An Incremental Spatiotemporal Learning Method for Online Modeling of Distributed Parameter Systems
A learning method and distributed technology, applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of online updating of space-time synthetic sets, data identification of space-time synthetic sets, time-consuming problems, etc., and achieve remarkable calculation results , broad application prospects, the effect of reducing time and memory usage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
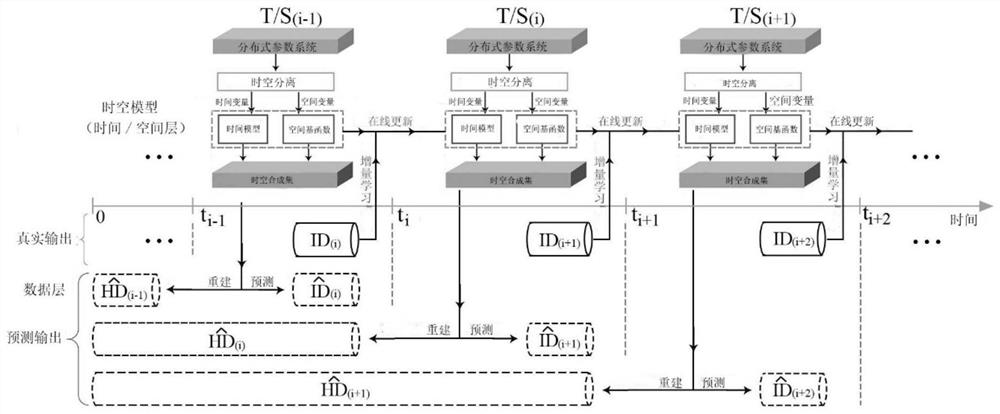
[0143] This example presents an incremental spatiotemporal learning method for online modeling of distributed parameter systems, including:
[0144] (1) After adding new data to the incremental data set, incrementally update the spatial basis functions;
[0145] (2) Update the time coefficient and identify the new timing model;
[0146] (3) Reconstruct historical data through the old space-time composite set, the updated spatial basis function in step (1) and the time series model identified in step (2), and predict future output;
[0147] (4) Repeat steps (1)-(3) to complete the online update of the spatio-temporal synthetic set.
[0148] Among them, the data increment set is the collected continuous data flow with a specific time step, the spatial basis function is the basis function of n-dimensional space, and the basis function of n-dimensional space is separated by time and space, with the time step as L, learned from the training data. , Incremental update refers to t...
Embodiment 2
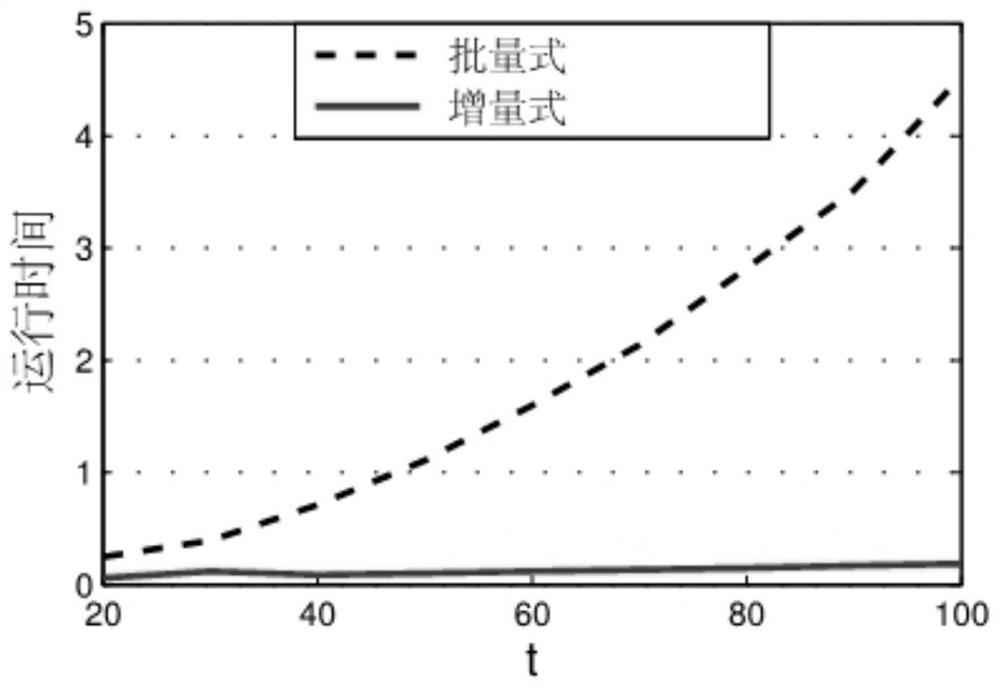
[0156] In order to prove the performance of the incremental space-time learning method for online modeling of distributed parameter systems in Example 1, we take the catalytic reaction rod experiment as an example, and compare Example 1 with the traditional batch processing mode method to illustrate Feasibility and advantages of incremental learning.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com