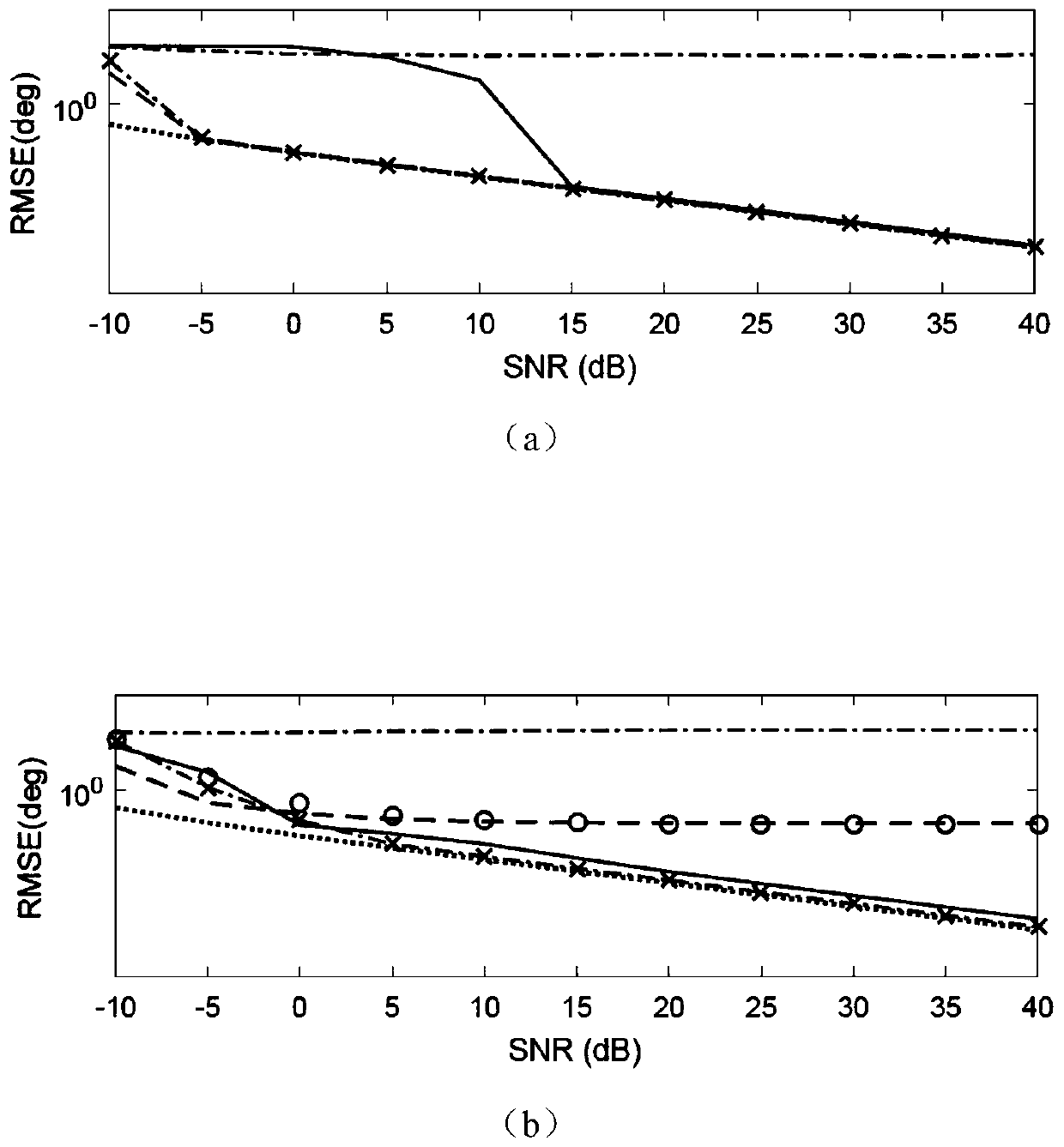
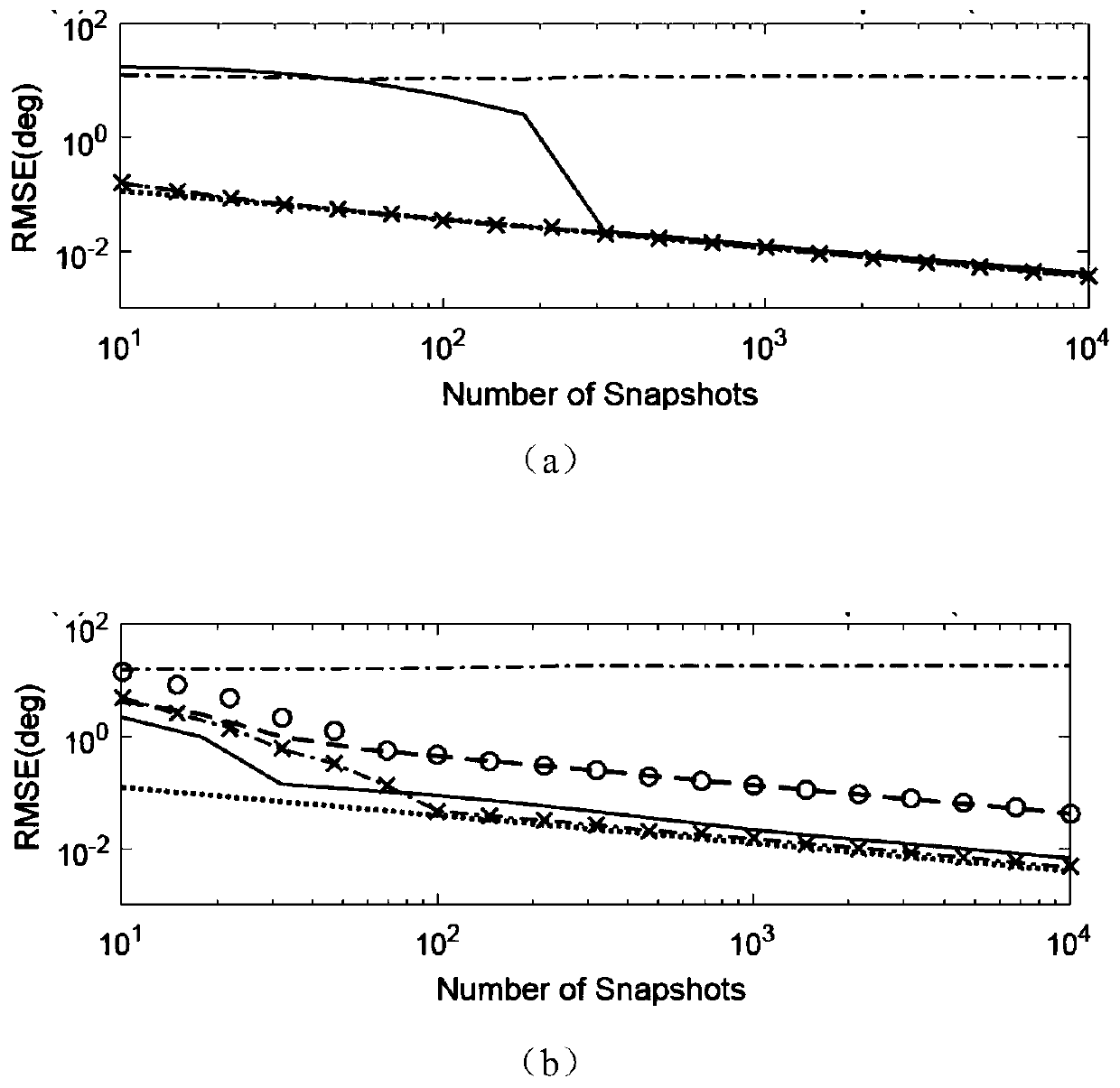
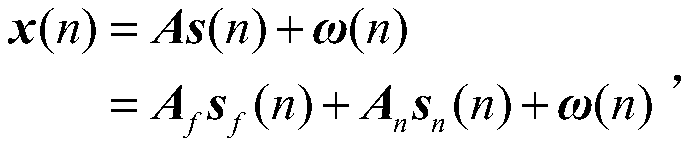Non-iterative mixed signal source positioning method based on rank loss
A mixed signal and signal source technology, applied in positioning, complex mathematical operations, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as poor reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0099] A non-iterative mixed signal source location method based on rank loss in an embodiment of the present invention includes:
[0100] Angle of Arrival Estimation for Mixed Signals:
[0101] First, from Estimation of DOA of mixed near-field and far-field signals from array element receiving signals and distance From formulas (6) to (8), it can be seen that the DOA of the mixed signal near-field signal and far-field signal to be estimated and distance can pass a f (θ k ) and a n (θ k ,r k )get. For a uniform symmetrical linear array, the present invention takes the central array source as a reference matrix, and a of the array f (θ k ) and a n (θ k ,r k ) can be expressed as:
[0102] a f (θ k )=D(θ k )b f (9)
[0103] a n (θ k ,r k )=D(θ k )b n (10)
[0104] Among them, b f and b n is a (M+1)×1 vector, and b f = 1,
[0105] D(θ k ) is a (2M+1)×(M+1) matrix,
[0106] Second, construct the array skew variance matrix as:
[0107] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com