A Null Sink Widening Method Based on Sparse Constraint Controlling Sidelobes
A sparsely constrained and null-widening technology, applied in the radar field, can solve the problems of shallow nulling depth, fluctuation of interference direction, and difficulty in controlling the loading amount, and achieve good nulling depth, zero-notching widening, and low sidelobe performance Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
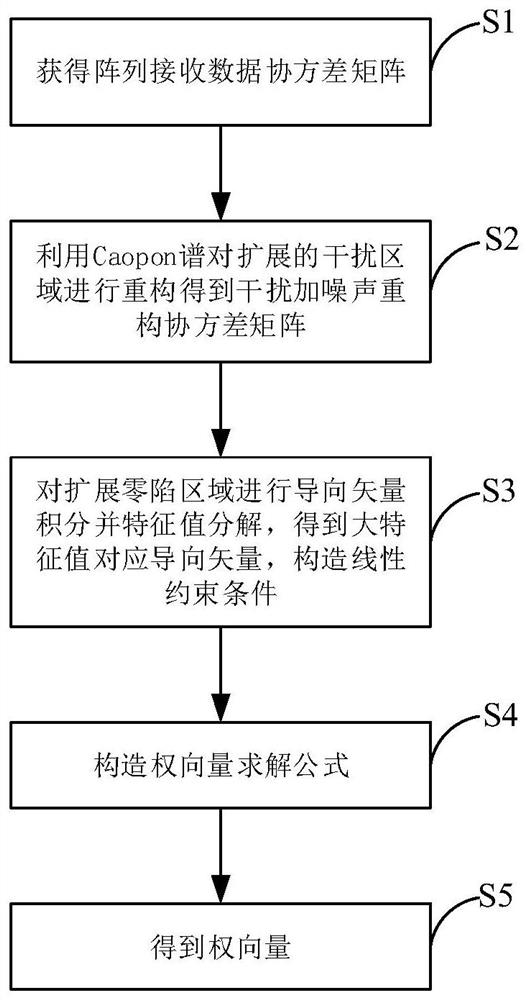
[0052] See figure 1 , figure 1It is a flow chart of a method for nulling widening of sidelobes based on sparse constraints to control side lobes provided by an embodiment of the present invention. As shown in the figure, a method for nulling widening of sidelobes based on sparse constraints to control side lobes in this embodiment includes:
[0053] S1: Obtain the received data covariance matrix of the antenna array
[0054] S2: Using the Capon power spectrum (traditional beamforming power spectrum) to analyze the received data covariance matrix The extended interference signal area is reconstructed, and the interference plus noise reconstruction covariance matrix is obtained
[0055] Specifically, the interference plus noise reconstruction covariance matrix for,
[0056]
[0057] S3: For the received data covariance matrix The extended null region of the steering vector is integrated to obtain the correlation matrix of the steering vector and the correlatio...
Embodiment 2
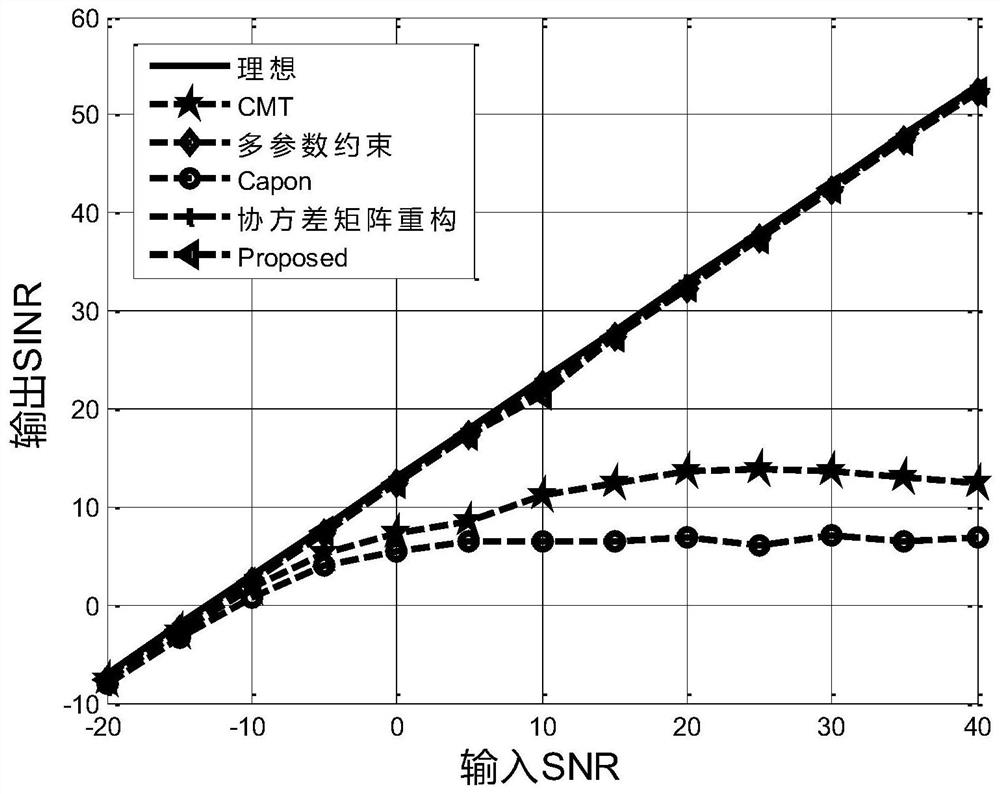
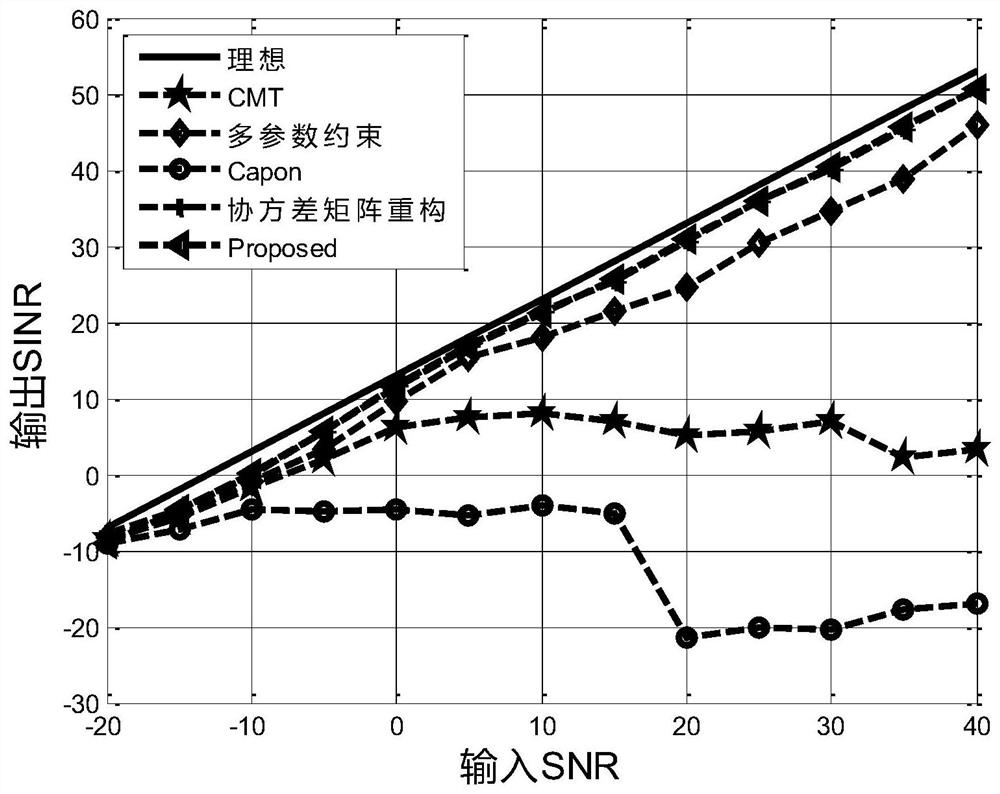
[0079] This embodiment is a further illustration of the nulling widening method based on sparsity constraints to control side lobes in the first embodiment through simulation experiments. In the simulation experiment process of this embodiment, the antenna array structure adopts a uniform linear array, the number of array elements N is 20, the spacing d between array elements is λ2, the interference directions are -30° and 40°, and the interference-to-noise ratio is 30dB, ideal The target direction is 0°, the range of SNR value is [-20:40], and the interval is 5dB.
[0080] In the experiment in which the simulated output SINR changes with the input SNR in this embodiment, the number of snapshots L is 200, and the received data covariance matrix of the array is estimated as follows:
[0081]
[0082] Among them, N represents the number of array elements, and L represents the number of snapshots.
[0083] During the simulation experiment of this embodiment, compared algorith...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com