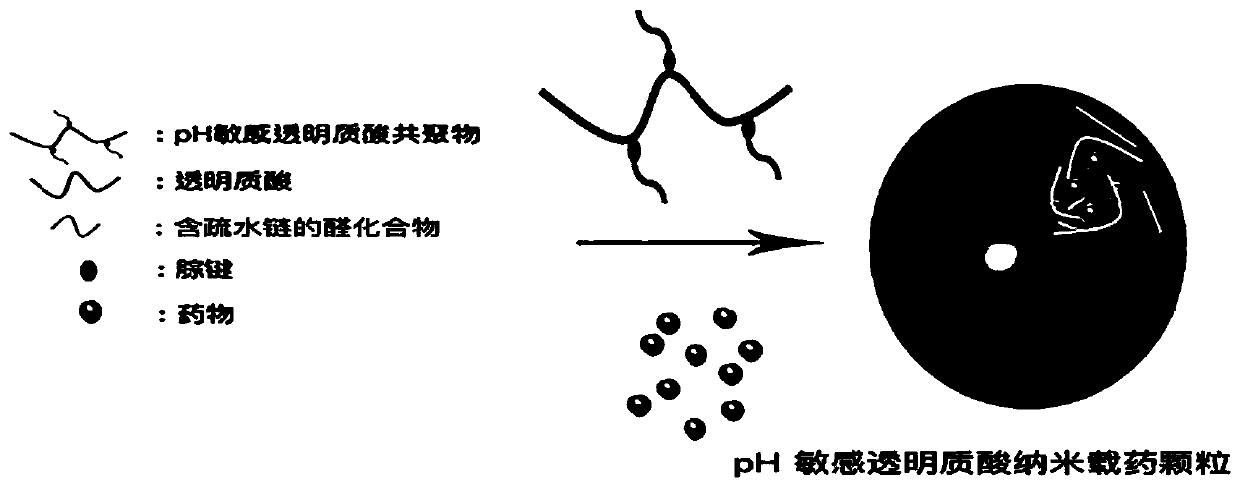
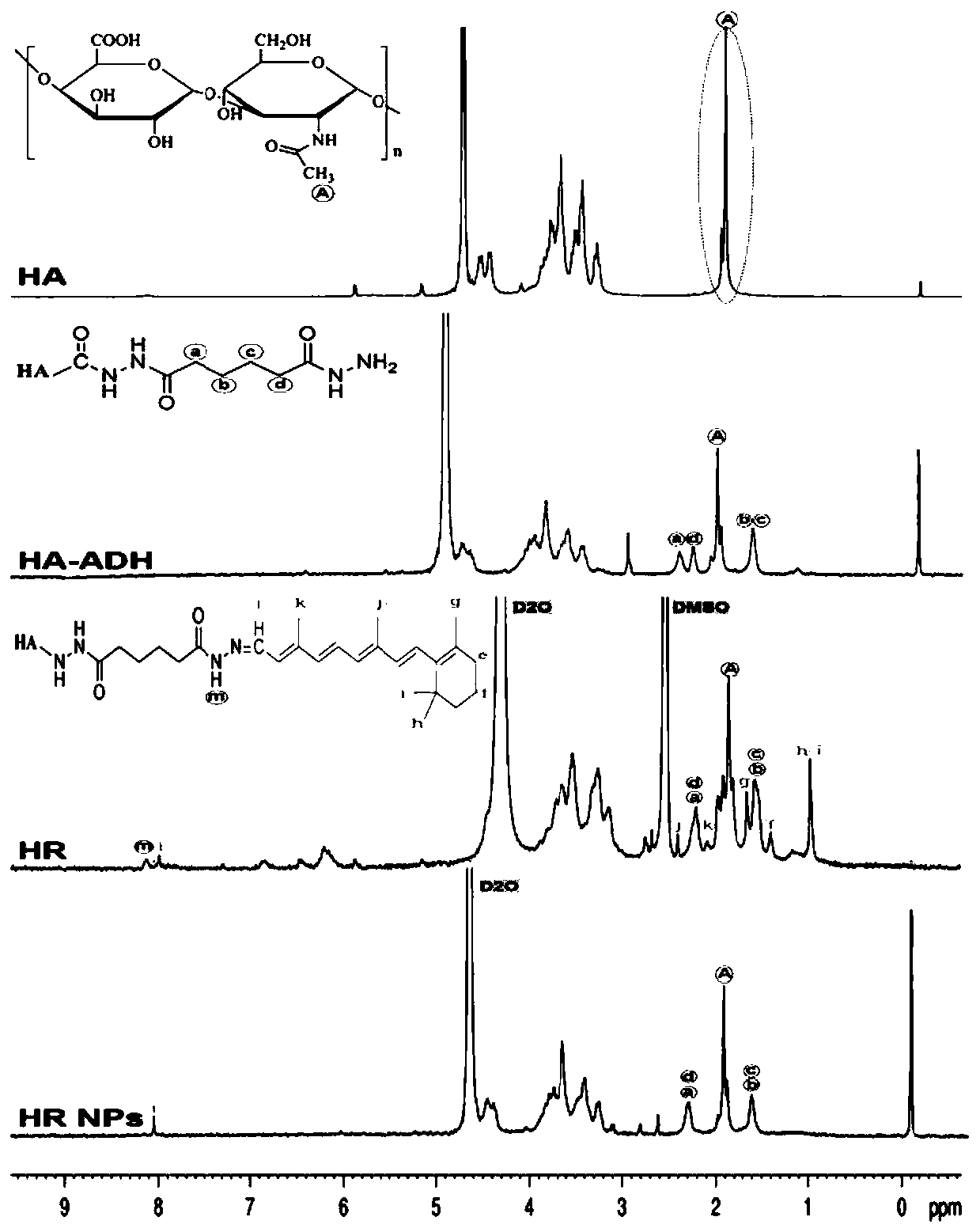
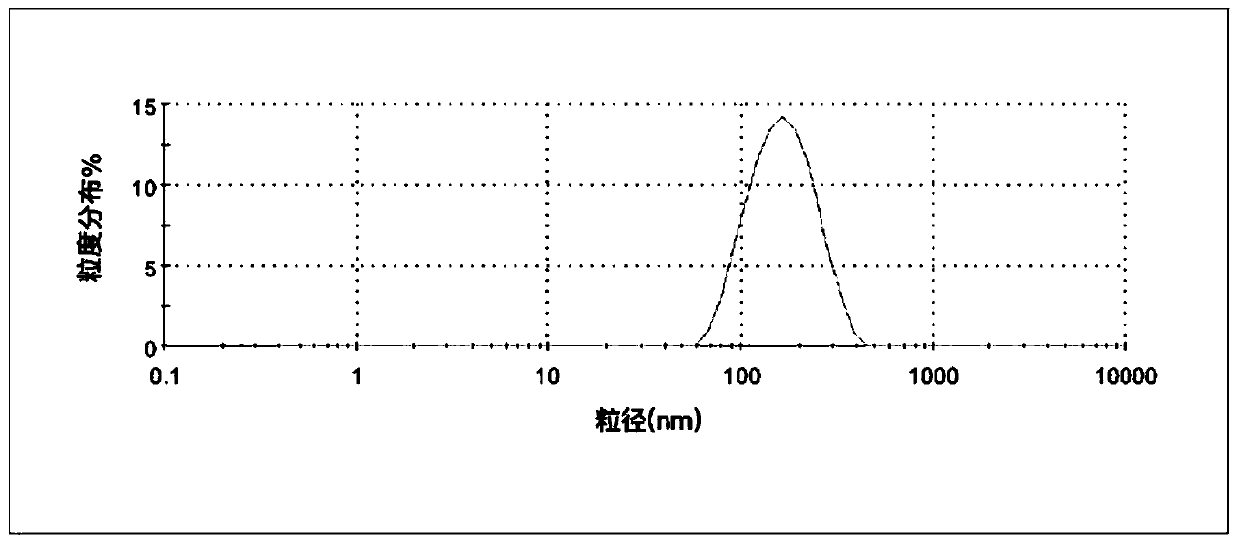
PH-sensitive hyaluronic acid nano drug-loading particles targeting atherosclerosis and preparation method thereof
A technology for atherosclerosis and hyaluronic acid, which is applied in pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations without active ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve the problem of low carboxyl group, all-trans retinoic acid accompanied by inflammatory reaction and other problems to avoid accumulation, improve intracellular internalization, and achieve good reproducibility.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0037] A preparation method for pH-sensitive hyaluronic acid nano drug-loaded particles targeting atherosclerosis, comprising the following steps:
[0038] 1) A linker having a terminal hydrazine group is covalently bonded to hyaluronic acid to obtain a hyaluronic acid derivative;
[0039] 2) Based on the hyaluronic acid derivative, the aldehyde compound containing the hydrophobic chain is grafted to the hyaluronic acid derivative through the terminal hydrazine group to obtain a pH-sensitive hyaluronic acid copolymer containing a hydrazone bond;
[0040] 3) Encapsulate the hydrophobic anti-atherosclerotic drug into the hydrophobic core of the pH-sensitive hyaluronic acid copolymer to obtain the pH-sensitive hyaluronic acid nano drug-loaded particles targeting atherosclerosis.
[0041] In step 1), the linker with a terminal hydrazine group is dihydrazide; in step 3), the hydrophobic drug can be selected from anti-atherosclerotic drugs, statin drugs, and anti-inflammatory drugs....
Embodiment 1
[0053] Using low molecular weight hyaluronic acid (about 10000Da) as raw material, a pH-sensitive hyaluronic acid copolymer HR (substitution degree of all-trans retinal is 7%) was synthesized.
[0054] 1) Synthesis of hyaluronic acid-modified adipic dihydrazide derivatives: 200 mg of hyaluronic acid (HA, molar mass about 10,000 Da) was dissolved in 50 mL of deionized water to obtain hyaluronic acid with a concentration of 4 mg / mL. 10 times mole of adipic hydrazide (ADH) was added to the solution, stirred at room temperature (250 rpm) for 30 min, and 0.1N HCl was added to adjust the pH value of the reaction mixture to 4.75. Then 96 mg of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC·HCl) in solid form was added to the mixture to start the reaction. Stir at room temperature for 1 h, and add 0.1M HCl in time to maintain the pH at 4.75. Finally, an appropriate amount of 0.1M sodium hydroxide solution was added to adjust the pH value to 7.0 to terminate the reac...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Using low molecular weight hyaluronic acid (about 10000Da) as raw material, a pH-sensitive HR polymer (substitution degree of all-trans retinal is 8%) was synthesized.
[0060] 1) Synthesis of hyaluronic acid-modified adipic dihydrazide derivatives: 200 mg of hyaluronic acid (HA, molar mass about 10,000 Da) was dissolved in 50 mL of deionized water to obtain hyaluronic acid with a concentration of 4 mg / mL. 10 times mole of adipic hydrazide (ADH) was added to the solution, stirred at room temperature (250 rpm) for 30 min, and 0.1N HCl was added to adjust the pH value of the reaction mixture to 4.75. Then 96 mg of 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC·HCl) in solid form was added to the mixture to start the reaction. Stir at room temperature for 1 h, and add 0.1M HCl in time to maintain the pH at 4.75. Finally, an appropriate amount of 0.1M sodium hydroxide solution was added to adjust the pH value to 7.0 to terminate the reaction. The resulti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| degree of substitution | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com