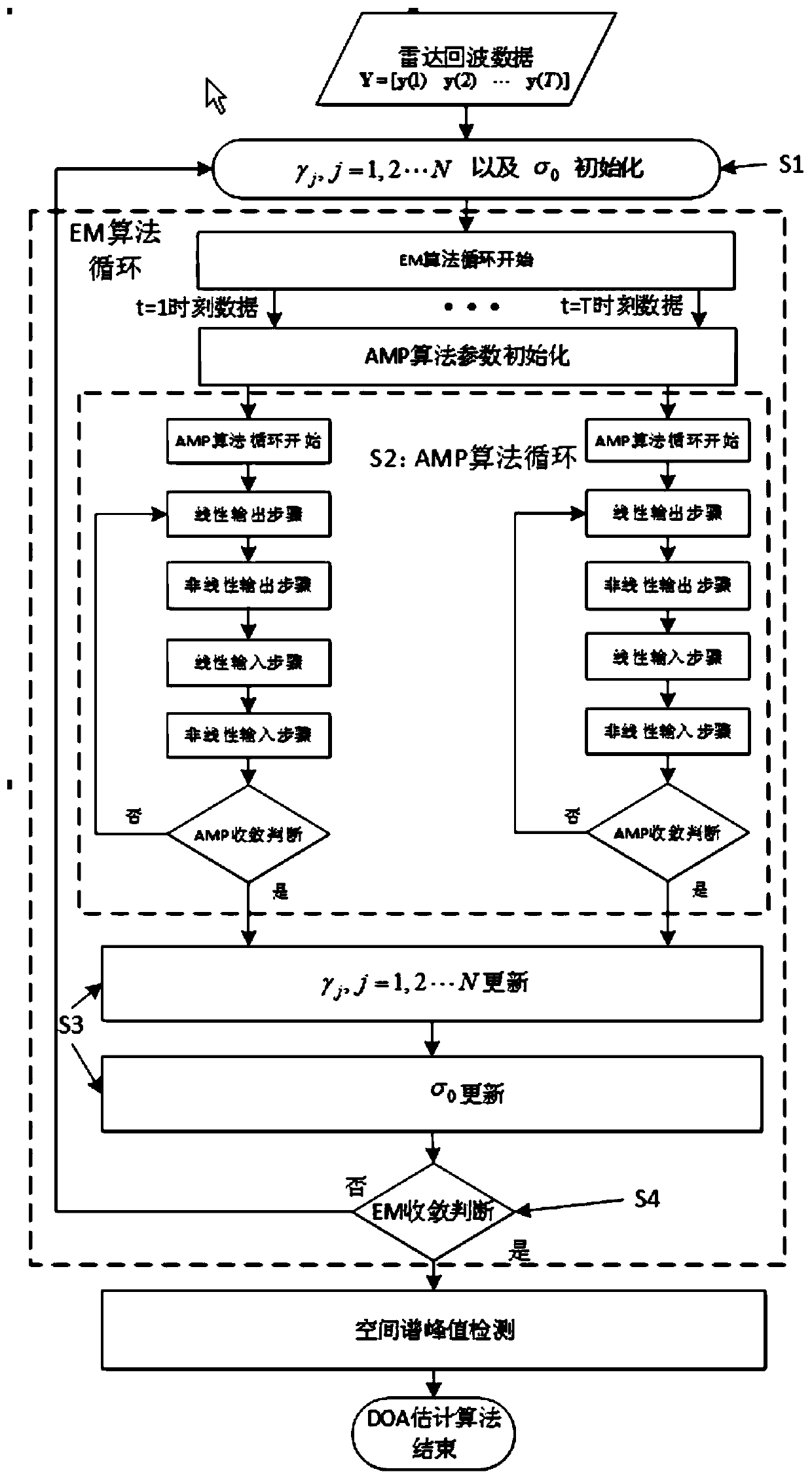
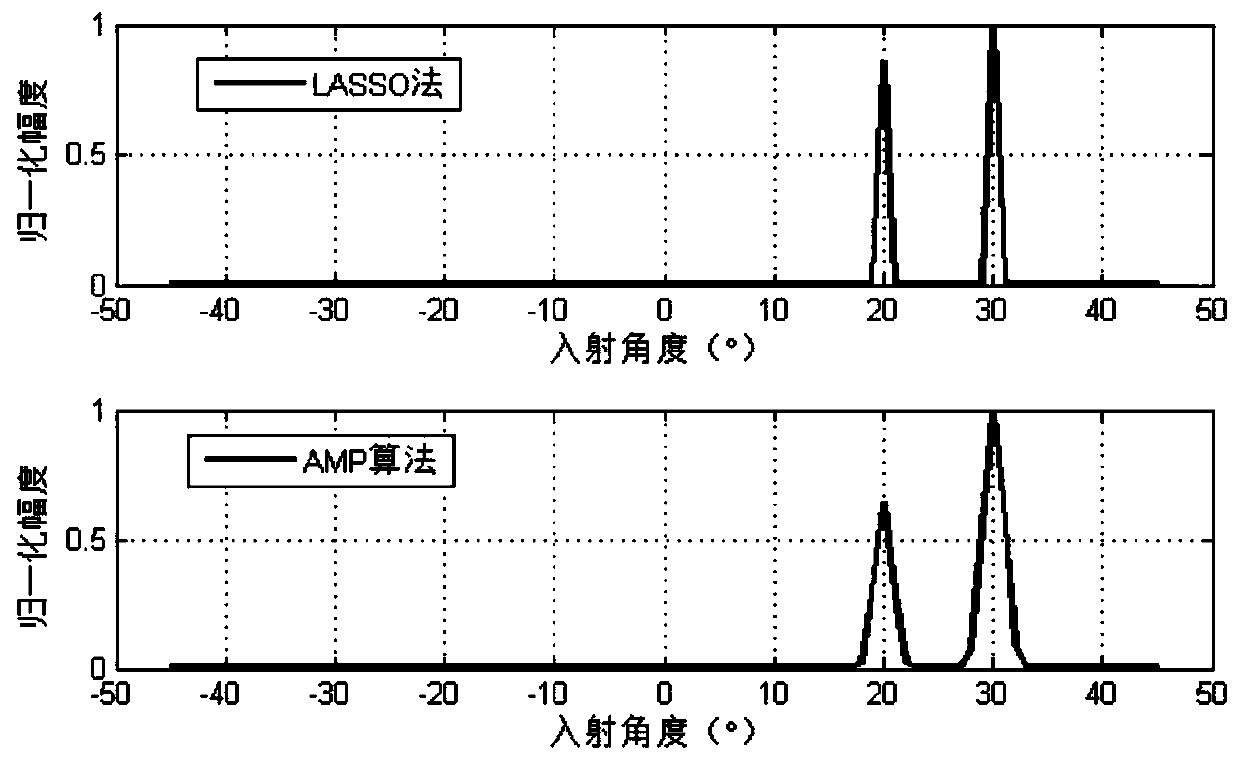
ActiveCN109752710AIterative convergence is fastImprove computing efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPosterior probability densitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention belongs to the field of array signal processing, and in particular relates to a fast target angle estimation method based on sparse Bayesian learning. The method comprises the followingsteps of S1, performing initialization on the parameters to be estimated of gammaj and sigma0, wherein j is equal to 1,2 to N; S2, quickly obtaining signal posterior probability density functions at each moment by using the AMP algorithm; S3, updating values of the parameters to be estimated of gammaj and sigma0 by using the EM algorithm, wherein j is equal to 1,2 to N; and S4, determining whetherthe update iterative process of the parameters to be estimated converges, returning to the S2 to re-iterate if not, and if so, jumping out of the loop and determining the direction and quantity of the target incoming waves. The method provided by the invention can improve the low signal-to-noise ratio and the multi-objective angle estimation accuracy under small sample conditions, and has the advantages of fast iterative convergence speed and high computational efficiency for estimating the target angle, which can be applied to the real-time multi-objective angle estimation system and has important engineering application value.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
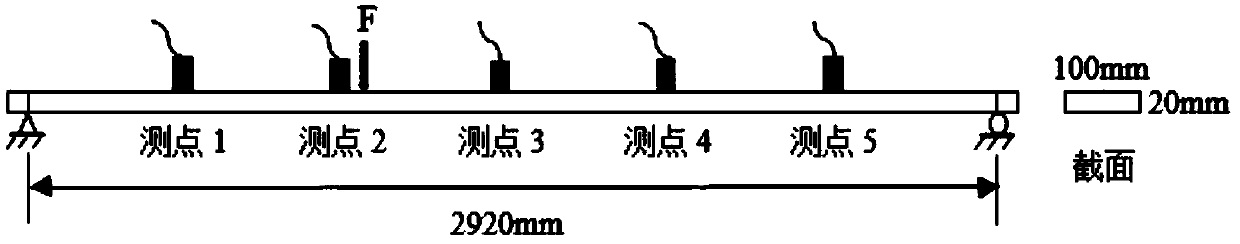
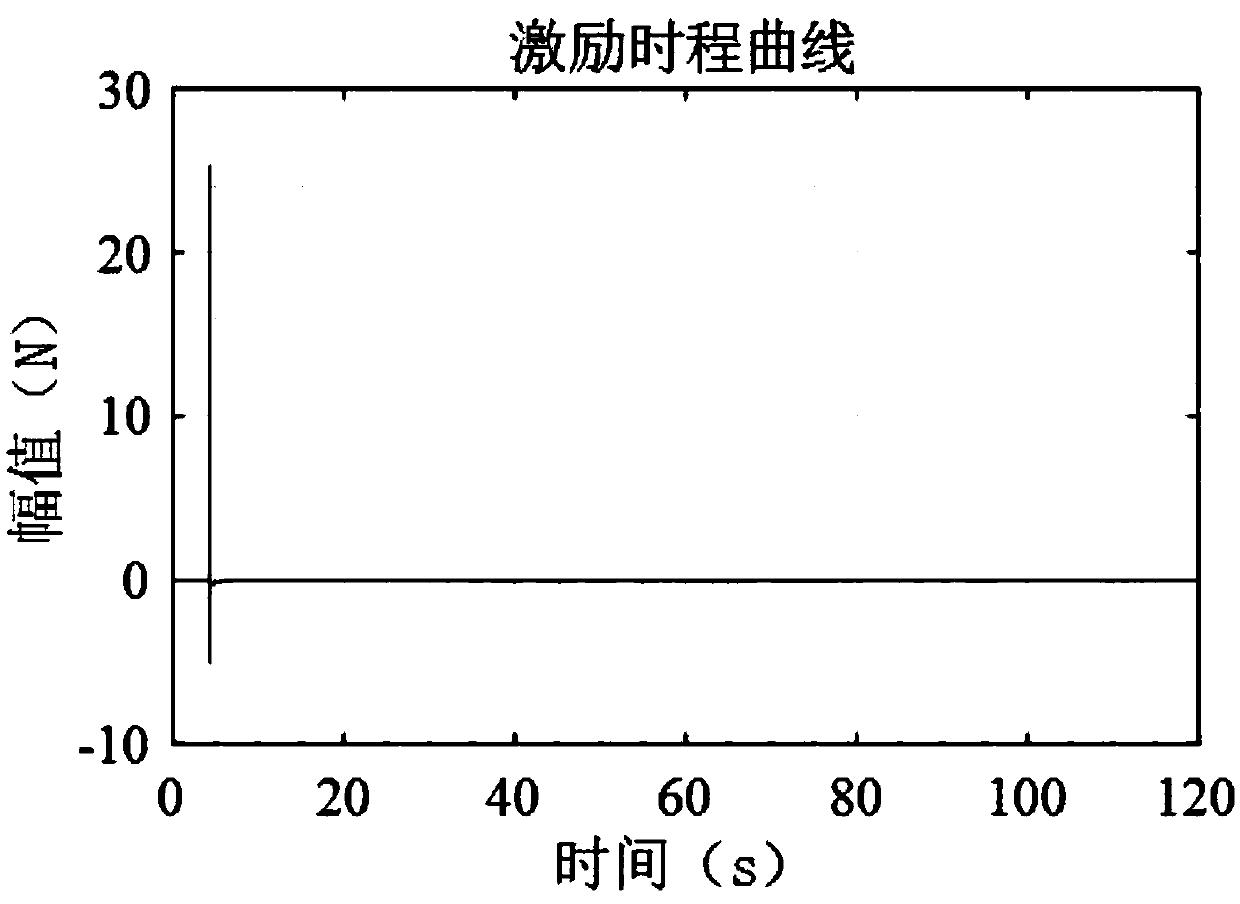
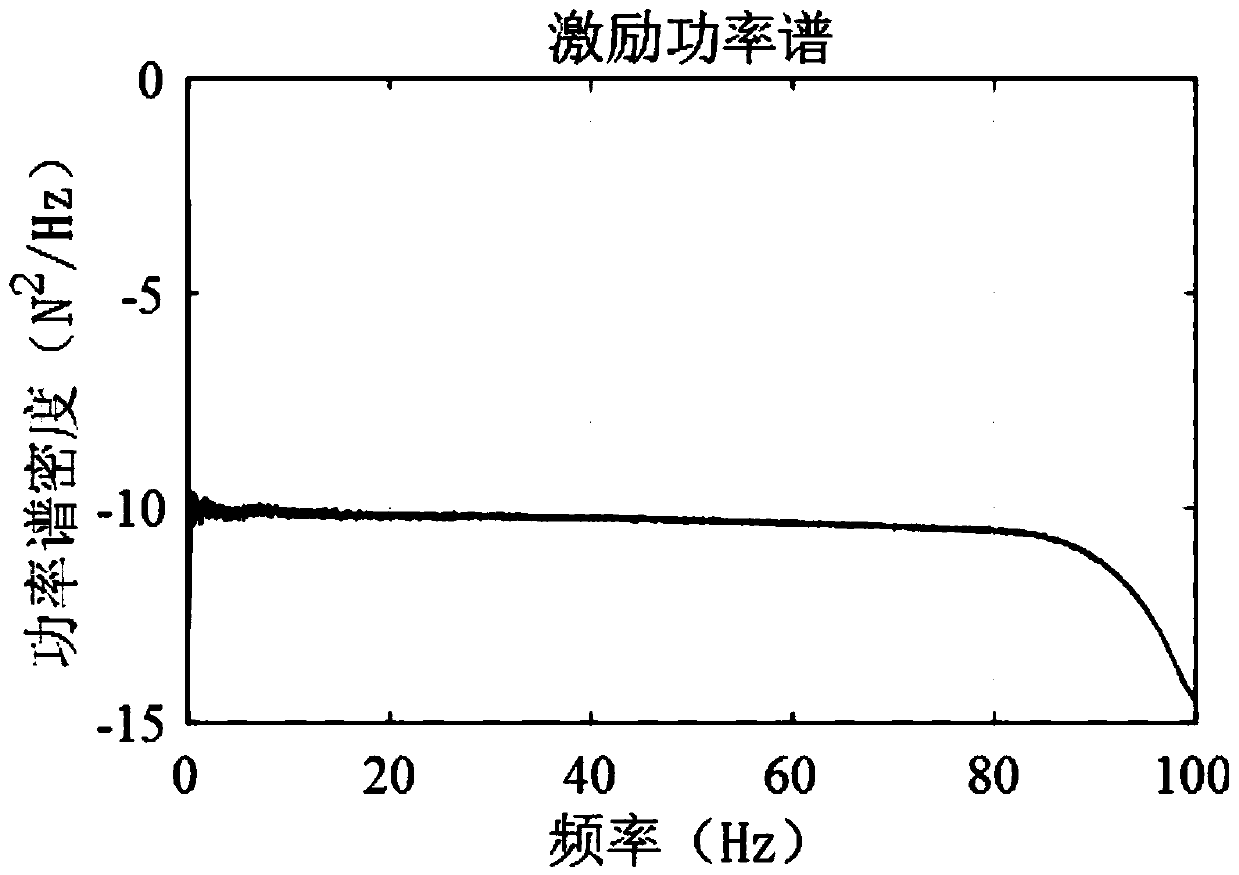
An algorithm for correcting structure model parameters based on a frequency response function
ActiveCN109598027AQuantitative uncertaintyImprove calculation accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsElement modelFrequency function
The invention relates to an algorithm for correcting structure model parameters based on a frequency response function, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring time history data and time history response data, and introducing a multivariate circle symmetry proportion distribution theorem to derive and obtain a probability density function and a covariance matrix of the actually measuredfrequency response function; Introducing a prediction error and a to-be-corrected parameter to obtain a covariance matrix containing the to-be-corrected parameter; Obtaining a probability density function of a frequency response function under the action of single-point excitation according to the determinant and the inverse theorem of the matrix; Obtaining a maximum likelihood function expressedin a form of a maximum likelihood function and a logarithm maximum likelihood function according to a maximum likelihood principle; Obtaining a posterior probability density function of the random variable according to the Bayesian theorem; And expressing the posterior probability density function as a logarithm likelihood function form, so that an objective function is obtained. The uncertainty of the correction parameters is quantized, the calculation precision of the correction parameters is improved, and the correction of the structure finite element model is realized.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
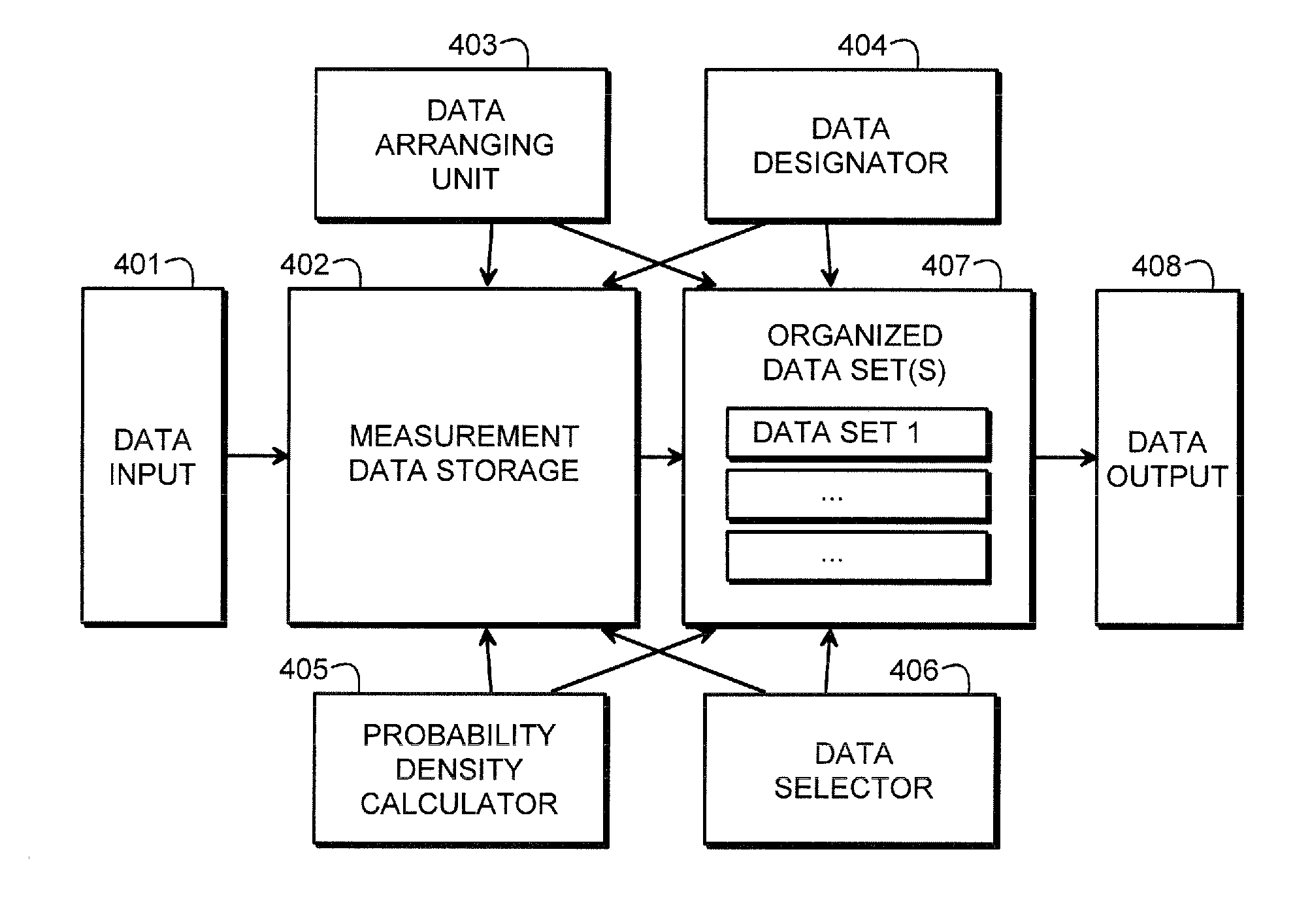
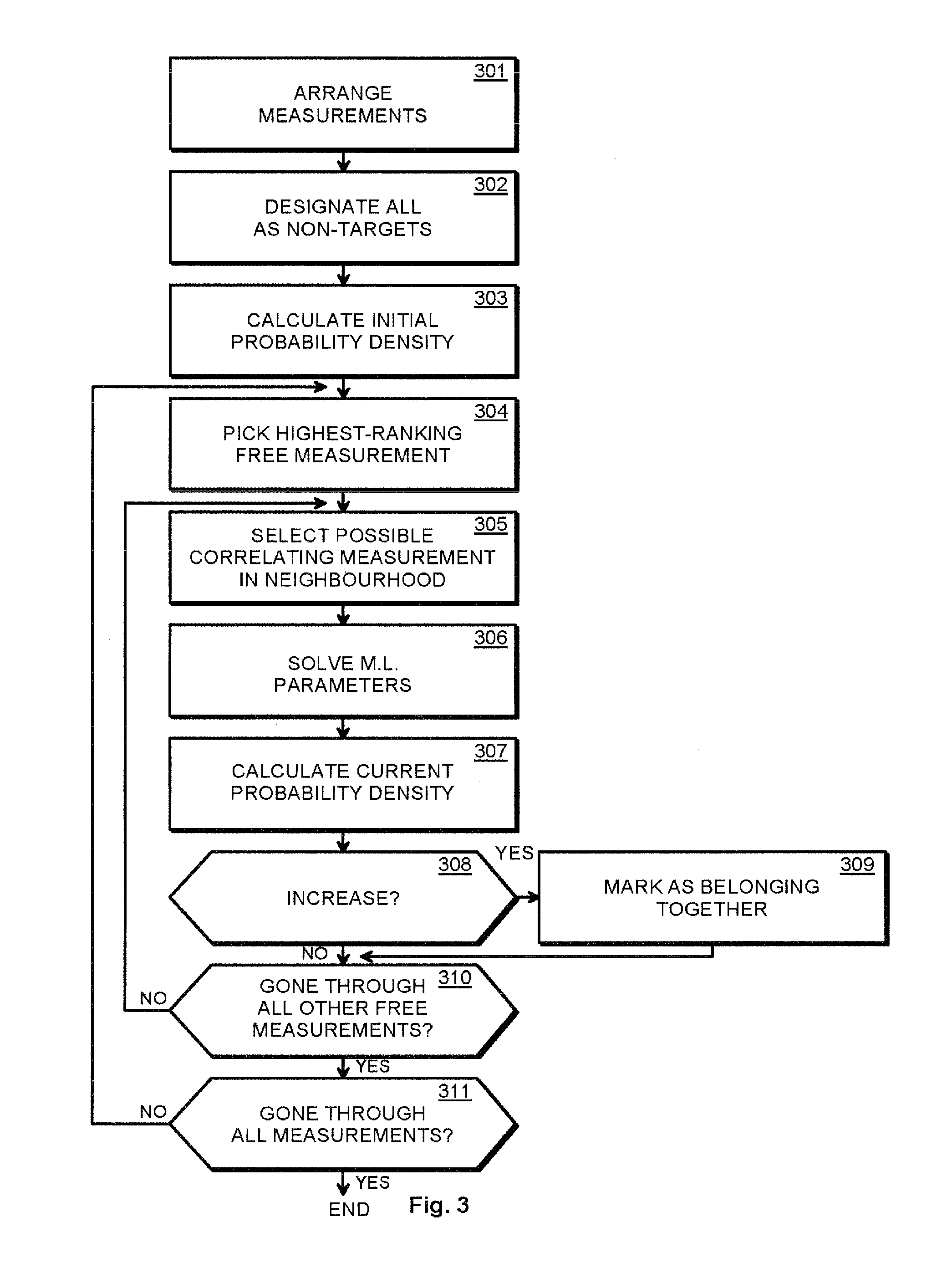
Methods and arrangements for detecting weak signals
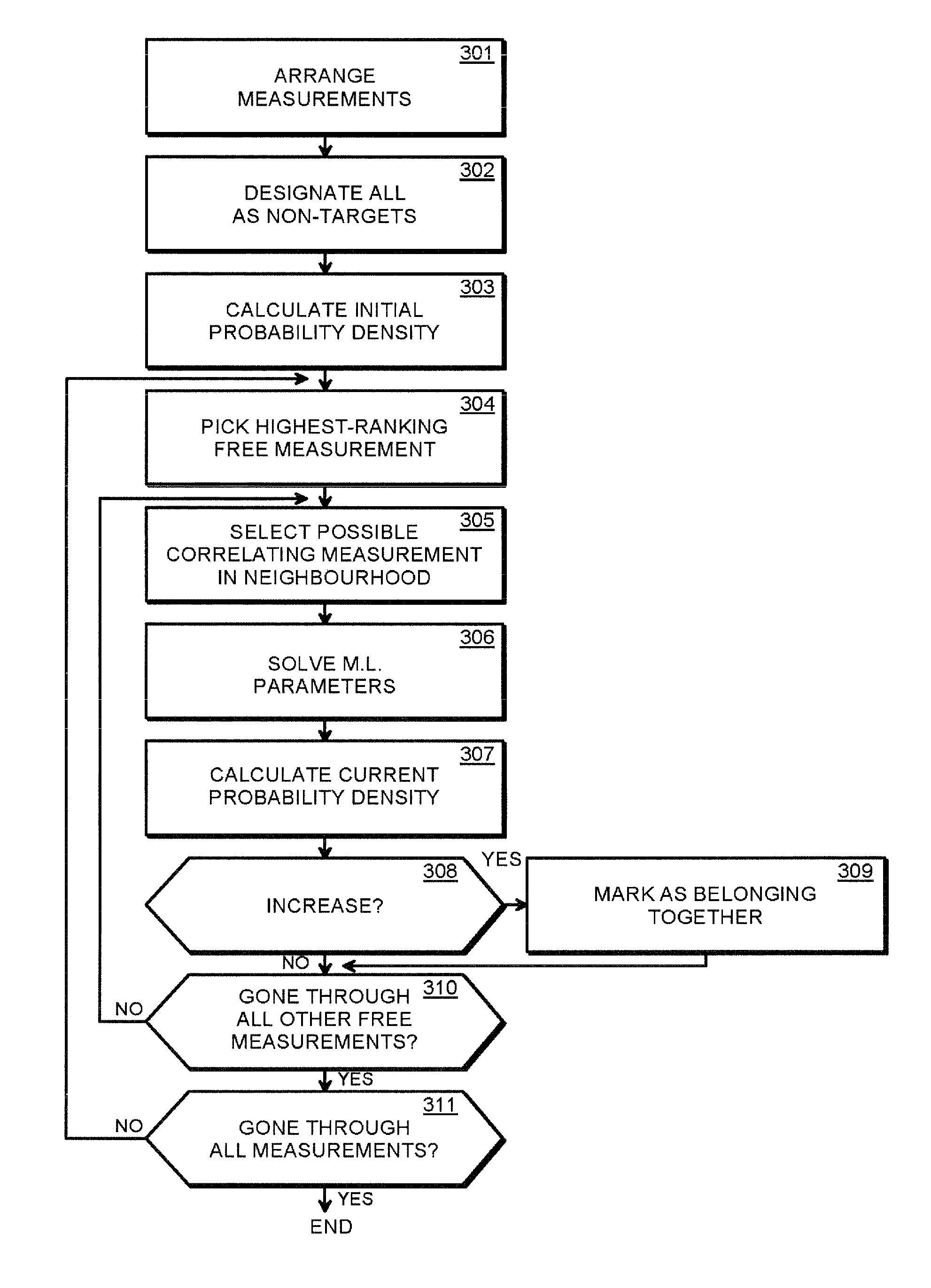
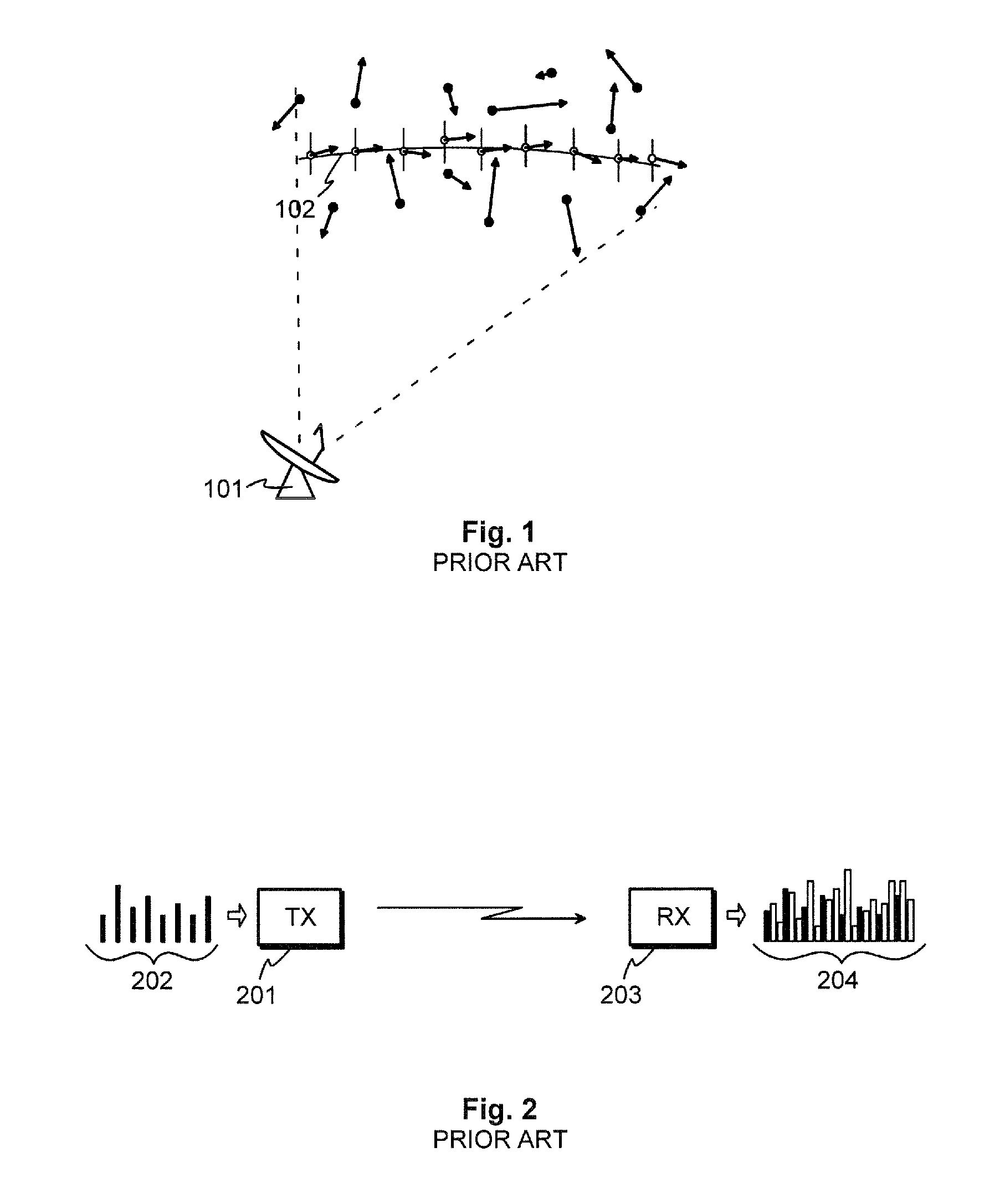
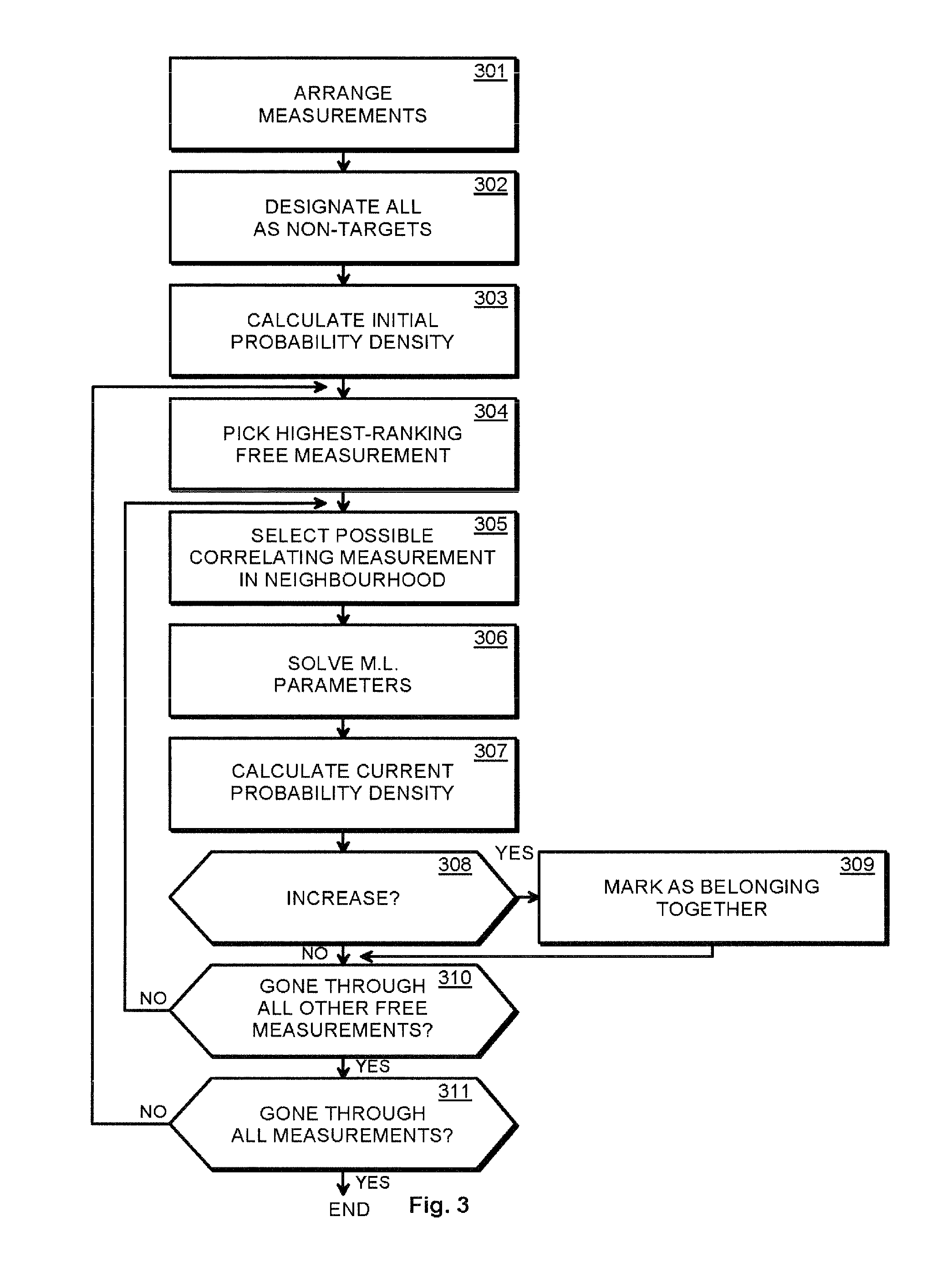
The invention provides a method and an arrangement for detecting moving point-targets within a large set of noisy measurements. The method is based on Bayesian model selection where the measurements containing targets are modeled with their physical trajectories and the non-target measurements are modeled with the statistical distribution of measurements containing no targets. An a posteriori probability density function is utilized together with a optimization algorithm specifically designed for this problem. Advantages of the invention involve a numerically efficient formulation of the a posteriori probability density, combined with the optimization algorithm. The main applications of the invention are in detecting moving targets within e.g., radar, sonar, lidar and telescopic measurements. The method is also applicable for multi-instrument data fusion.
Owner:RADAREAL
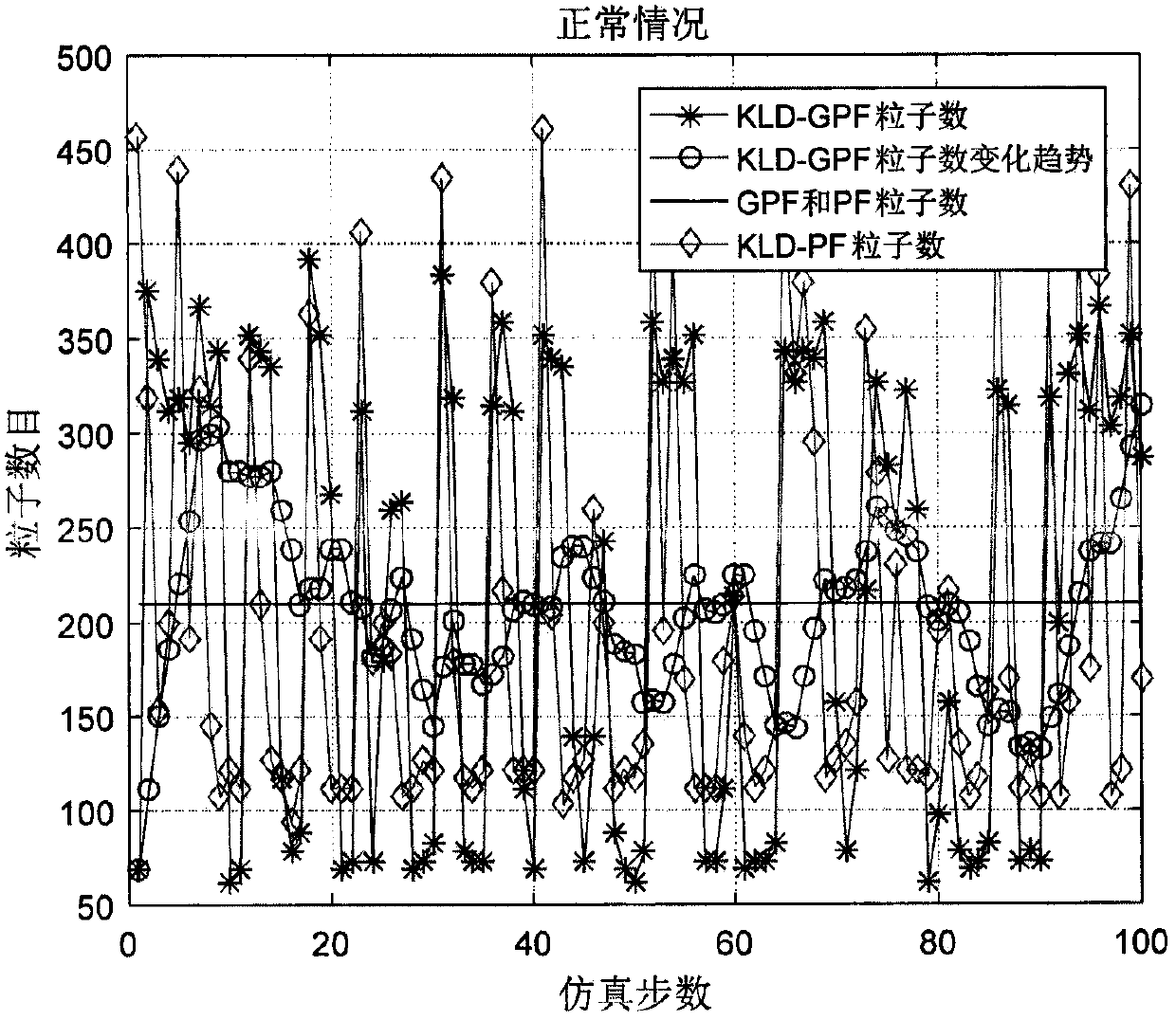
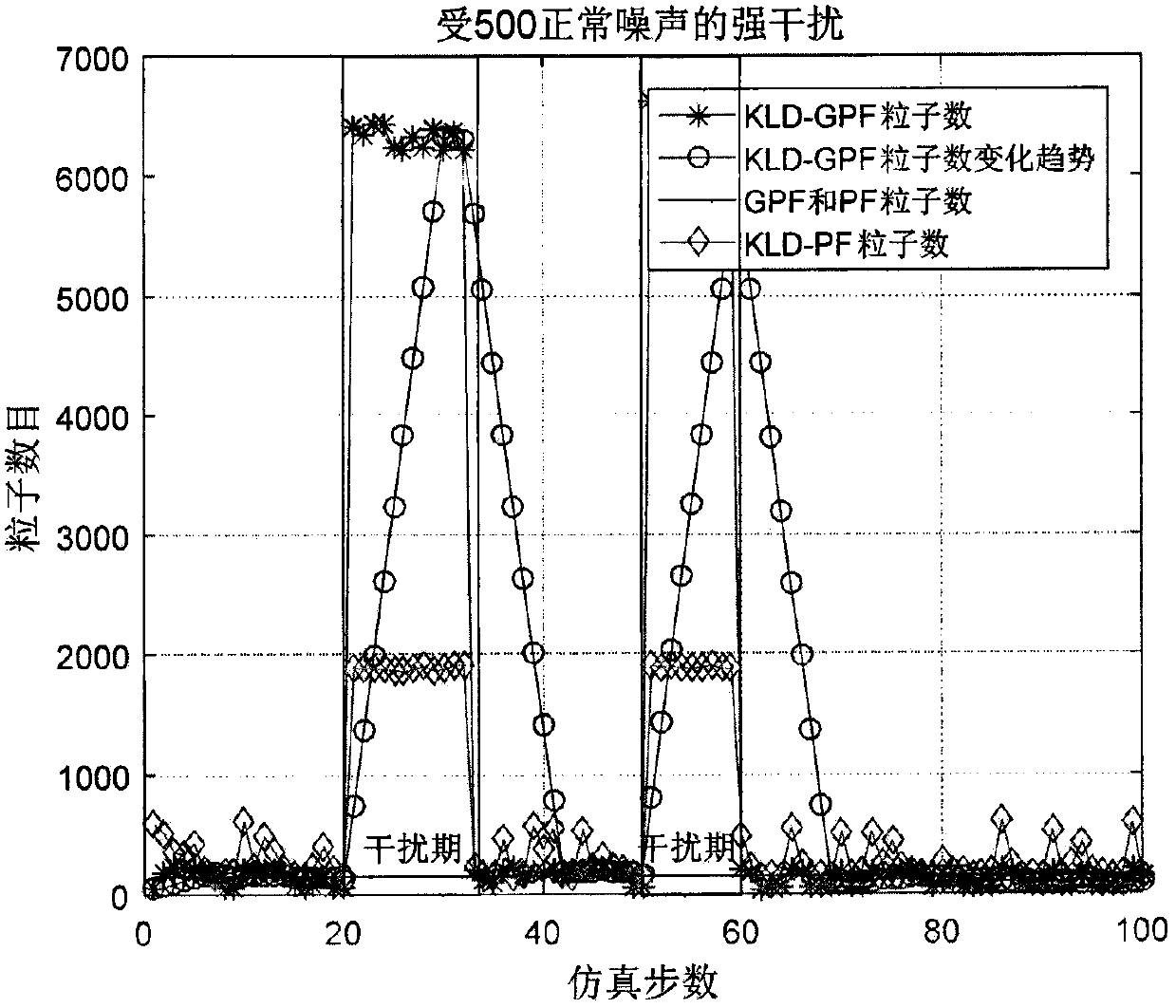
Improved Gaussian particle filter data fusion algorithm based on KLD sampling
InactiveCN110401430AImprove bindingSolving Gaussian Particle FilteringDigital technique networkNormal densityFilter algorithm
The invention provides an improved Gaussian particle filter algorithm (KLD-GPF) based on KLD, belongs to the technical field of signal processing, and relates to nonlinear filtering, and the method provided by the invention is suitable for state estimation of a nonlinear dynamic system. The algorithm can adaptively adjust the number of particles, and has a remarkable effect under the conditions that noise obeys Gaussian distribution and the statistical property of the noise is suddenly changed. According to the filtering algorithm, the Kullback-Leibler (KL) distance between a discrete probability density function (PDF) of particles and a real posterior probability density function is calculated online in the sampling process, and the size of a particle set is adjusted online according to the KL distance, so that the algorithm has relatively good robustness. The KLD-GPF can maintain a good estimation effect under the condition of sudden change of noise statistical characteristics. Compared with a KLD improved particle filtering algorithm (KLD-PF), although some filtering precision is lost, the filtering speed is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
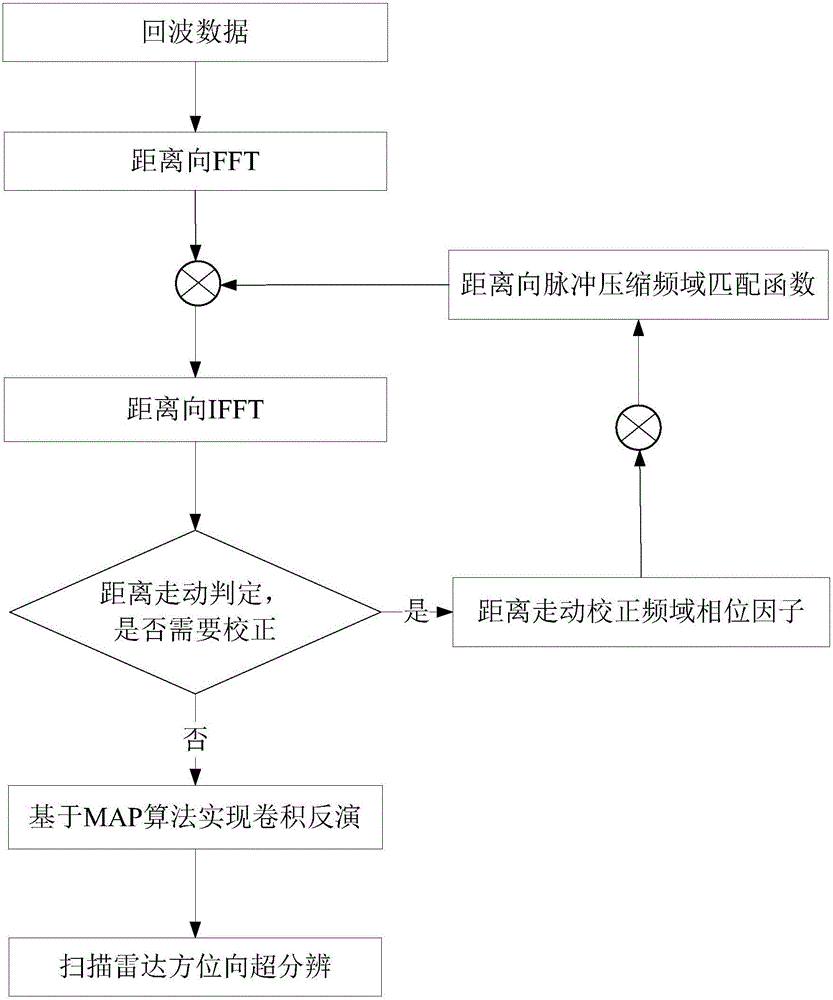
Bayesian seismic inversion method based on [tau] distribution
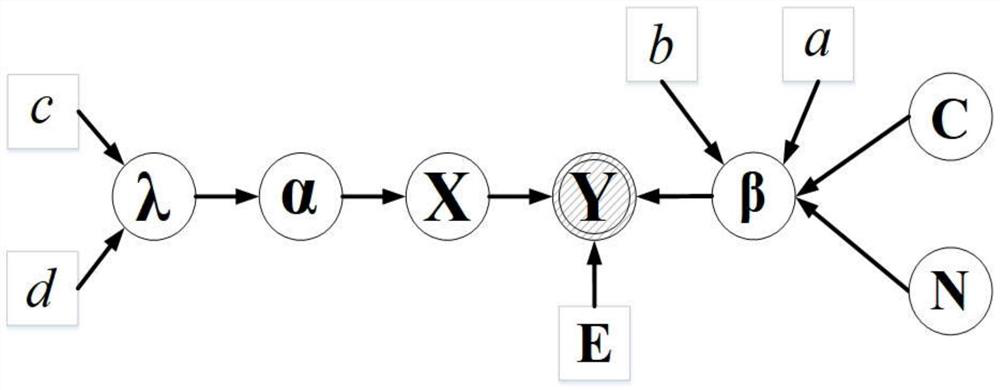
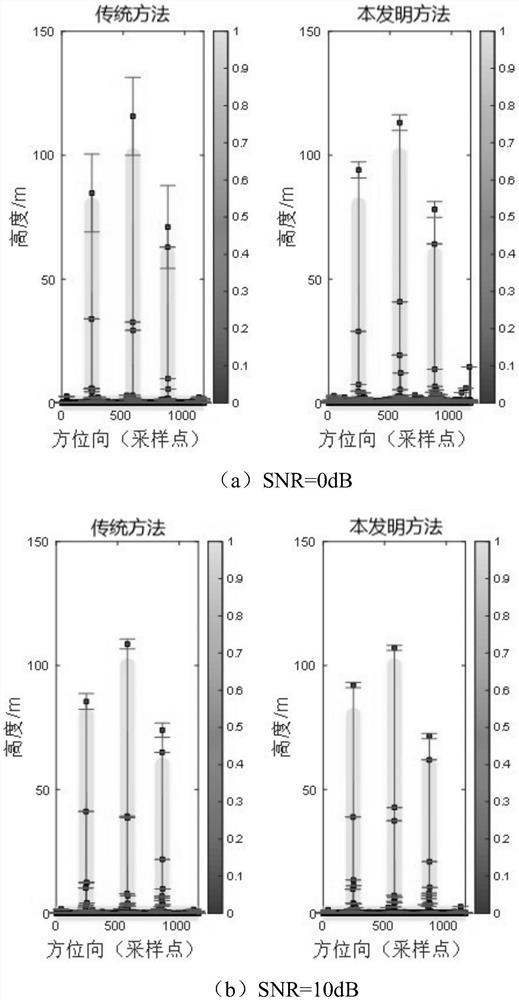
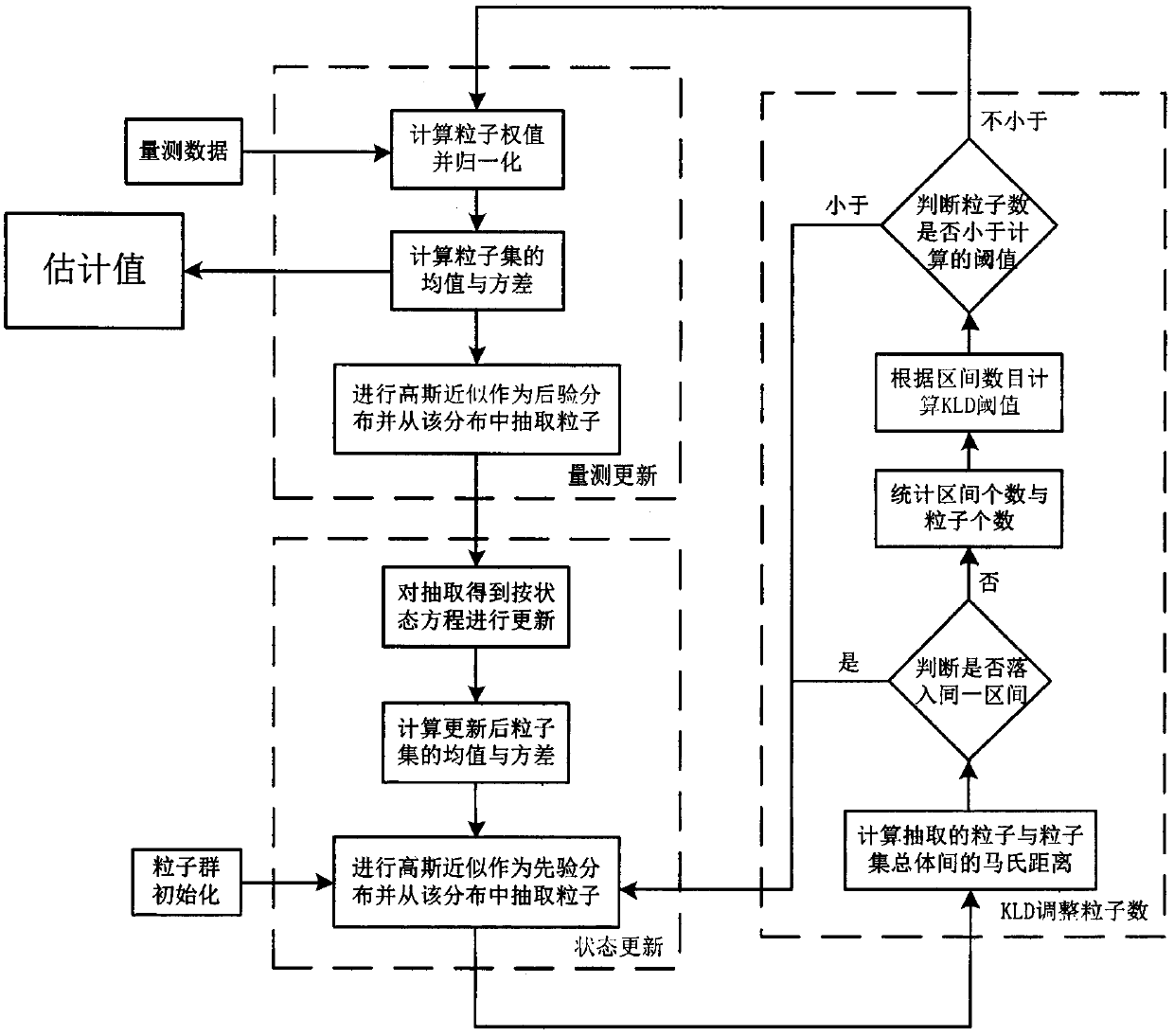
ActiveCN108663711ASolve the accuracy problemResolve resolutionSeismic signal processingImage resolutionGeophysical inversion
The invention discloses a Bayesian seismic inversion method based on [tau] distribution, and relates to the geophysical inversion and oil and gas reservoir prediction field. The method comprises the following steps: 1, inputting data to obtain an initial model of parameters to be inverted and determining parameters of [tau] distribution; 2, selecting an initial model of the t-th channel parameteras an iteration initial model, determining a prior probability density distribution function by parameterized [tau] distribution, inputting data to obtain posterior probability density function and performing MCMC inversion to obtain an inversion result; and 3, determining whether t is greater than seismic data in the input data, if yes, ending inversion to obtain a to-be-inverted wave impedance profile based on the inversion result, and if not, accumulating t and jumping to the step 2 for continuous inversion. The method solves the problem that the existing seismic inversion uses the Gaussiandistribution to simulate the seismic reflection coefficient distribution, resulting in the low precision and resolution of inversion physical parameters, and achieves the effect of improving the accuracy and resolution of the inversion physical parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Nonlinear filtering method for underwater navigation
ActiveCN102252672AGuaranteed smoothnessImprove edge sharpnessNavigation instrumentsTerrainUnderwater navigation
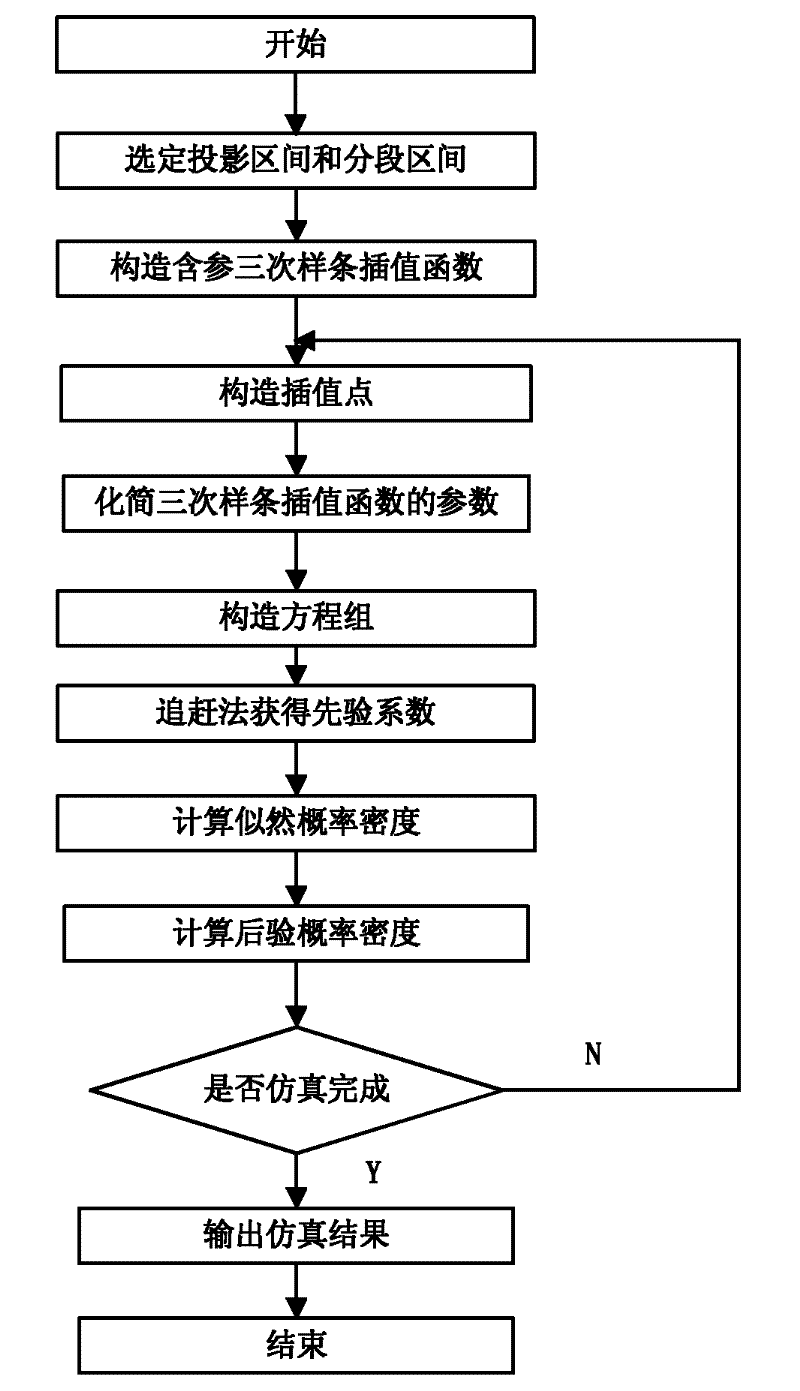
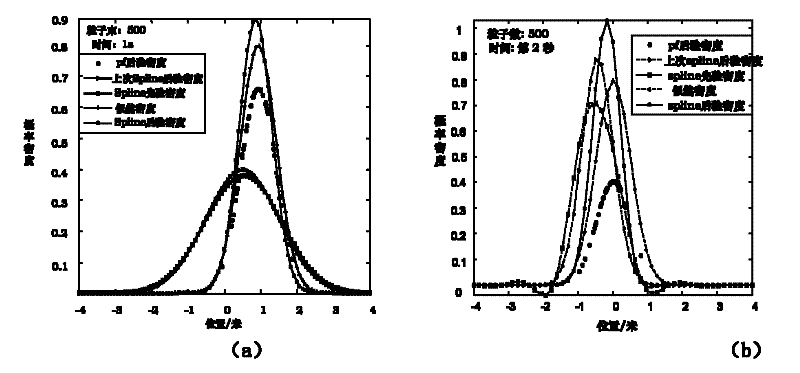
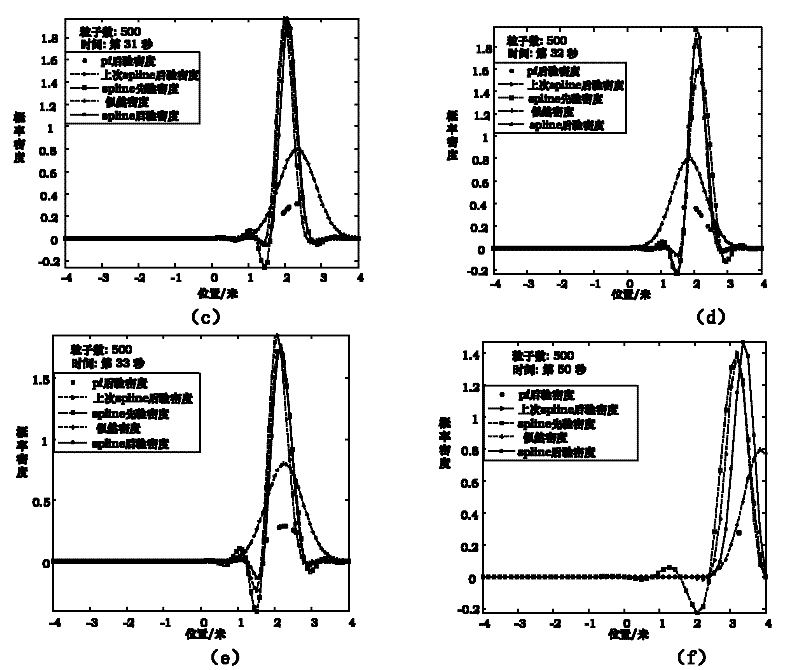
The invention discloses a nonlinear filtering method for underwater navigation, and is used to solve a weak solution from a random differential model of underwater terrain navigation. According to the invention, segmental approach to a weak solution of a navigation random differential model is performed by using a cubic spline interpolation function so as to obtain a prior probability density function of a state, wherein difficult problems for constructing a cubic spline interpolation point are solved by using a forward Kolmogorov equation, and a posterior probability density function of the state is obtained by a Bayes formula. The method of the invention makes full use of the cubic spline interpolation, has the characteristics of simple calculation, good stability, guaranteed convergence, easy realization on computers, and guaranteed smoothness of a whole curve, can track various possibility of the system state better, has extremely high estimation accuracy, convergence speed, and convergence smoothness, and can track the change of the system state well.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

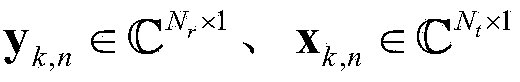
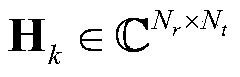
![Bayesian seismic inversion method based on [tau] distribution Bayesian seismic inversion method based on [tau] distribution](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/90667bbd-5df0-4e7f-8cc1-6b62faf50728/HDA0001618632460000011.png)
![Bayesian seismic inversion method based on [tau] distribution Bayesian seismic inversion method based on [tau] distribution](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/90667bbd-5df0-4e7f-8cc1-6b62faf50728/HDA0001618632460000021.png)
![Bayesian seismic inversion method based on [tau] distribution Bayesian seismic inversion method based on [tau] distribution](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/90667bbd-5df0-4e7f-8cc1-6b62faf50728/HDA0001618632460000022.png)