Construction process of composite ladle bottom of steel ladle
It is a construction technique and bottom-covering working layer technology, which is applied in the direction of manufacturing tools, metal processing equipment, casting molten material containers, etc., and can solve the problems of high labor intensity of refractory materials, difficulty in ensuring the safety of the bottom cover, and high repair costs, so as to reduce the cost of dismantling. Reduce labor intensity, improve the safety of use, and reduce the effect of refractory material replacement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
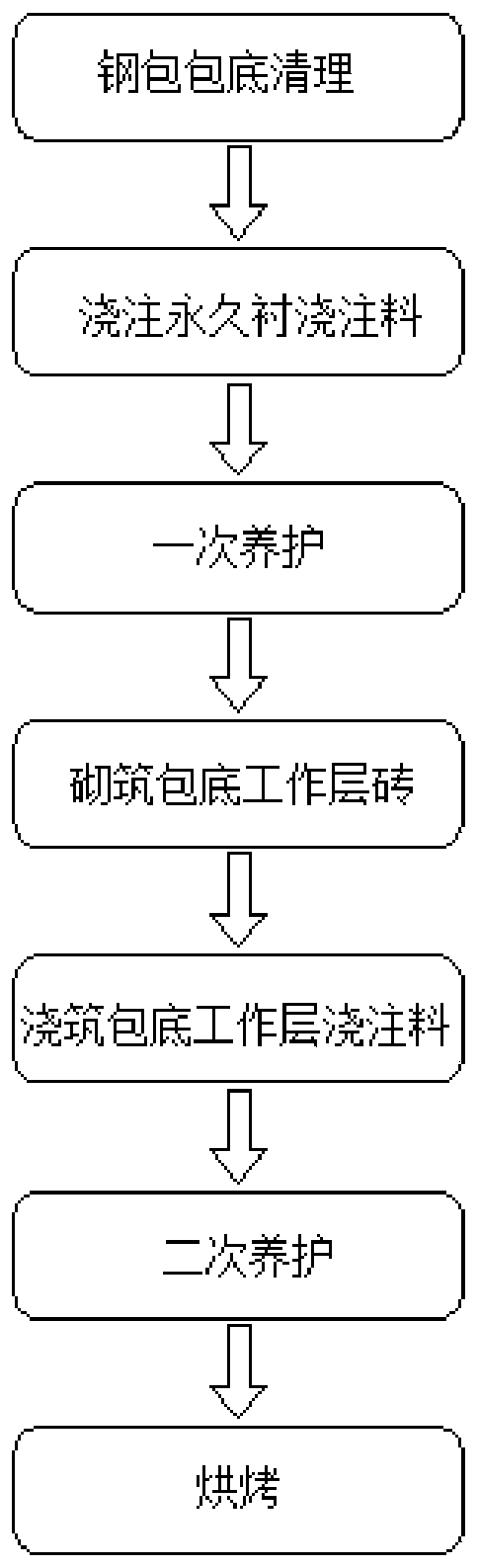
[0032] A construction process for ladle composite bottom cladding, the specific construction process is as follows:
[0033] (1) Ladle bottom cleaning: cleaning the bottom of the ladle to remove sundries and dust on the bottom of the ladle;
[0034] (2) Pouring permanent lining castables: Put the permanent lining castables in a mixer and add water to stir. The proportion of water added is 5.8%, and the stirring time is 4 minutes. Exhaust the material body so that the thickness of the permanent layer castable at the bottom of the bag is 120mm;
[0035] (3), one-time maintenance: the ladle with a layer of permanent lining castable is left to stand at room temperature for 8 hours to solidify the permanent lining castable;
[0036] (4) Masonry bricks for the bottom-covering working layer: On the surface of the solidified bottom-covering permanent lining castable, fire mud is used to build the bottom-covering working layer of aluminum-magnesium-carbon bricks, and the corners and c...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com