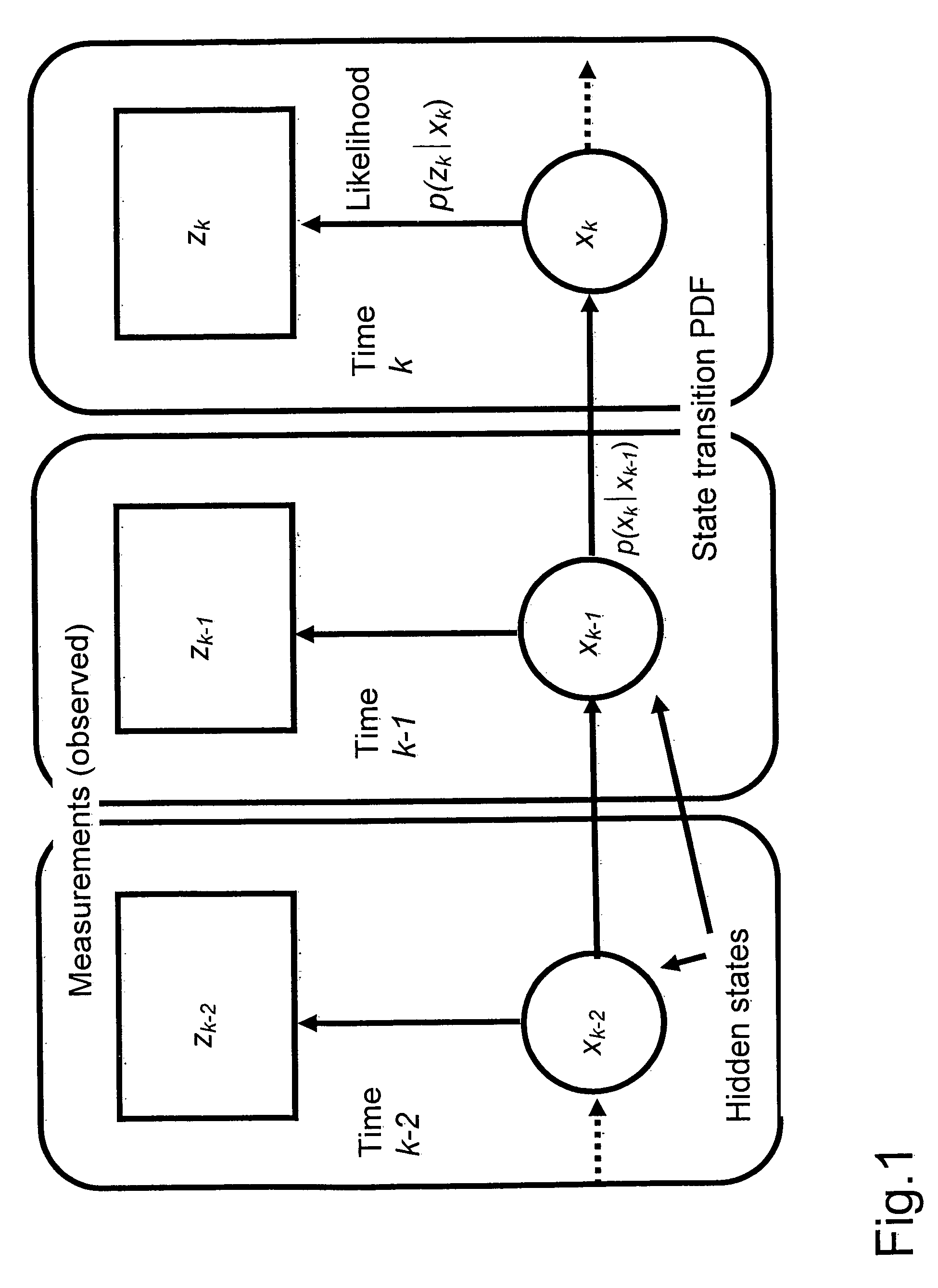
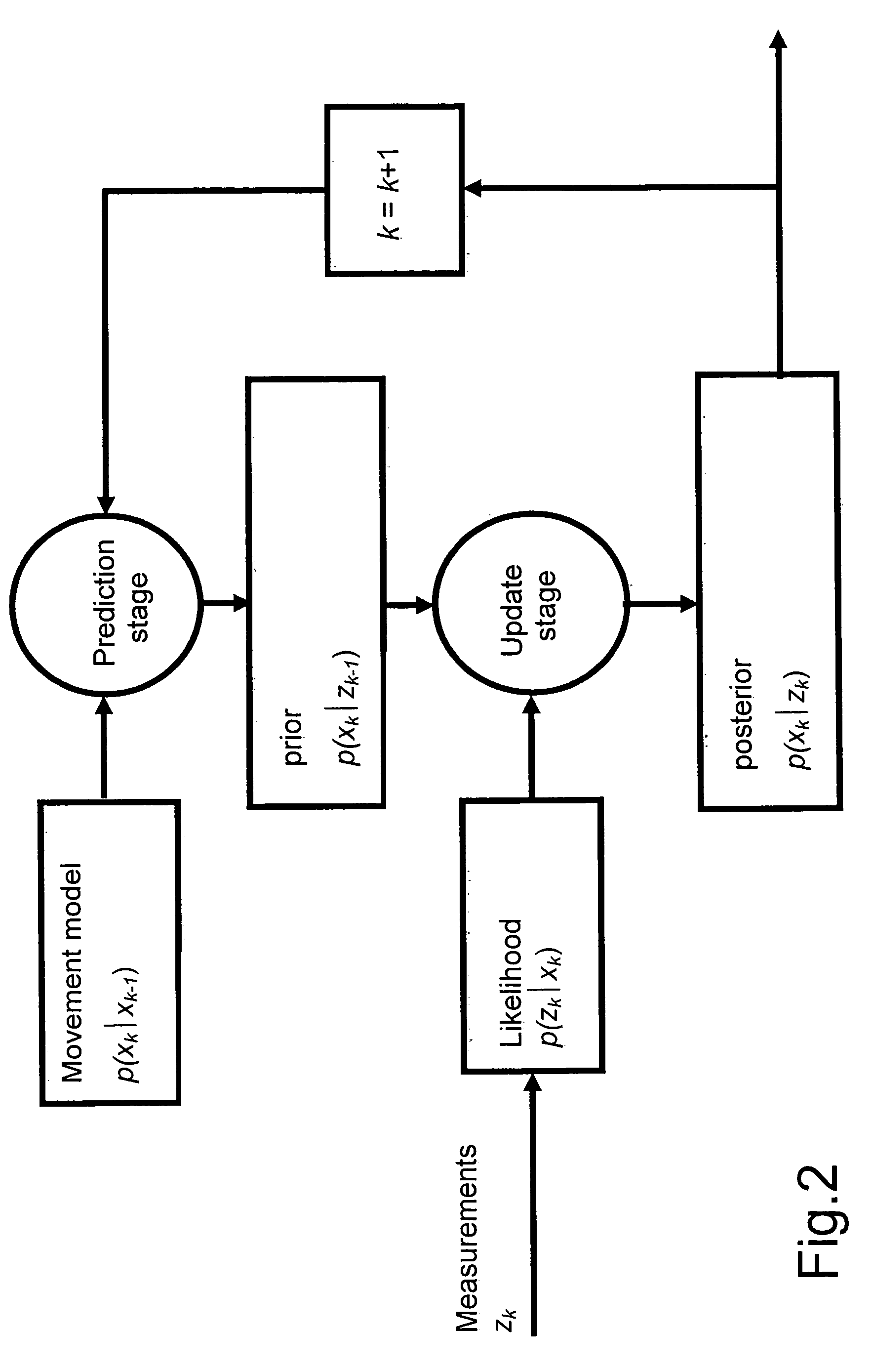
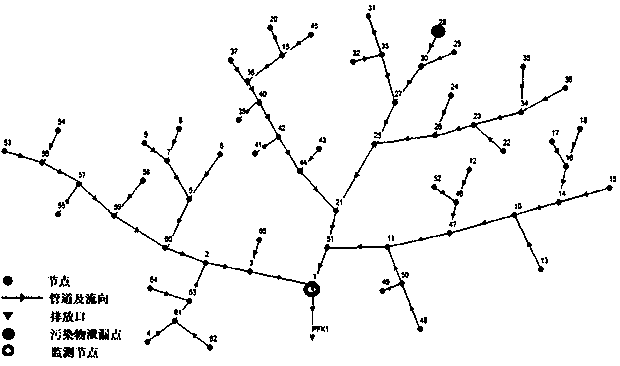
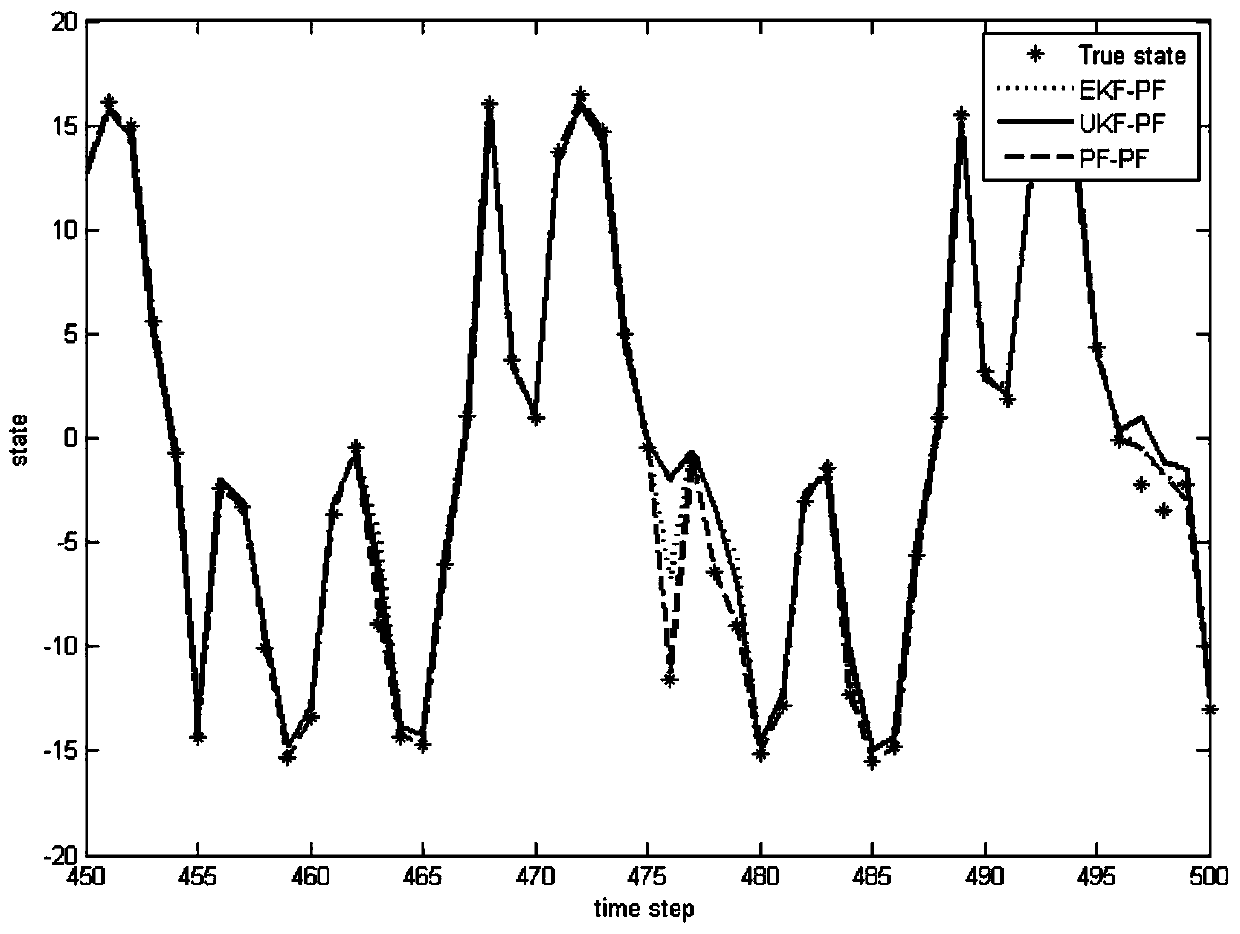
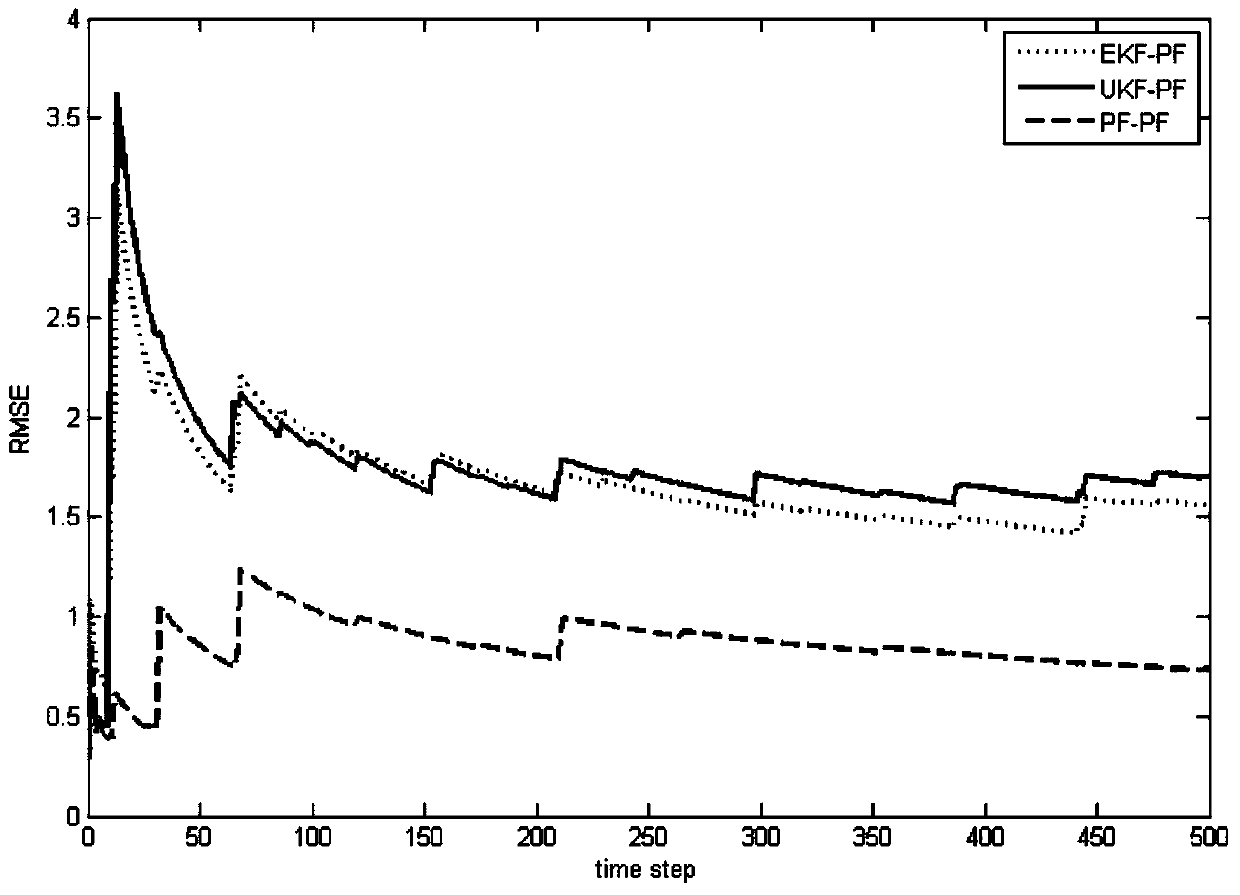
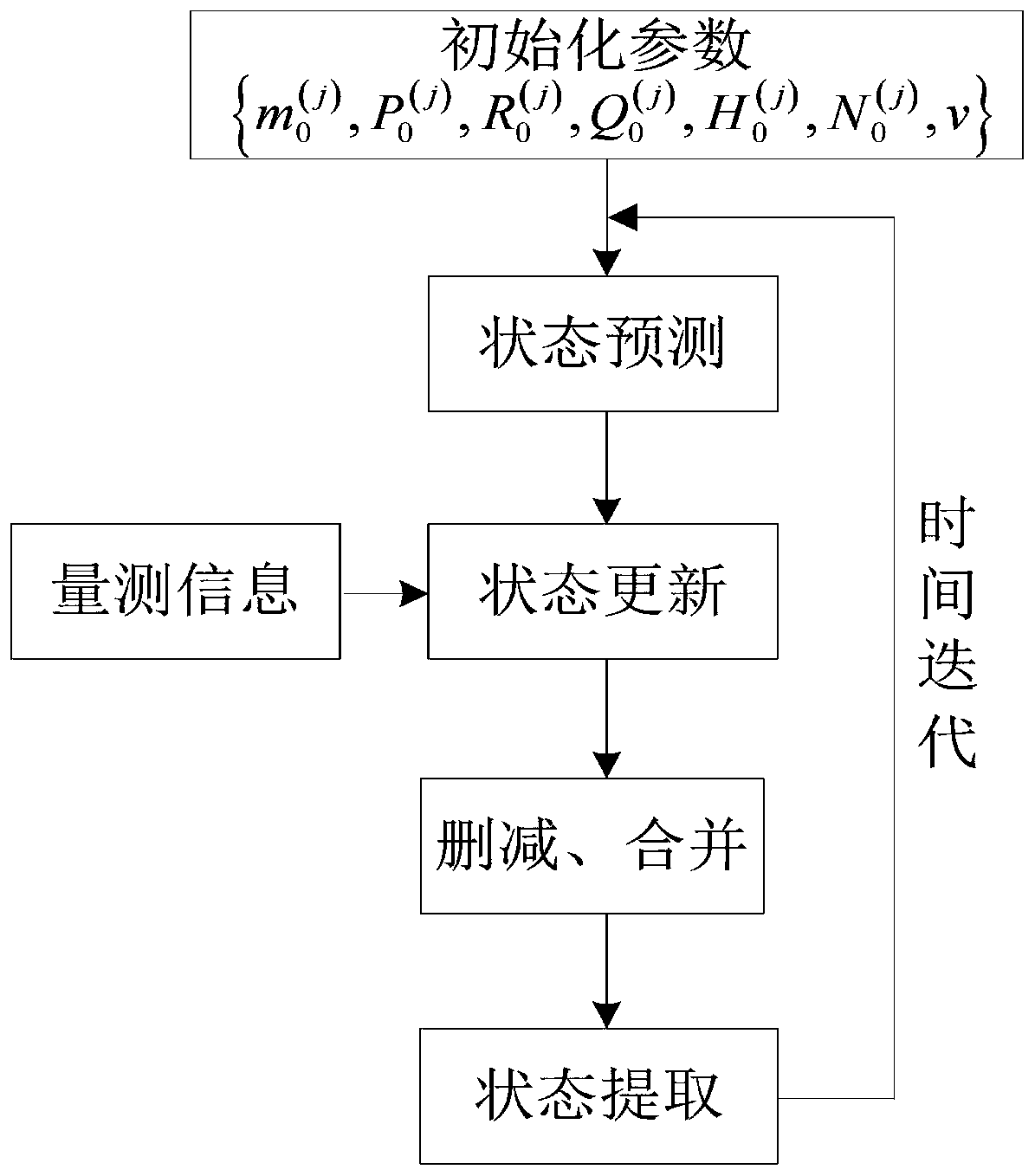
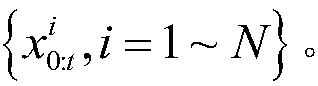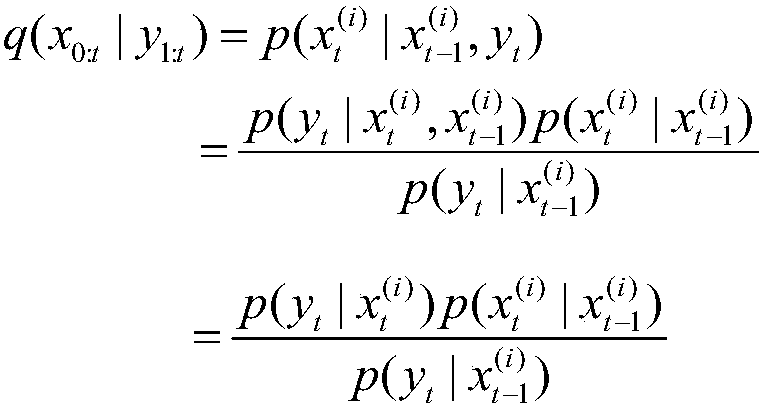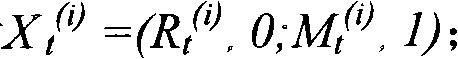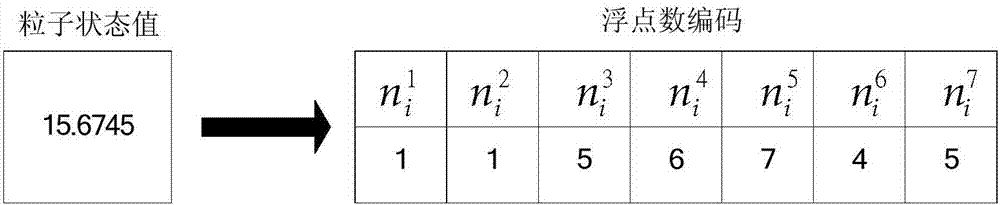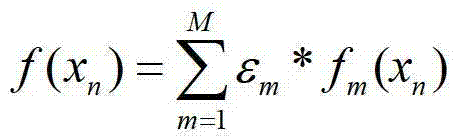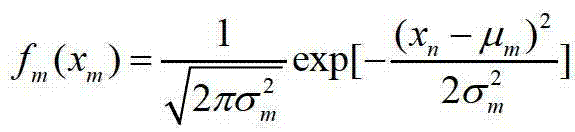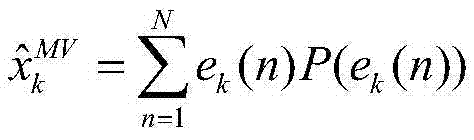Patents
Literature
58 results about "Posterior probability density" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for simultaneous localization and mapping of mobile robot based on improved particle filter
InactiveCN107246873AEasy to keepReduce the impactNavigational calculation instrumentsPosterior probability densitySimultaneous localization and mapping
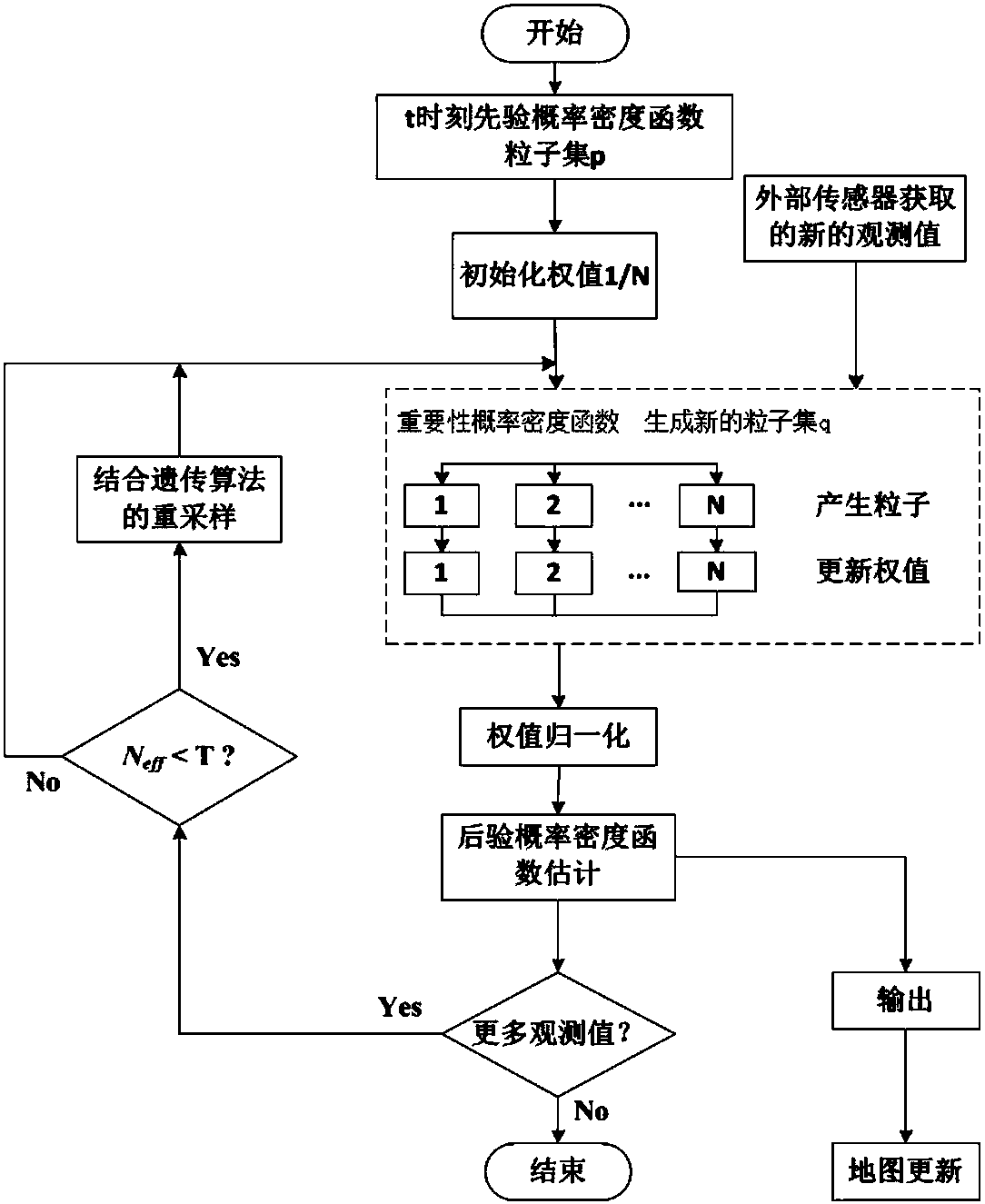
The invention discloses a method for simultaneous localization and mapping of a mobile robot based on an improved particle filter. The method comprises the following steps: initializing an initial-moment pose of a robot; obtaining a t-moment prior probability density function according to the pose information at a t-1 moment, and generating a sampling particle set p; initializing the weights of particles; selecting an importance probability density function, generating a new sampling particle set q, calculating the weights of particles, updating the weights of the particles, and normalizing the weights; calculating the weighted sum of random sample particles at current moment t to express posterior probability density, and obtaining the moving pose and environmental map information; judging whether a new observed value is input; if so, returning; otherwise, ending the cycle; before returning, judging whether resampling is needed or not. According to the difference of the system state, a dynamic threshold is set for judgment, and a genetic algorithm is combined. According to the method disclosed by the invention, influence of a problem of particle degeneration on SLAM is reduced, and the calculated amount of the SLAM problem is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for estimating hidden channel parameters of a received GNNS navigation signal
ActiveUS20090074038A1Reduce complexityImprove reliabilityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSatellite radio beaconingPosterior probability densityDynamic channel
For the reduction of the multipath error of received GNSS navigation signals, a sequential Bayesian estimation is used, with a movement model underlying this estimation, which model is particularly designed for dynamic channel situations. Sequential Monte Carlo methods are used to calculate the posterior probability density functions of the signal parameters. To facilitate an efficient integration in received signal tracking loops, the invention builds on complexity reduction concepts that have previously been used in maximum likelihood (ML) estimators.Applicable with GNSS satellite navigation receivers, e.g. GPS and Galileo.
Owner:DEUTSCHES ZENTRUM FUER LUFT & RAUMFAHRT EV
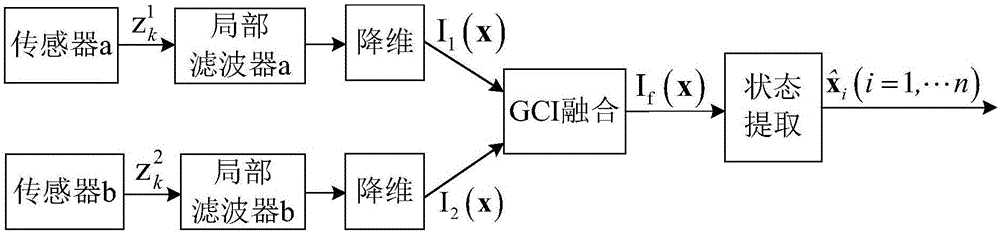
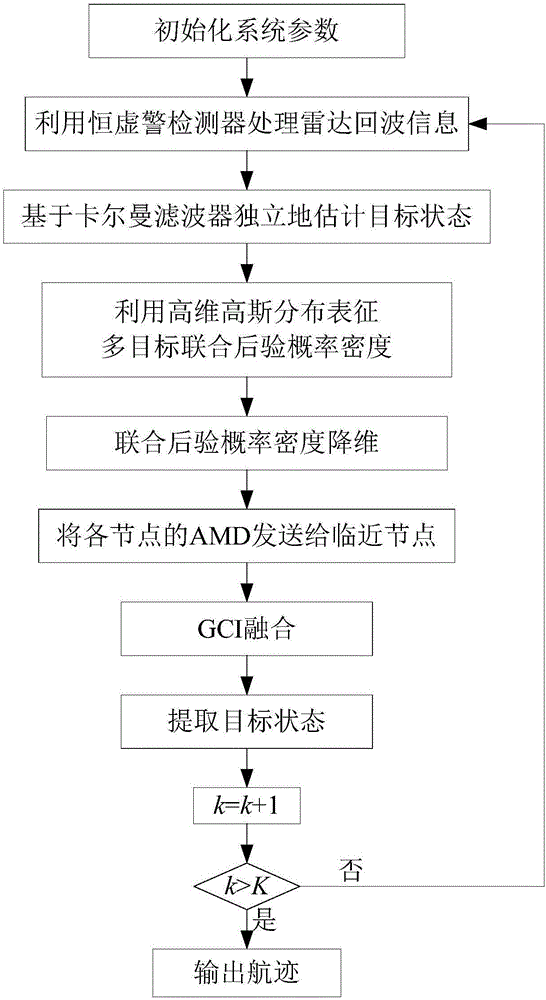
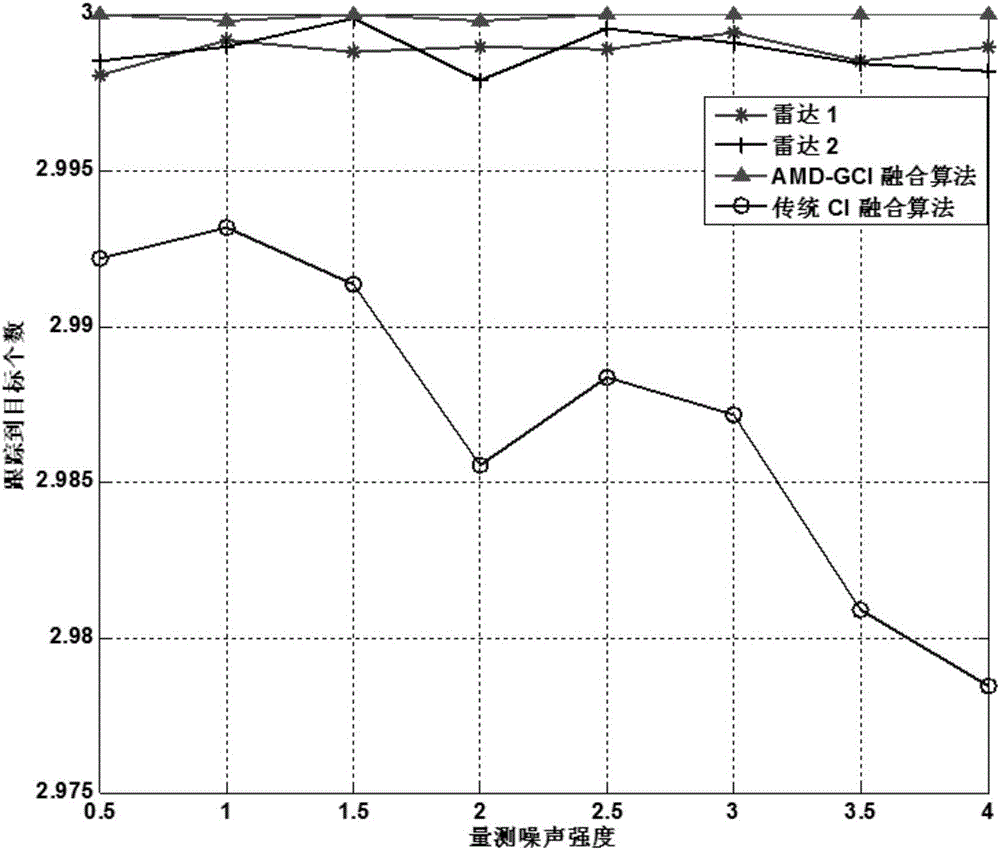
Distributed multi-sensor fusion algorithm based on AMDs
ActiveCN106291533AAchieve integrationFusion simpleRadio wave reradiation/reflectionAlgorithmHigh dimensional
The invention discloses a distributed multi-sensor fusion algorithm based on AMDs. The algorithm comprises the following steps: S1, initializing system parameters; S2, using a constant false alarm detector to process radar echo information to obtain a measurement information set; S3, independently estimating a target state based on a kalman filter, S4, using high dimensional Gaussian distribution to represent the multi-objective joint posterior probability density; S5, carrying out the dimensionality reduction operation on the joint posterior probability density; S6, sending the AMD of each node to the adjacent nodes; S7, fusing the AMDs by using a generalized cross-covariance algorithm; S8, extracting the target state; S9, setting k = k + 1, if k>K, outputting the target state extracted in the S8 as a track; otherwise, returning to step S2. The distributed multi-sensor fusion algorithm realizes the joint fusion of a plurality of targets under the condition that the estimation errors of the different sensors are considered cross-correlated, has higher adaptability and better robustness, and effectively solves the problem of multi-target joint posteriori fusion in the traditional tracking system.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
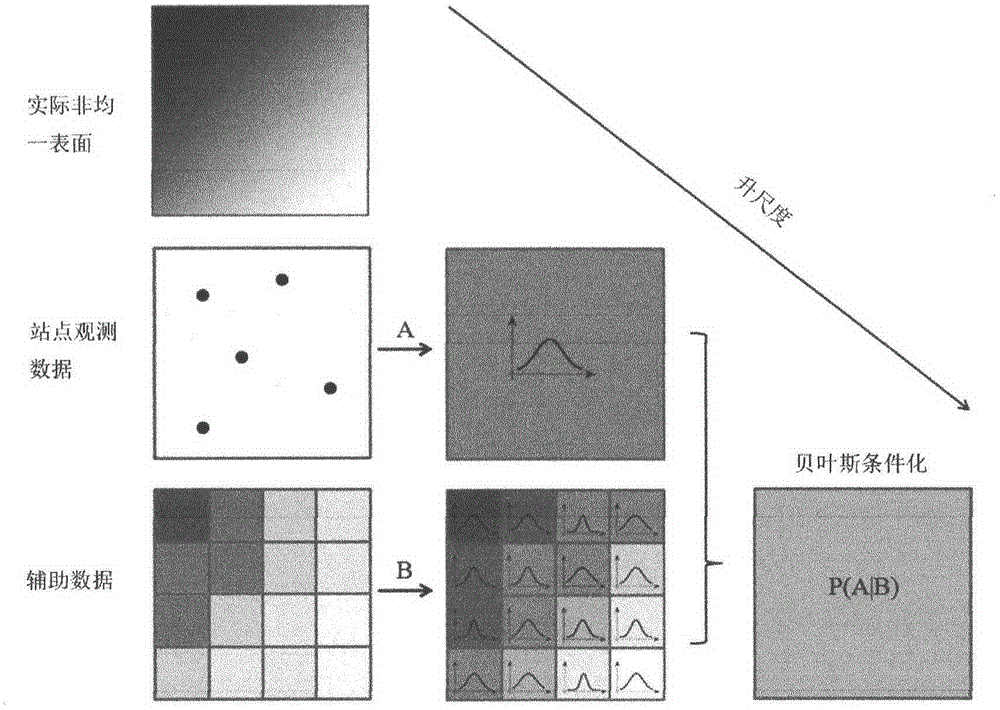
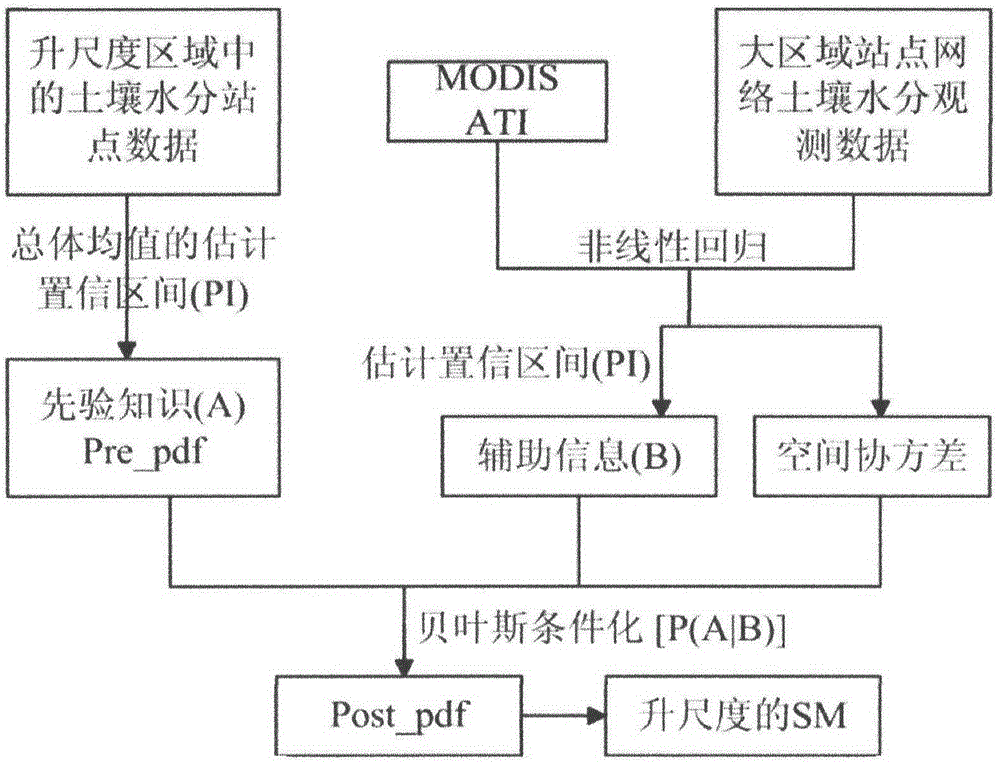
Soil moisture site data upscaling method based on Bayesian theory
InactiveCN104573393AReduce uncertaintySpecial data processing applicationsConfidence intervalSoft data
The invention discloses a soil moisture site data upscaling method based on the Bayesian theory. The soil moisture site data upscaling method includes steps of estimating prior probability density distribution function pre_pdf of a target variable on the basis of sparse site observation data in an upscaling area; inversing MODIS ATI into SM by establishing nonlinear regression relation between the SM and the MODIS ATI, estimating an estimated confidence interval of the soil moisture nonlinear regression and probability distribution as soft data in a probability form; integrating the prior distribution of the target variable and auxiliary information of the probability form from the MODIS ATI through the Bayesian theory, and acquiring posterior probability density distribution function post_pdf of the target variable; calculating the value of the target variable in the maximum probability through maximization of the posterior probability distribution function. By the soil moisture site data upscaling method, uncertainties caused by scale difference between soil moisture remote sensing products and ground site authentication data are effectively reduced. The soil moisture site data upscaling method can be applied to upscaling application of other ground surface parameters.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
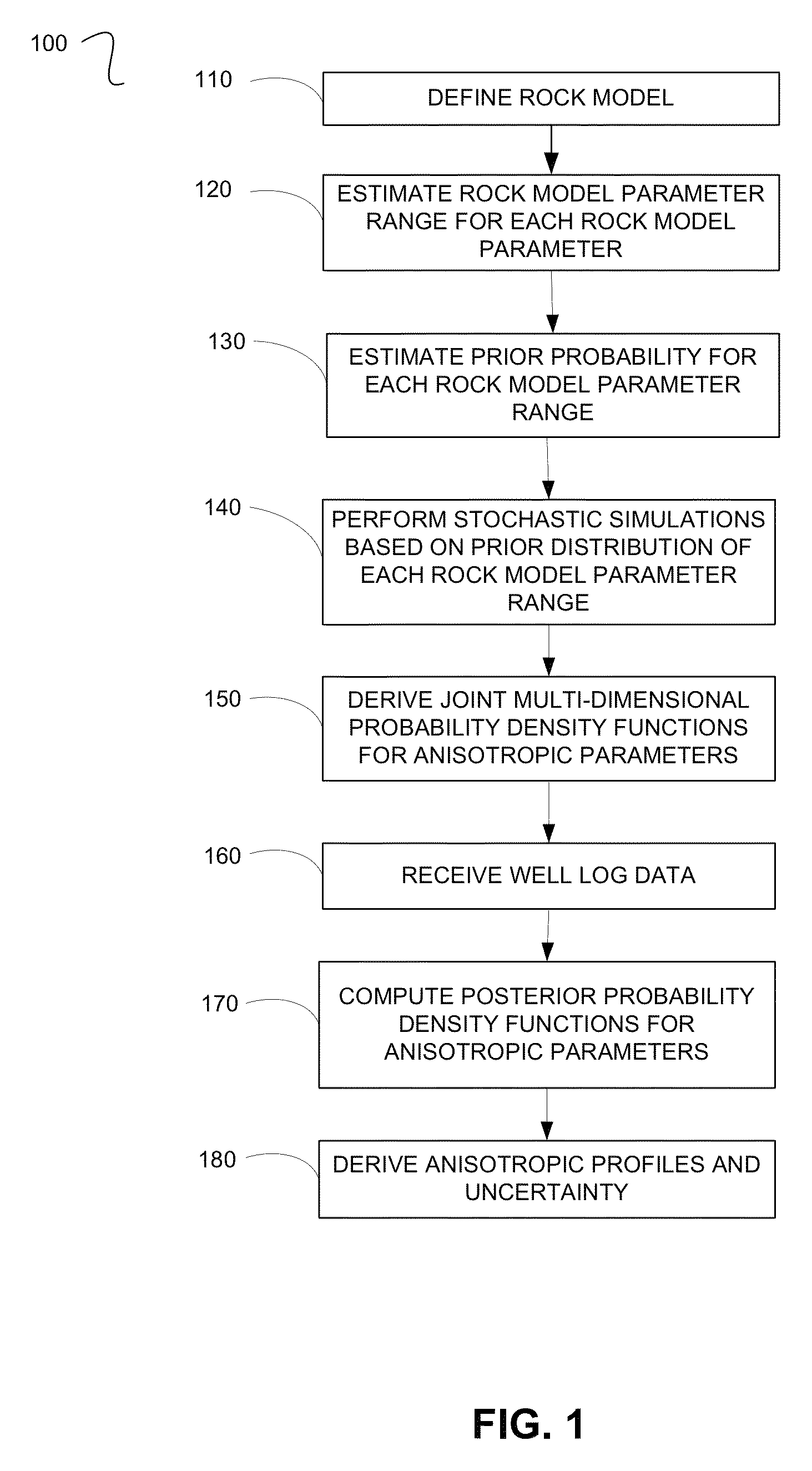
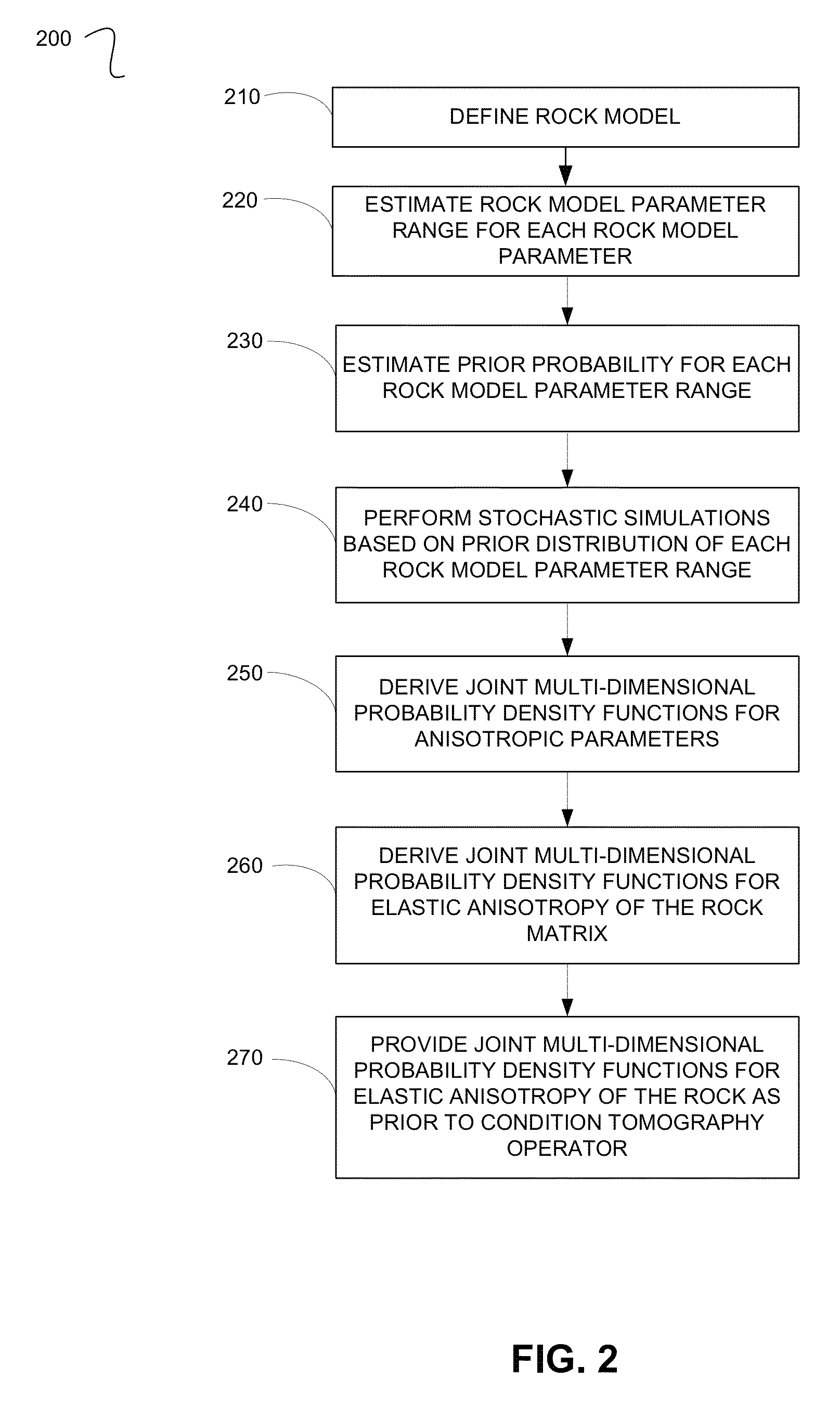
Estimating Anisotropic Parameters
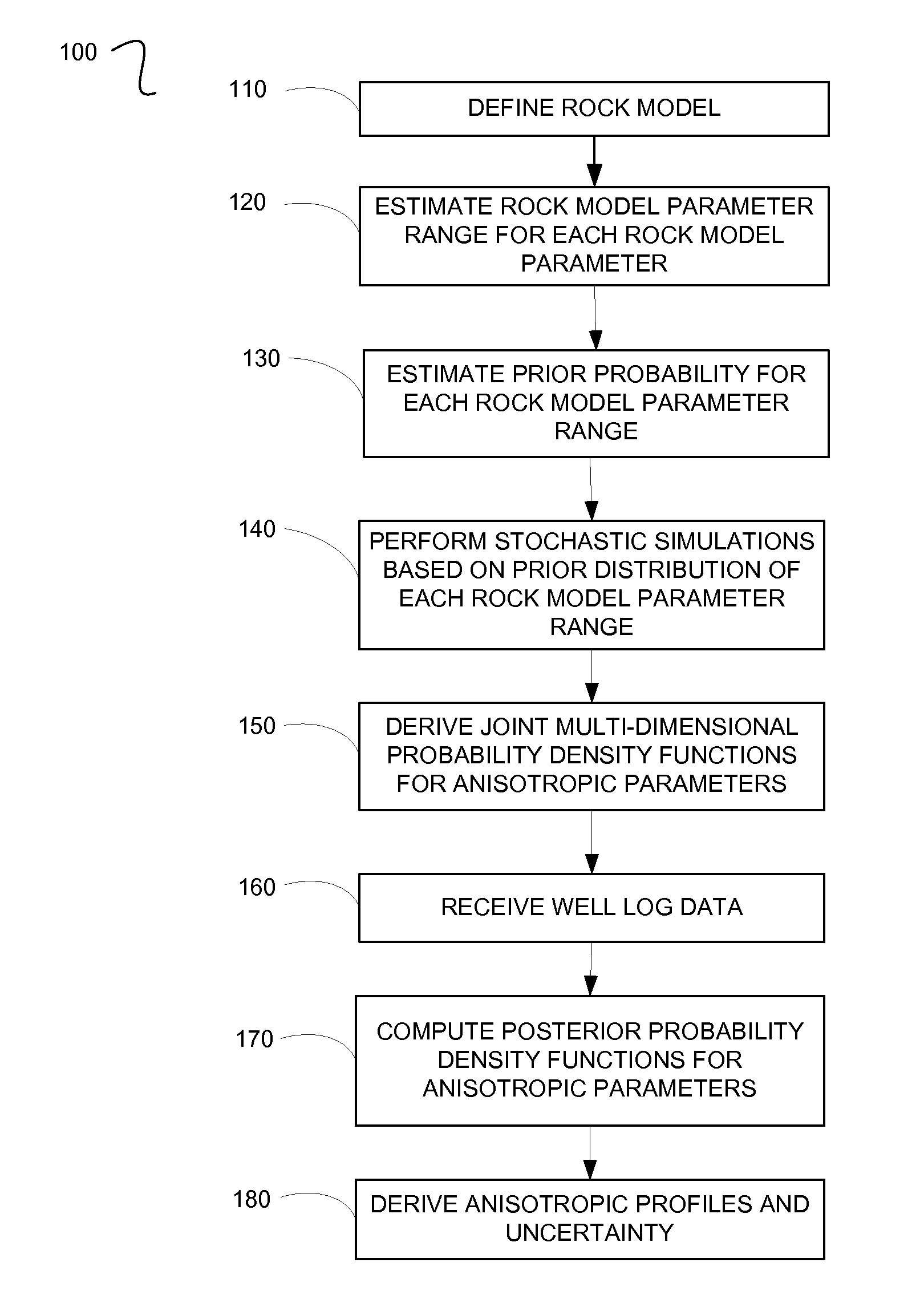
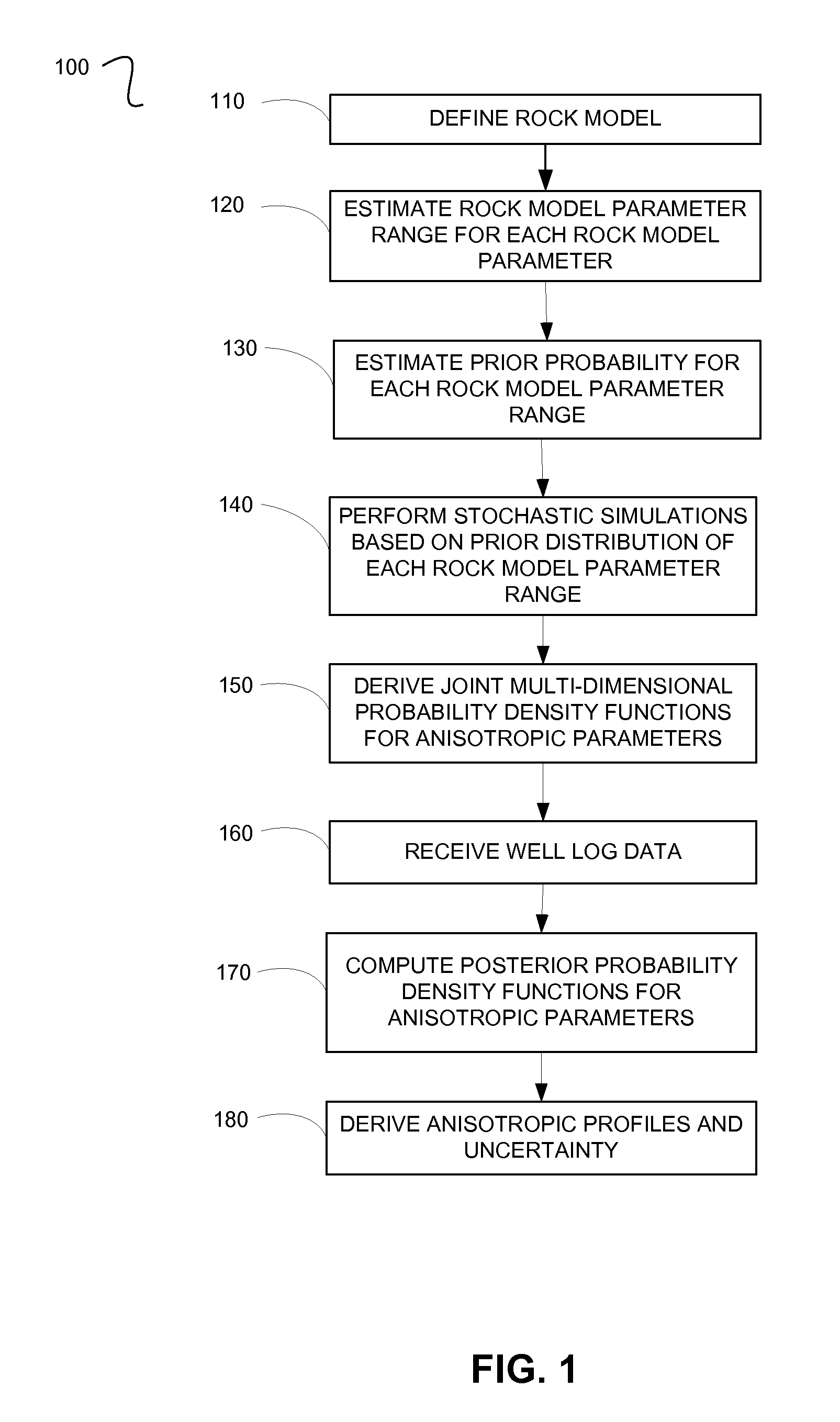
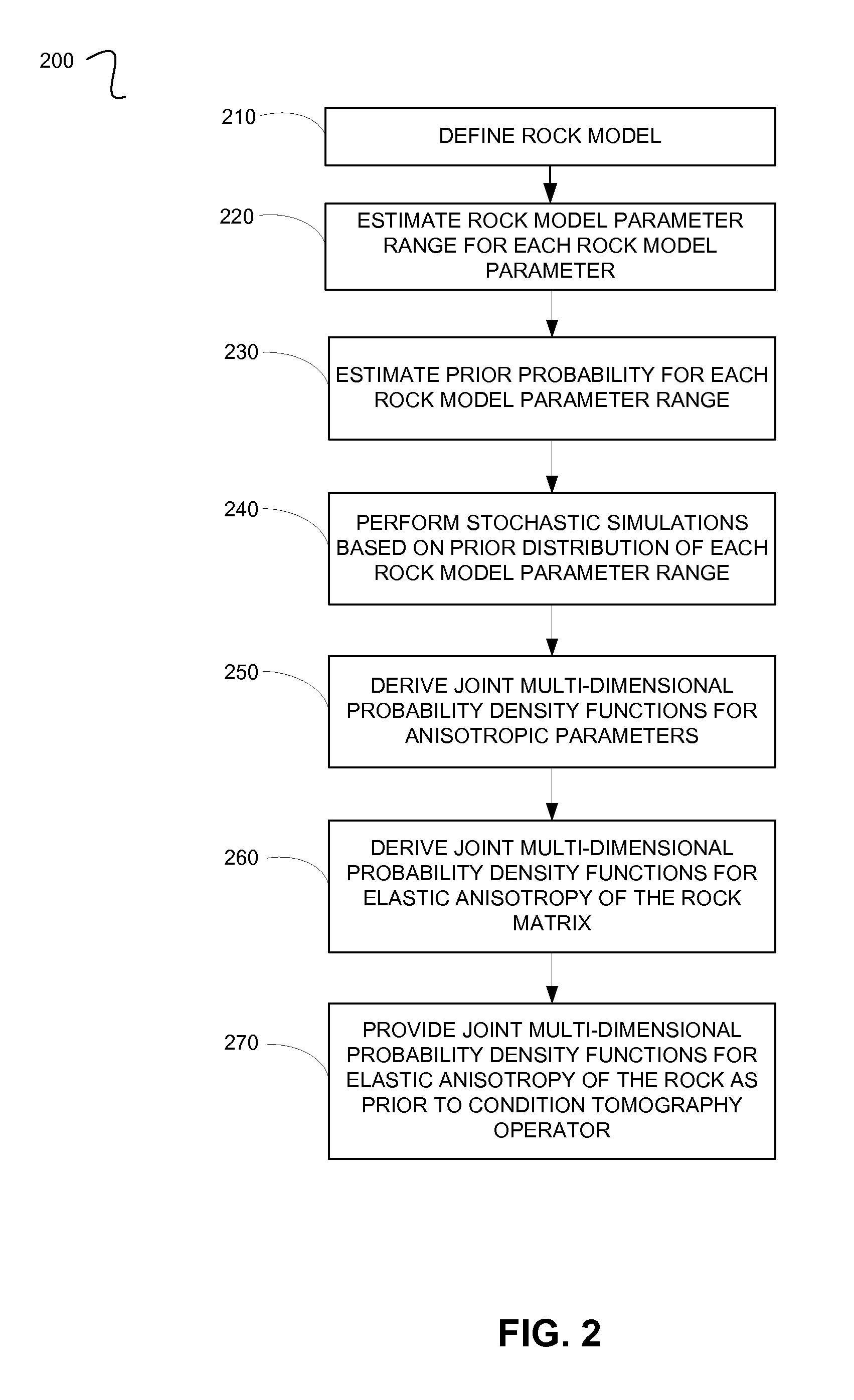
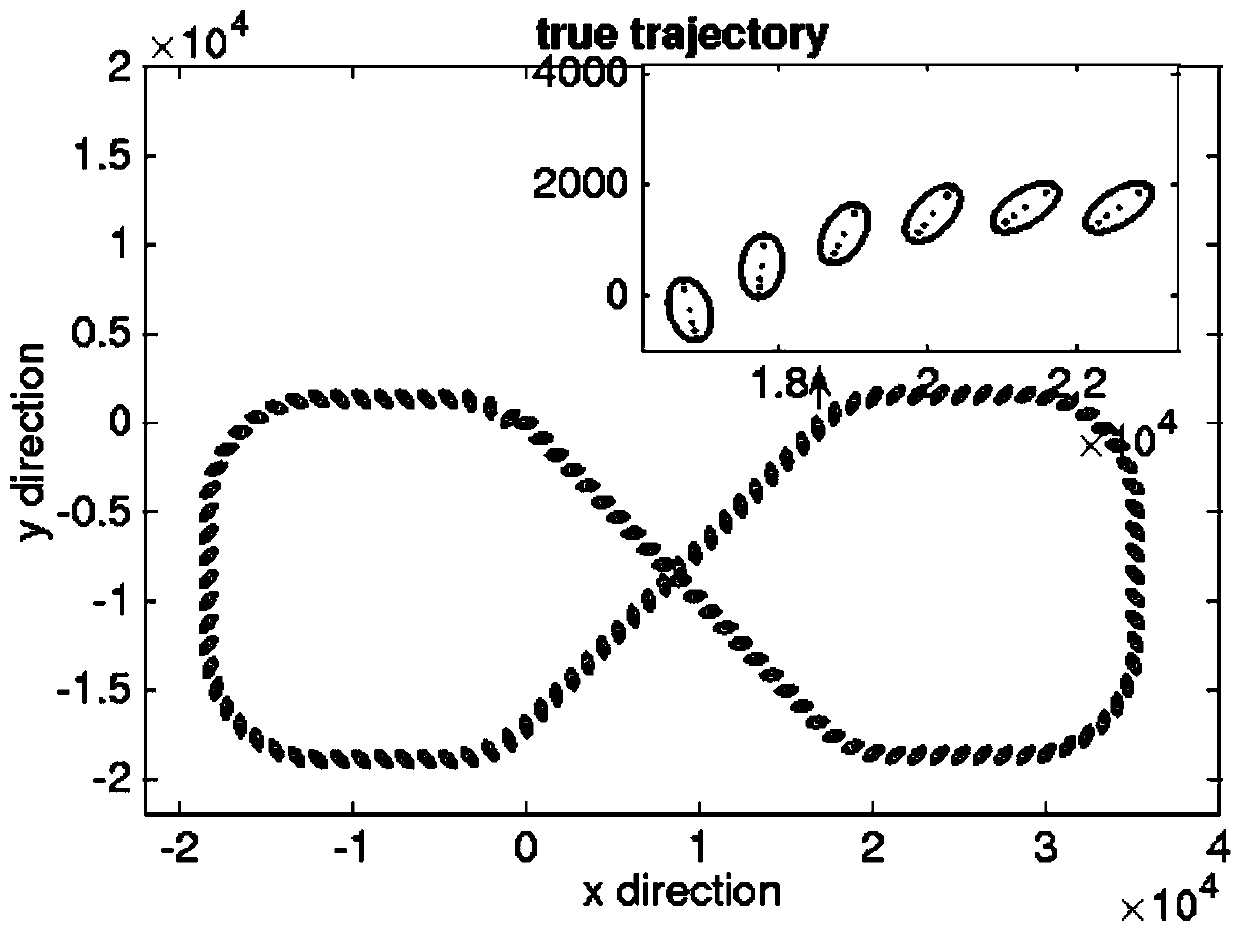
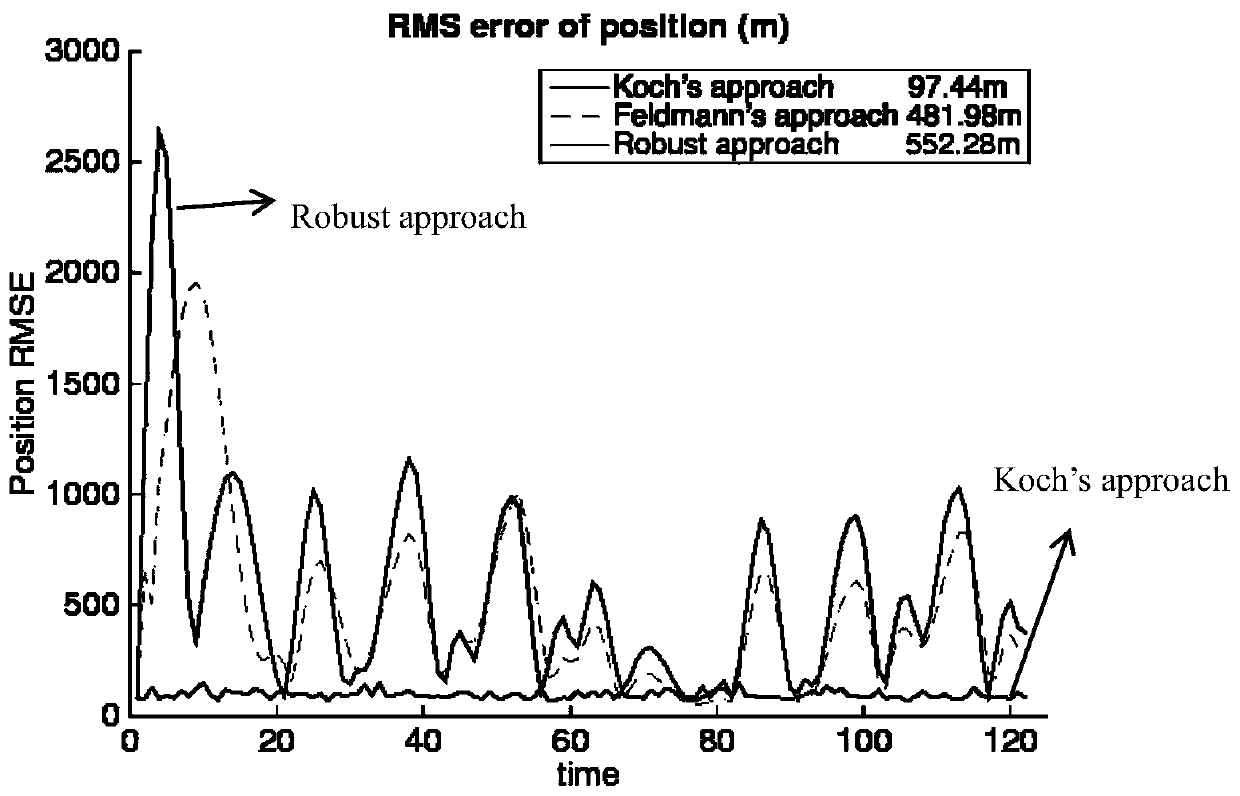
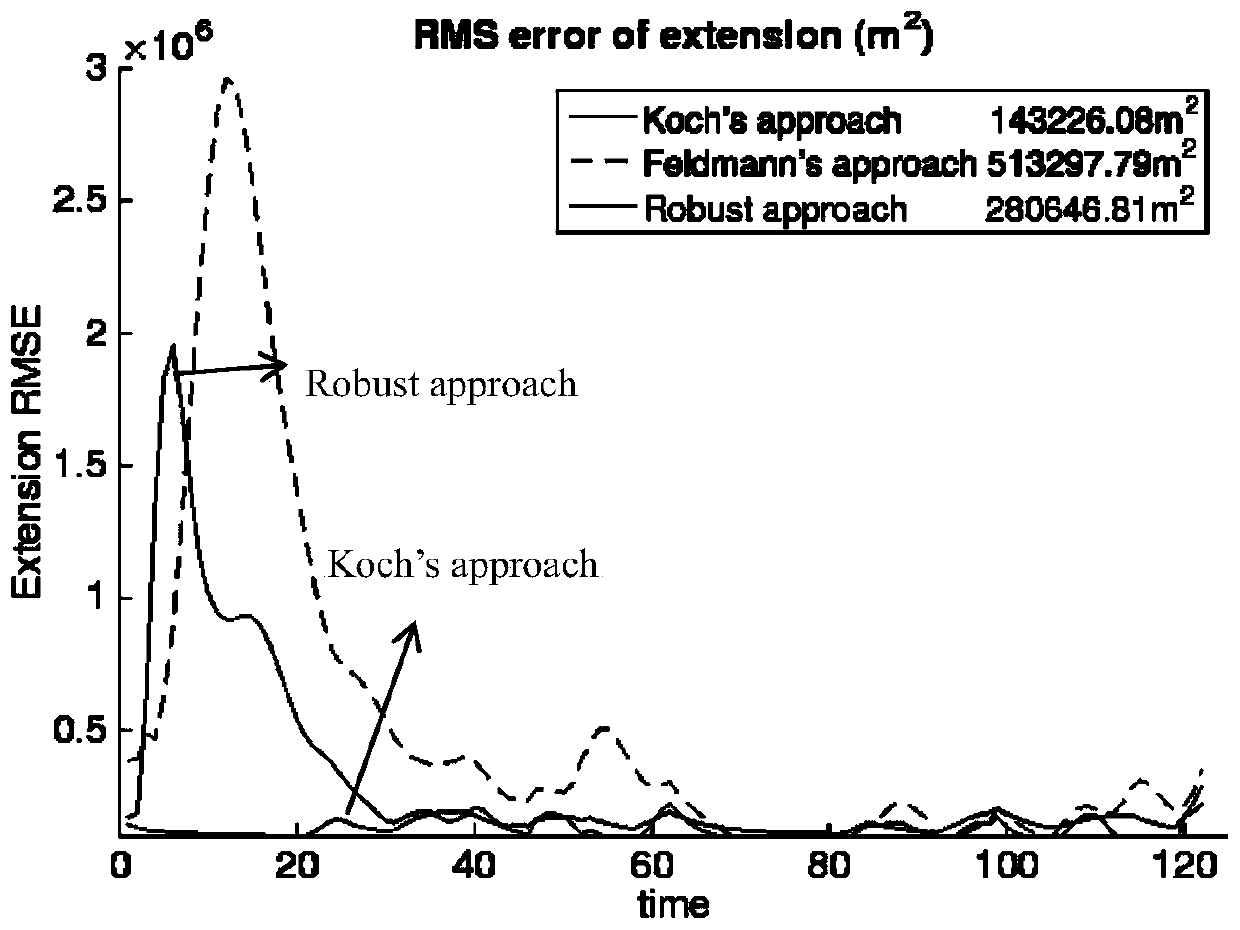
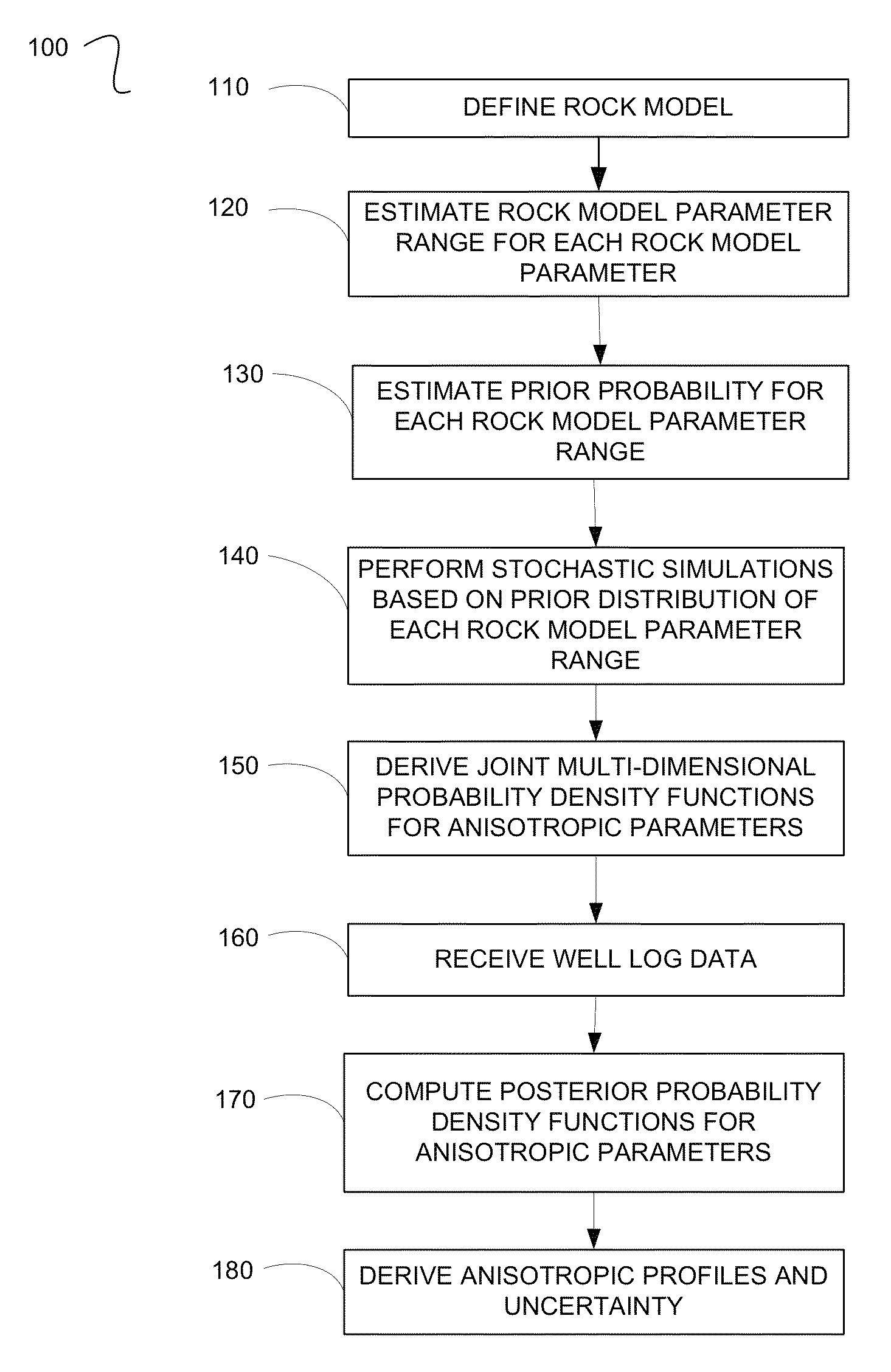
A method for processing seismic data. The method includes performing a plurality of stochastic simulations for one or more rock model parameters to generate one or more anisotropic parameters for a subsurface area of the earth. The method then derives one or more joint multi-dimensional probability density functions for the anisotropic parameters. Using the joint multi-dimensional probability density functions and measured well log data, the method computes one or more posterior probability density functions. The method then includes deriving one or more anisotropic profiles from the posterior probability density functions and generating a seismic image from the anisotropic profiles.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
A Bayesian statistical traceability method for discharging industrial waste water exceeding the standard of sewage pipe network
PendingCN108897964ARealize transport simulationHigh precisionDesign optimisation/simulationComplex mathematical operationsIndustrial waste waterTime series
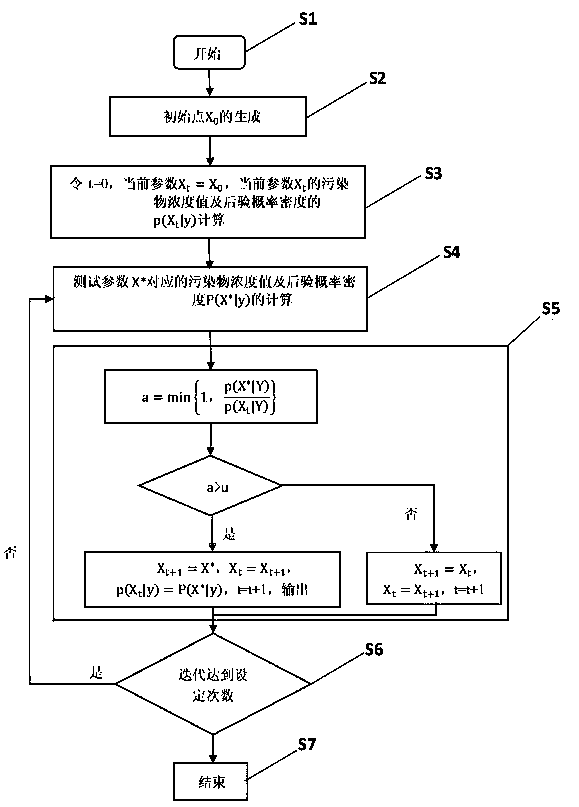
The invention discloses a Bayesian statistical traceability method for discharging industrial waste water exceeding the standard of sewage pipe network, It includes: 1. Random generation of the initial point (img file = 'DEST_PATH_IMAGE002. TIF' wi= '17' he= '19' / ) in the range of the prior information of the unknown parameters; 2, simulate that time series of pollutant concentration of the current parameter (img file = 'DEST_PATH_IMAGE004. TIF' wi= '16' he= '18' / ) correspond to the monitoring point, The posterior probability density of unknown parameters (img file = 'DEST_PATH_IMAGE006. TIF'wi= '45' he= '20' / ) was obtained by comparing with the actual monitoring data. 3, generate candidate parameters accord to that suggested distribution (img file= 'DEST_PATH_IMAGE008. TIF' wi= '17' he='15' / ), (img file= '928204DEST_PATH_IMAGE008. TIF' wi= '17' he= '15' / ), The posterior probability density of unknown parameters (img file = 'DEST_PATH_IMAGE010. TIF' wi= '47' he= '19' / ) is obtained bycomparing the likelihood degree with the actual monitoring data, 4, extract a random number (img file = 'DEST_PATH_IMAGE012. TIF' wi= '11' he= '13' / ), jud whether that candidate value is accepted ornot, outputting an accepted value and a posterior probability density; 5, repeat steps 3 and 4 until that iteration is complete. The invention has the advantages of effectively narrowing the value range of unknown parameters, utilizing the characteristics of the MCMC sampling method, reducing the workload and the sampling time under the condition of ensuring the rationality of the sampling, and improving the traceability efficiency.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Particle filter method
ActiveCN103684350AImprove the degradation problemImprove filtering effectAdaptive networkPosterior probability densityImportance Weight
The invention provides a particle filter method. The method comprises the step 1 of initializing particles; the step 2 of obtaining a measurement value at the k moment, then utilizing the particle filter method to calculate a mean value and variance in a parallel mode in N particle filter process, then conducting approximate treatment to obtain an importance density function and extracting sampling particles; step 3 of calculating the importance weight of each sampling particle according to the importance density function obtained in the step 2; step 4 of conducting normalization processing on the importance weight obtained in the step 3; step 5 of conducting re-sampling according to the weight obtained after normalization processing in the step 4 to obtain a new particle sequence and step 6 of testing the probability density after calculating the particle sequence xik obtained in the step 5, and outputting a filter result. The particle filter method is simple in calculating process, and can solve the particle degeneracy problem to a certain degree and improve the particle filter performance.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Methods and arrangements for detecting weak signals
ActiveUS20120183035A1Increase probabilityDigital computer detailsTransmission monitoringModel selectionInstrument Data
Owner:RADAREAL
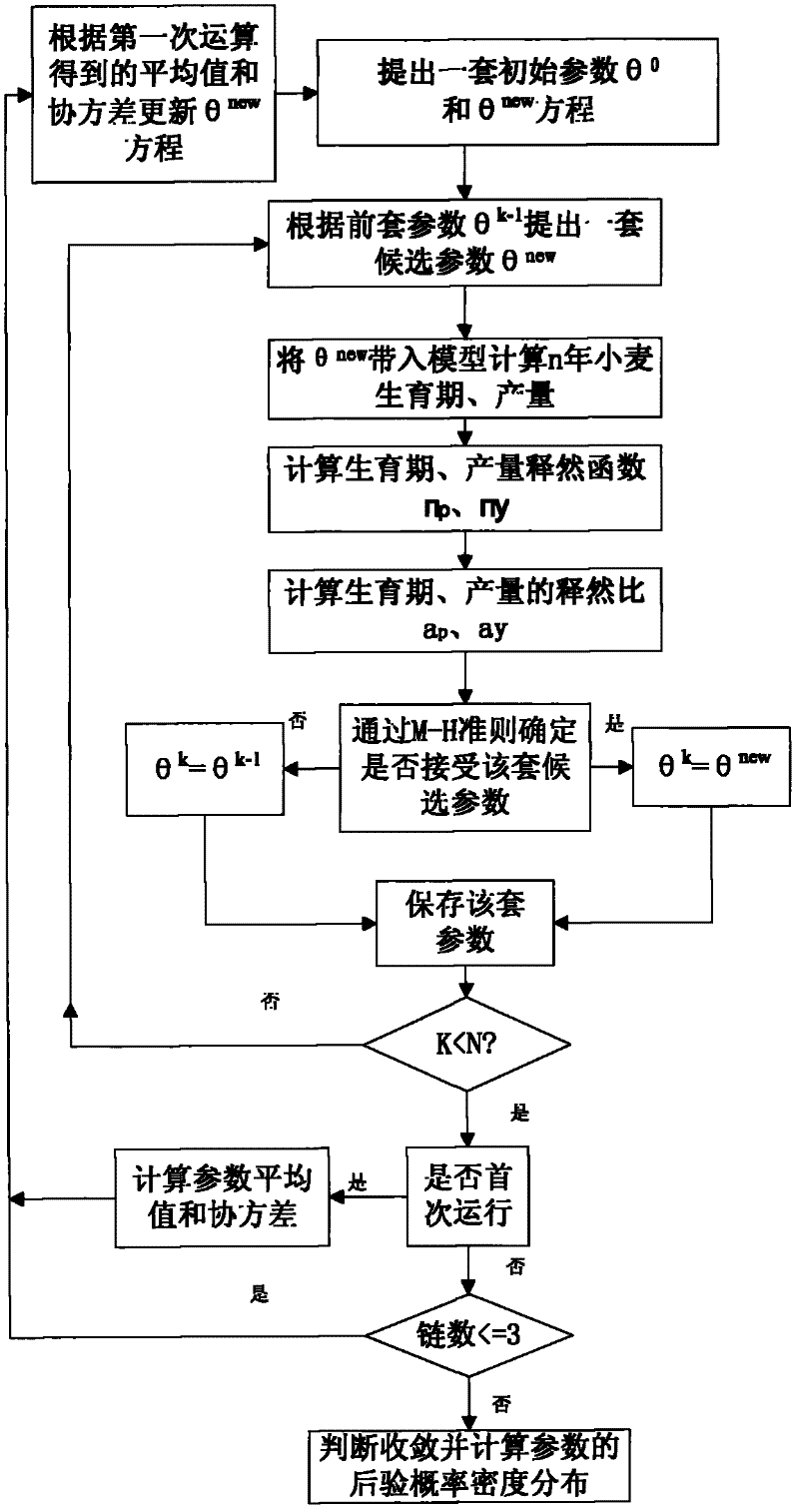
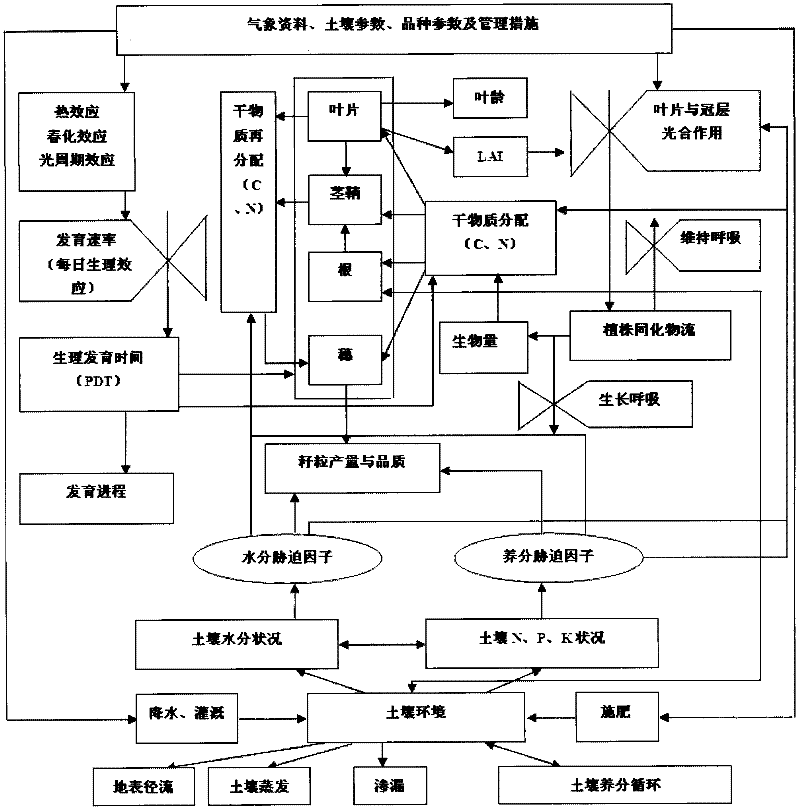
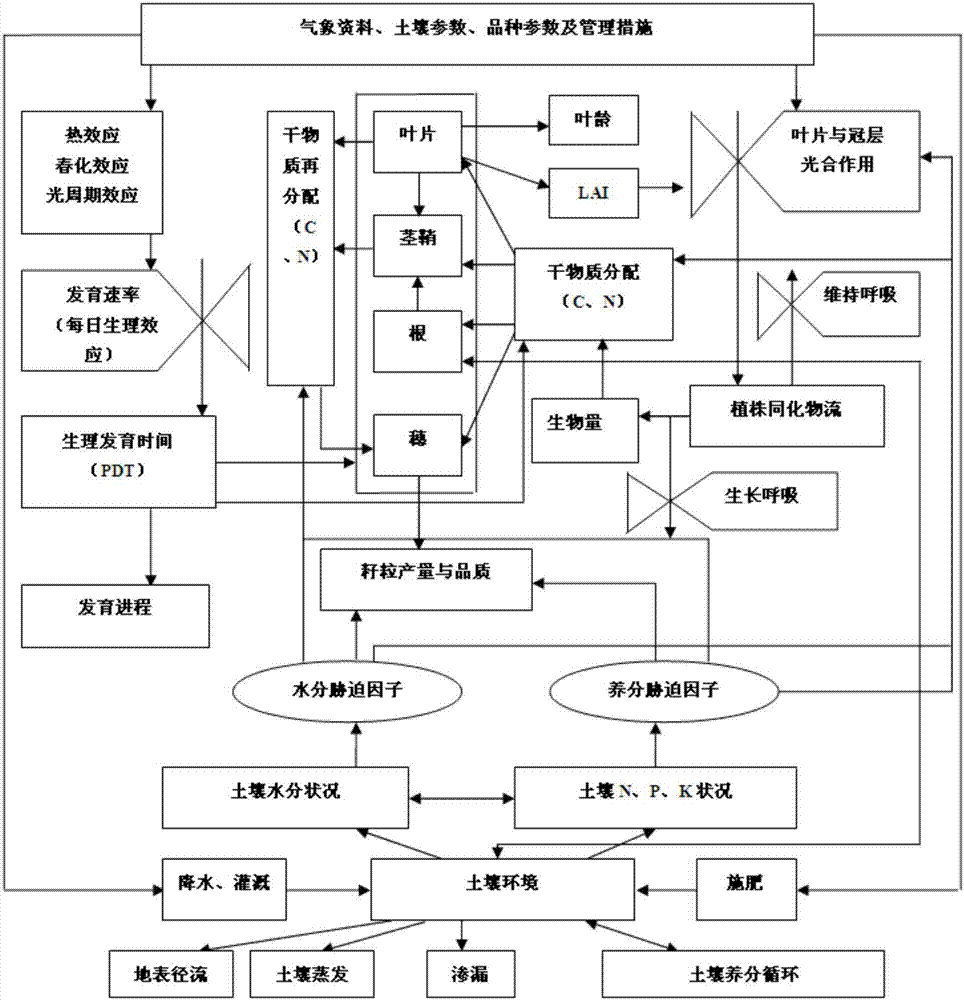
Wheat variety characteristic parameter estimating method based on MCMC
ActiveCN102495948AEffective inversion of characteristic parametersThe estimated result is accurateSpecial data processing applicationsPosterior probability densityNormal density
The invention discloses a wheat variety characteristic parameter estimating method based on the MCMC, which mainly includes building probability density function through wheat variety growth period and yield which are actually measured in the field and growth period and yield of wheat growth models and utilizing the MCMC method for inversion to obtain the wheat variety characteristic parameter. The main process includes first obtaining prior probability distribution of the wheat variety characteristic parameter through test calculation, presenting candidate parameter according to initial parameter and the prior probability distribution, calculating probability density function and relieving ratio of the yield and the growth period, judging whether new parameter is accepted or not according to the M-H criterion and finally obtaining posterior probability density distribution of various variety characteristic parameter. The method is accurate and efficient in result estimation and has general serviceability in estimation of wheat variety characteristic parameter of like models.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
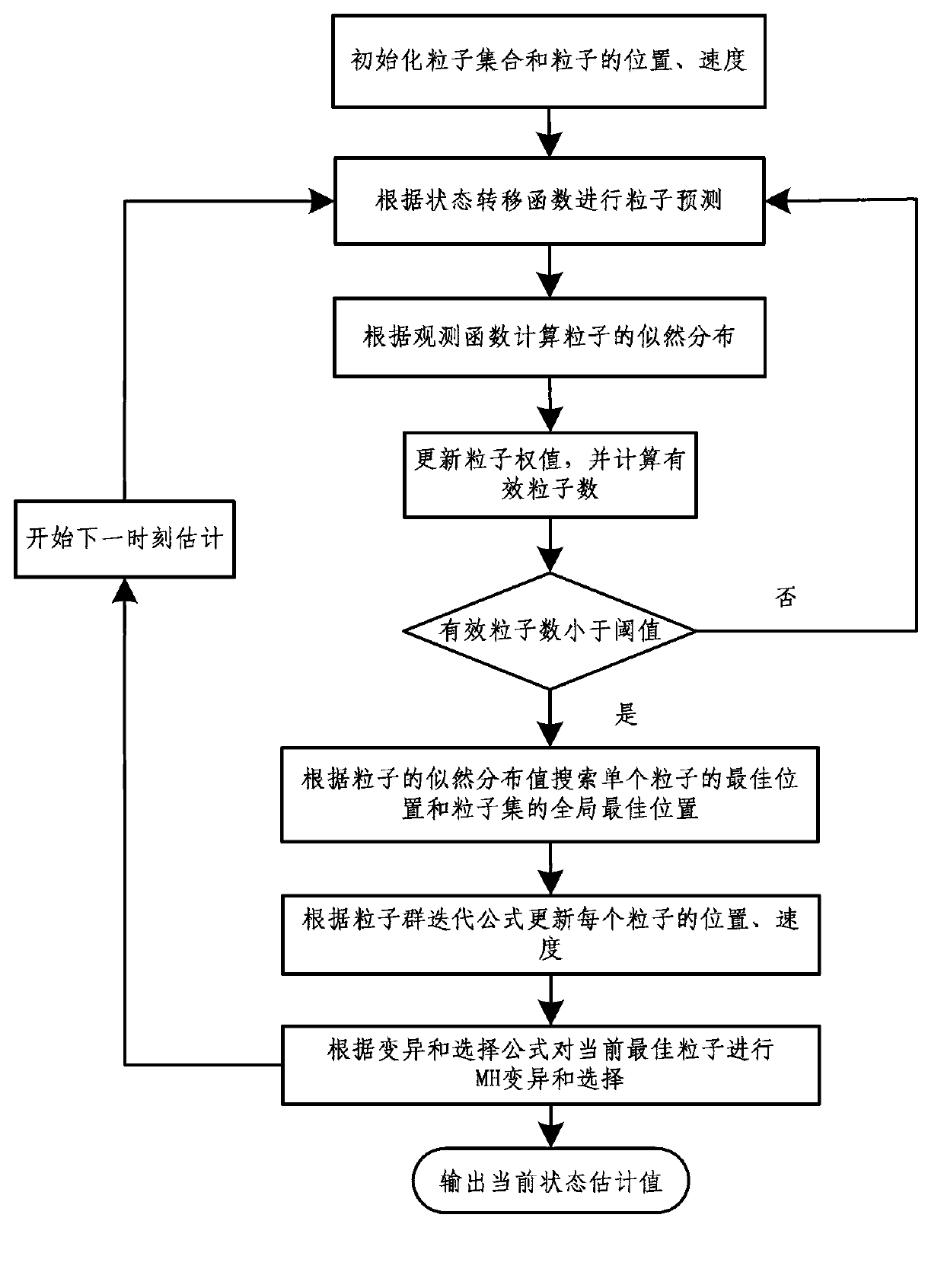
Implementation method of Metropolis-Hastings variation particle swarm resampling particle filter
The invention relates to an implementation method of a particle swarm resampling particle filter based on Metropolis-Hastings variation. The invention provides the implementation method of the particle swarm resampling particle filter based on the Metropolis-Hastings variation so as to solve the problem that estimated accuracy of a particle filter is not high when the number of particles is small. The implementation method enables Metropolis-Hastings (MH) movement to be used as a variation operator of particle swarm optimization, an MH variation rule is combined with a speed-position search process of a particle swarm, a resampled particle swarm is more approximate to a real posterior probability density distribution, the problem that a common variation particle swarm algorithm diverges easily is effectively solved, a convergence speed of the particle filter in a sequential estimation process is accelerated, and estimation accuracy of the particle filter is improved. Proved by a simulation test, the particle swarm optimization particle filter based on the Metropolis-Hastings variation can effectively overcome the phenomenon of particle depletion and improve tracking and estimating effects of a nonlinear system.
Owner:PLA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fast target angle estimation method based on sparse Bayesian learning
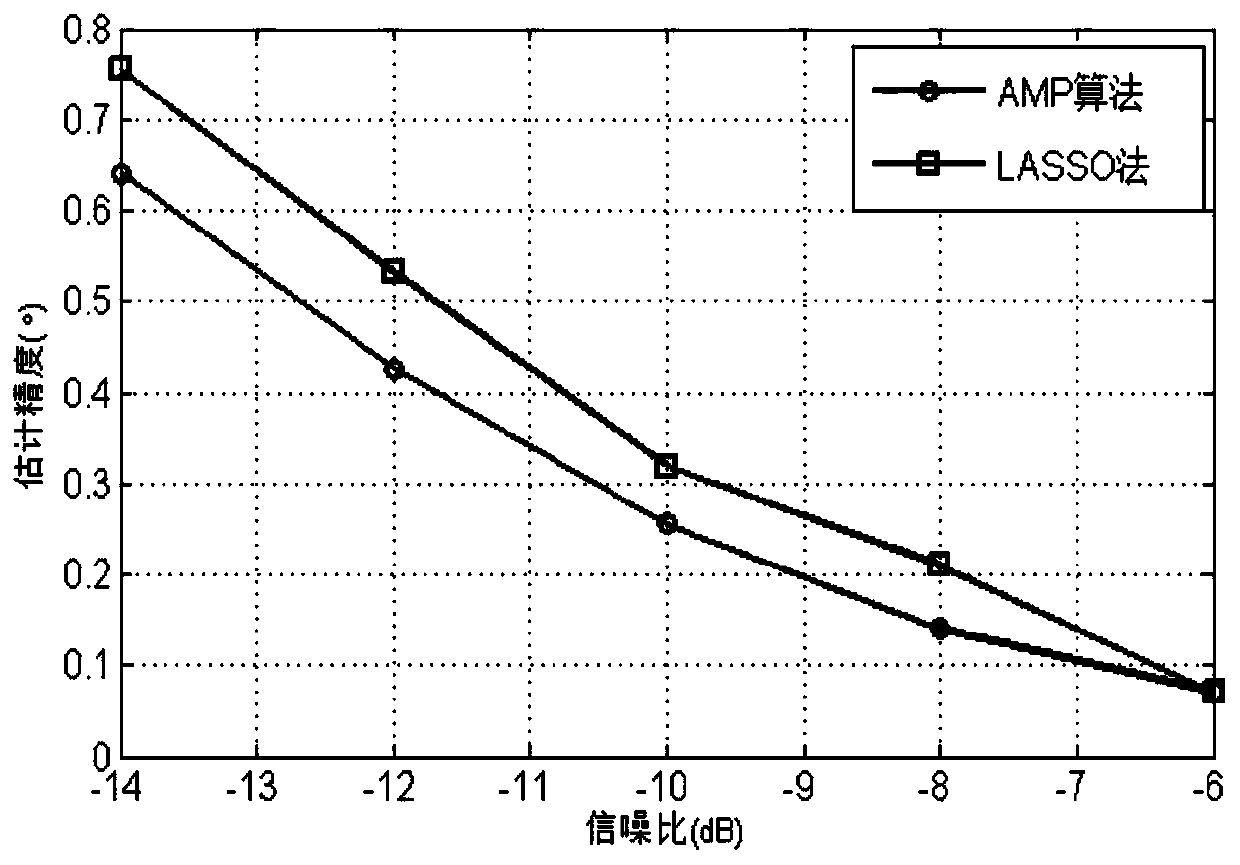
ActiveCN109752710AIterative convergence is fastImprove computing efficiencyRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPosterior probability densitySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
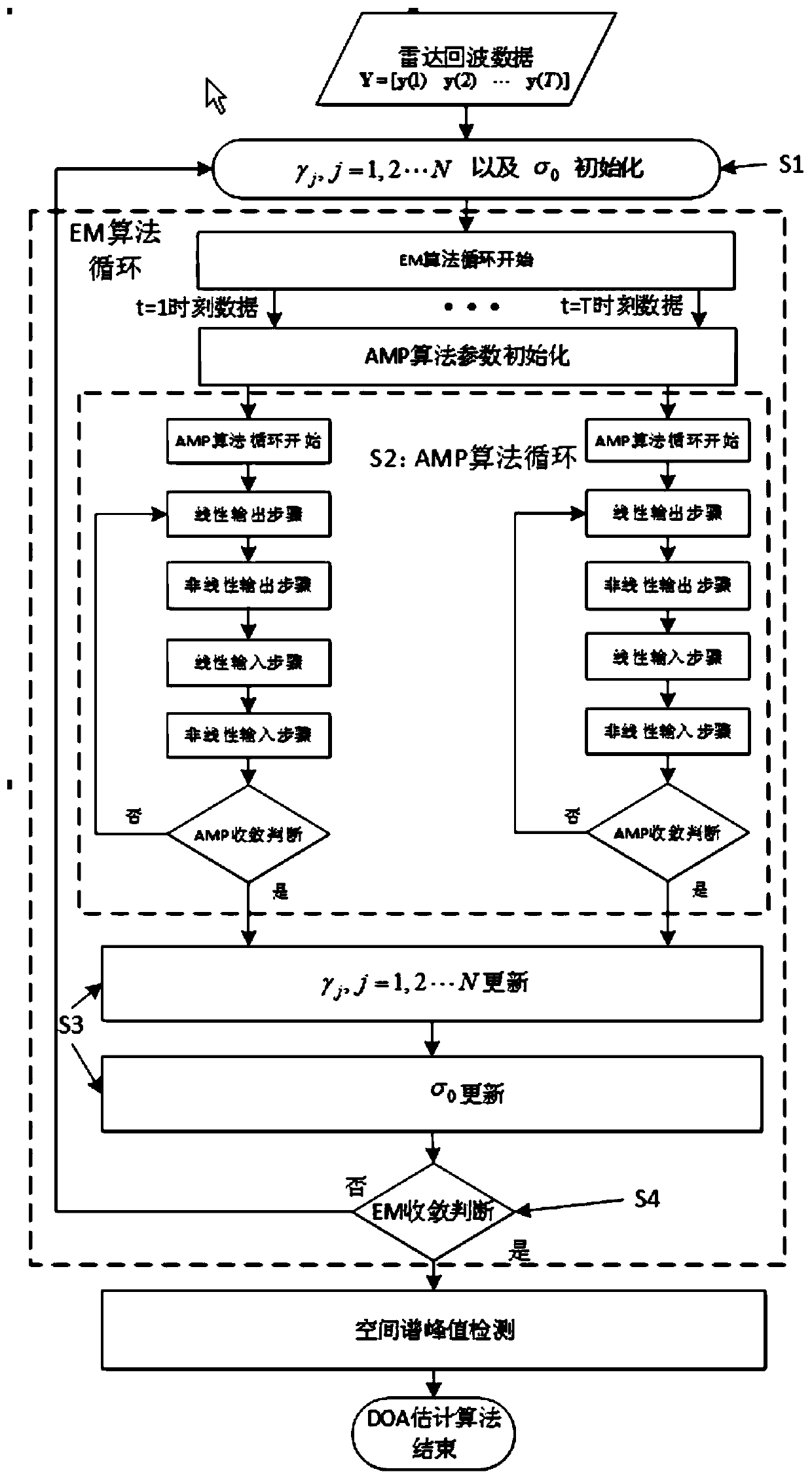
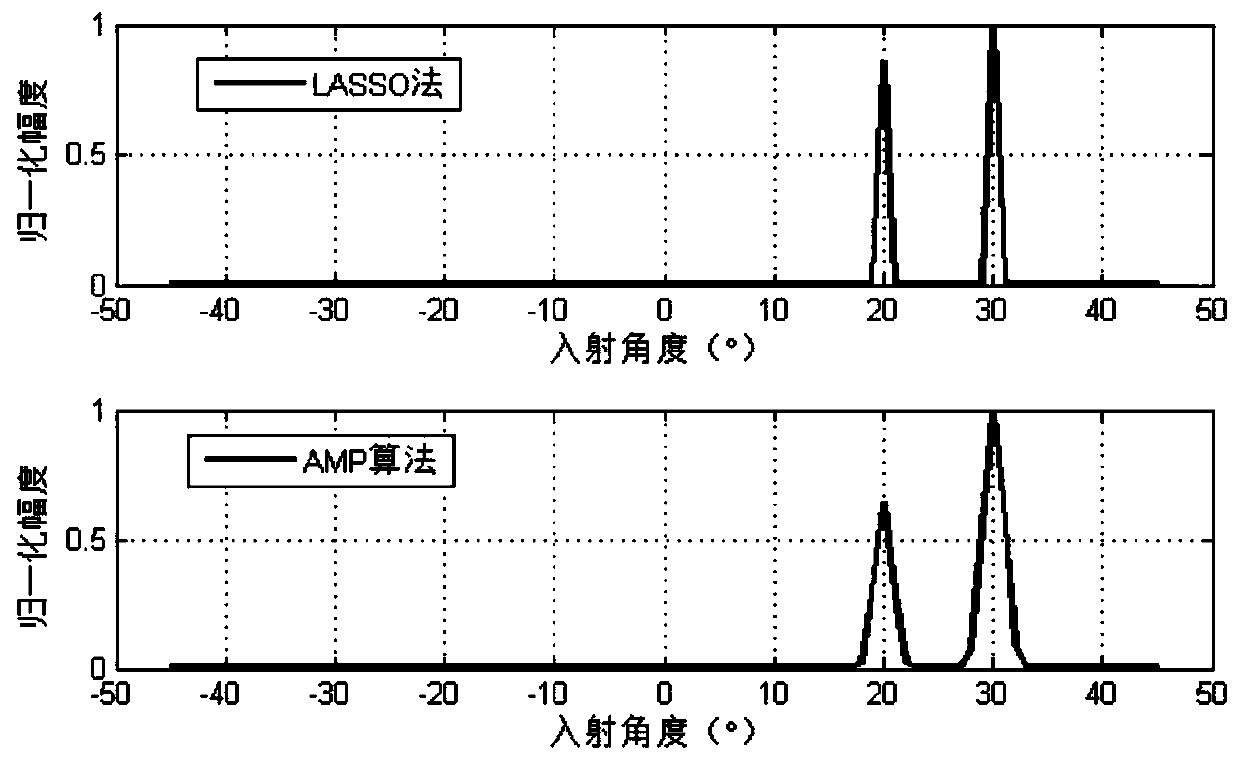
The invention belongs to the field of array signal processing, and in particular relates to a fast target angle estimation method based on sparse Bayesian learning. The method comprises the followingsteps of S1, performing initialization on the parameters to be estimated of gammaj and sigma0, wherein j is equal to 1,2 to N; S2, quickly obtaining signal posterior probability density functions at each moment by using the AMP algorithm; S3, updating values of the parameters to be estimated of gammaj and sigma0 by using the EM algorithm, wherein j is equal to 1,2 to N; and S4, determining whetherthe update iterative process of the parameters to be estimated converges, returning to the S2 to re-iterate if not, and if so, jumping out of the loop and determining the direction and quantity of the target incoming waves. The method provided by the invention can improve the low signal-to-noise ratio and the multi-objective angle estimation accuracy under small sample conditions, and has the advantages of fast iterative convergence speed and high computational efficiency for estimating the target angle, which can be applied to the real-time multi-objective angle estimation system and has important engineering application value.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Battery SOC estimation method based on HCKF
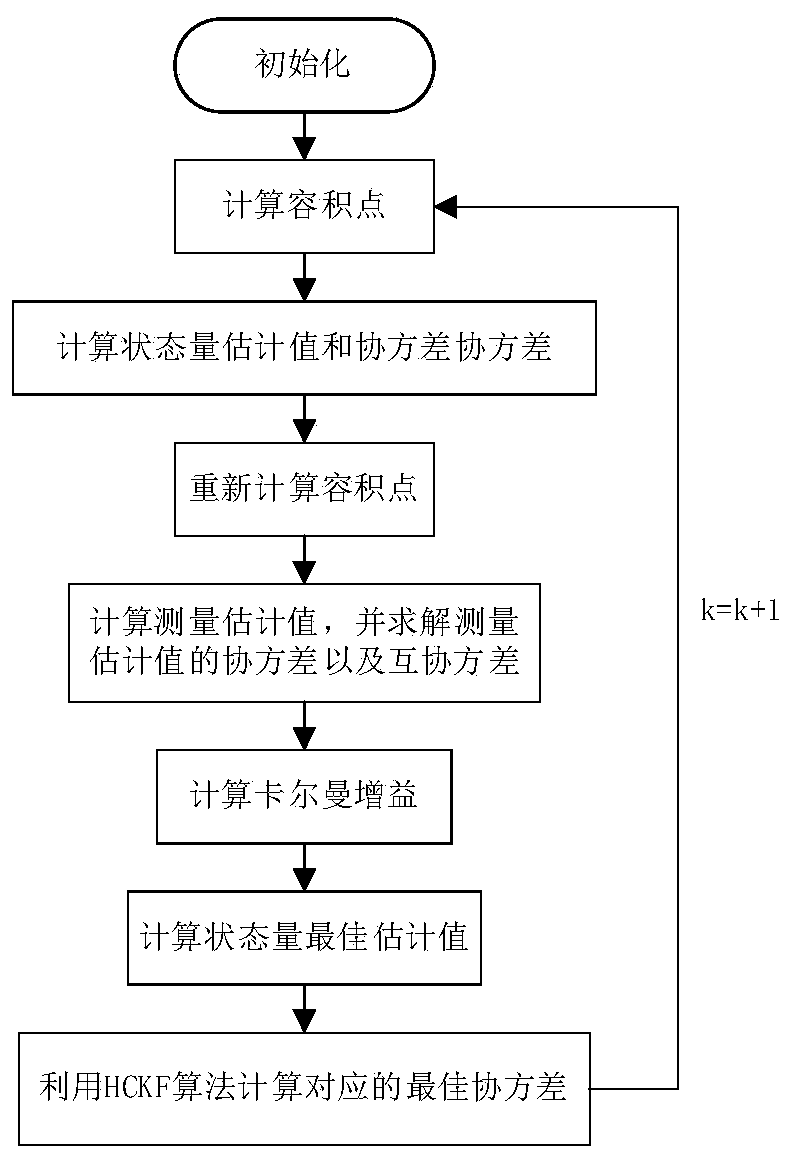
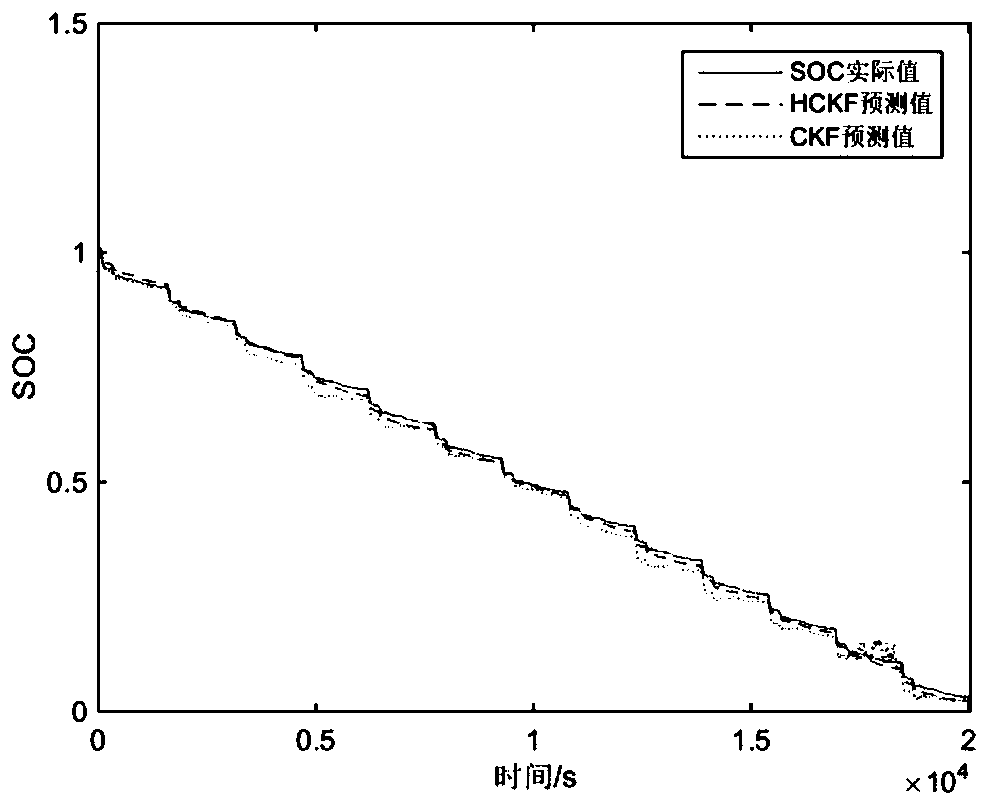
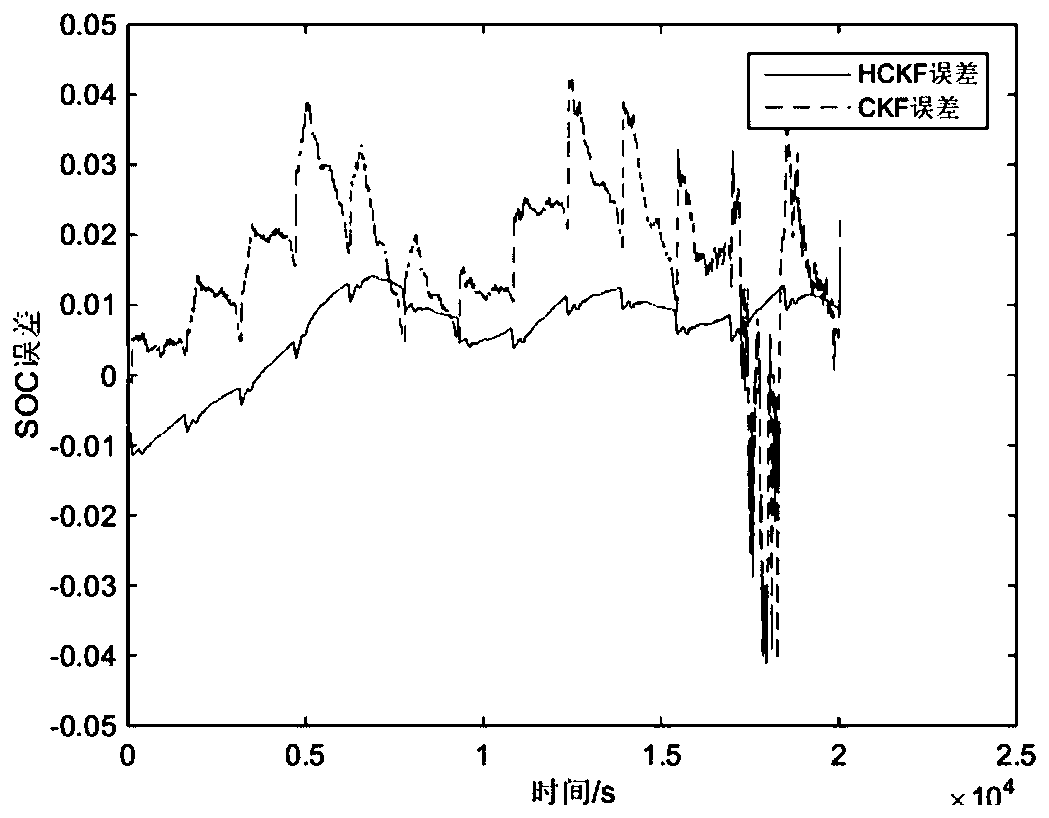
ActiveCN111537903AImprove execution efficiencyImprove real-time performanceElectrical testingVehicular energy storagePosterior probability densityElectrical battery
The invention discloses a battery SOC estimation method based on HCKF. On the basis of a battery electrochemical model, parameters are identified through a least square method; the CKF is used as a determined sampling type filtering algorithm; when the nonlinear equation is processed, a point set is generated according to the mean value and the covariance of the prior probability density distribution of the system state and a certain sampling strategy, then each sampling point in the point set is directly subjected to nonlinear propagation, and finally the mean value and the covariance of theposterior probability density distribution of the system state are calculated through weighted summation. According to the method, the nonlinear equation does not need to be linearized, linearizationerrors are eliminated, a Jacobian matrix in the EKF does not need to be calculated in the iterative process of the filtering algorithm, and the method is easier to use in practice; an HCKF algorithm combining a CKF and an H _ infinity filter is proposed to be used for estimating the SOC; the situation that SOC estimation is not accurate enough when battery model errors, unknown measurement noise characteristics and other problems exist is effectively avoided; and the robustness is greatly improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
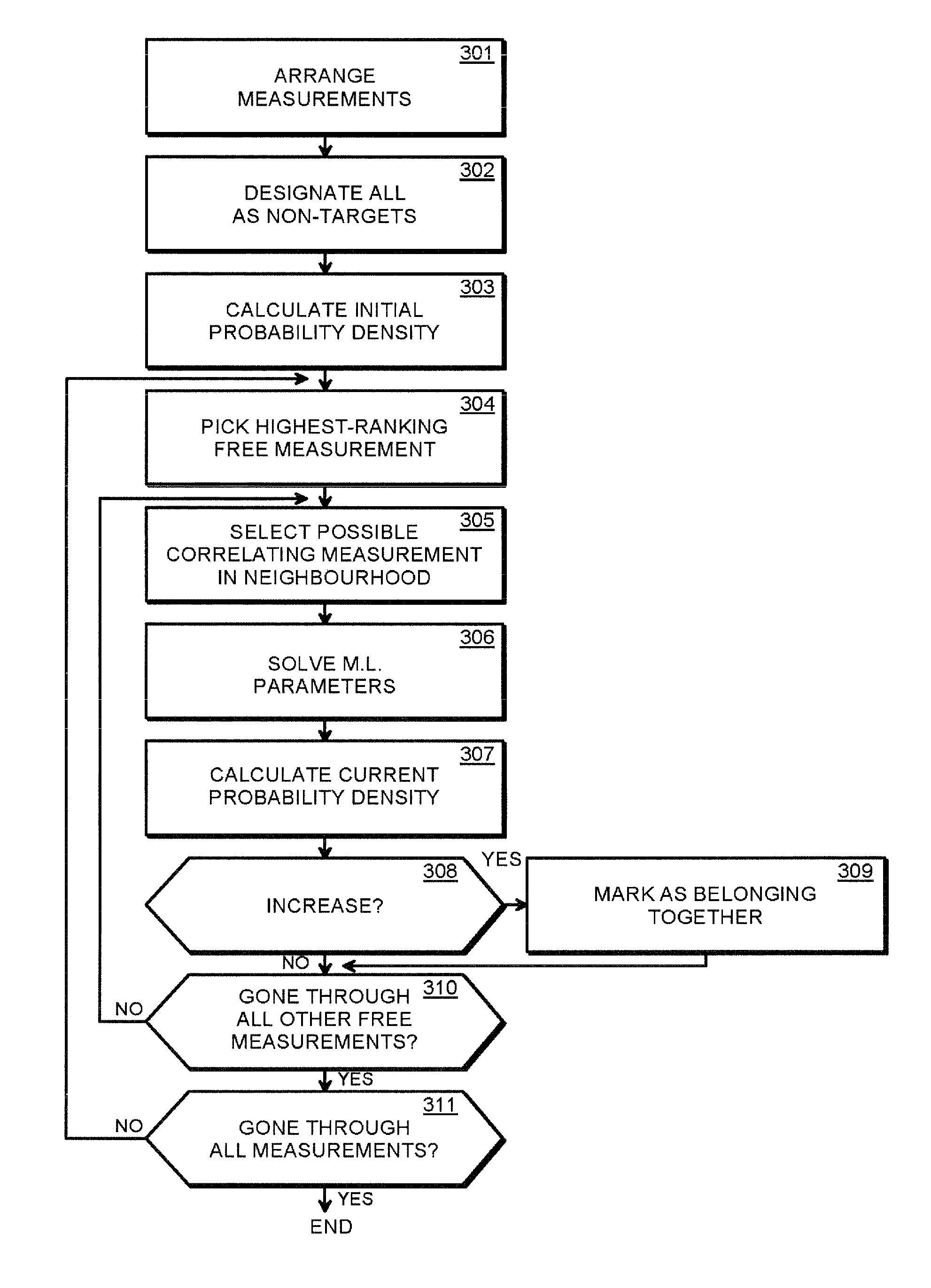
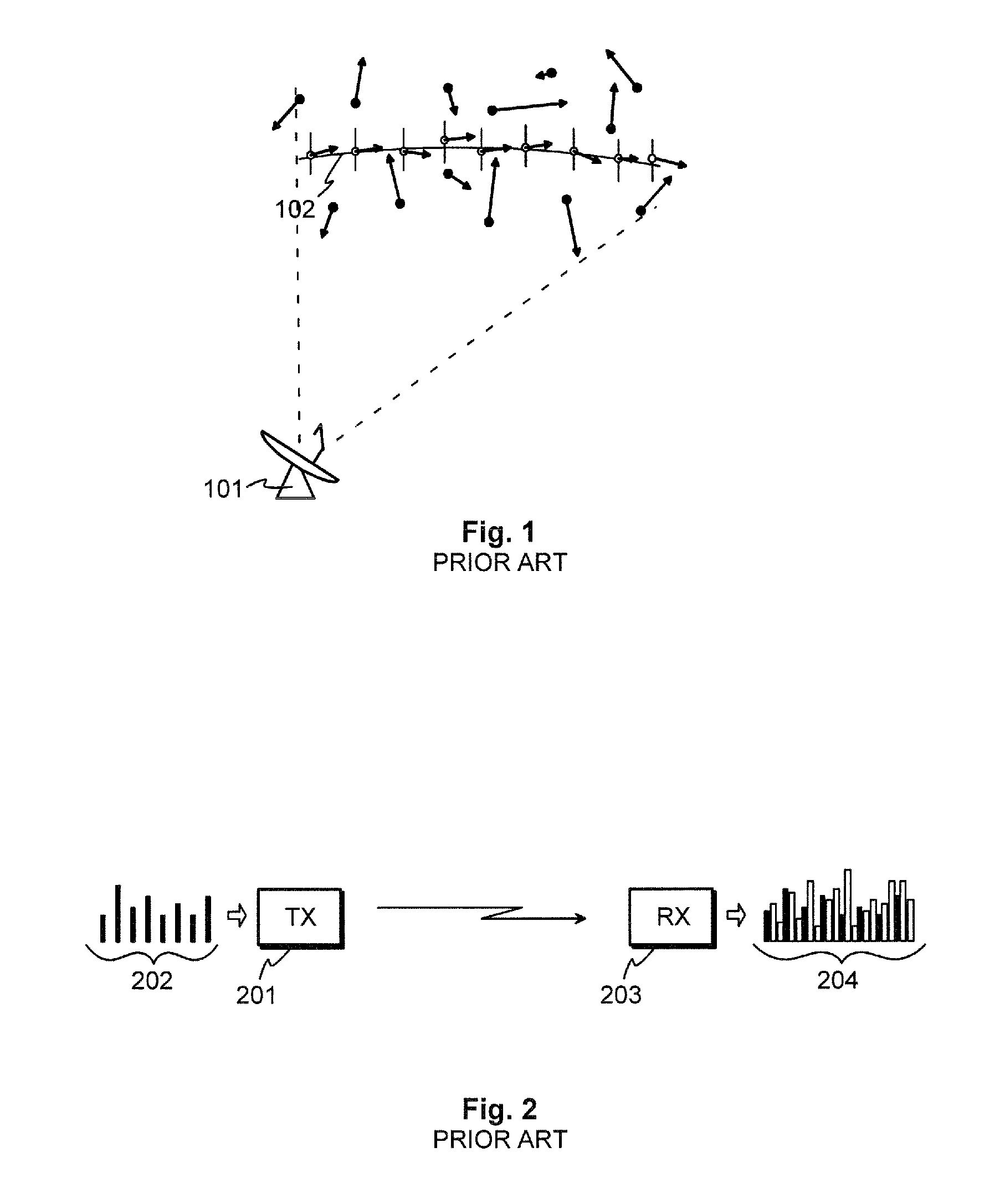
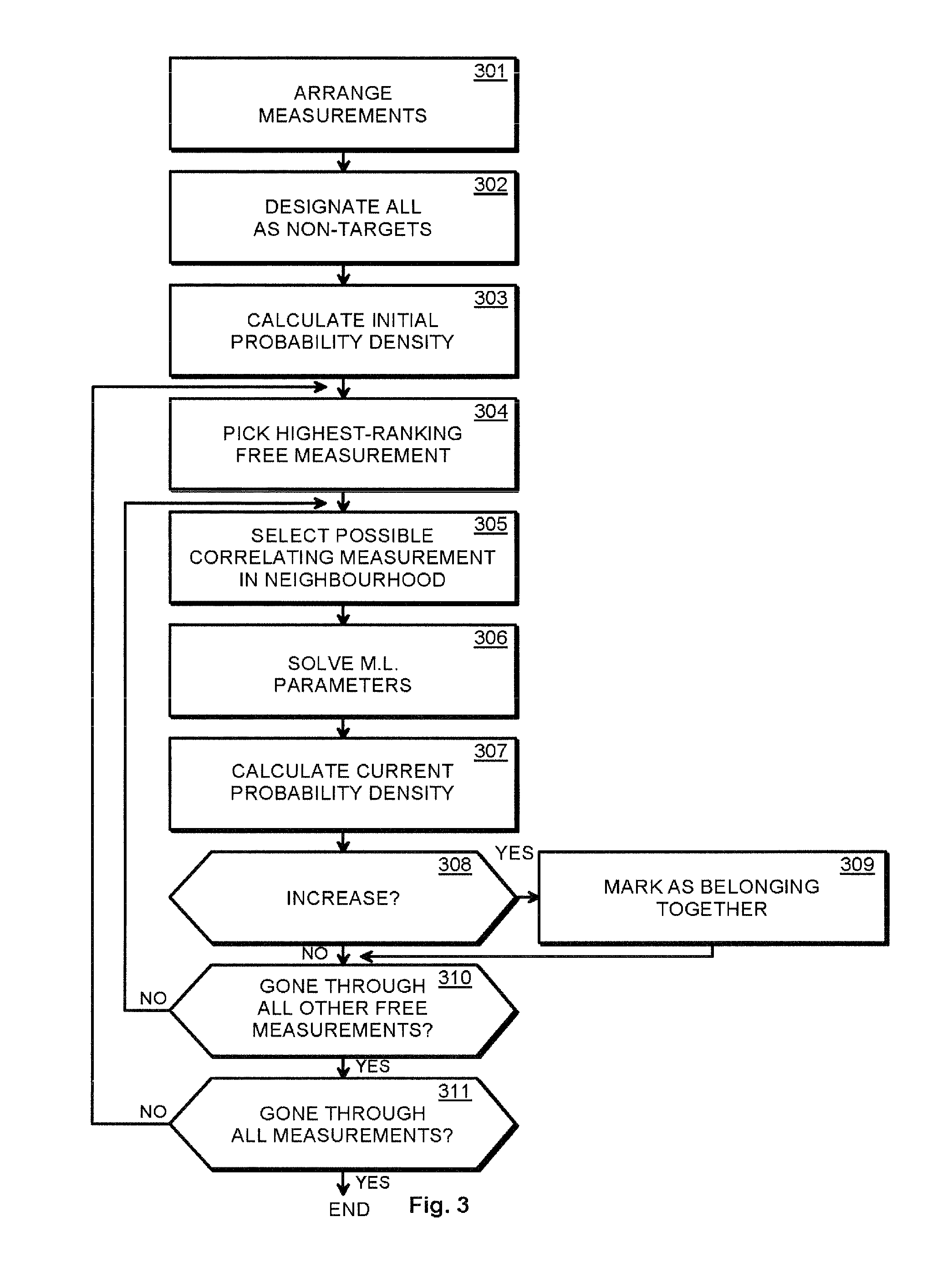
Methods and arrangements for detecting weak signals
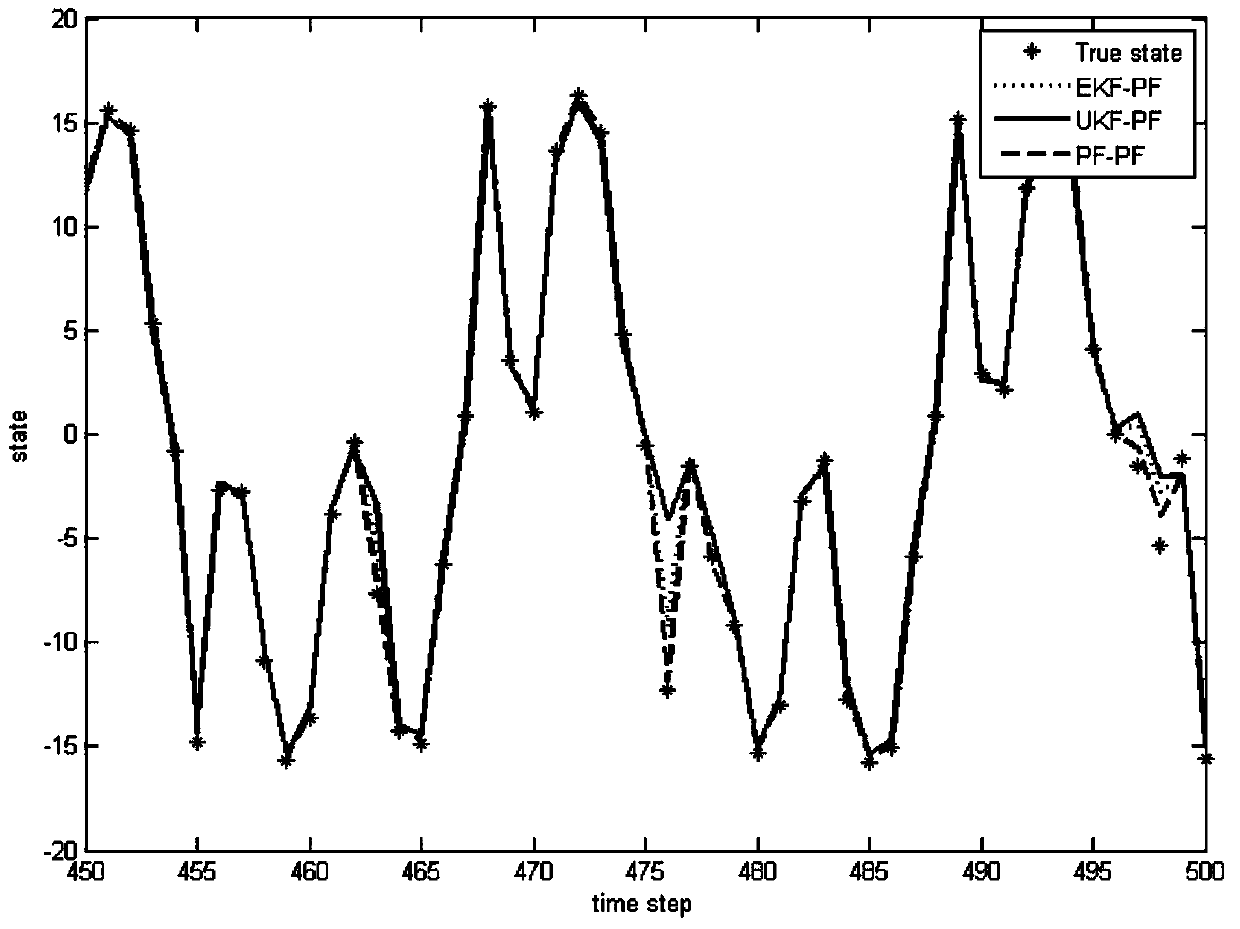
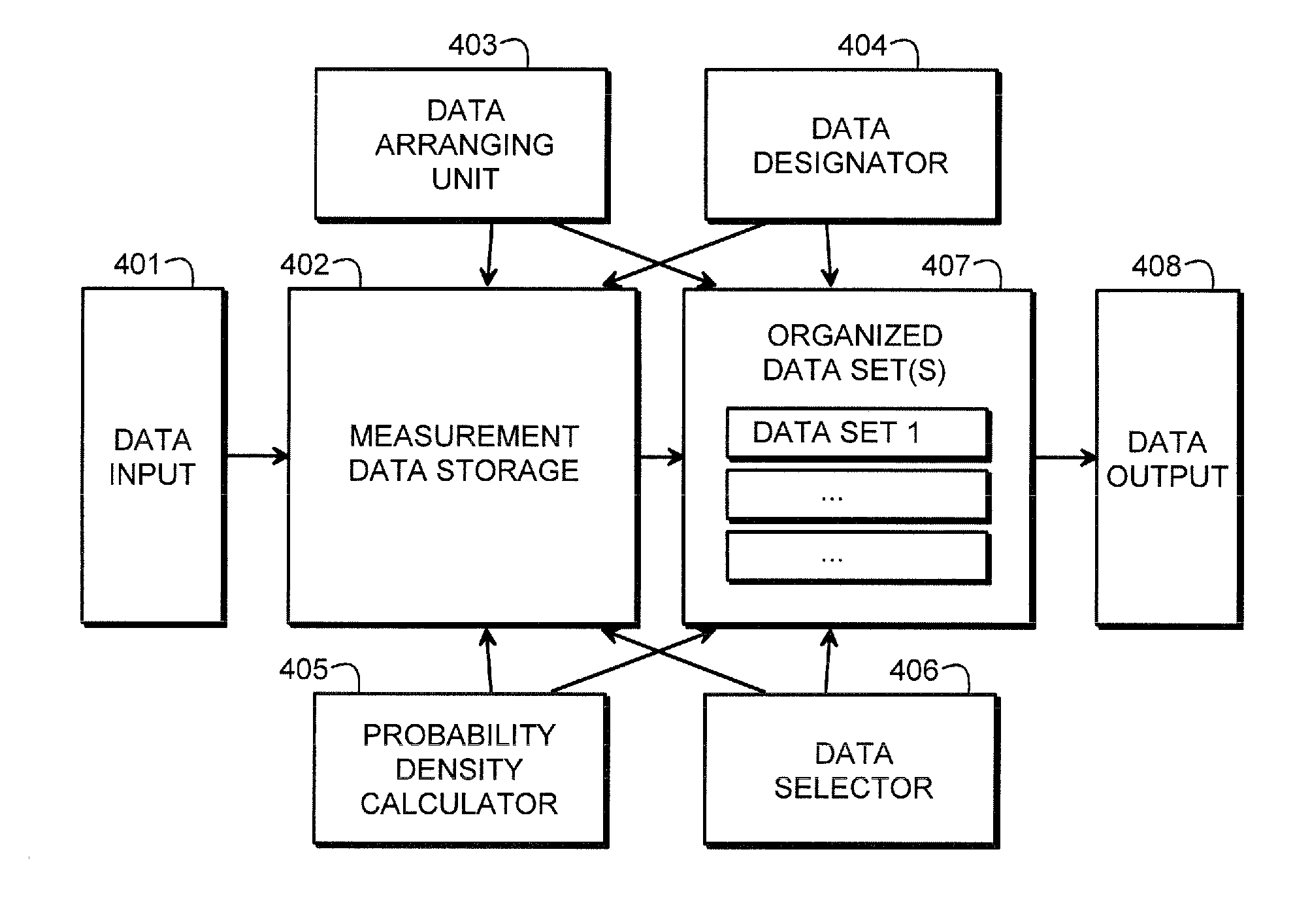
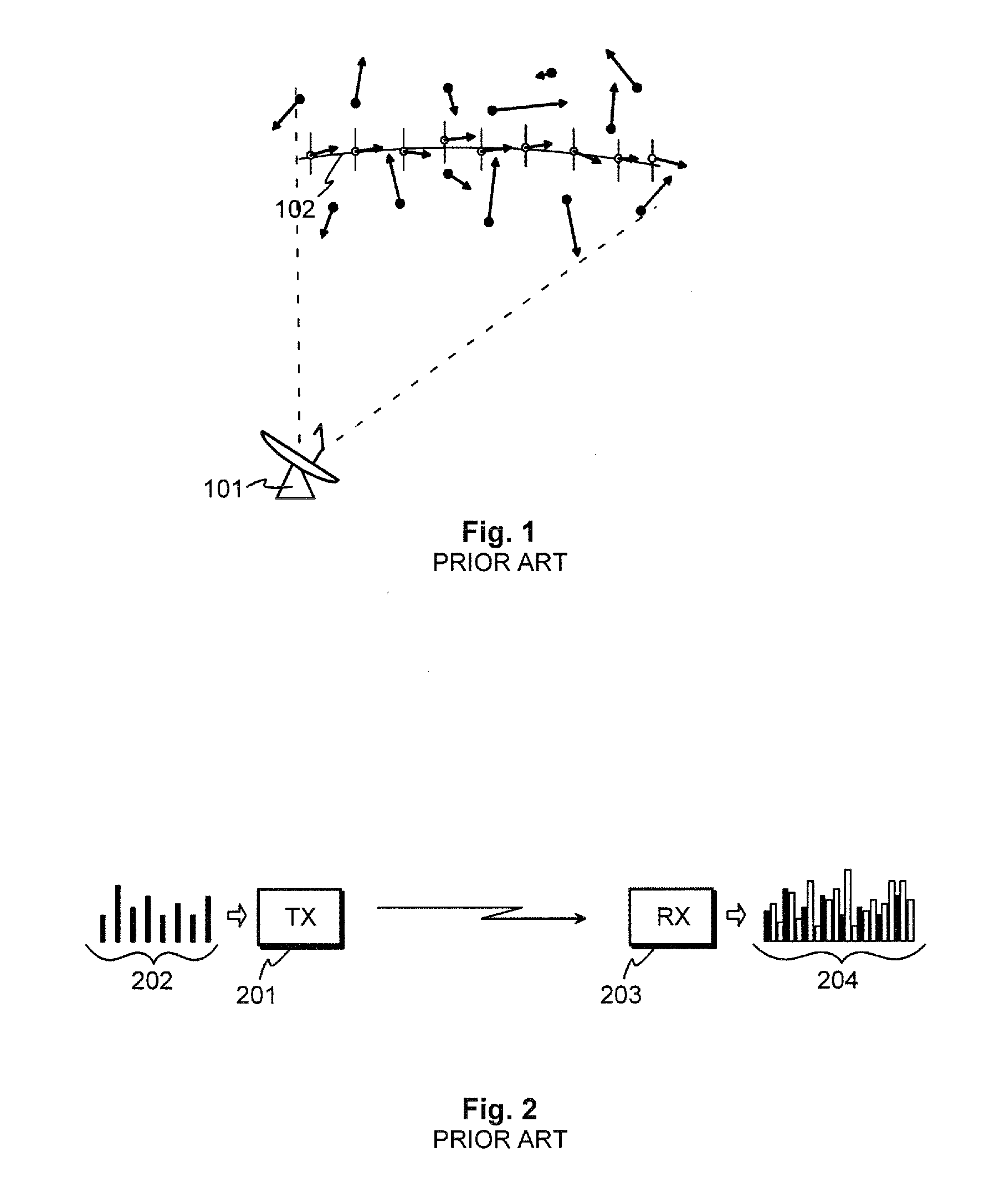
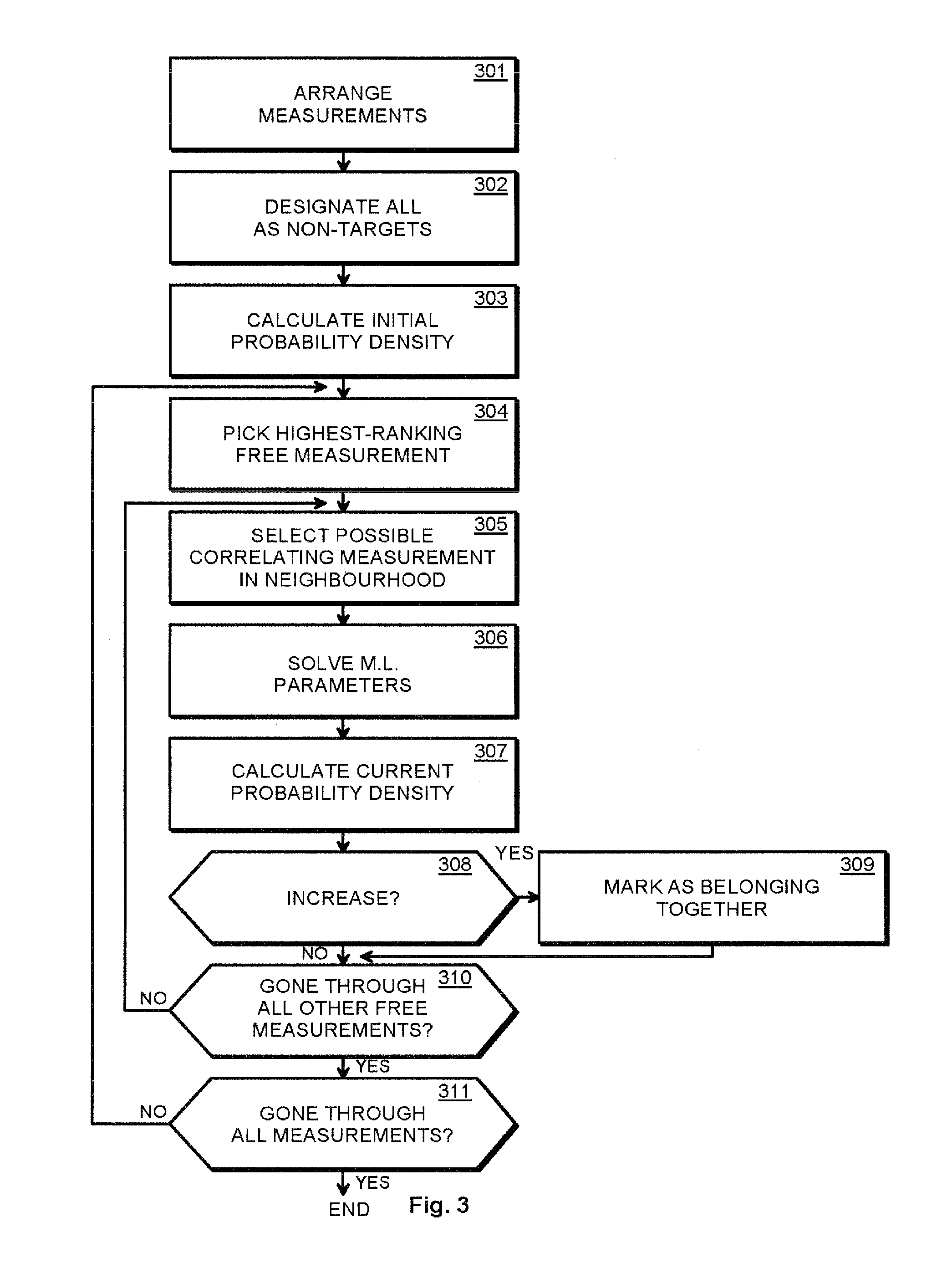
The invention provides a method and an arrangement for detecting moving point-targets within a large set of noisy measurements. The method is based on Bayesian model selection where the measurements containing targets are modeled with their physical trajectories and the non-target measurements are modeled with the statistical distribution of measurements containing no targets. An a posteriori probability density function is utilized together with a optimization algorithm specifically designed for this problem. Advantages of the invention involve a numerically efficient formulation of the a posteriori probability density, combined with the optimization algorithm. The main applications of the invention are in detecting moving targets within e.g., radar, sonar, lidar and telescopic measurements. The method is also applicable for multi-instrument data fusion.
Owner:RADAREAL
Tracking method of multiple feature points of microscopic sequence image
ActiveCN101976446AReduce 3D reconstruction errorsImprove tracking performanceImage analysisPosterior probability densityMicroscopic image
The invention provides a tracking method of multiple feature points of a microscopic sequence image, which comprises the following steps: 1) initializing a center coordinate of a tracking template of feature points as well as the size of a tracking window; 2) showing the status; 3) forecasting the status in an exponential function space described by Lie algebra; 4) calculating the distance between two covariance descriptors as the elements in a covariance value of a sample; 5) updating the status, figuring out a measurement function, and calculating posterior probability density at time t by a measuring value yt(i); and 6) estimating the optimum status, calculating weight and normalizing the weight by the posterior probability, judging whether to perform resampling, and outputting the estimated particles or ending multipoint tracking of the current frame; and repeating the steps, and finally completing multipoint tracking of the long-sequence microscopic image. The tracking method of the invention can help effectively reduce three-dimensional reconstruction errors and enhance tracking effect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
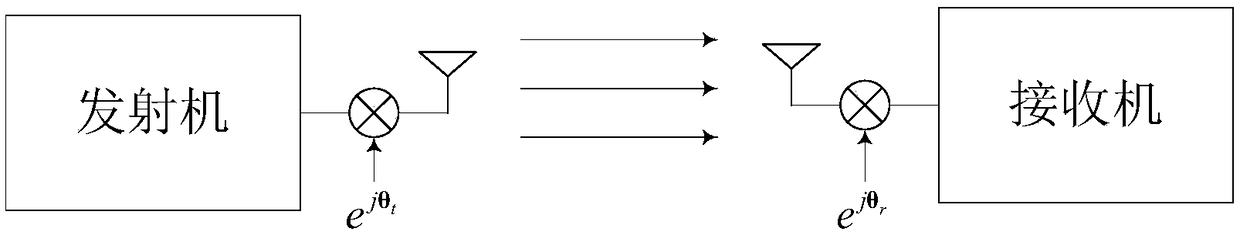
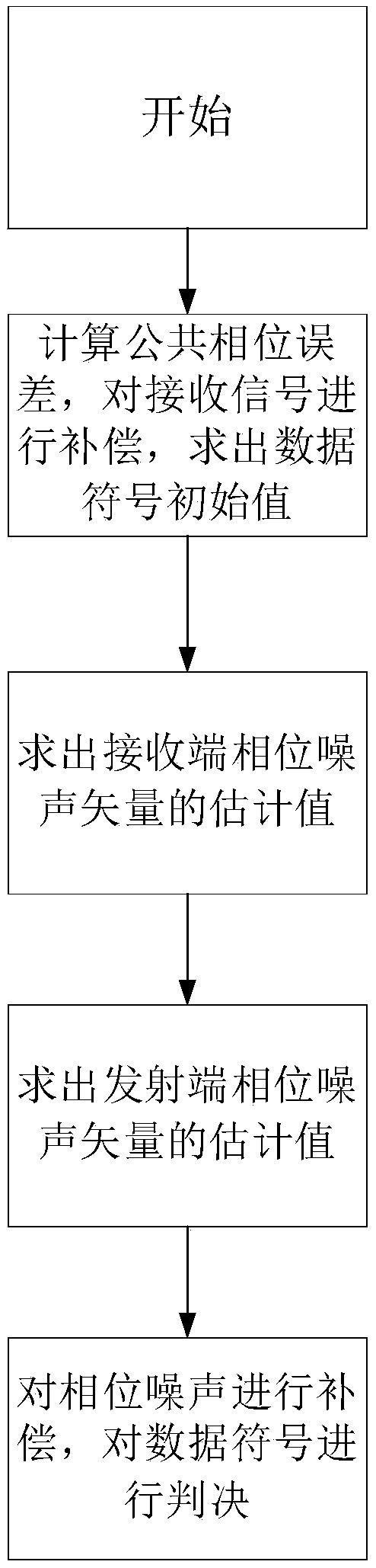
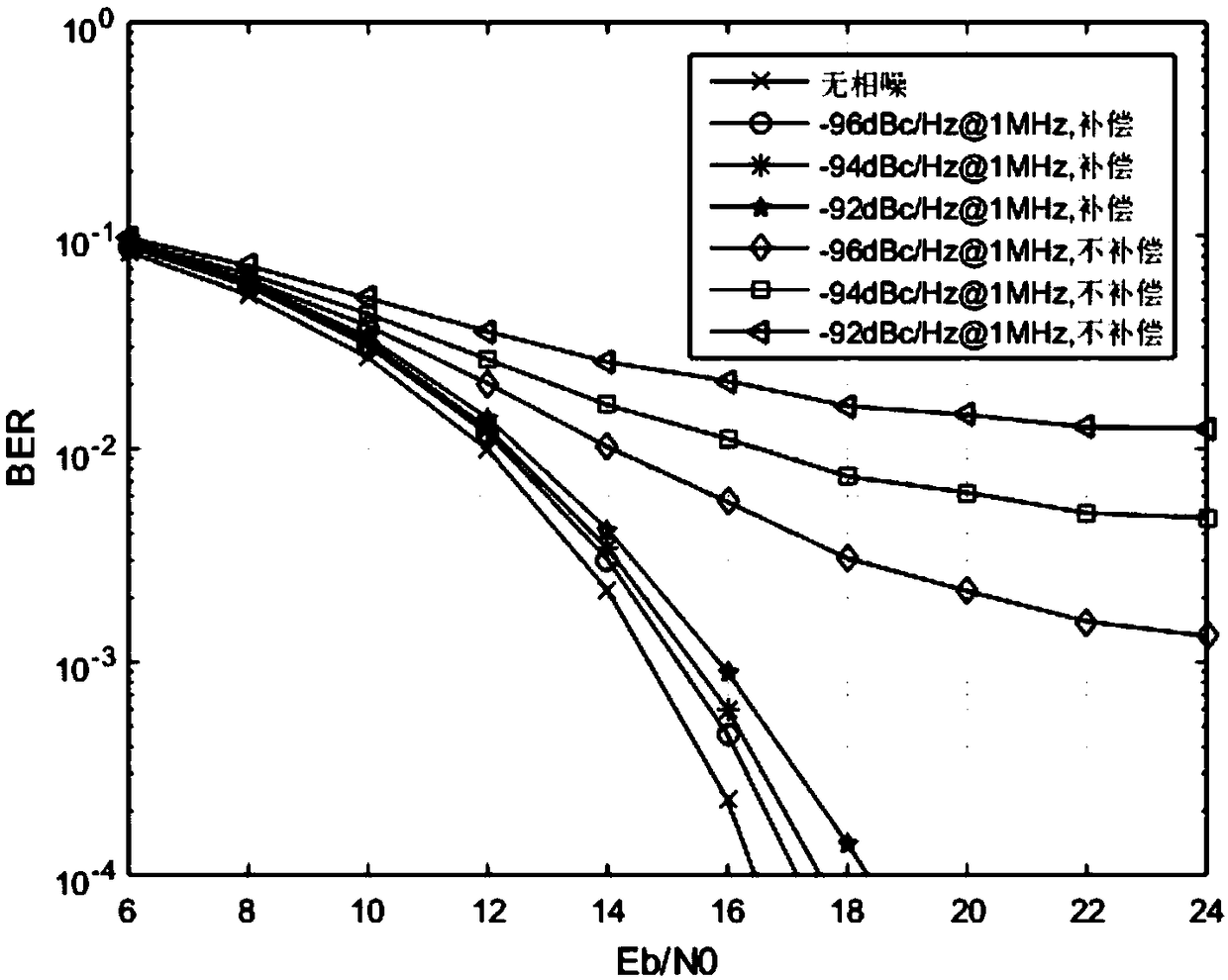
Double-ended phase noise suppression method of millimeter wave system based on maximum posteriori criterion
ActiveCN108924075AAccurate Data Sign EstimationImprove bit error rate performanceMulti-frequency code systemsPosterior probability densityMillimeter wave communication systems
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and relates to a double-ended phase noise suppression method of a millimeter wave system based on a maximum posteriori criterion. The maximum posteriori criterion is adopted in the double-ended phase noise suppression method provided by the invention, and the maximum posteriori criterion is a method of a corresponding signal estimated value for figuring out a derivative of posterior probability distribution and performing continuous iteration, so that the posterior probability density is the maximal. The double-ended phasenoise suppression method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that accurate data symbol estimation can be realized under the condition that phase noise exists at both of transmittingand receiving ends in the millimeter wave communication system, and the bit error rate performance of the system is remarkably improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
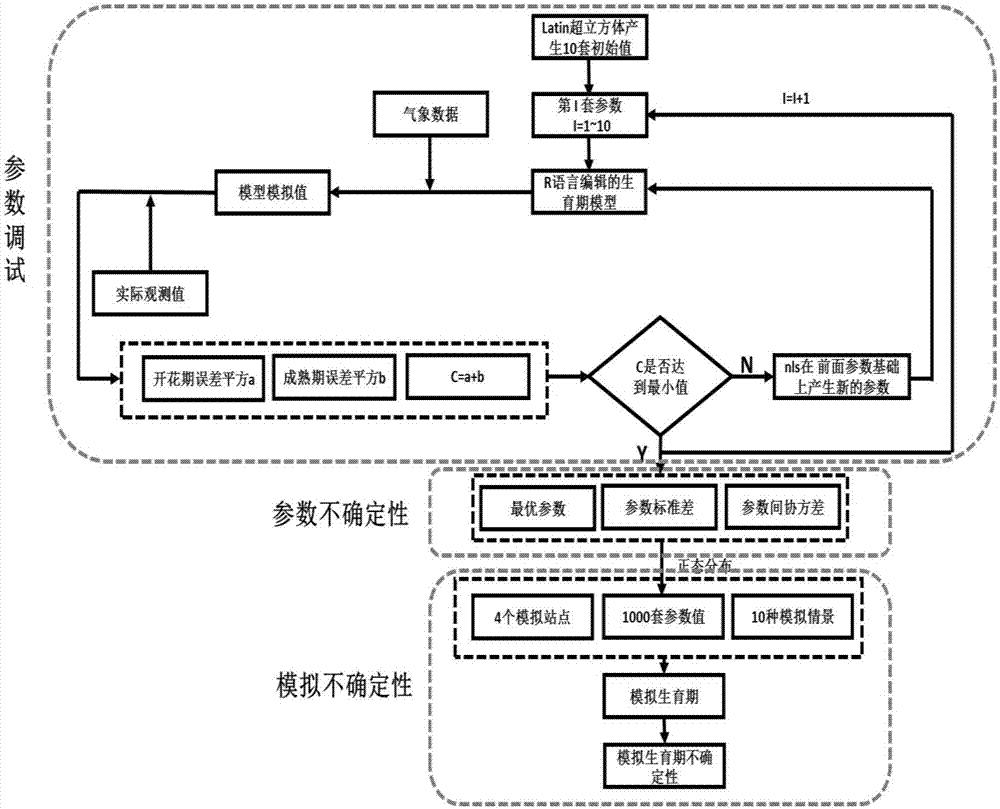
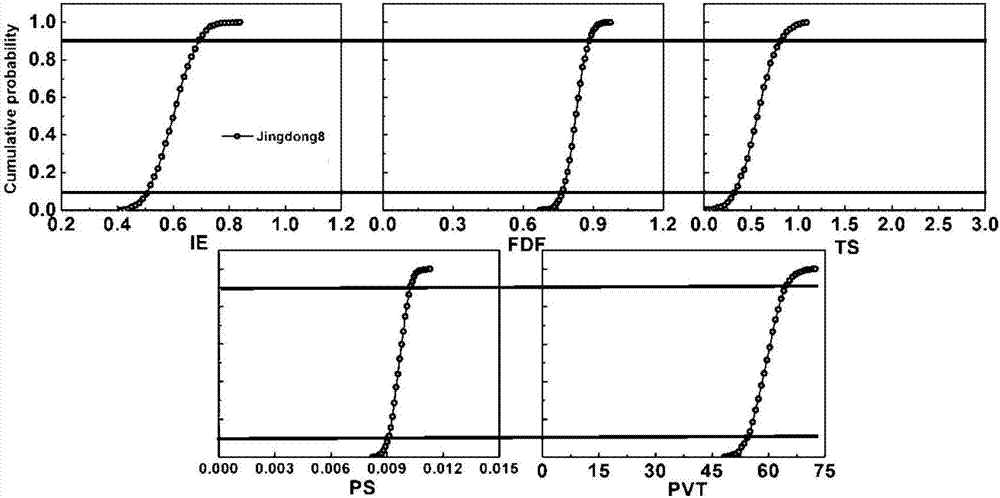
Wheat growth period characteristic parameter evaluation method based on R language
ActiveCN107038501AEffective inversion of characteristic parametersGuaranteed accuracyForecastingPosterior probability densityLocal optimum
The invention provides a wheat growth period characteristic parameter evaluation method based on R language. The wheat growth period characteristic parameter evaluation method based on R language is characterized in that recompiling a wheat growth analogy model by means of R language; setting a parameter initial value through Latin hypercube, and obtaining prior probability distribution of wheat variety characteristic parameters through operation; according to the initial value and prior probability distribution, selecting the candidate parameters; calculating the probability density function of the growth period, and determining whether or not to receive the new parameter; and then finally obtaining posterior probability density distribution of each characteristic parameter of varieties. The wheat growth period characteristic parameter evaluation method based on R language utilizes the non-linear least square method to improve the sampling efficiency to avoid the parameter falling into local optimum; based on the Bayesian theory framework, prior distribution of parameters are effectively considered; the error correlation problem between stations can be solved through conversion of the original data, so that the parameter debugging result can be accurate and efficient; and the wheat growth period characteristic parameter evaluation method based on R language has general applicability in characteristic parameter evaluation of the same wheat variety.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Global optimum particle filtering method and global optimum particle filter
InactiveCN106921366AIncrease diversityAvoid the problem of impoverishmentMathematical modelsDigital technique networkPosterior probability densityGaussian signal
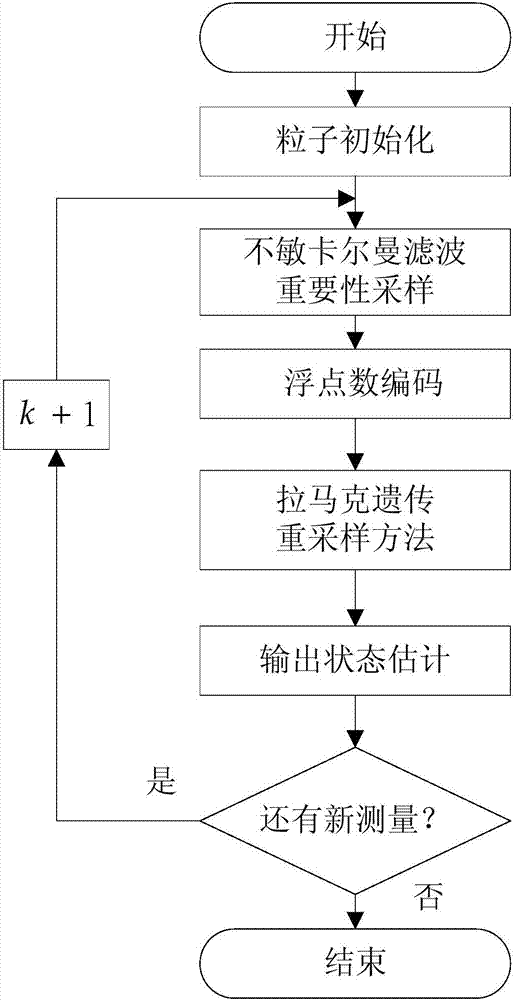
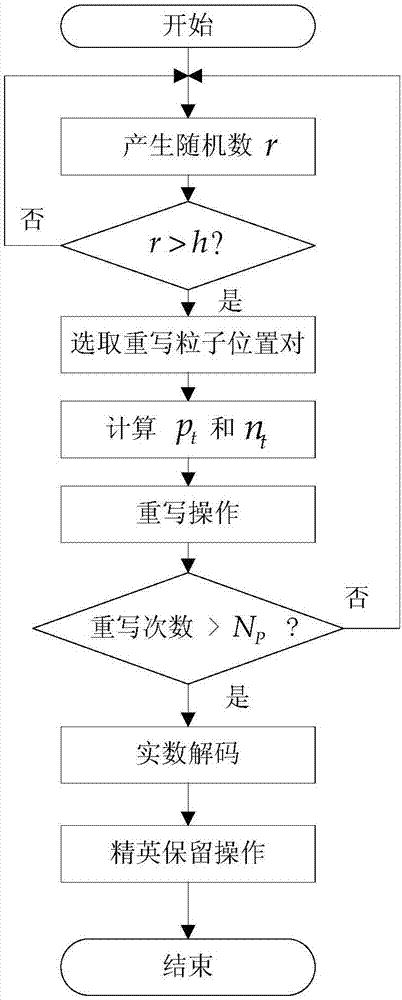
The invention relates to a global optimum particle filtering method and a global optimum particle filter and belongs to the field of signal processing. The defect that according to an existing particle filter, relatively high deviation exists between samples and true posterior probability density samples is overcome, and the problem of processing nonlinearity and non-Gaussian signal through particle filtering is effectively solved. The main technical way is establishing the global optimum particle filter through utilization of a Lamarch genetic natural law. The global optimum particle filtering method comprises the steps of generating an initial particle set; carrying out importance sampling on the initial particle set through unscented Kalman filter, thereby obtaining sample particles; carrying out float-point encoding on each sample particle, thereby obtaining an encoded particle set; setting an initial population; taking the initial population as an original test initial and carrying out Lamarch rewrite operation, real number decoding operation and elitism reservation operation in sequence; and taking real number form optimum candidate particles as prediction samples of the next moment, thereby obtaining a state estimation value of a system. The method and the filter are applicable to machine learning.
Owner:李琳 +1
Parameter estimation method of electron multiplying CCD (Charge Coupled Device) noise model
InactiveCN103077303AFit closelyEffective estimateSpecial data processing applicationsPosterior probability densityEstimation methods
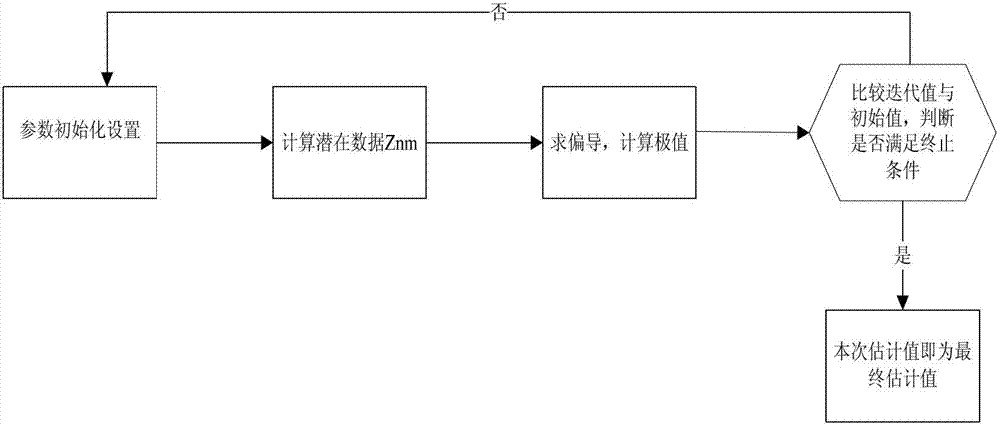
The invention discloses a parameter estimation method of an electron multiplying CCD (Charge Coupled Device) noise model. The method comprises the steps of: first, initially setting a noise distribution model as a mixed Gaussian distribution model to process; then, carrying out maximum likelihood iteration on the noise distribution model, substituting the set initial value to the mixed model to solve a posterior probability density of a sample value from a Gaussian source, and then substituting potential data to a log function with incomplete data to calculate a partial derivative to solve an extreme value so as to obtain an iteration estimated value of the parameter; and finally, judging and comparing the iteration estimated value with the initial value; judging whether the terminating condition is met or not according to a circulation terminating condition, if so, stopping iteration; if not, setting the iteration value as the initial value, and carrying out maximum likelihood iteration again. According to the invention, maximum likelihood estimation of the noise parameter of the electron multiplying CCD image is realized by simple steps, so that the complexity of the maximum likelihood method is effectively reduced, and the electron multiplying CCD image noise can be quickly and accurately estimated.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Filter for BDS (beidou navigation satellite system) and SINS (strapdown inertial navigation systems) navigation and positioning system and filtering method
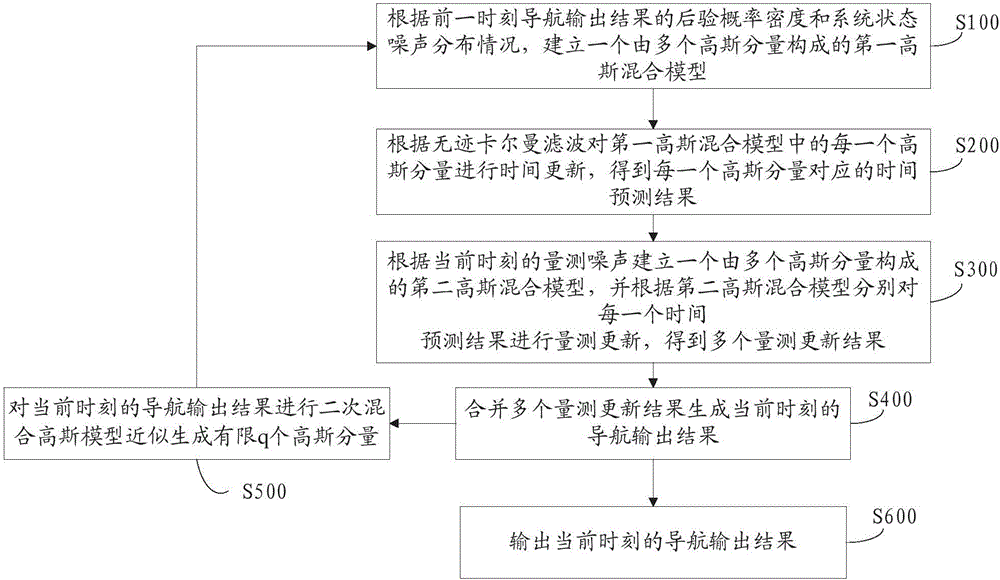
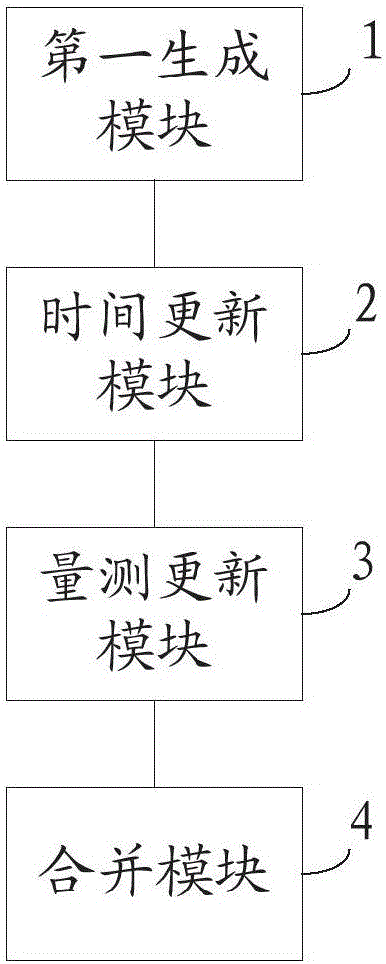
InactiveCN106323280AImprove robustnessImprove filtering accuracyNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsPosterior probability densityBeiDou Navigation Satellite System
The invention discloses a filter for a BDS (beidou navigation satellite system) and SINS (strapdown inertial navigation systems) navigation and positioning system and a filtering method, and relates to the technical field of navigation and positioning. The method comprises the steps of building a first Gaussian mixture model formed by a plurality of Gaussian components according to the system state noise distribution condition and the posterior probability density of the navigation output result at the former moment; performing time updating on each Gaussian component in the first Gaussian mixture model according to the unscented kalman filtering, and obtaining the time predicating result corresponding to each Gaussian component; building a second Gaussian mixture model formed by a plurality of Gaussian components according to the measuring noise at the current moment; performing measurement updating according to each time predicating result according to the second Gaussian mixture model to obtain a plurality of measurement updating results; merging the plurality of measurement results to generate the navigation output result of the current moment. After the filter is applied to the BDS / SINS vehicle-mounted combined navigation system, the navigation parameter precision is ensured; meanwhile, the calculation rate is high; the work real-time performance is better.
Owner:CHONGQING WATER RESOURCES & ELECTRIC ENG COLLEGE
Multi-pore reservoir pre-stack seismic probabilistic multi-channel inversion method
ActiveCN112965103AInversion uncertainty increasesGood for quantitative interpretationSeismic signal processingMarkov chainPosterior probability density
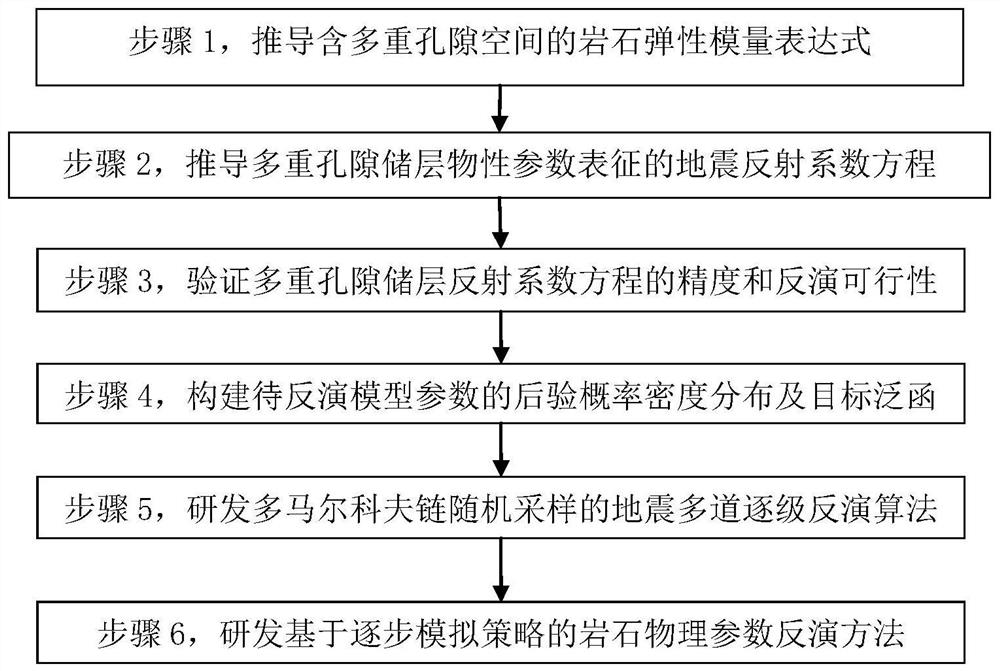
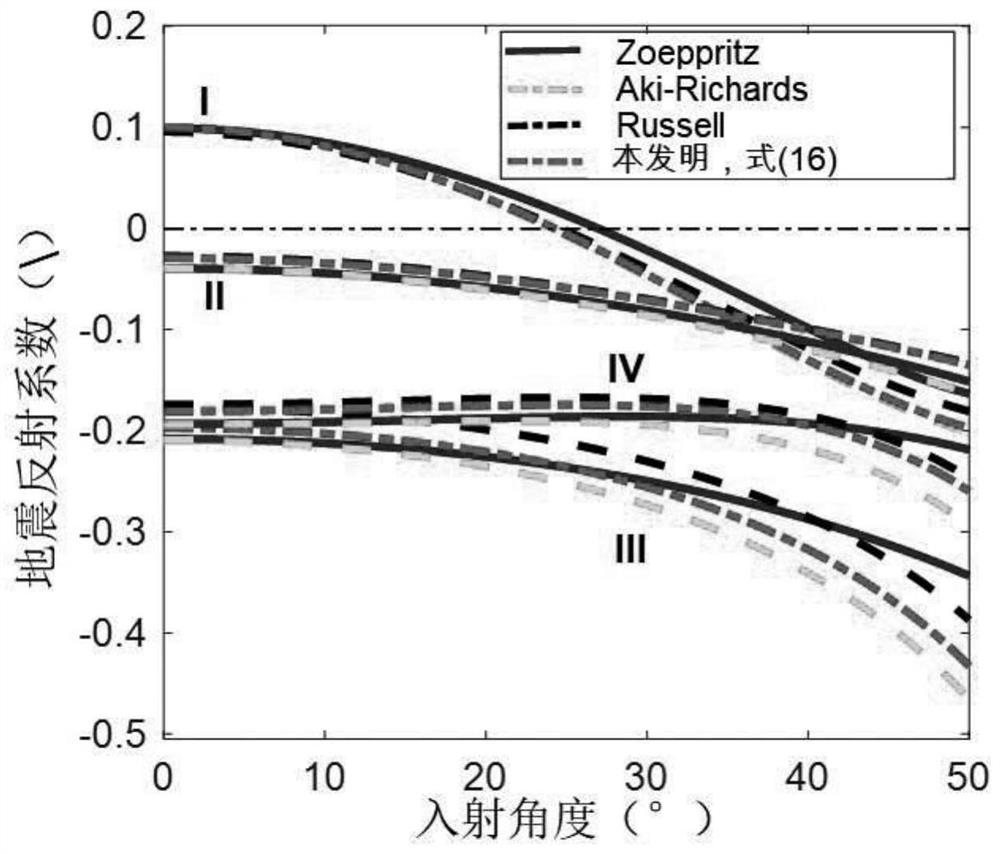
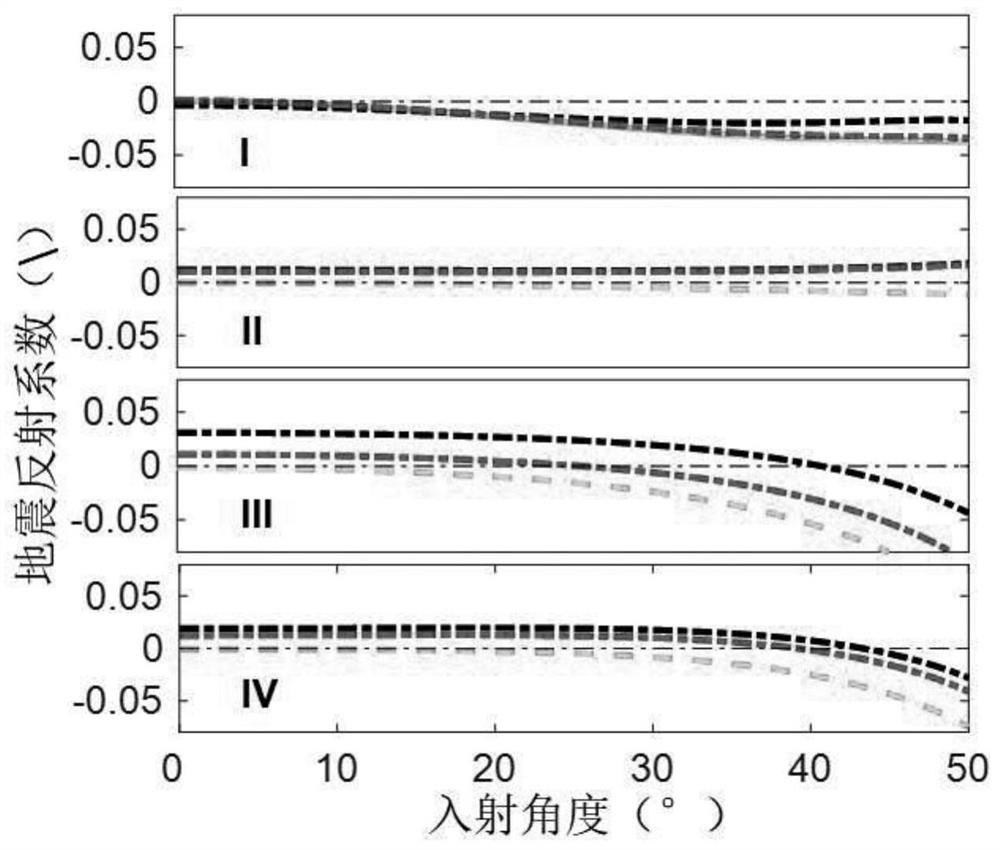
The invention discloses a multi-pore reservoir pre-stack seismic probabilistic multi-channel inversion method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, deducing a rock elastic modulus expression containing multiple pore spaces; 2, deducing a seismic reflection coefficient equation represented by the physical property parameters of a multi-pore reservoir; 3, verifying the precision and inversion feasibility of the reflection coefficient of the multi-pore reservoir; 4, constructing posterior probability density distribution and a target functional of to-be-inverted model parameters; 5, researching and developing a pre-stack seismic multi-channel step-by-step inversion algorithm of multi-Markov chain random sampling; and 6, researching and developing a rock physical parameter inversion method based on a step-by-step simulation strategy. According to the method, the influence of the reservoir pore structure on the seismic reflection coefficient is considered, the seismic reflection coefficient parameterization method of the multi-pore reservoir and the pre-stack seismic probabilization multi-channel inversion technology are researched and developed, and stable inversion of parameters such as the multi-pore volume fraction, the fluid volume modulus and the porosity is achieved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Ultrasonic tomography method based on Bayesian regularization
ActiveCN107389789ARealize non-destructive testingSolve the problem of difficulty in determining suitable regularization parametersAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructivePosterior probability density
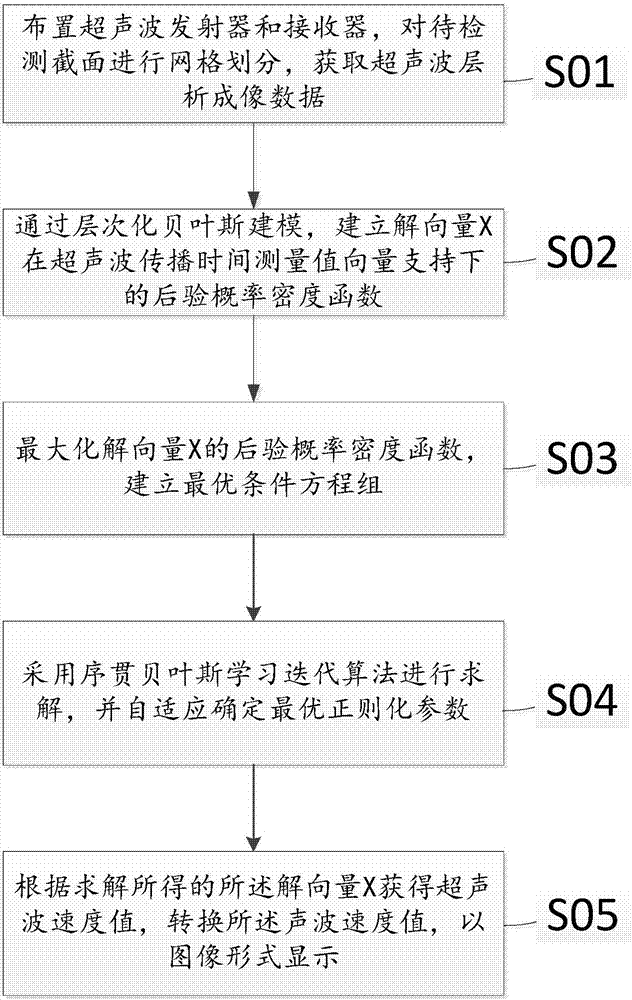
The embodiments of the present invention disclose an ultrasonic tomography method based on Bayesian regularization, and relates to the technical field of non-destructive detection. The ultrasonic tomography method can improve the calculation speed and the calculation precision of the inverse problem of ultrasonic tomography, and comprises: arranging an ultrasonic transmitter and a receiver, carrying out mesh dividing on a cross section to be detected, and obtaining ultrasonic tomography data; establishing the posterior probability density function pi (X, [sigma]2, [lambda]2|b) of a solution vector X under the support of an ultrasonic propagation time measurement value vector through layered Bayesian modeling; maximizing the posterior probability density function pi (X, [sigma]2, [lambda]2|b) of the solution vector X, and establishing an optimal condition equation set; solving the solution vector X, the [sigma]2 and the [lambda]2 by using a sequential Bayesian learning iterative algorithm, and adaptively determining an optimal regularization parameter; and obtaining the ultrasonic velocity value according to the solved solution vector X, and displaying in an image form. The ultrasonic tomography method of the present invention is suitable for the ultrasonic tomography of solids.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
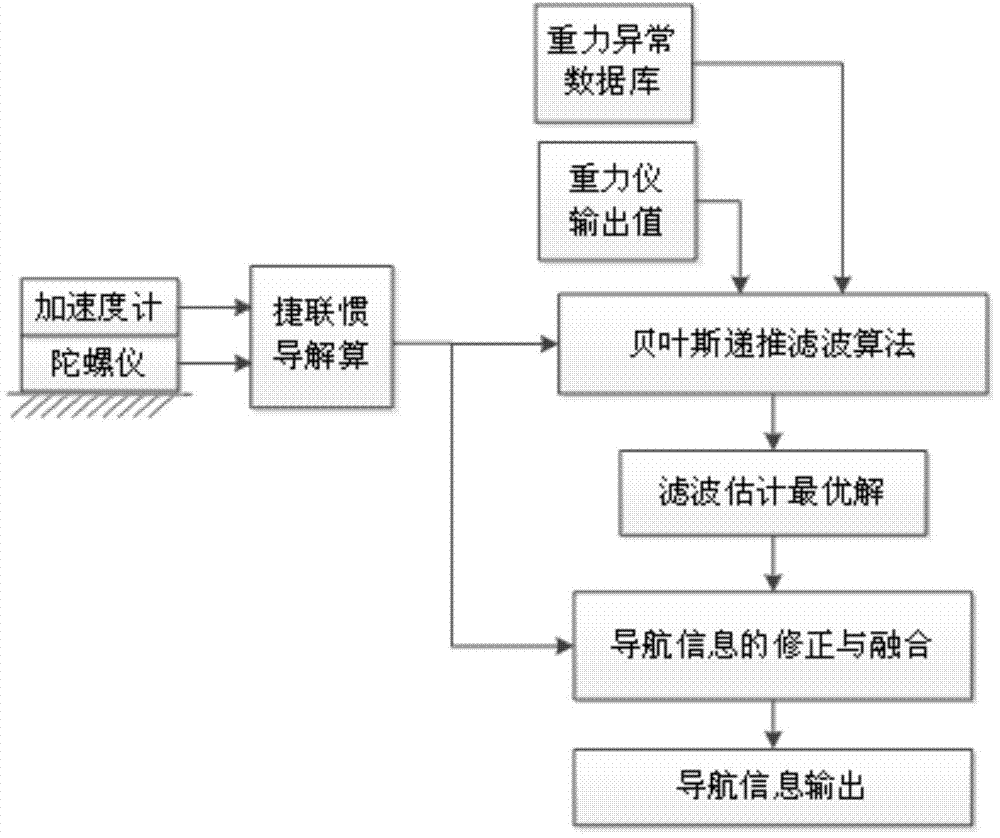
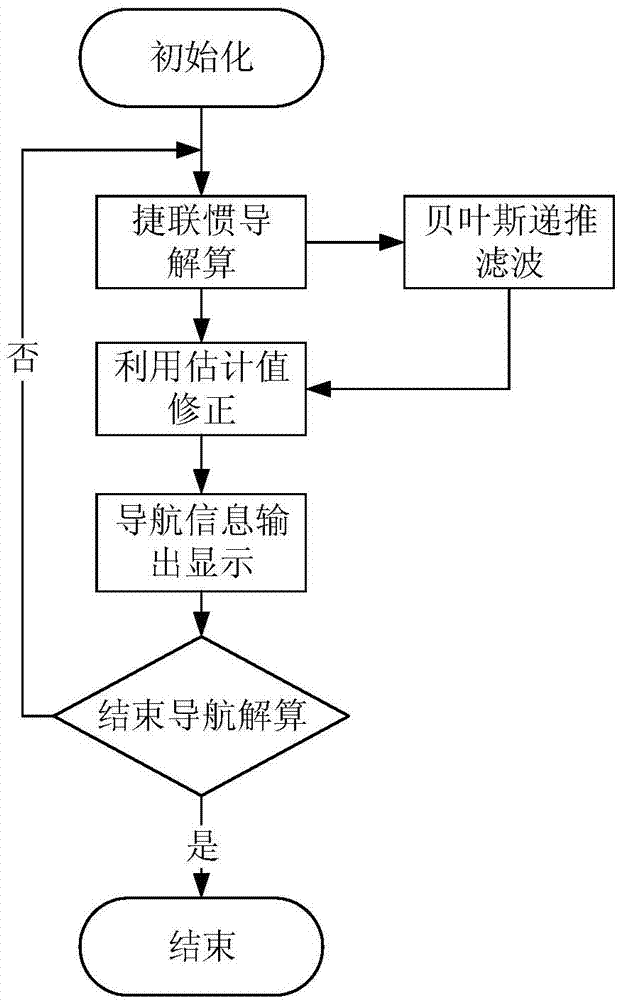
Gravity-assisted strapdown inertial navigation method based on bayesian recursion filtering
ActiveCN103900567AAchieve estimatesUnrestricted Gaussian distributionNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsLongitudeGravity assist
The invention provides a gravity-assisted strapdown inertial navigation method based on bayesian recursion filtering. In a strapdown inertial navigation system, under the condition without correction, the error in longitude of the strapdown inertial navigation system is diverged along with the time. In order to inhibit divergency of the error of the system and under the premise without damaging the concealment of the strapdown inertial navigation system, the invention provides the gravity-assisted strapdown inertial navigation method based on the bayesian recursion filtering. The gravity-assisted strapdown inertial navigation method provided by the invention has the advantages that after the measurement information is obtained, the posterior probability density of a state variable is gained by utilizing the bayesian law from the prior probability of the state variable, so that a globally optimal solution of the state variable is obtained; and after being gained, the globally optimal solution of the state variable is utilized for correcting the position error of the strapdown inertial navigation system, so that the purpose of improving the positioning accuracy of the system is achieved.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
PHD multi-target tracking method based on variational Bayesian T distributed Kalman filtering
PendingCN111325776AImprove robustnessImprove tracking accuracyImage enhancementMathematical modelsInformation processingPosterior probability density
The invention discloses a PHD multi-target tracking method based on variational Bayesian T distribution Kalman filtering, belongs to the technical field of guidance and intelligent information processing, and mainly solves the problem that the precision of a multi-target tracking algorithm is reduced under the conditions of nonlinearity and abnormal measurement values. The method is based on a variational Bayesian inference framework. The target state is updated by adopting the T distributed Kalman filtering technology, and the posterior probability density of the target is deduced based on the variational Bayesian framework and the T distributed Kalman filtering, so that the robustness and the overall tracking precision of the PHD tracking algorithm are improved, the design requirements of an actual engineering system can be met, and the engineering application value is high.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF TECH
Robust group target tracking method and tracking system for monitoring system
InactiveCN110120066AImprove performanceMeet the actual engineering needsImage enhancementImage analysisPosterior probability densityComplete data
The invention provides a robust group target tracking method for a monitoring system. The method comprises the following steps: S1, establishing a hybrid observation model; S2, calculating the joint probability density of each state variable and the measured complete data of the monitoring system; S3, calculating the approximate posterior probability density; S4, calculating clutter density parameters in measurement; S5, according to the approximate posterior probability density of each state variable and a clutter density parameter in measurement, calculating the mathematical expectation of each state variable so as to obtain an estimated value of each state variable, repeatedly executing the steps S2 to S4 for appointed times, and considering that tracking is finished; and S6, performingtracking estimation of the group target: realizing estimation of the motion state, the shape and the environment clutter density of the group target according to the finally obtained estimation valueof each state variable and the clutter density parameter. According to the method, the problems caused by observation noise obeying heavy tail distribution and environmental clutters are solved, andmeanwhile, the clutter density is estimated when the group target is tracked.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Estimating anisotropic parameters
InactiveUS8792302B2Seismic signal processingAnalogue computers for heat flowPosterior probability densityNormal density
A method for processing seismic data. The method includes performing a plurality of stochastic simulations for one or more rock model parameters to generate one or more anisotropic parameters for a subsurface area of the earth. The method then derives one or more joint multi-dimensional probability density functions for the anisotropic parameters. Using the joint multi-dimensional probability density functions and measured well log data, the method computes one or more posterior probability density functions. The method then includes deriving one or more anisotropic profiles from the posterior probability density functions and generating a seismic image from the anisotropic profiles.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
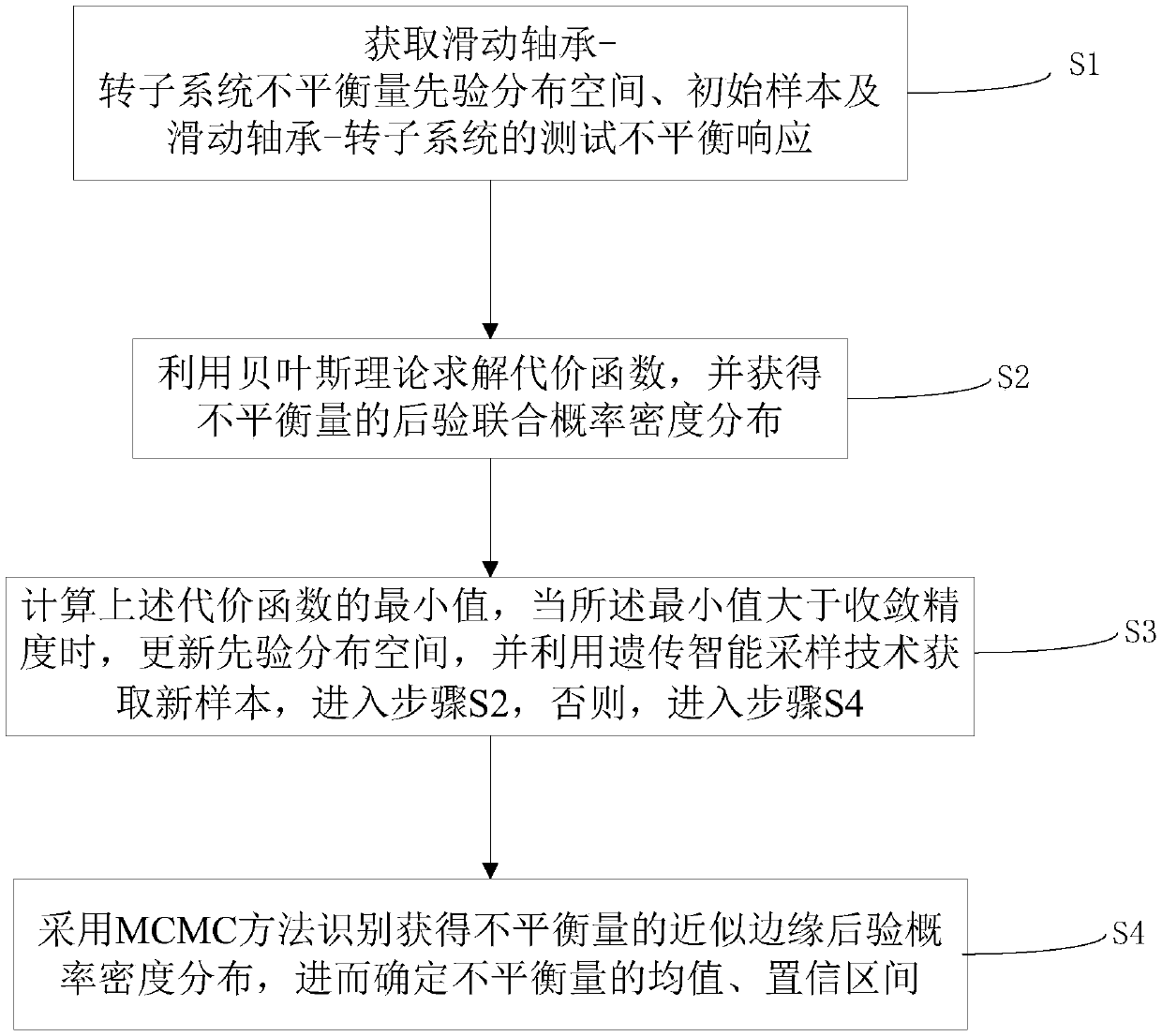
Sliding bearing-rotor system unbalance amount recognition method
PendingCN108694417AReduce the number of calculationsReduce the impactStatic/dynamic balance measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionPosterior probability densityConfidence interval
The invention relates to a sliding bearing-rotor system unbalance amount recognition method, belongs to the technical field of inverse problems of uncertainty, and aims at solving the problems that the Bayesian theory and an MCMC method need to generate plenty of sampling points in sampling and the solution of forward problems consumes time and is low in efficiency. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining an unbalance amount prior distribution space, an initial sample and a test unbalance response; solving a cost function and obtaining a posterior joint probability density distribution; calculating a minimum value of the cost function, when the minimum value is greater than convergence precision, updating the prior distribution space and obtaining a new sample by utilizing agenetic intelligent sampling technology so as to calculate the new cost function, and otherwise, recognizing and obtaining an approximate edge posterior probability density distribution of the unbalance amount by adoption of the MCMC method so as to determine a mean value and a confidence interval of the unbalance amount. According to the method, relatively high calculation efficiency can be obtained without sacrificing the calculation precision, and information such as the mean value and the confidence interval of the unbalance amount can be correctly and rapidly recognized.
Owner:HUNAN INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING
Device residual life prediction method based on multi-hidden state fractional Brownian motion
ActiveCN108829983AAchieve Life PredictionAchieving Effective Lifetime PredictionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFractional Brownian motionPosterior probability density
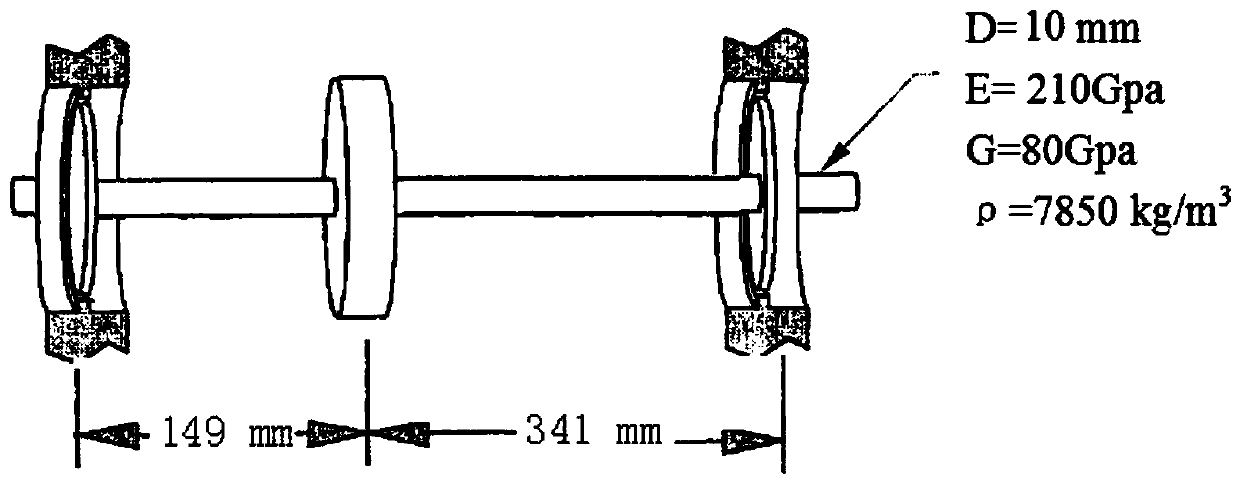
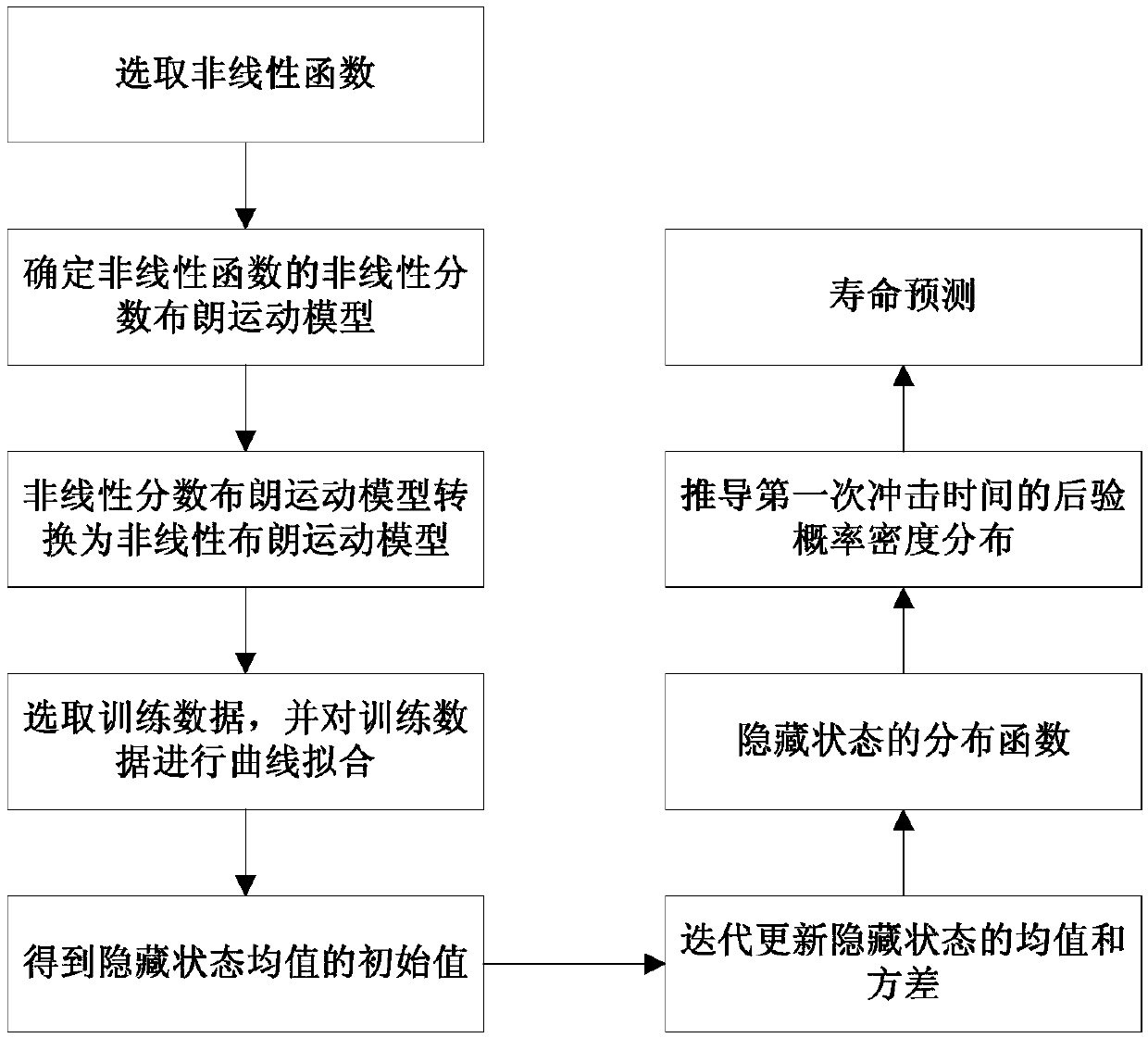
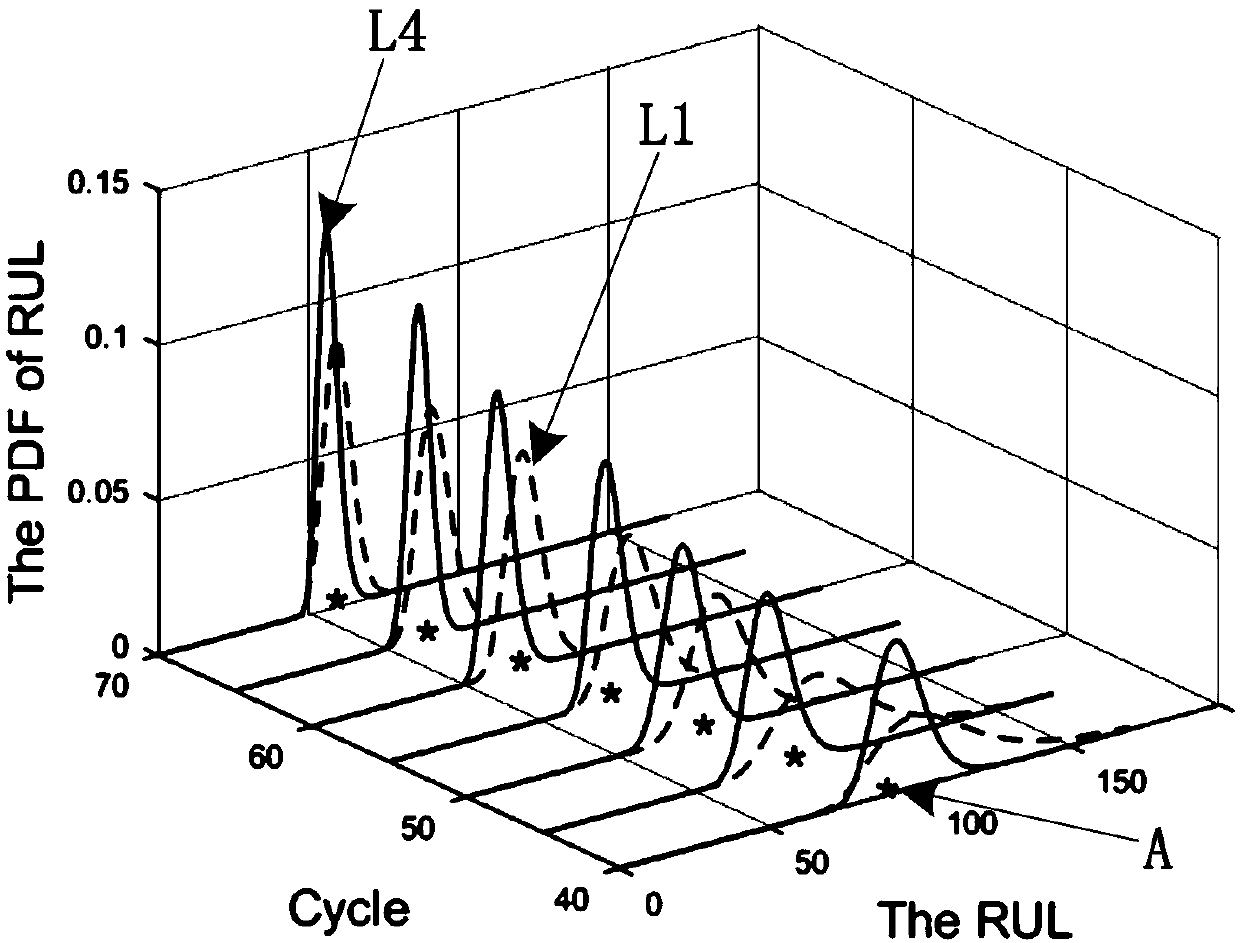
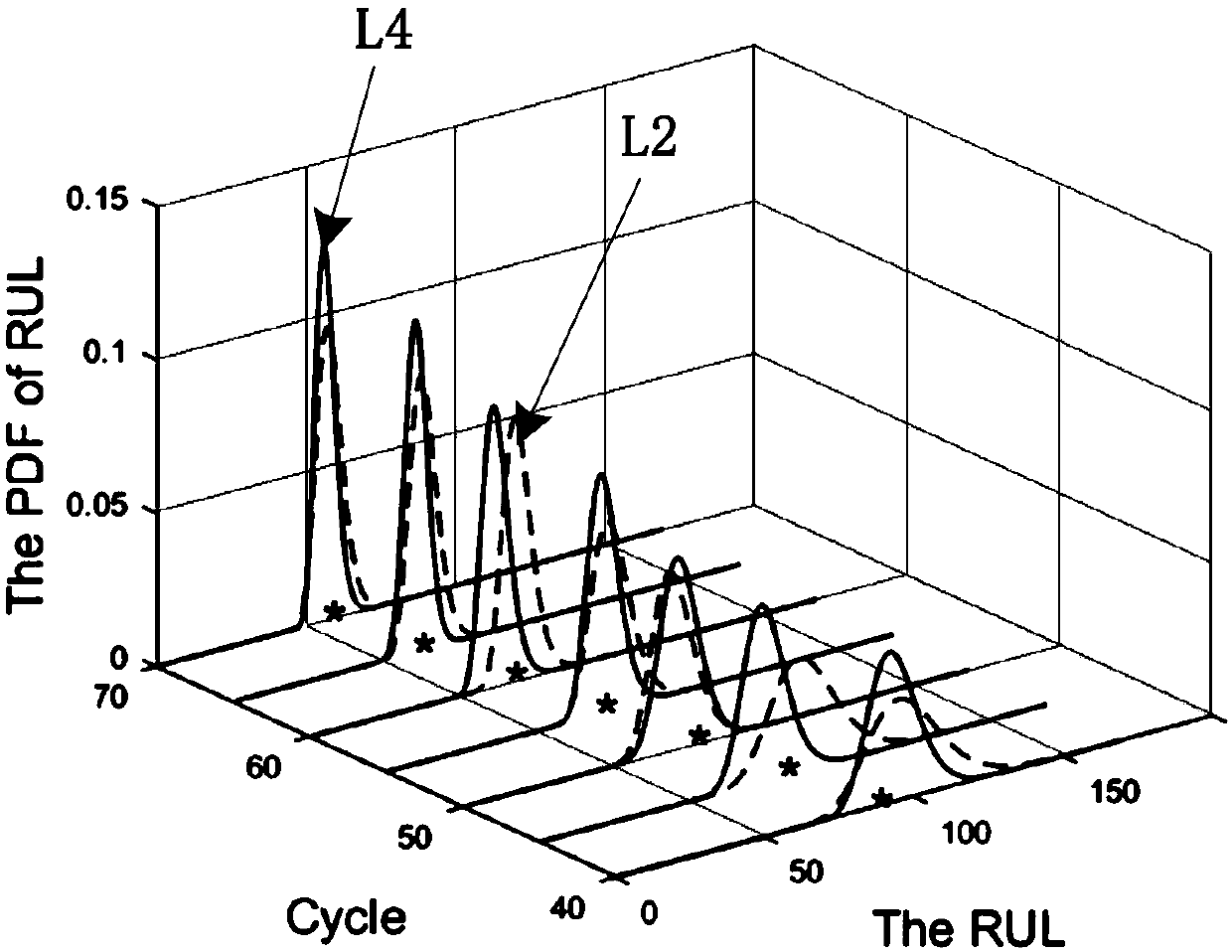
The invention relates to the field of life prediction of electromechanical equipment, and discloses a device residual life prediction method based on multi-hidden state fractional Brownian motion, which solves the problem that only the current observation value is taken into account in the prior residual life prediction method based on fractional Brownian motion, the device life prediction precision is low. Firstly, a nonlinear function is selected according to the life degradation trend of the device, a nonlinear fractional Brownian motion model is determined, and the parameter in the nonlinear function is taken as a hidden state; the nonlinear fractional Brownian motion model is converted into the nonlinear Brownian motion model; then, curve fitting is carried out on the training data toobtain an initial value of the hidden state mean value; then iteration is carried out to update the mean value and variance of the hidden state to obtain a distribution function of the hidden state;then the posterior probability density distribution of a first impact time is deduced; Finally, the posterior probability density distribution of the first impact time is used for life prediction. Themethod is applicable to the prediction of residual effective service life of the electromechanical equipment.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Information-theory-based research method of single-objective Cramer-Rao bound of sensor system
ActiveCN109375156ARadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsHigh level techniquesStudy methodsProbit
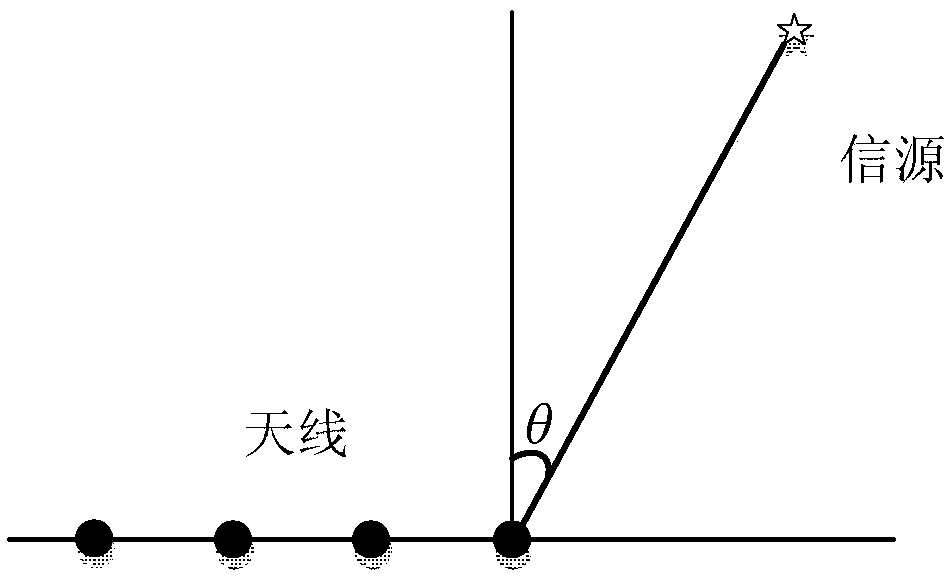
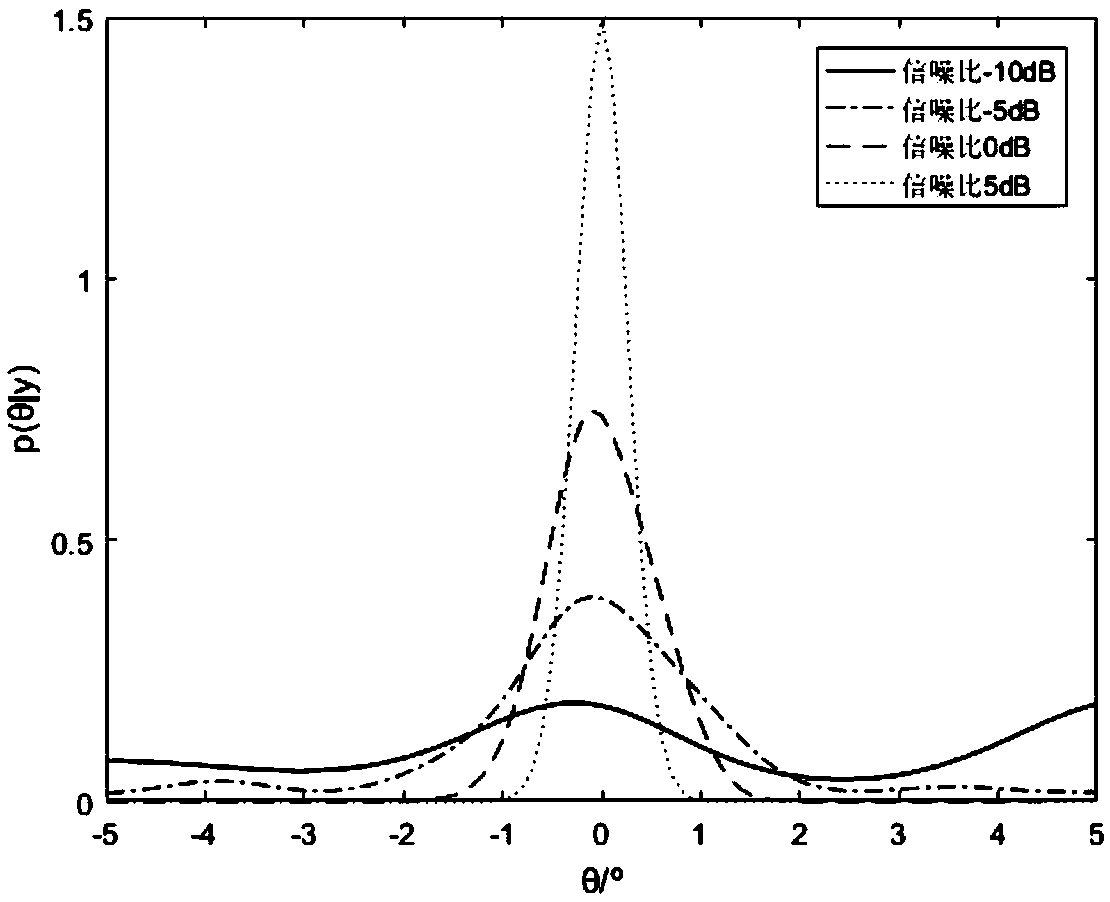
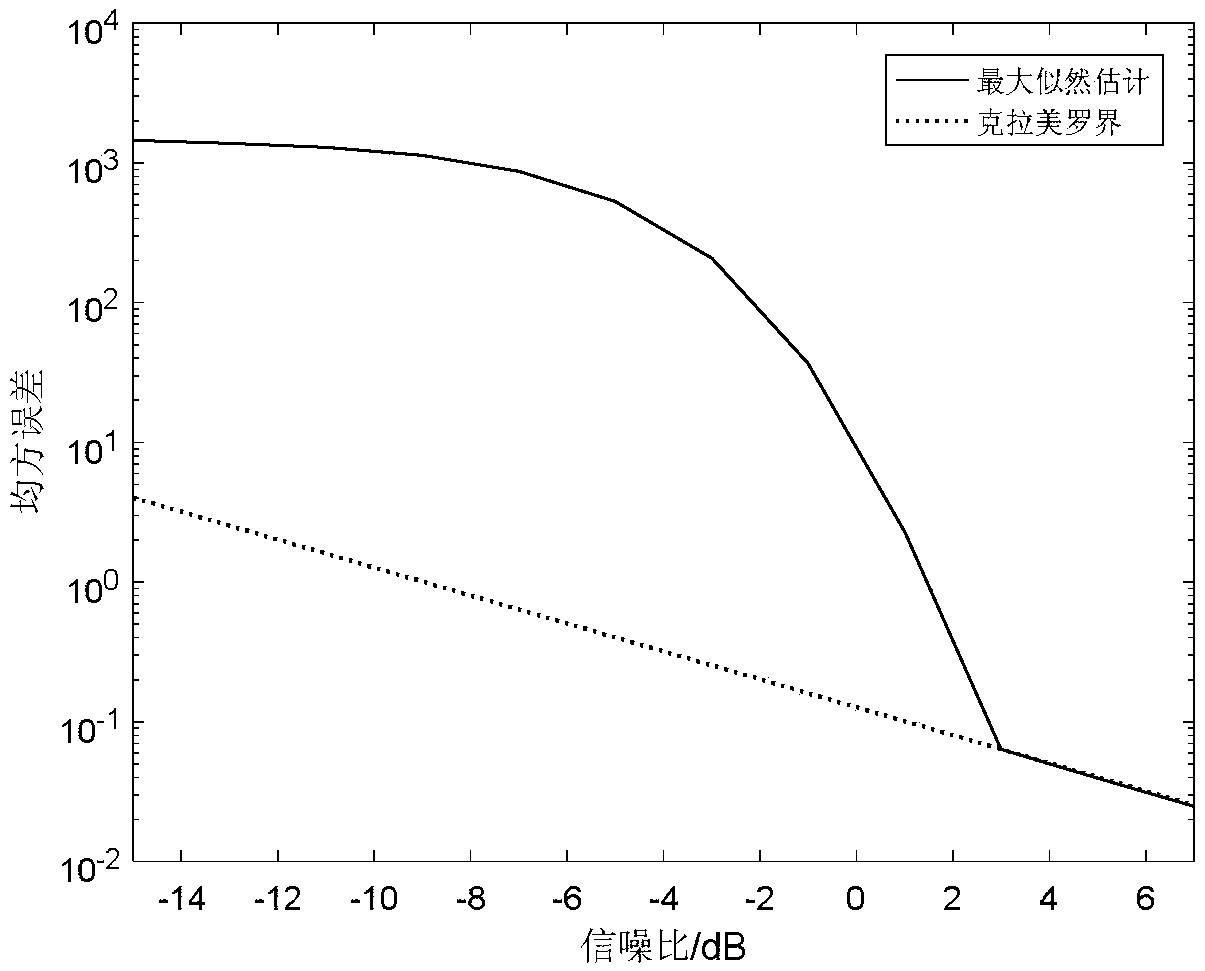
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of information transmission and processing, provides an information-theory-based research method of a single-objective Cramer-Rao bound (CRB) of a sensor system. The bound serves as a lower bound of a DOA estimation performance of a spatial signal. On the basis of the Shannon's information theory, a theoretical model of maximum likelihood communication in a complex additive white Gaussian noise (CAWGN) environment is proposed. For the single source estimation, posterior probability density distribution of the to-be-measured angle is derived from a likelihood function and an expression of the Gaussian approximation of the posterior probability distribution under high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) is obtained, so that the variance is CRB. Thesimulation results show that the CRB derived by the method is an approximate lower bound of the maximum likelihood algorithm (MLE). The correctness of the theoretical analysis is verified by the simulation results. The conclusion made by the method has the important theoretical guiding significance in the DOA estimation based on an MLE algorithm.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
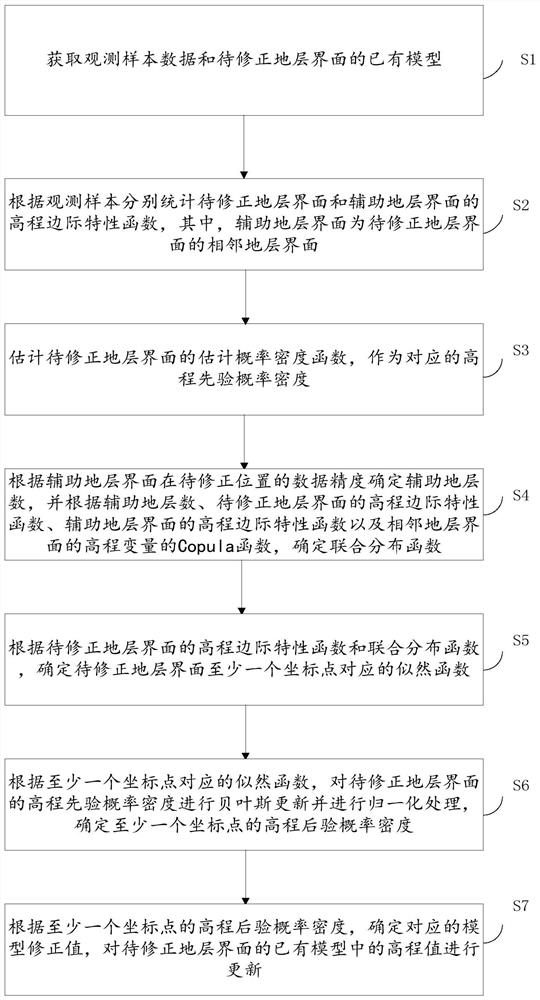
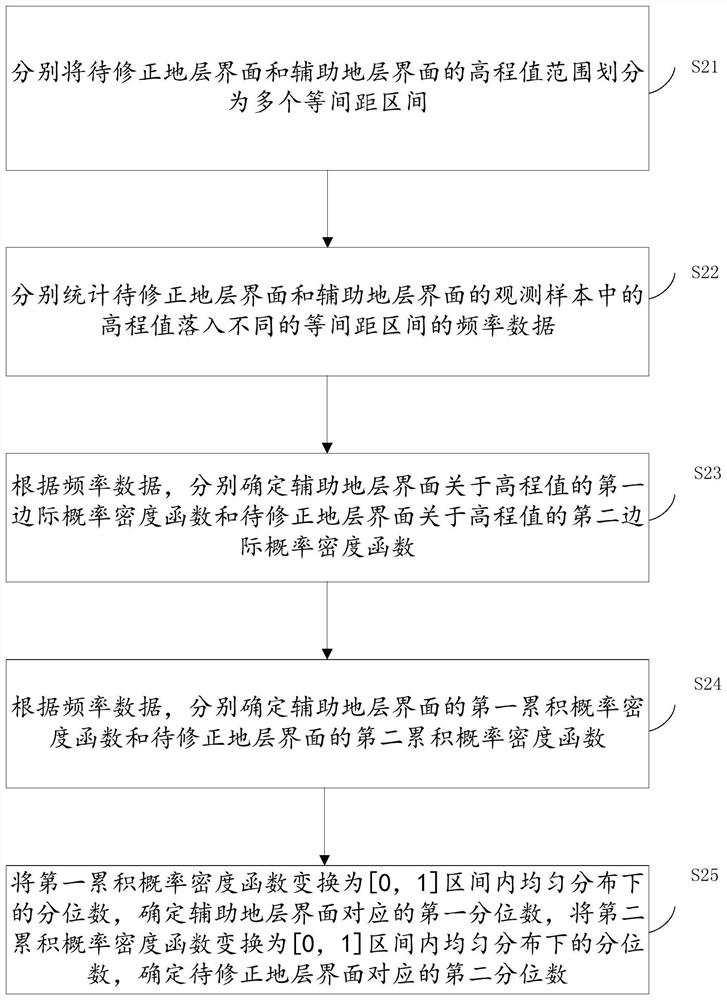
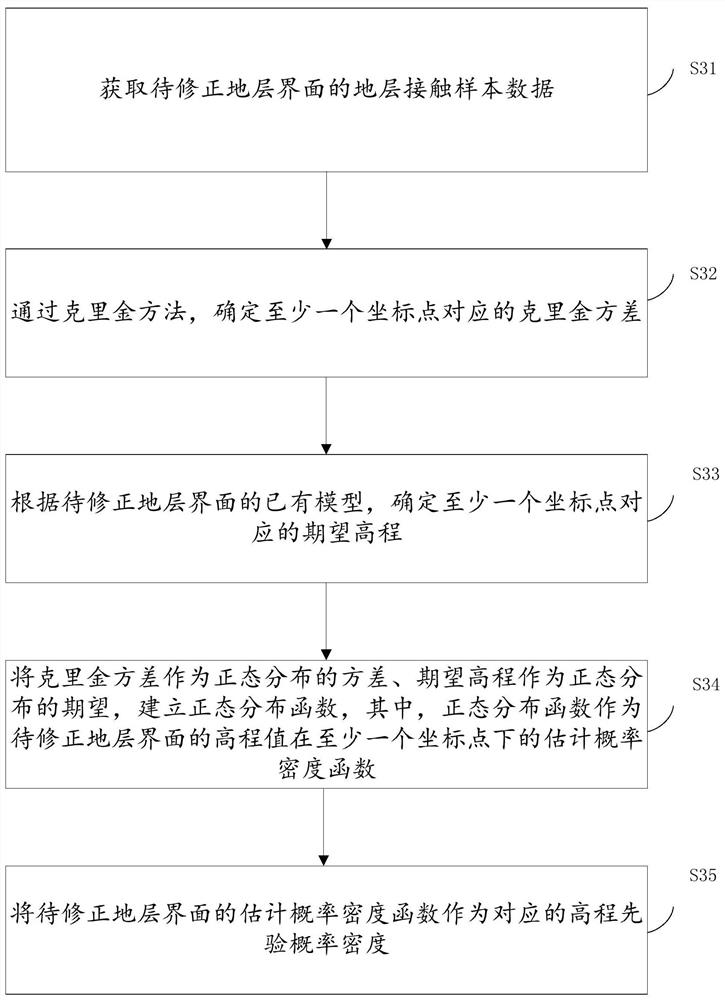
Method for correcting stratum surface model by utilizing cross-correlation constraint of adjacent stratums
ActiveCN112800518AImprove modeling accuracyIt is convenient for subsequent calculation of the posterior distributionGeometric CADComplex mathematical operationsPosterior probability densityComputational physics
The invention relates to a method for correcting a stratum surface model by utilizing cross-correlation constraint of adjacent stratums. The method comprises the following steps of: counting elevation marginal characteristic functions of a stratum interface to be corrected and an auxiliary stratum interface; estimating the elevation prior probability density corresponding to the stratum interface to be corrected; determining a joint distribution function according to the number of the auxiliary strata, the elevation marginal characteristic functions of the to-be-corrected strata interface and the auxiliary strata interface and the Copula function of the adjacent strata interface; determining a likelihood function corresponding to at least one coordinate point of the stratum interface to be corrected according to the elevation marginal characteristic function and the joint distribution function; according to the likelihood function, performing Bayesian updating on the elevation prior probability density of the stratum interface to be corrected, and determining elevation posterior probability density; and according to the elevation posterior probability density, updating an elevation value in the existing model of the stratum interface to be corrected. According to the method, the complex related structures of the adjacent stratums are described through the Copula method, model correction is carried out through correlation, and the modeling precision of an existing model is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
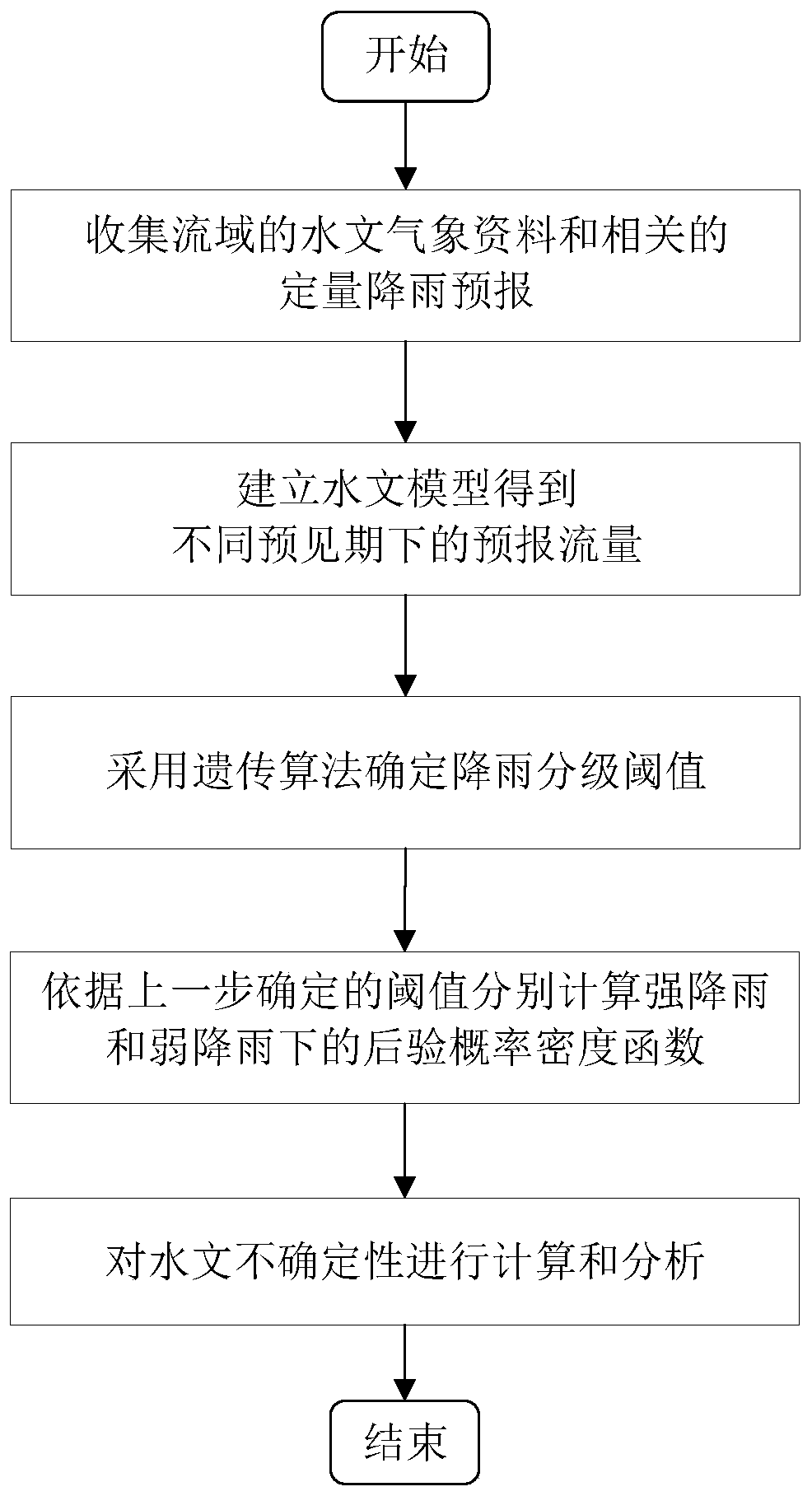
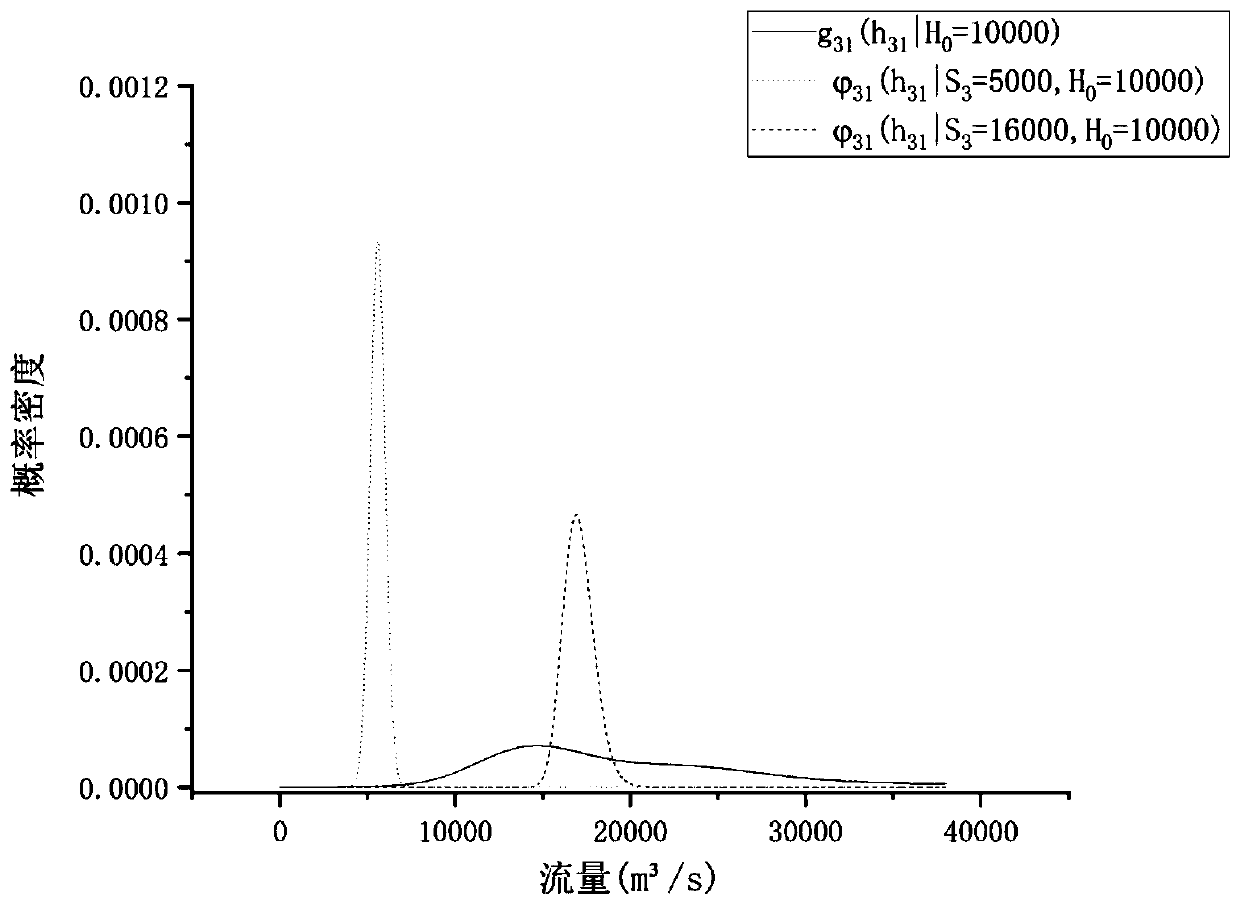
Hydrological forecasting method and system considering rainfall grades
ActiveCN111126699AImprove efficiencyImprove general performanceForecastingGenetic algorithmsHydrometryPosterior probability density
The invention discloses a hydrological forecasting method and system considering rainfall grades and also discloses a hydrological uncertainty processor application method considering rainfall grades.The method comprises the following steps of: (1) collecting the hydrometeorological data and related quantitative rainfall forecast of a drainage basin; (2) establishing a hydrological model to obtain forecast flows in different forecast periods; (3) determining a rainfall grading threshold by adopting a genetic algorithm; (4) respectively calculating posterior probability density functions underheavy rainfall and weak rainfall according to the threshold determined in the previous step; and (5) calculating and analyzing hydrological uncertainty. According to the method of the invention, therainfall grading threshold is determined by adopting the genetic algorithm; a Gaussian mixture model is used for fitting the edge distribution of actually measured flow and forecast flow; the hydrological uncertainty under the conditions of heavy rainfall and weak rainfall is analyzed; and with the hydrological uncertainty processor application method considering the rainfall grades adopted, the application of a hydrological uncertainty processor is improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com