Organism identification method based on membrane-bound complex
A complex, membrane-bound technology, applied in the field of cell identification, can solve the problems of seldom application in the pharmaceutical field, difficult to control the reaction, difficult to scale up the process, etc., and achieve the effect of mild process, short time-consuming, high repeatability and accuracy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
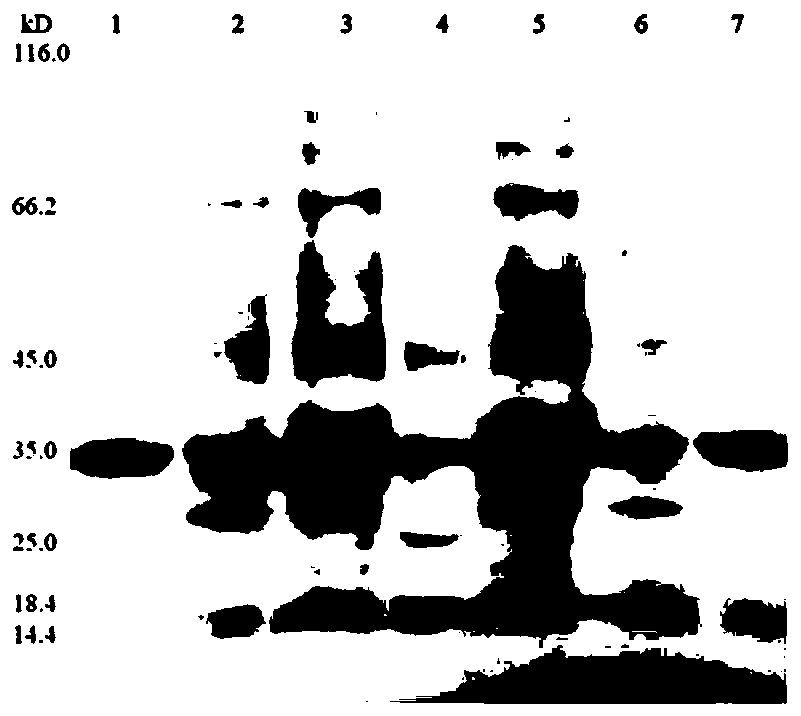
[0022] Design and expression of transmembrane binding proteins
[0023] Ib-AMP4 is a plant antimicrobial peptide, which was first discovered in Impatiens balsamina plants and is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptide. GFP is green fluorescent protein, which is often used for molecular tracking. The amount of GFP can be judged by the fluorescence intensity in the solution. Ib-AMP4-GFP, GFP-Ib-AMP4, thanatin-GFP and Ib-AMP4-GFP-RGD four fusion proteins are prepared in the same way, all by designing corresponding nucleic acid sequences and applying genetic engineering methods to construct expression plasmids And express and purify in Escherichia coli, the specific preparation process of the fusion protein will be introduced below by taking Ib-AMP4-GFP and GFP-Ib-AMP4 as examples. Through the method of gene synthesis, synthesize the DNA expressing Ib-AMP4 and GFP protein, between two protein molecules (GGGSG) 4 In order to verify the difference in the membrane binding ability of...
Embodiment 2
[0025] Solid Phase Synthesis of Ib-AMP4-FITC
[0026] Antimicrobial peptides were synthesized by solid-phase synthesis using FMOC (9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl) as a protecting group. It was cleaved from the resin with 95% trifluoroacetic acid, 2.5% water and 2.5% triisopropylsilane (TIA). After repeated precipitation with diethyl ether, the polypeptide was purified by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. A C18 reverse-phase column was used in the purification: 0%-60% acetonitrile containing 0.05% trifluoroacetic acid was used as the mobile phase, and gradient elution was performed at a flow rate of 3 mL / min. The polypeptide was then dissolved in oxidation buffer (100 mmol / L ammonium acetate, pH 8.5) at a concentration of 1 mg / mL, and stirred continuously at room temperature for 3 days to fully oxidize and fold to form disulfide bonds. Finally, it was purified to over 95% by reverse-phase HPLC and freeze-dried for use. After amination of the C-terminus, comme...
Embodiment 3
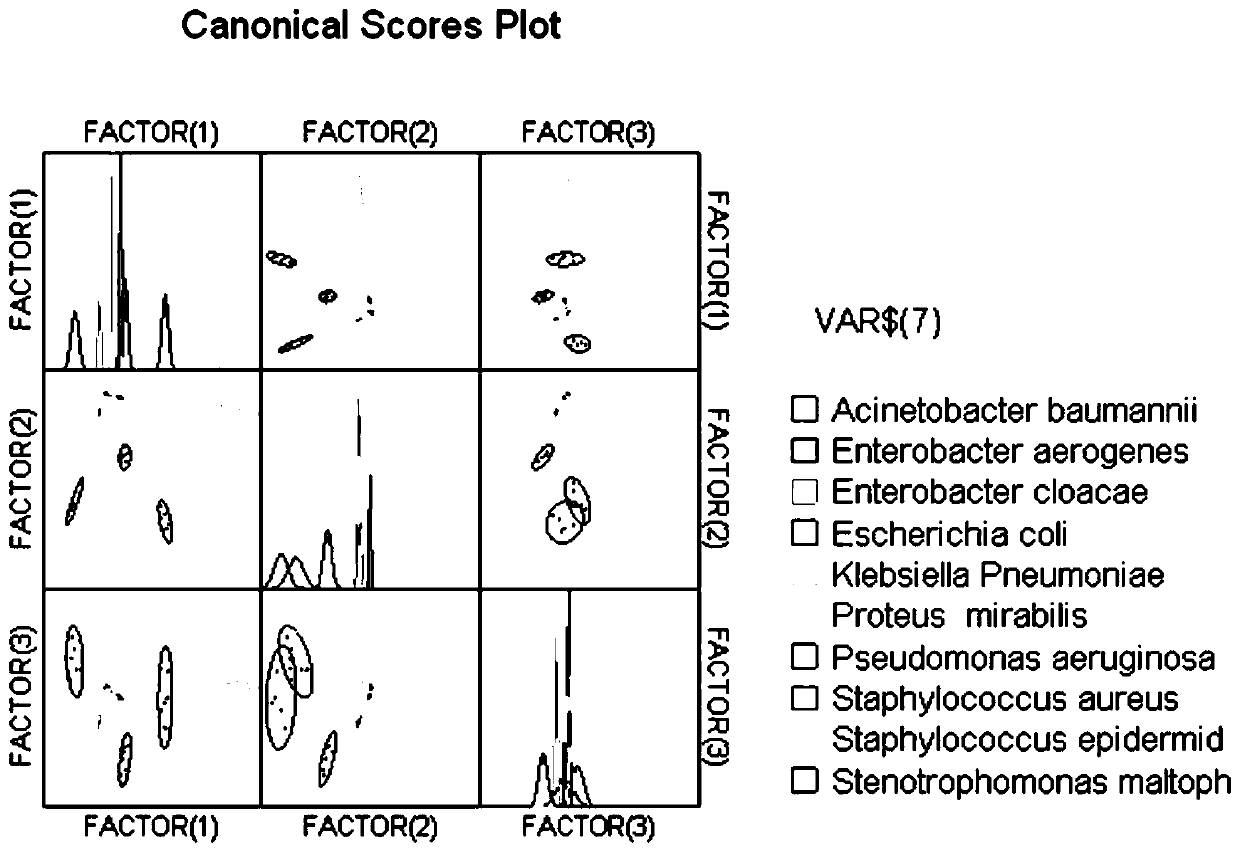
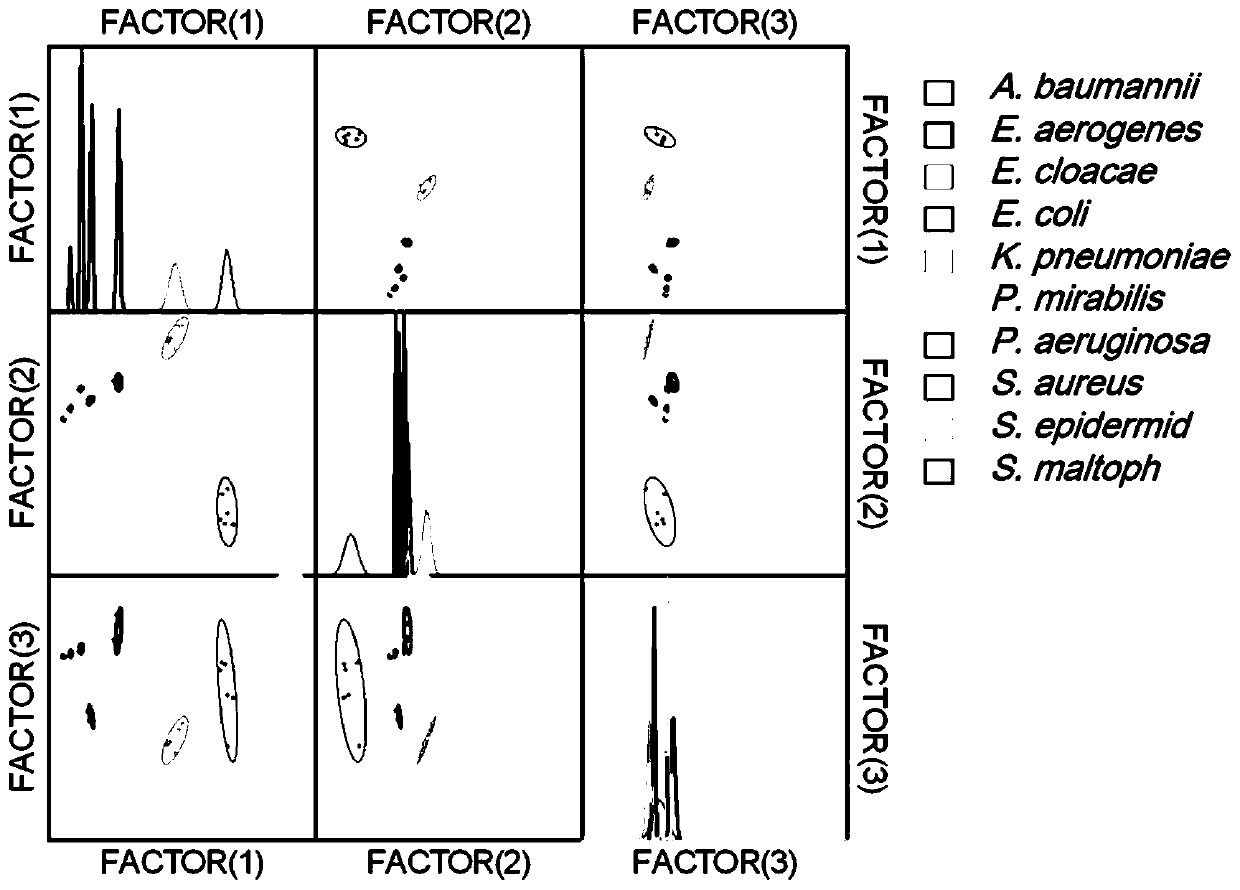
[0028] Application of Ib-AMP4-GFP, thanatin-GFP and Ib-AMP4-FITC in clinical bacterial identification
[0029] Pick 10 clinical strains and inoculate them in fresh culture medium, cultivate them overnight, recover the bacteria by centrifugation and wash with 5% glucose solution for 3 times, then dilute the bacterial solution to a bacterial suspension with OD600=0.5. Take 1 mL of bacterial suspension and add 1 mL of different concentrations of Ib-AMP4-GFP, thanatin-GFP or Ib-AMP4-FITC, incubate in a shaker at 37 degrees Celsius for 20 minutes, wash the bacteria three times with PBS, and observe under a fluorescence microscope Fluorescence, and measure the green fluorescence intensity of the bacteria with a fluorescence spectrophotometer. The resulting data were used to classify bacteria using linear discriminant analysis. The results showed that after being treated with transmembrane protein, the bacteria were marked with green fluorescence, and the fluorescence intensity rang...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com