Wind power non-parametric interval prediction method based on self-adaptive double-layer optimization
A wind power, two-layer optimization technology, applied in forecasting, complex mathematical operations, data processing applications, etc., can solve problems such as improving the robust operation of power systems and controlling potential costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
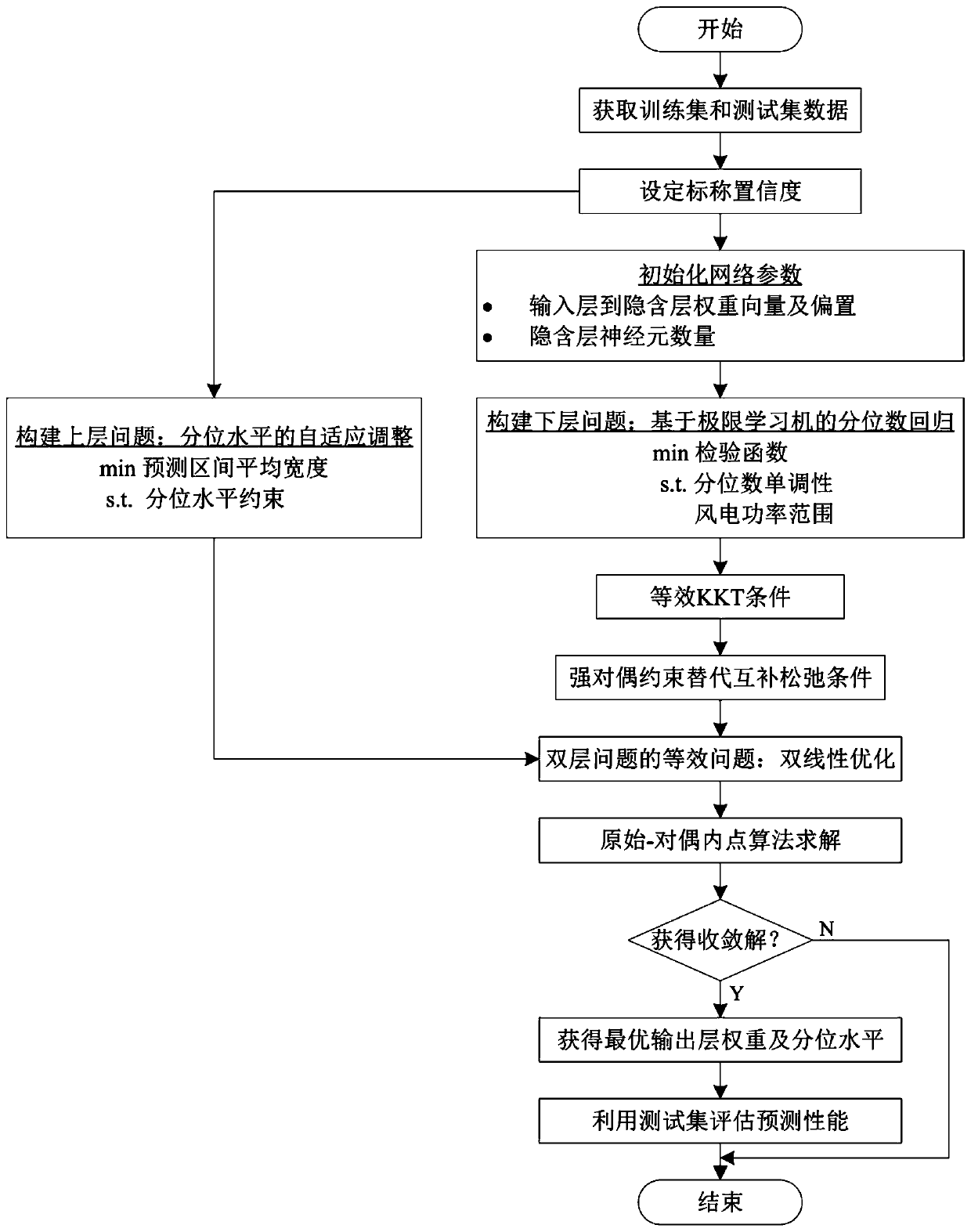
[0053] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and implementation examples.
[0054] (1) First obtain the training set data where x t is the explanatory variable, y t is the target variable, and for the short-term prediction of wind power within 3 hours, the historical power data can be used as the explanatory variable;
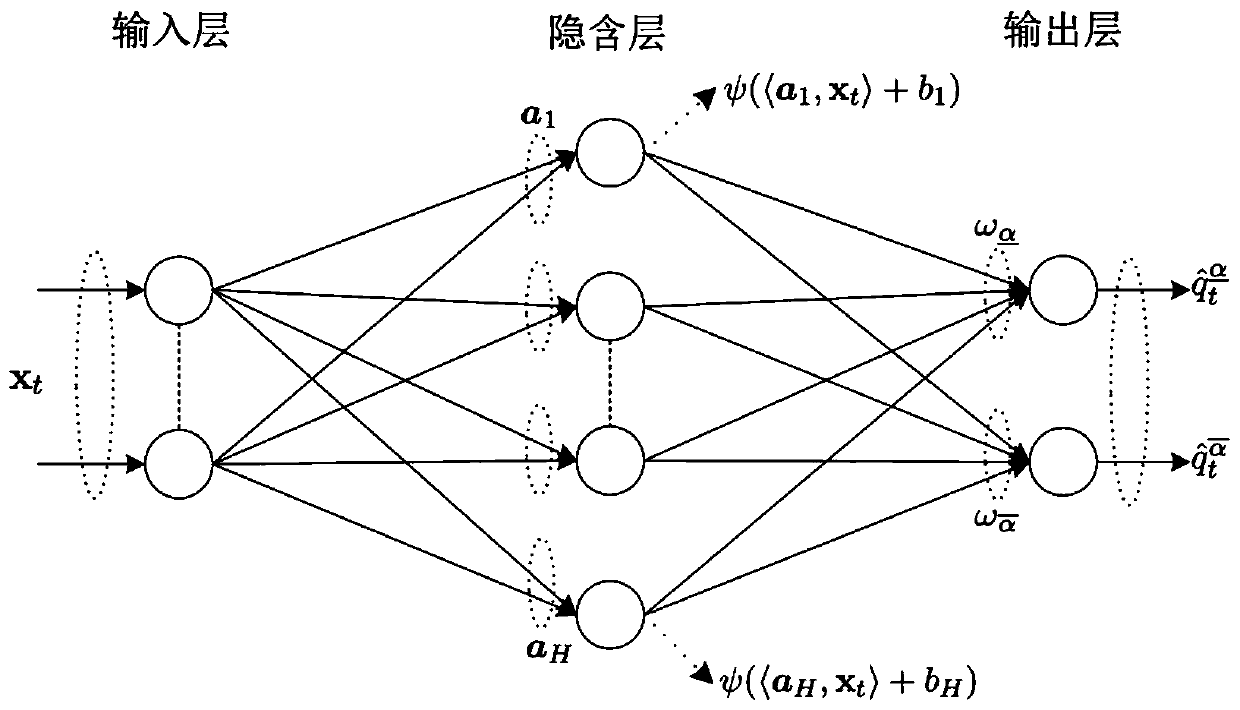
[0055] (2) Set the nominal confidence of the prediction interval to 100(1-β)%; for example figure 1 As shown, the weight vector and bias from the input layer to the hidden layer of the extreme learning machine are randomly given I and H are the number of neurons in the input layer and hidden layer of the extreme learning machine, respectively;
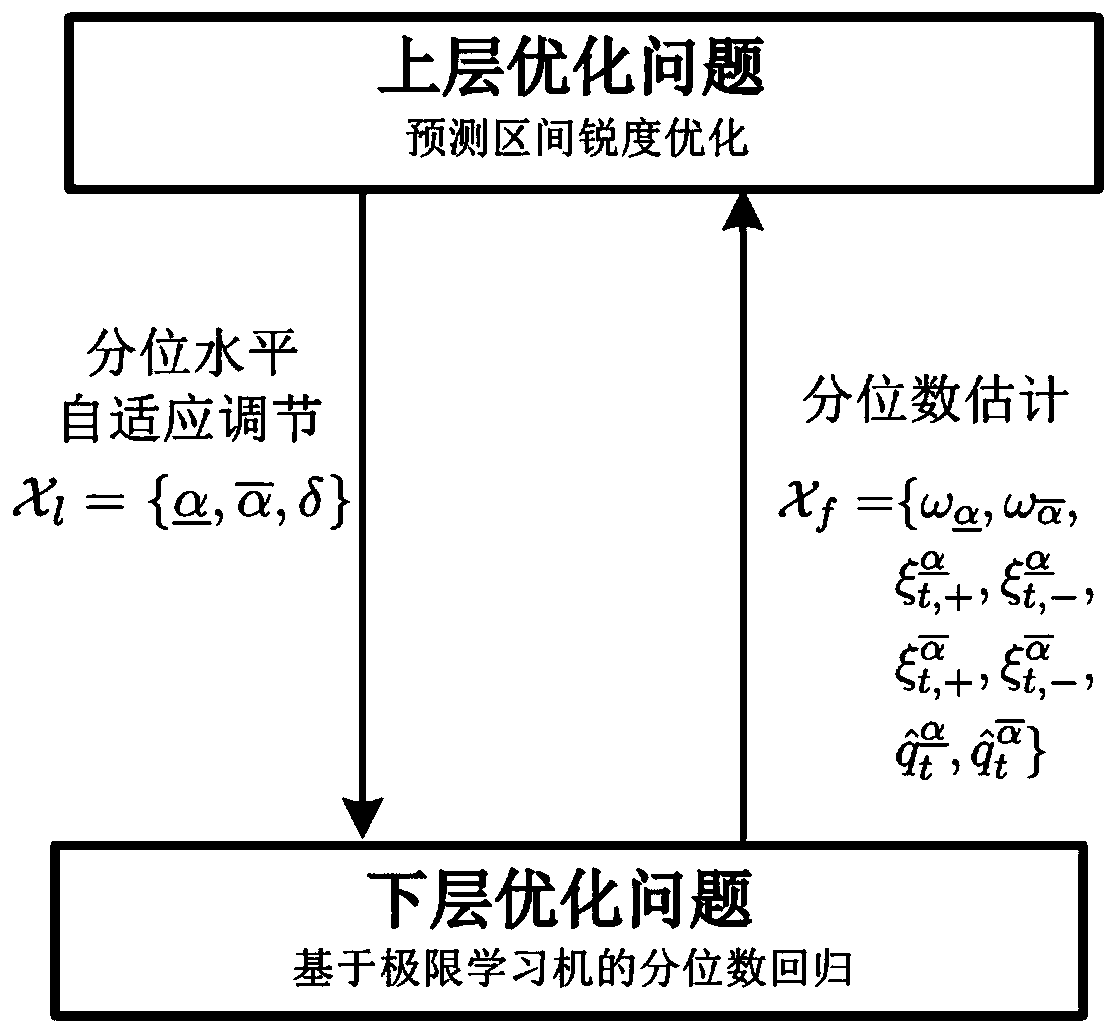
[0056] (3) Establish a non-parametric interval prediction model of wind power based on adaptive double-layer optimization:
[0057]
[0058]
[0059]
[0060]
[0061]
[0062]
[0063]
[0064] where h t =[ψ(1 ,x 1 >+b 1 ) … ψ(1...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com