Electroencephalogram identification method and device
A technology of EEG signals and recognition methods, applied in medical science, sensors, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve problems such as time-consuming, not well solved at the same time, and low recognition accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0091] The exemplary embodiments will be described in detail here, and examples thereof are shown in the accompanying drawings. When the following description refers to the accompanying drawings, unless otherwise indicated, the same numbers in different drawings represent the same or similar elements. The implementation manners described in the following exemplary embodiments do not represent all implementation manners consistent with the present invention. Rather, they are merely examples of devices and methods consistent with some aspects of the present invention as detailed in the appended claims.
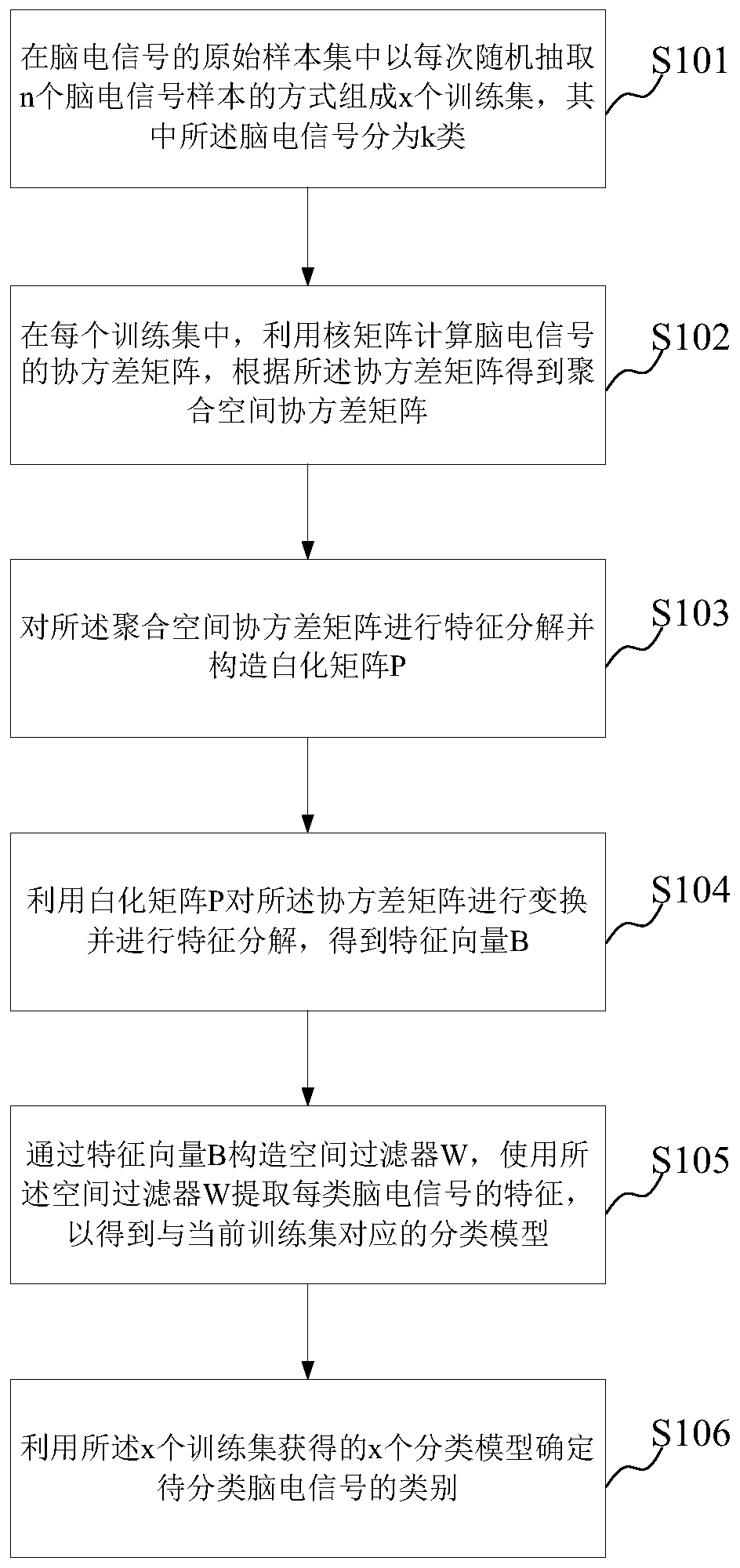
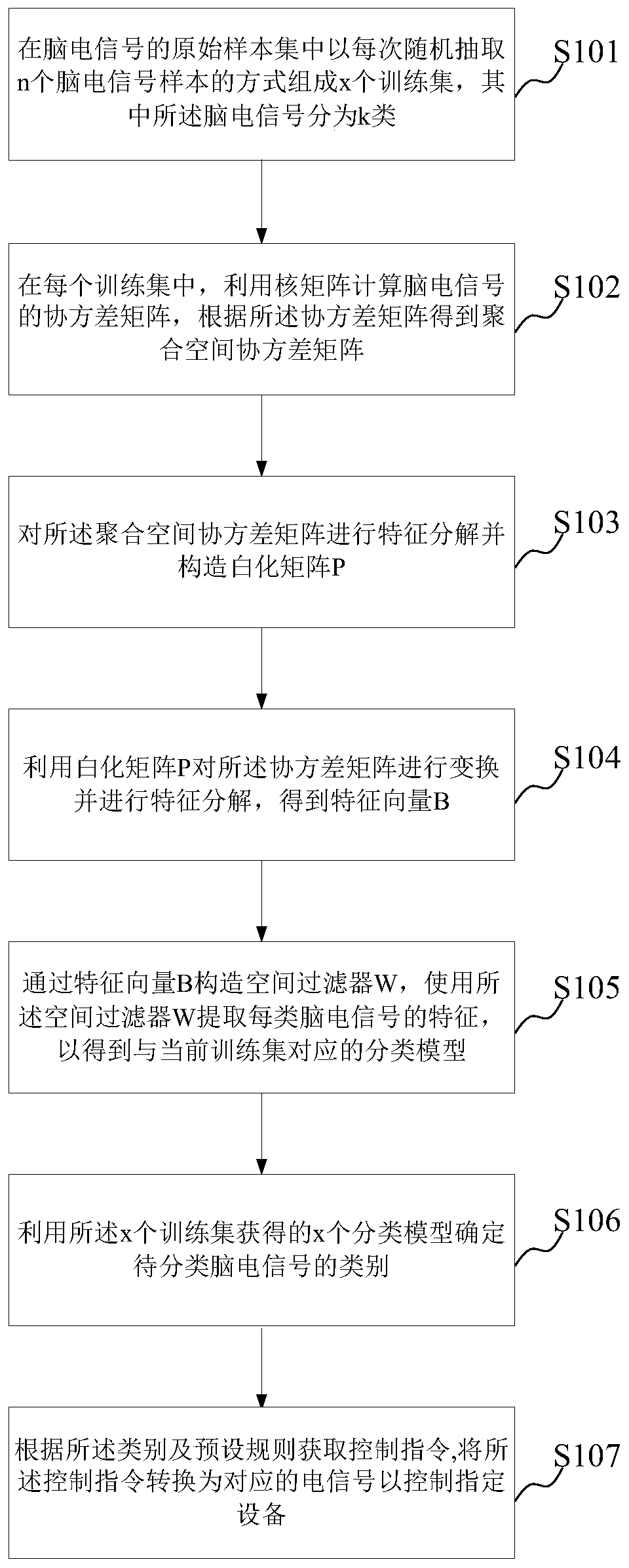
[0092] figure 1 It is a flowchart of a method for identifying brain electrical signals according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention. See figure 1 As shown, the method can include:
[0093] Step S101, forming x training sets in the original sample set of the brain electrical signals by randomly extracting n brain electrical signal samples each time. The EEG signa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com