High-frequency endoscopic surgical electrode
A surgical electrode and endoscope technology, applied in the field of high-frequency endoscopic surgical electrodes, can solve the problems of insufficient electrical connection reliability between the guide wire and the connecting wire, low efficiency of electrode ablation and coagulation, and poor stretching of the electrode body. To achieve the effect of shortening the operation time, smooth operation of the doctor and smooth operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
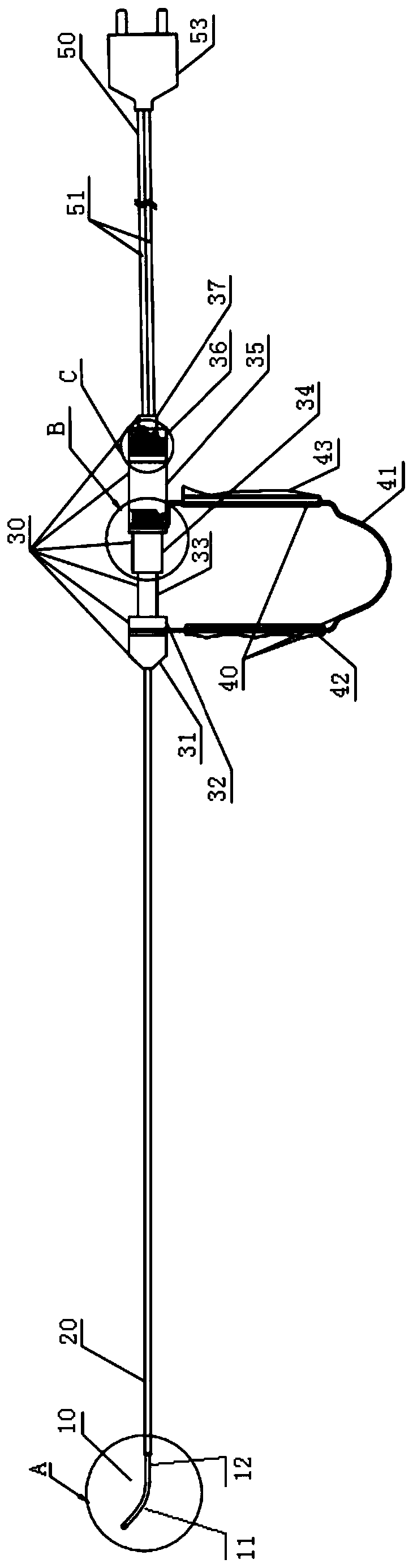
[0050] refer to figure 1 and Figure 6 As shown, the present embodiment provides a high-frequency endoscopic surgical electrode, including an electrode body 10 with a proximal end and a distal end, an outer sheath 20, a fixed sleeve assembly 30 and a handle 40, and the electrode body 10 is movable The electrode body 10 can be stretched and moved in the outer sheath 20 under the action of the handle 40 .
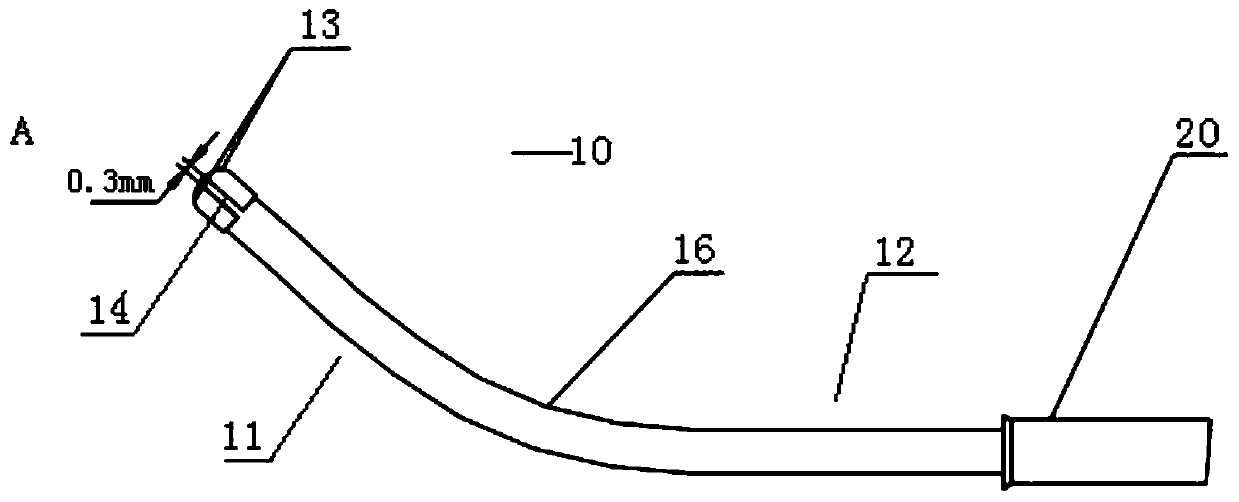
[0051] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, the electrode body 10 includes a distal curved section 11 and a proximal straight section 12. The distal end of the curved section 11 is provided with two electrode tips 13 arranged at intervals. The insulating layer 14 together forms an arc surface, and the two electrode tips 13 are separated by a certain distance through the insulating layer 14 in the middle, and the size of the distance affects the range of action of the electrodes. The two-pole electrode head 13 and the insulating layer 14 in the middle together form a sphe...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Different from the above-mentioned embodiment 1, refer to figure 2 As shown, in the high-frequency endoscopic surgery electrode provided by this embodiment 2, the electrode body 10 is composed of two electrode heads 13, an insulating layer 14, two guide wires 15 and a double-lumen tube 16, and the two guide wires 15 It is arranged in the double-lumen tube 16 and its distal ends are respectively connected to the two electrode tips 13 one by one. The distal ends of the two guide wires 15 have the same structure and are formed by one stamping. In addition, the insulating layer 14 is a part of the middle wall at the distal end of the double-lumen tube 16 and is integrally formed.
[0055] In this embodiment, the distal end of the guide wire 15 is composed of at least three continuous sections 151 bent at a certain angle. Preferably, as Figure 5 As shown, it is a side view and a top view structure schematic diagram of the guide wire in the high-frequency endoscopic surge...
Embodiment 3
[0059] The difference from the above Example 1 is that please continue to refer to figure 1 As shown, in the high-frequency endoscopic surgical electrode provided in Embodiment 3, the fixed sleeve assembly 30 includes a concentric distal nut 31, a shaft sleeve 33, a distal end sleeve 34 , proximal sleeve 35 and proximal nut 36 .
[0060] In this example, if figure 1 As shown, the distal end of the distal nut 31 is fixedly connected to the proximal end of the outer sheath tube 20, and its proximal end is connected to the distal end of the shaft sleeve 33, and the proximal end of the shaft sleeve 33 is movable. Sleeved in the distal sleeve 34; the proximal end of the distal sleeve 34 is fixed in the proximal sleeve 35, and the proximal end of the proximal sleeve 35 is connected to the proximal nut 36 Fixed connection; the straight section 12 of the proximal end of the electrode body 10 passes through the distal nut 31, shaft sleeve 33, distal sleeve 34, and proximal sleeve seq...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com