Arrangement method of a distributed optical fiber sensor
A technology of distributed optical fibers and layout methods, applied in the directions of instruments, measuring devices, measuring instrument components, etc., can solve the problems of slow paving speed of asphalt surface, difficult leveling, and increased difficulty in grooving, so as to ensure smoothness and smoothness. Overall, the production process is simple, the effect of slowing down the rhythm of the layout
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
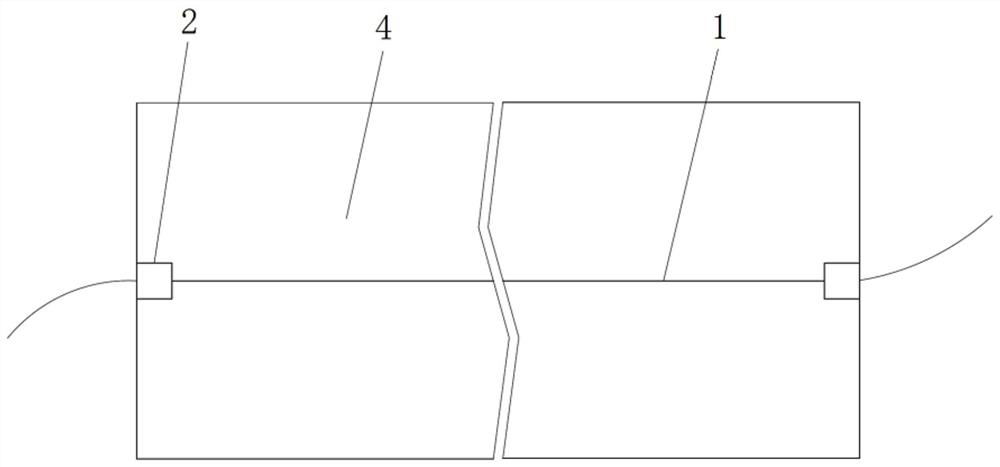
[0033] Specific implementation mode one: combine Figure 1-Figure 2 To illustrate this embodiment, a method for arranging distributed optical fiber sensors on asphalt roads in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0034] A. Install fixed seats 2 that restrict axial movement at both ends of the existing distributed optical fiber sensor 1, and coat the surface of the distributed optical fiber sensor 1 with a thermoplastic colloid material;
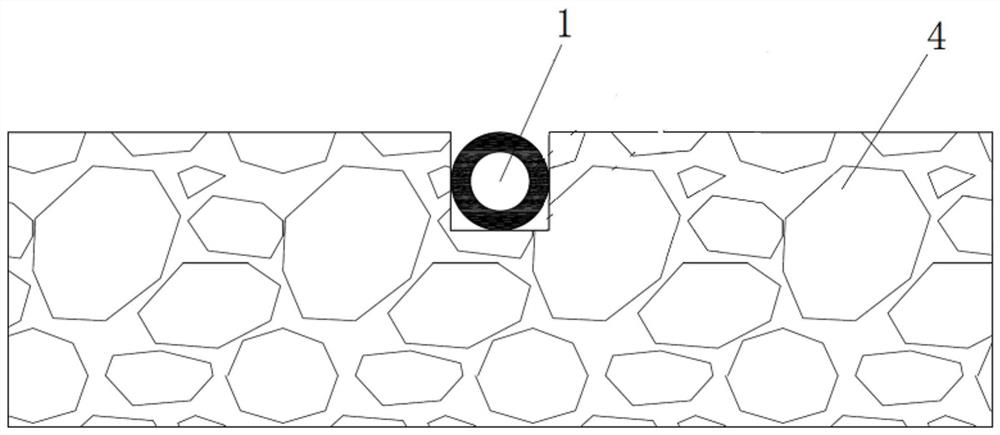
[0035] B. Slotting the existing pavement 4, expanding the position where the notch on the pavement 4 is installed with the fixing seat 2 to ensure that the fixing seat 2 is smoothly installed into the groove of the road surface 4;
[0036] C. Fix the fixed seat 2 in the groove of the road surface 4, fill the mixed high-temperature asphalt mixture into the groove of the road surface 4 when the road surface 4 is paved, and the thermoplastic colloid coated on the surface of the distributed optical fiber sensor 1 will be caused by the ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
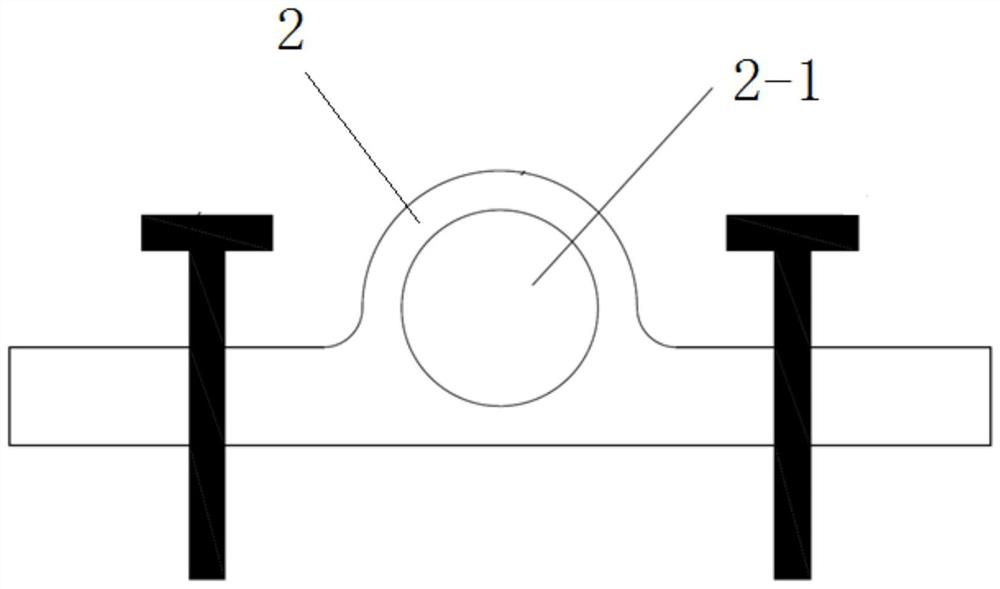
[0037] Specific implementation mode two: combination image 3 and Figure 4 To illustrate this embodiment, in step A of this embodiment, before installing the fixing seat 2, the two ends of the distributed optical fiber sensor 1 are respectively processed with annular grooves, and then two sets of semi-circular rings 3 are processed, each set of semi-circular rings 3 It consists of two symmetrical semi-circular rings 3, the inner surface of each semi-circular ring 3 is processed with a protrusion matching the annular groove, and the outer surface of each semi-circular ring 3 is processed with threads. The circular ring 3 is fastened on both ends of the distributed optical fiber sensor 1, and the fixed seat 2 is processed with a threaded hole 2-1, and each set of semi-circular rings 3 is screwed into the threaded hole 2-1 of the fixed seat 2 Inside.
[0038] In this embodiment, two semi-circular rings 3 are provided, and protrusions matching the annular grooves are arranged i...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] Specific embodiment three: Step B of this embodiment uses GPS or a total station for positioning, and uses a cutting machine to cut the road surface 4, so that the grooves opened on the road surface 4 are straight and consistent in depth.
[0041] Such setting makes the slotting more accurate.
[0042] Its composition and connections are the same as those in the first embodiment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com