Service sending and receiving method and device in optical transport network
A technology for optical transport network and service transmission, which is applied in the field of communication and can solve problems such as bandwidth waste
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
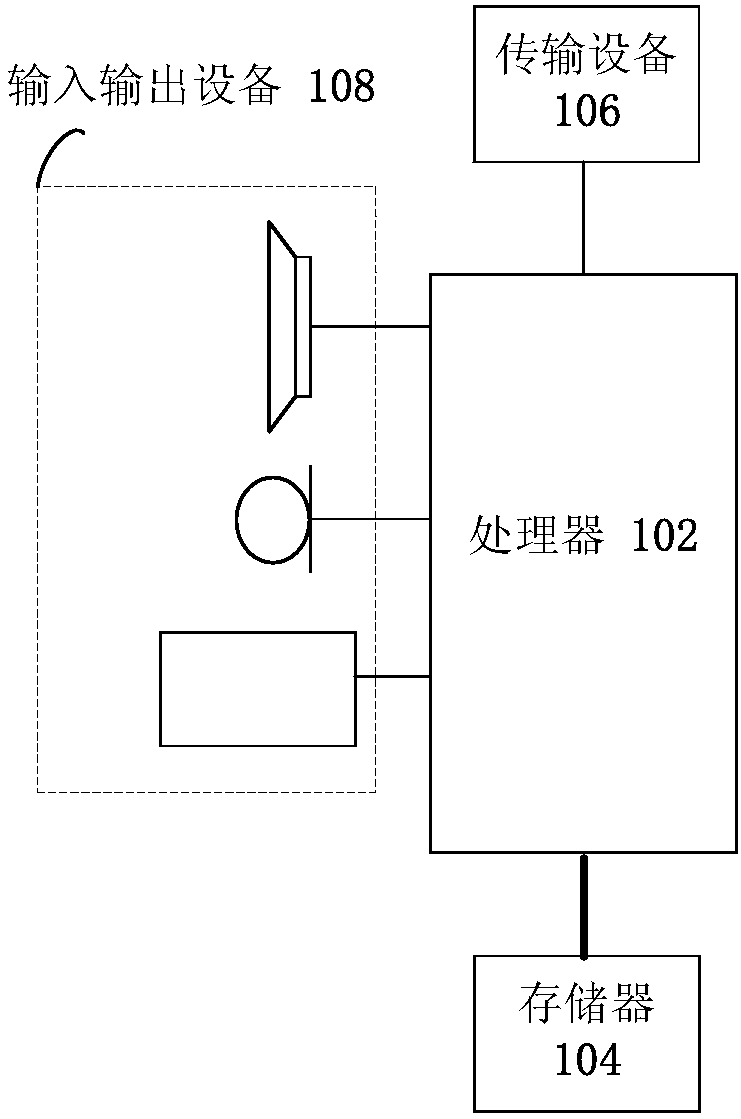
[0100] The method embodiment provided in Embodiment 1 of the present application may be executed in a mobile terminal, a computer terminal, or a similar computing device. Taking running on a mobile terminal as an example, image 3 It is a hardware structural block diagram of a mobile terminal of a service sending method in an optical transport network according to an embodiment of the present invention. Such as image 3 As shown, the mobile terminal 10 may include one or more ( image 3 Only one is shown in the figure) a processor 102 (the processor 102 may include but not limited to a processing device such as a microprocessor MCU or a programmable logic device FPGA) and a memory 104 for storing data. Optionally, the above-mentioned mobile terminal also A transmission device 106 for communication functions as well as input and output devices 108 may be included. Those of ordinary skill in the art can understand that, image 3 The shown structure is only for illustration, ...
Embodiment 2
[0144] According to another embodiment of the present invention, a service receiving method in an optical transport network is also provided, Figure 8 is a flowchart of a service receiving method in an optical transport network according to an embodiment of the present invention, such as Figure 8 As shown, the process includes the following steps:
[0145] Step S802, receiving an OTN interface frame of the optical transport network, wherein the payload area of the OTN interface frame includes N cells of a fixed size, one cell carries one ODU service, and N is an integer greater than or equal to 1;
[0146] Step S804, demapping ODU services from the N cells in the payload area of the OTN interface frame.
[0147] Through the above steps, since the ODU service is demapped from the N cells in the payload area of the OTN interface frame, it is possible to solve the problem of transmitting optical transmission by dividing the payload area into time slots in the related art...
example 1
[0160]Two OTN devices transmit two Ethernet services with a bandwidth of 5GE through the OTU2, and the OTU2 payload area is divided by cells provided by the present invention instead of time slots.
[0161] Step 1, the size of the payload area of OTU2 is 4*3808 bytes, and the cell size is set to 32 bytes, which can be divided into (4*3808) / 32=476 cells in total, and the bandwidth of each cell is OPU2 Payload bandwidth / 476, all cell numbers are 0, the first bit of each cell is cell type identification, and 0 means that all (32*8-1) bits in this cell are services , which is 1 means that (32*8-1) bits in this cell are all control information.
[0162] Step 2. At the sending end, map the two 5GE Ethernets to the corresponding two ODUflexes, and the bandwidth of each ODUflex is about 5G.
[0163] Step 3: Calculate the number of cells occupied by each ODUflex according to the ODUflex bandwidth and the cell bandwidth. In this example, 238 cells need to be allocated to each ODUflex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com