Blind equalizer and blind equalization processing method
A blind equalization and equalization technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve the problems of insufficient steady-state performance and slow convergence speed, and achieve the effect of improving the convergence speed and steady-state performance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] In the embodiment of the present invention, by using the steepest descent gradient algorithm, in order to minimize the error term of the first weight update module and maximize the logarithm of the local posterior probability density function adopted by the second weight update module, the update weight Value vector, and then according to the updated weight vector, the received signal vector is equalized and output, and a blind equalizer is realized.
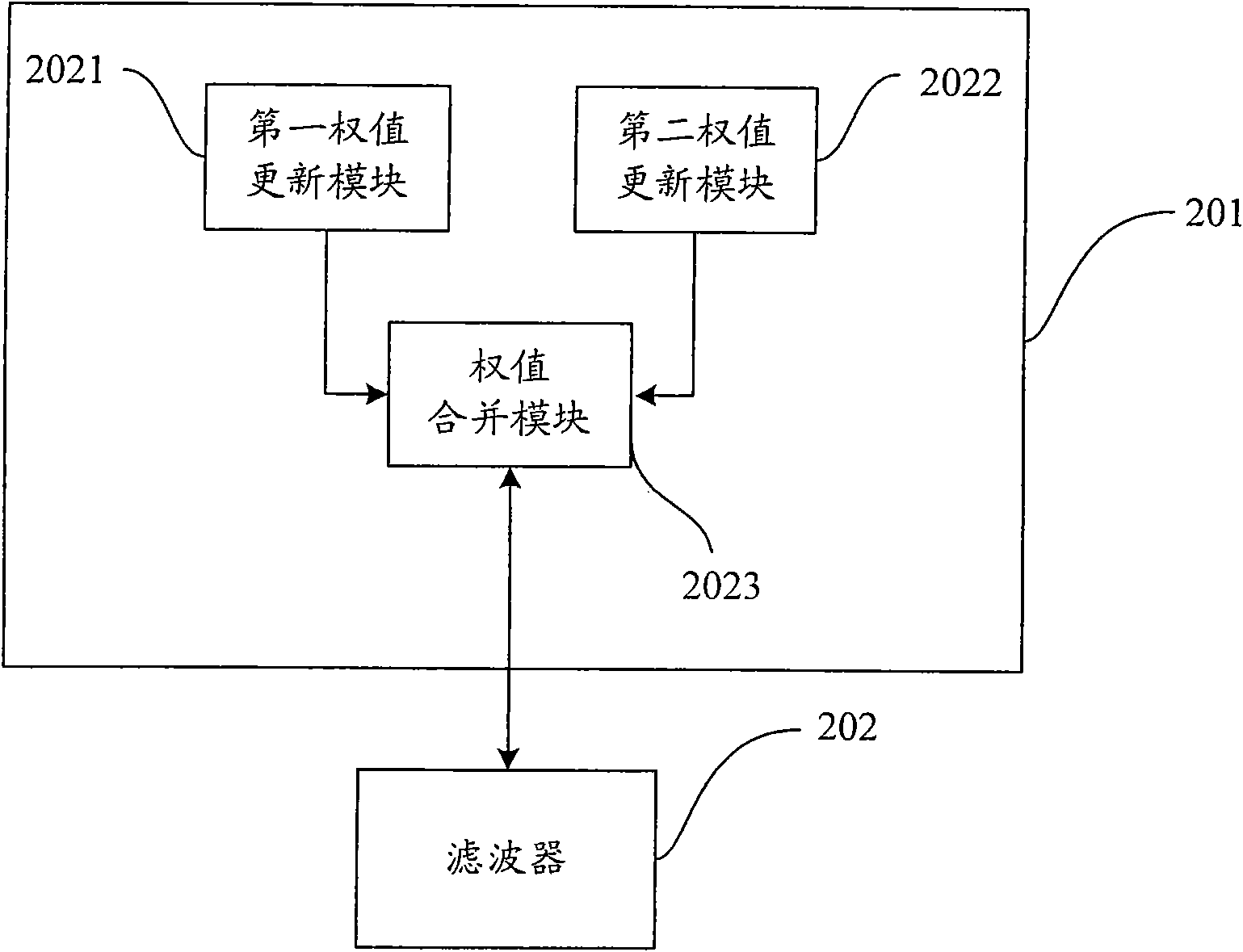
[0039] figure 2 The structure of the blind equalizer provided by the embodiment of the present invention is shown, and only the parts related to the embodiment of the present invention are shown for convenience of description.
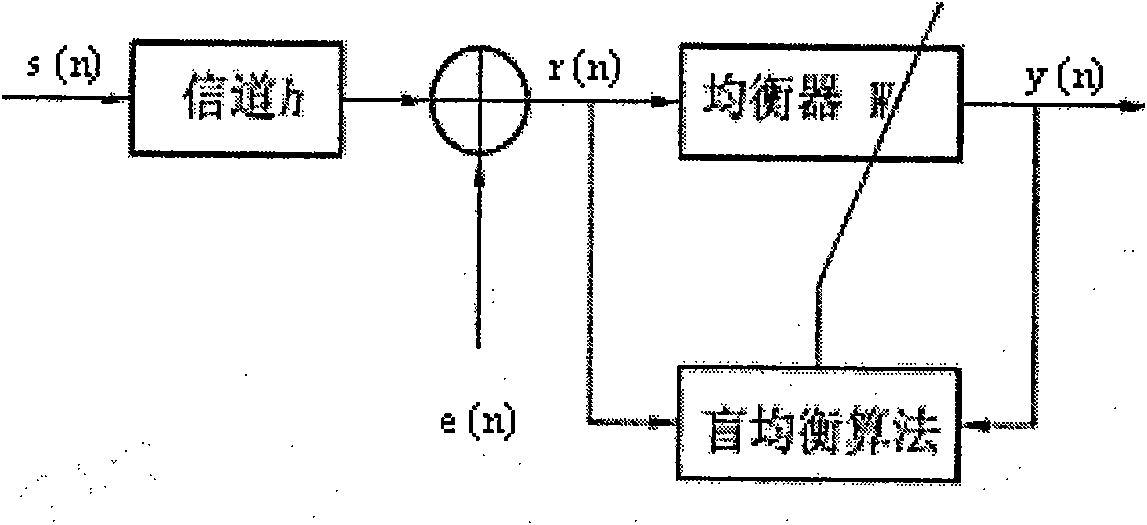
[0040] The blind equalizer can be used in a receiver of a wireless mobile communication system, and can be a software unit, a hardware unit or a combination of software and hardware running in these receivers, wherein:
[0041] The weight update unit 201, according to the steepest descent gradie...
Embodiment 2
[0071] In order to reduce the phase offset and further improve the convergence speed, as a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the first weight update module 2011 divides the CMA error term into two parts, the real part and the imaginary part, according to the steepest descent gradient algorithm, and then Adding a dithering random signal and performing a sign operation to form a new error term. In order to reduce the new error term and continuously update the first weight vector until convergence, the Dithered Signed-Error-Improved Constant Modulus Algorithm (Dithered Signed-Error- Modified Constant Modulus Algorithm, DSE-MCMA) algorithm updates the first weight vector, specifically, adopts the following iterative formula to update the first weight vector:
[0072] w c (n+1)=w c (n)+μ c ε(y n , d n )r * (n);
[0073] Among them, w c (n) represents the weight vector of the first weight update module 2011 at time n; μ c is the (positive) iterative step size of...
Embodiment 3
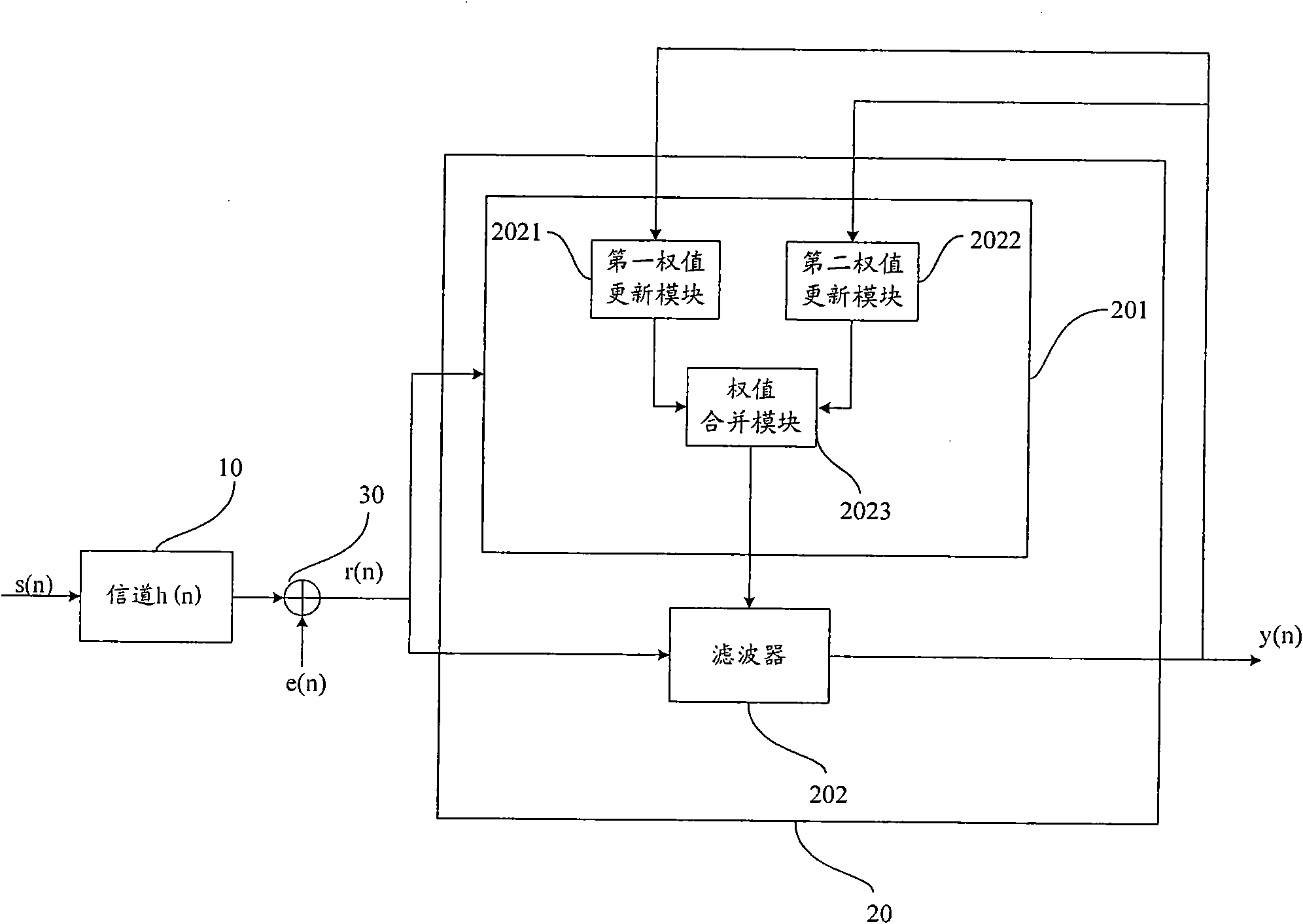
[0084] Figure 7 The implementation flow of the blind equalization processing method provided by the embodiment of the present invention is shown, and the details are as follows:
[0085] In step S701, the DSE-CMA algorithm is used to update the first weight vector;
[0086] In step S702, the maximum a posteriori probability theory is used as the judgment basis, and the steepest descent gradient algorithm is adopted to maximize the logarithmic value of the local a posteriori p.d.f., and update the second weight vector;
[0087] In step S703, merge the updated first weight vector and the second weight vector;
[0088] In step S704, according to the weight vector obtained after merging, the received signal vector is equalized and then output, and the received signal vector is equalized by the following formula:
[0089] y(n)=w(n) T r(n);
[0090] Among them, the superscript "T" indicates matrix transposition, w(n) is the weight vector obtained after merging in step S703, r(n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com