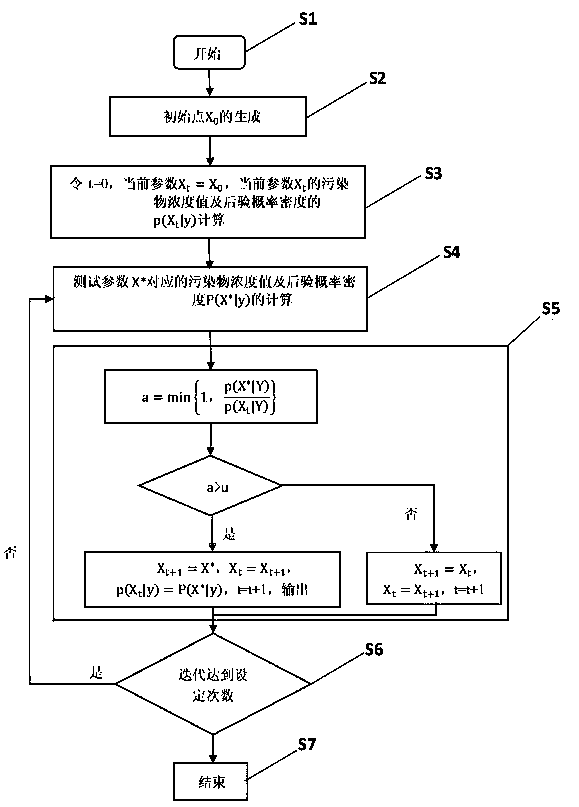
A Bayesian statistical traceability method for discharging industrial waste water exceeding the standard of sewage pipe network
A sewage pipe network and industrial wastewater technology, applied in the field of municipal engineering information, can solve the problems of heavy sampling calculation workload, slow traceability feedback, long back-estimation time, etc., to ensure the rationality of sampling, improve accuracy, and reduce sampling time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
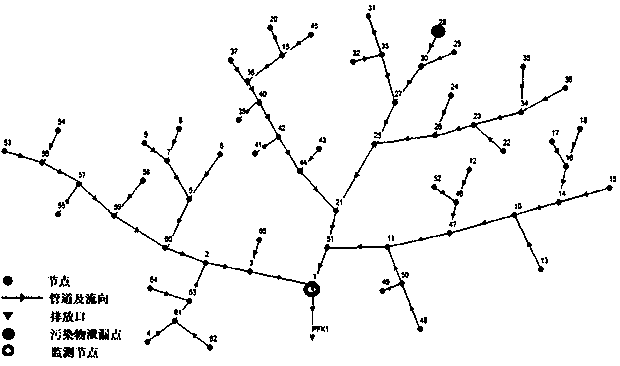
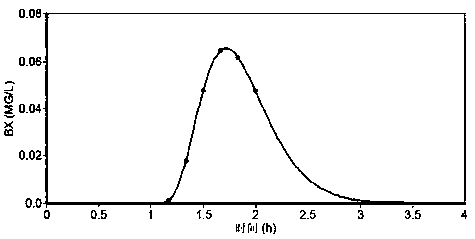
[0059] figure 2 It is the layout diagram of the regional sewage pipe network. The water flow in the pipe network is shown by the arrow. The sewage pipe network has 64 sections and 65 nodes in total, with a pipe diameter of 400-800mm. PFK1 is the main discharge port of the sewage pipe network. , and set up water quality monitoring points at node J1 on the main pipe downstream of the pipe network. The flow state of the sewage pipe network is constant, the migration and transmission of pollutants in the sewage pipes obeys the one-dimensional water quality model, and the degradation process is a first-order attenuation with an attenuation coefficient of 0.25. Assume that at 1:00 on a certain day, a factory at node 28 discharges pollutant BX with a weight of 1000kg instantaneously, and the concentration change curve of BX is observed at the downstream monitoring point J1. Now use the disturbed concentration field distribution of the monitoring node J1 to invert the emission inten...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com